section header
section header table 是一个section header的集合,每个section header是一个描述section的结构体。在同一个ELF文件中,每个section header大小是相同的。
每个section都有一个section header描述它,但是一个section header可能在文件中没有对应的section,因为有的section是不占用文件空间的。每个section在文件中是连续的字节序列。section之间不会有重叠。
一个目标文件中可能有未覆盖到的空间,比如各种header和section都没有覆盖到。这部分字节的内容是未指定的,也是没有意义的。
1. section header定义
section header结构体的定义可以在 /usr/include/elf.h 中找到。
/* Section header. */
typedef struct
{
Elf32_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */
Elf32_Word sh_type; /* Section type */
Elf32_Word sh_flags; /* Section flags */
Elf32_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */
Elf32_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */
Elf32_Word sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */
Elf32_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */
Elf32_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */
Elf32_Word sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */
Elf32_Word sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */
} Elf32_Shdr;
typedef struct
{
Elf64_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */
Elf64_Word sh_type; /* Section type */
Elf64_Xword sh_flags; /* Section flags */
Elf64_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */
Elf64_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */
Elf64_Xword sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */
Elf64_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */
Elf64_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */
Elf64_Xword sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */
Elf64_Xword sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */
} Elf64_Shdr;
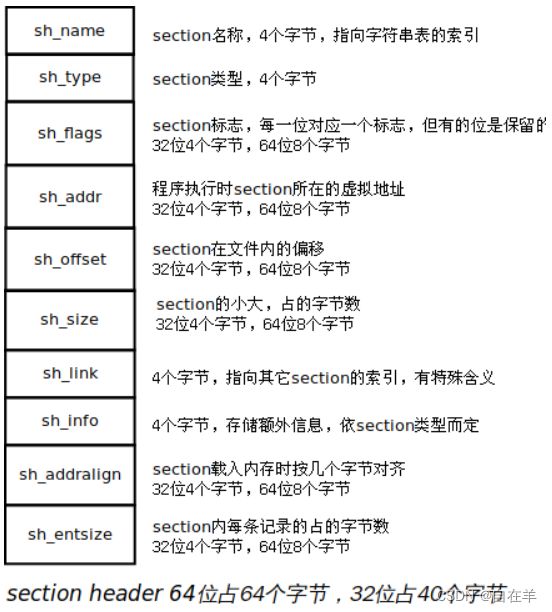
下面我们依次讲解结构体各个字段:
(1)sh_name,4字节,是一个索引值,在shstrtable(section header string table,包含section name的字符串表,也是一个section)中的索引。第二讲介绍ELF文件头时,里面专门有一个字段e_shstrndx,其含义就是shstrtable对应的section header在section header table中的索引。
(2)sh_type,4字节,描述了section的类型,常见的取值如下:
- SHT_NULL 0,表明section header无效,没有关联的section。
- SHT_PROGBITS 1,section包含了程序需要的数据,格式和含义由程序解释。
- SHT_SYMTAB 2, 包含了一个符号表。当前,一个ELF文件中只有一个符号表。SHT_SYMTAB提供了用于(link editor)链接编辑的符号,当然这些符号也可能用于动态链接。这是一个完全的符号表,它包含许多符号。
- SHT_STRTAB 3,包含一个字符串表。一个对象文件包含多个字符串表,比如.strtab(包含符号的名字)和.shstrtab(包含section的名称)。
- SHT_RELA 4,重定位节,包含relocation入口,参见Elf32_Rela。一个文件可能有多个Relocation Section。比如.rela.text,.rela.dyn。
- SHT_HASH 5,这样的section包含一个符号hash表,参与动态连接的目标代码文件必须有一个hash表。目前一个ELF文件中只包含一个hash表。讲链接的时候再细讲。
- SHT_DYNAMIC 6,包含动态链接的信息。目前一个ELF文件只有一个DYNAMIC section。
