PyTorch实现LeNet-5网络模型
温故而知新,可以为师矣!
一、参考资料
pytorch-models
【pytorch】(七)卷积网络:LeNet-5
二、LeNet-5相关介绍
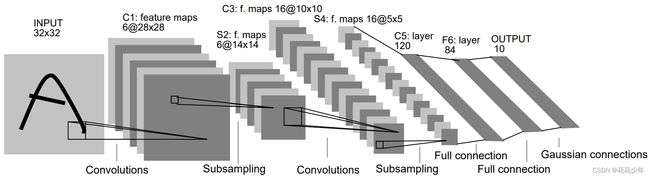
1. LeNet-5网络结构
三、代码实现
1. 搭建LeNet-5模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class LeNet5(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet5, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5, stride=1)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride=1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x))) # [32,32,1]-->[28,28,6]-->[14,14,6]
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x))) # [14,14,6]-->[10,10,16]-->[5,5,16]
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5) # [n,5,5,16]-->[n,5*5*16],其中n代表batch样本个数
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) # [n,256]-->[n,120]
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) # [n,120]-->[n,84]
x = self.fc3(x) # [n,84]-->[n,10]
return x
实例化LeNet5,并输入一个样本。
net = LeNet5()
print(net)
input = torch.rand(1, 1, 32, 32) # 代表一个32x32黑白图像样本
print('\nImage batch shape:')
print(input.shape)
output = net(input)
print('\nRaw output:')
print(output)
print(output.shape)
输出结果:
LeNet(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(pool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
Image batch shape:
torch.Size([1, 1, 32, 32])
Raw output:
tensor([[-0.0358, -0.0731, -0.1067, 0.0200, 0.0267, -0.0497, -0.0783, 0.0410,
-0.0123, -0.0634]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
torch.Size([1, 10])
2. 训练LeNet-5模型
使用LeNet-5对CIFAR10数据集进行分类。CIFAR10是32x32三通道图像的数据集,有10类图像:6种动物(鸟、猫、鹿、狗、青蛙、马)和4种车辆(飞机、汽车、轮船、卡车)。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
class LeNet5(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet5, self).__init__()
# conv1改为3通道
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def train_loop(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer, device):
running_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
# 获取输入
inputs, labels = data
inputs = inputs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
# 计算预测值和损失
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs, labels)
# 反向传播优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('[Batch%4d] loss: %.3f' %
(i + 1, running_loss / 100))
running_loss = 0.0
def test_loop(dataloader, model, device):
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in dataloader:
images, labels = data
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%' % (
100 * correct / total))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 设备
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(device)
# 数据集
transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) # 标准化图像数据
trainset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./cifar10_data', train=True,
download=True, transform=transform)
# 使用num_workers个子进程进行数据加载
trainloader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=32,
shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
testset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./cifar10_data', train=False,
download=True, transform=transform)
testloader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=32,
shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
# 超参数
lr = 0.001
epochs = 10
# 模型实例
model = LeNet5().to(device)
# 损失函数实例
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 优化器实例
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
for t in range(epochs):
print(f"Epoch {t + 1}\n-------------------------------")
train_loop(trainloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer, device=device)
test_loop(testloader, model, device=device)
print("Done!")