【数据结构】树及其应用
树及其应用
- 问题 A: DS树--二叉树高度
- 问题 B: DS树--二叉树之最大路径
- 问题 C: DS树--带权路径和
- 问题 D: DS二叉树--赫夫曼树的构建与编码(含代码框架)
问题 A: DS树–二叉树高度
题目描述
给出一棵二叉树,求它的高度。二叉树的创建采用前面实验的方法。
注意,二叉树的层数是从1开始
输入
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个二叉树
第二行起输入每个二叉树的先序遍历结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,连续输入t行
输出
每行输出一个二叉树的高度
样例输入
1
AB0C00D00
样例输出
3
题解
#include问题 B: DS树–二叉树之最大路径
题目描述
给定一颗二叉树的逻辑结构(先序遍历的结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,例如AB0C00D00),建立该二叉树的二叉链式存储结构
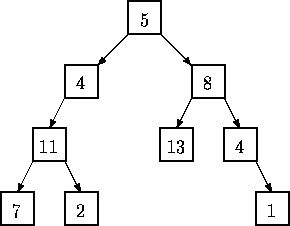
二叉树的每个结点都有一个权值,从根结点到每个叶子结点将形成一条路径,每条路径的权值等于路径上所有结点的权值和。编程求出二叉树的最大路径权值。如下图所示,共有4个叶子即有4条路径,
路径1权值=5 + 4 + 11 + 7 = 27
路径2权值=5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22
路径3权值=5 + 8 + 13 = 26
路径4权值=5 + 8 + 4 + 1 = 18
可计算出最大路径权值是27。
该树输入的先序遍历结果为ABCD00E000FG00H0I00,各结点权值为:
A-5,B-4,C-11,D-7,E-2,F-8,G-13,H-4,I-1
输入
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个测试数据
第二行输入一棵二叉树的先序遍历,每个结点用字母表示
第三行先输入n表示二叉树的结点数量,然后输入每个结点的权值,权值顺序与前面结点输入顺序对应
以此类推输入下一棵二叉树
输出
每行输出每棵二叉树的最大路径权值,如果最大路径权值有重复,只输出1个
样例输入
2
AB0C00D00
4 5 3 2 6
ABCD00E000FG00H0I00
9 5 4 11 7 2 8 13 4 1
样例输出
11
27
题解
#include问题 C: DS树–带权路径和
题目描述
计算一棵二叉树的带权路径总和,即求赫夫曼树的带权路径和。
已知一棵二叉树的叶子权值,该二叉树的带权案路径和APL等于叶子权值乘于根节点到叶子的分支数,然后求总和。如下图中,叶子都用大写字母表示,权值对应为:A-7,B-6,C-2,D-3
树的带权路径和 = 71 + 62 + 23 + 33 = 34
本题二叉树的创建参考前面的方法
输入
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个二叉树
第二行输入一棵二叉树的先序遍历结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,注意输入全是英文字母和0,其中大写字母表示叶子
第三行先输入n表示有n个叶子,接着输入n个数据表示n个叶子的权值,权值的顺序和前面输入的大写字母顺序对应
以此类推输入下一棵二叉树
输出
输出每一棵二叉树的带权路径和
样例输入
2
xA00tB00zC00D00
4 7 6 2 3
ab0C00D00
2 10 20
样例输出
34
40
题解
#include问题 D: DS二叉树–赫夫曼树的构建与编码(含代码框架)
题目描述
给定n个权值,根据这些权值构造huffman树,并进行huffman编码
参考课本算法,注意数组访问是从位置1开始
要求:赫夫曼的构建中,默认左孩子权值不大于右孩子权值
代码框架参考如下:
输入
第一行输入t,表示有t个测试实例
第二行先输入n,表示第1个实例有n个权值,接着输入n个权值,权值全是小于1万的正整数
依此类推
输出
逐行输出每个权值对应的编码,格式如下:权值-编码
即每行先输出1个权值,再输出一个短划线,再输出对应编码,接着下一行输入下一个权值和编码。
以此类推
样例输入
1
5 15 4 4 3 2
样例输出
15-1
4-010
4-011
3-001
2-000
题解
#include