- SHT_NOTE 7,note section, 以某种方式标记文件的信息,以后细讲。
- SHT_NOBITS 8,这种section不含字节,也不占用文件空间,section header中的sh_offset字段只是概念上的偏移。
- SHT_REL 9, 重定位节,包含重定位条目。和SHT_RELA基本相同,两者的区别在后面讲重定位的时候再细讲。
- SHT_SHLIB 10,保留,语义未指定,包含这种类型的section的elf文件不符合ABI。
- SHT_DYNSYM 11, 用于动态连接的符号表,推测是symbol table的子集。
- SHT_LOPROC 0x70000000 到 SHT_HIPROC 0x7fffffff,为特定于处理器的语义保留。
- SHT_LOUSER 0x80000000 and SHT_HIUSER 0xffffffff,指定了为应用程序保留的索引的下界和上界,这个范围内的索引可以被应用程序使用。
(3)sh_flags, 32位占4字节, 64位占8字节。包含位标志,用 readelf -S 可以看到很多标志。常用的有:
- SHF_WRITE 0x1,进程执行的时候,section内的数据可写。
- SHF_ALLOC 0x2,进程执行的时候,section需要占据内存。
- SHF_EXECINSTR 0x4,节内包含可以执行的机器指令。
- SHF_STRINGS 0x20,包含0结尾的字符串。
- SHF_MASKOS 0x0ff00000,这个mask为OS特定的语义保留8位。
- SHF_MASKPROC 0xf0000000,这个mask包含的所有位保留(也就是最高字节的高4位),为处理器相关的语义使用。
(4)sh_addr, 对32位来说是4字节,64位是8字节。如果section会出现在进程的内存映像中,给出了section第一字节的虚拟地址。
(5)sh_offset,对于32位来说是4字节,64位是8字节。section相对于文件头的字节偏移。对于不占文件空间的section(比如SHT_NOBITS),它的sh_offset只是给出了section逻辑上的位置。
(6)sh_size,section占多少字节,对于SHT_NOBITS类型的section,sh_size没用,其值可能不为0,但它也不占文件空间。
(7)sh_link,含有一个section header的index,该值的解释依赖于section type。
- 如果是SHT_DYNAMIC,sh_link是string table的section header index,也就是说指向字符串表。
- 如果是SHT_HASH,sh_link指向symbol table的section header index,hash table应用于symbol table。
- 如果是重定位节SHT_REL或SHT_RELA,sh_link指向相应符号表的section header index。
- 如果是SHT_SYMTAB或SHT_DYNSYM,sh_link指向相关联的符号表,暂时不解。
- 对于其它的section type,sh_link的值是SHN_UNDEF
(8)sh_info,存放额外的信息,值的解释依赖于section type。
- 如果是SHT_REL和SHT_RELA类型的重定位节,sh_info是应用relocation的节的节头索引。
- 如果是SHT_SYMTAB和SHT_DYNSYM,sh_info是第一个non-local符号在符号表中的索引。推测local symbol在前面,non-local symbols紧跟在后面,所以文档中也说,sh_info是最后一个本地符号的在符号表中的索引加1。
- 对于其它类型的section,sh_info是0。
(9)sh_addralign,地址对齐,如果一个section有一个doubleword字段,系统在载入section时的内存地址必须是doubleword对齐。也就是说sh_addr必须是sh_addralign的整数倍。只有2的正整数幂是有效的。0和1说明没有对齐约束。
(10)sh_entsize,有些section包含固定大小的记录,比如符号表。这个值给出了每个记录大小。对于不包含固定大小记录的section,这个值是0。
2. 系统预定义的section name
系统预定义了一些节名(以.开头),这些节有其特定的类型和含义。
- .bss:包含程序运行时未初始化的数据(全局变量和静态变量)。当程序运行时,这些数据初始化为0。 其类型为SHT_NOBITS,表示不占文件空间。SHF_ALLOC + SHF_WRITE,运行时要占用内存的。
- .comment 包含版本控制信息(是否包含程序的注释信息?不包含,注释在预处理时已经被删除了)。类型为SHT_PROGBITS。
- .data和.data1,包含初始化的全局变量和静态变量。 类型为SHT_PROGBITS,标志为SHF_ALLOC + SHF_WRITE(占用内存,可写)。
- .debug,包含了符号调试用的信息,我们要想用gdb等工具调试程序,需要该类型信息,类型为SHT_PROGBITS。
- .dynamic,类型SHT_DYNAMIC,包含了动态链接的信息。标志SHF_ALLOC,是否包含SHF_WRITE和处理器有关。
- .dynstr,SHT_STRTAB,包含了动态链接用的字符串,通常是和符号表中的符号关联的字符串。标志 SHF_ALLOC
- .dynsym,类型SHT_DYNSYM,包含动态链接符号表, 标志SHF_ALLOC。
- .fini,类型SHT_PROGBITS,程序正常结束时,要执行该section中的指令。标志SHF_ALLOC + SHF_EXECINSTR(占用内存可执行)。现在ELF还包含.fini_array section。
