【Vue 2】Props
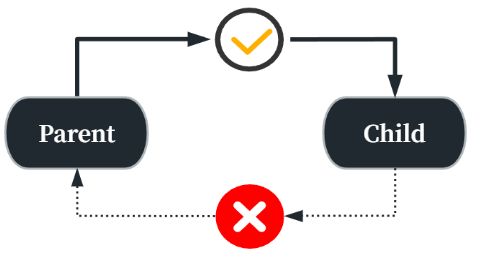
Vue中的props是父组件向子组件传递数据的方式。
下面会介绍prop的使用。
Prop大小写
Prop的命名规则有camelCase(驼峰命名)和kebab-case(短横线分隔)。由于HTML对大小写不敏感,所以浏览器会把大写字母解释为小写字母。因此当我们使用camelCase方法命名prop时,在Dom中的template模板使用该prop就需要换成对应的kebab-case命名形式。如果在字符串模板中使用,该限制就不存在。下面的代码示例展示这一点。
<div id="app">
<blog-post post-title="hello1">blog-post>
<profile>profile>
div>
<script>
Vue.component('blog-post', {
// camelCase in JavaScript
props: ['postTitle'],
template: '{{ postTitle }}
'
});
Vue.component('profile',{
template:`Prop类型
props可以简单地写为一个数组,但也可以使用对象的形式为每个prop指定其类型:
props: {
title: String,
likes: Number,
isPublished: Boolean,
commentIds: Array,
author: Object,
callback: Function,
contactsPromise: Promise // or any other constructor
}
传递静态或动态的Prop
静态传递prop:
<blog-post title="My journey with Vue">blog-post>
使用v-bind动态传递prop:
<blog-post v-bind:title="post.title">blog-post>
<blog-post
v-bind:title="post.title + ' by ' + post.author.name"
>blog-post>
上述示例的post.title是字符串类型,我们也可以传递任何类型。
如果我们使用比如Number、Boolean、Array、Object等类型的原始值作为prop,怎么避免它们被当成字符串传递呢?使用v-bind即可。
特殊的,如果我们想要传递一个对象的所有prop而非对象本身,可以使用不带参数的v-bind:
<blog-post v-bind="post">blog-post>
等价于:
<blog-post
v-bind:id="post.id"
v-bind:title="post.title"
>blog-post>
单向数据流
数据通过prop的传递是单向的,只能从父组件传递到子组件,而无法反向传递。如果没有这种限制,那么我们就很难掌控数据流的流向。
父组件prop的更新也会刷新传递给子组件的prop。
一旦我们尝试修改父组件传递给子组件的prop,Vue会在浏览器控制台发出警告。
子组件中有两种常见的需要修改传递来的prop的情况:
-
用来初始化本地的prop
props: ['initialCounter'], data: function () { return { counter: this.initialCounter } } -
需要修改传递来的prop
props: ['size'], computed: { normalizedSize: function () { return this.size.trim().toLowerCase() } }
要小心使用传递来的Object或Array类型的prop,修改了它们就会修改了原数据。我们可以进行深拷贝来避免这种情况。
Prop验证
基础的类型检查
null和undefined会通过任何类型验证。
props:{
propA: Number
}
多个可能的类型
props:{
propB: [String, Number],
}
必填项
props:{
propc:{
type: String,
required: true
}
}
默认值
props:{
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
propE: {
type: Object,
// 对象或数组默认值必须从一个工厂函数获取
default: function () {
return { message: 'hello' }
}
},
}
自定义验证函数
props: {
propF: {
validator: function (value) {
// 这个值必须匹配下列字符串中的一个
return ['success', 'warning', 'danger'].includes(value)
}
}
}
prop会在组件实例创建前进行验证,开发环境构建版本的Vue验证prop失败会给出浏览器控制台警告。
类型检查
type的值可以是以下原生构造函数之一:
| String | Number | Boolean | Array | Object | Date | Function | Symbol |
|---|
type也可以使用自定义的构造函数:
function Person (firstName, lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName
this.lastName = lastName
}
Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: {
author: Person
}
})
Non-Prop Attributes
non-prop attributes是指传递给了一个组件但是该组件中没有相关定义的prop,现在叫做attributes。
一些第三方组件的设计者只会定义那些组件所必需的、常见的的prop,而其他需要额外的prop的场景就会使用non-prop attribute,这些额外的attribute会被添加到组件的root element。
替换/合并已有的Attributes
通常传递给子组件的attributes会替换其已经设置好了的值,但是class和style attributes将会被合并处理。
禁用Attributes继承
我们可以设置inheritAttrs: false来阻止组件的根元素继承attributes。
Vue.component('my-component', {
inheritAttrs: false,
// ...
})
接下来可以使用$attrs来获取传递给组件的所有attribute(除了class和style)。
Vue.component('base-input', {
inheritAttrs: false,
props: ['label', 'value'],
template: `
`
})
<base-input
label="Username:"
v-model="username"
required
placeholder="Enter your username"
>base-input>
上面示例的placeholder作为non-prop attribute传递,但是我们禁用了组件根元素继承attributes,然后通过v-bind="$attrs"将class和style以外的attributes传递给了base-input。
参考资料
- Props-Vue 2
- vm.$attrs