- .got,类型SHT_PROGBITS,全局偏移表(global offset table),以后会重点讲。
- .hash,类型SHT_HASH,包含符号hash表,以后细讲。标志SHF_ALLOC。
- .init,SHT_PROGBITS,程序运行时,先执行该节中的代码。SHF_ALLOC + SHF_EXECINSTR,和.fini对应。现在ELF还包含.init_array section。
- .interp,SHT_PROGBITS,该节内容是一个字符串,指定了程序解释器的路径名。如果文件中有一个可加载的segment包含该节,属性就包含SHF_ALLOC,否则不包含。
- .line,SHT_PROGBITS,包含符号调试的行号信息,描述了源程序和机器代码的对应关系。gdb等调试器需要此信息。
- .note Note Section, 类型SHT_NOTE,以后单独讲。
- .plt 过程链接表(Procedure Linkage Table),类型SHT_PROGBITS,以后重点讲。
- .relNAME,类型SHT_REL, 包含重定位信息。如果文件有一个可加载的segment包含该section,section属性将包含SHF_ALLOC,否则不包含。NAME,是应用重定位的节的名字,比如.text的重定位信息存储在.rel.text中。
- .relaname 类型SHT_RELA,和.rel相同。SHT_RELA和SHT_REL的区别,会在讲重定位的时候说明。
- .rodata和.rodata1。类型SHT_PROGBITS, 包含只读数据,组成不可写的段。标志SHF_ALLOC。
- .shstrtab,类型SHT_STRTAB,包含section的名字。有读者可能会问:section header中不是已经包含名字了吗,为什么把名字集中存放在这里? sh_name 包含的是.shstrtab 中的索引,真正的字符串存储在.shstrtab中。那么section names为什么要集中存储?我想是这样:如果有相同的字符串,就可以共用一块存储空间。如果字符串存在包含关系,也可以共用一块存储空间。
- .strtab SHT_STRTAB,包含字符串,通常是符号表中符号对应的变量名字。如果文件有一个可加载的segment包含该section,属性将包含SHF_ALLOC。字符串以\0结束, section以\0开始,也以\0结束。一个.strtab可以是空的,它的sh_size将是0。针对空字符串表的非0索引是允许的。
- symtab,类型SHT_SYMTAB,Symbol Table,符号表。包含了定位、重定位符号定义和引用时需要的信息。符号表是一个数组,Index 0 第一个入口,它的含义是undefined symbol index, STN_UNDEF。如果文件有一个可加载的segment包含该section,属性将包含SHF_ALLOC。
3. 练习:读取section names
示例:从一个ELF文件中读取存储section name的字符串表。前面讲过,该字符串表也是一个section,section header table中有其对应的section header,并且ELF文件头中给出了节名字符串表对应的section header的索引,e_shstrndx。
我们的思路是这样:
从ELF header中读取section header table的起始位置,每个section header的大小,以及节名字符串表对应section header的索引。
计算section_header_table_offset + section_header_size * e_shstrndx 就是节名字符串表对应section header的偏移。
读取section header,可以从中得到节名字符串表在文件中的偏移和大小。
把节名字符串表读取到内存中,打印其内容。
代码如下:
/* 64位ELF文件读取section name string table */
#include 把以上代码存为chap3_read_section_names.c,执行gcc -Wall -o secnames chap3_read_section_names.c进行编译,输出的执行文件名叫secnames。执行secnames,输出如下:
./secnames
section header offset in file: 14768 (0x39b0)
section header entry size: 64
section header number: 29
section header string table index: 28
section name string table offset: 14502
section name string table size: 259
\0.symtab\0.strtab\0.shstrtab\0.interp\0.note.ABI-tag\0.note.gnu.build-id\0.gnu.hash\0.dynsym\0.dynstr\0.gnu.version\0.gnu.version_r\0.rela.dyn\0.rela.plt\0.init\0.text\0.fini\0.rodata\0.eh_frame_hdr\0.eh_frame\0.init_array\0.fini_array\0.dynamic\0.got\0.got.plt\0.data\0.bss\0.comment\0
可以发现,节头字符串表以\0开始,以\0结束。如果一个section的name字段指向0,则他指向的字节值是0,则它没有名称,或名称是空。