java实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
目录
- 说明
- 一、LinkedHashMap实现
- 二、HashMap+双链表实现
- 三、HashMap+LinkedHashSet实现
说明
LRU算法:最近最少使用淘汰算法(Least Recently Used)。LRU是淘汰最长时间没有被使用的缓存(即使该缓存被访问的次数最多)。
LFU算法:最不经常使用淘汰算法(Least Frequently Used)。LFU是使用次数最少的缓存(若有多个相同的最少使用次数缓存,则删除距今最久的缓存。也就是淘汰使用次数最少且距今最久的缓存)。
LFU算法可参考 :java实现LFU缓存淘汰算法
下面给出三种不同方式来实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
一、LinkedHashMap实现
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private int cap;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public LRUCache(int cap) {
super(16, 0.75f, true);
this.cap = cap;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return size() > cap;
}
}
测试:
LRUCache<Integer, Integer> lruCache = new LRUCache<>(4);
lruCache.put(9, 3);
lruCache.put(7, 4);
lruCache.put(5, 9);
lruCache.put(3, 4);
System.out.println(lruCache);
lruCache.get(9);
lruCache.put(10, 10);
lruCache.put(11, 11);
System.out.println(lruCache);
输出:
{9=3, 7=4, 5=9, 3=4}
{3=4, 9=3, 10=10, 11=11}
二、HashMap+双链表实现
hashMap用于存储缓存,其中value存储链表的节点,节点中存key和value。
当访问某一个缓存或put缓存时会将该缓存移动或插入到链表的尾部,当链表满了后要删除缓存时会删除链表的头节点。
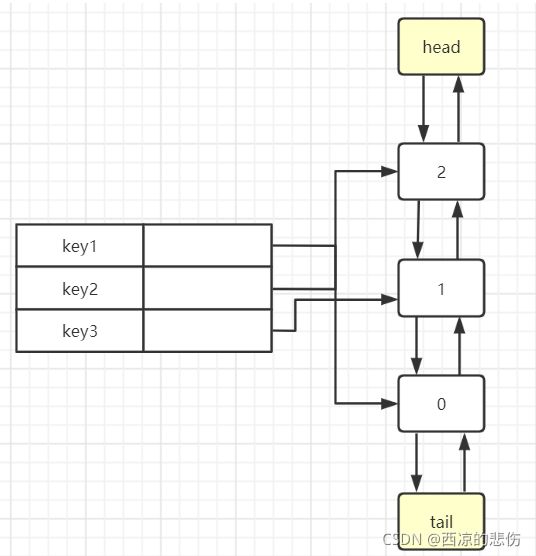
代码如下:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCache<K, V> {
Map<K, Node> map;//缓存
int cap;//最大缓存的数量
/**
* 链表长度
*/
public int size;
/**
* 头节点
*/
private Node head = null;
/**
* 尾节点
*/
private Node tail = null;
private class Node {
public K key;
public V value;
public Node preNode;
public Node nexNode;
public Node(K key, V value, Node pre, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.preNode = pre;
this.nexNode = next;
}
}
public LRUCache(int cap) {
this.size = 0;
this.cap = cap;
map = new HashMap<>(cap);
}
/**
* (双链表方法)默认插入数据节点到尾部
*/
public void add(K key, V value) {
if (size != 0) {
Node node = new Node(key, value, tail, null);
tail.nexNode = node;
tail = tail.nexNode;
} else {
this.head = new Node(key, value, null, null);
this.tail = head;
}
size++;
}
/**
* (双链表方法)删除头节点
*/
public void removeHead(int index) {
head.nexNode = null;
Node afterNode = getIndexNode(1);
afterNode.preNode = null;
}
/**
* (双链表方法)根据索引返回其节点
*/
public Node getIndexNode(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引越界");
}
//根据index大小来确定从头部查还是尾部查,以增加查询速度
if (index < size / 2) {
Node currentNode = head;
for (int i = 0; i < size / 2 && currentNode != null; i++) {
if (i == index) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.nexNode;
}
} else {
Node currentNode = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i >= size / 2 && currentNode != null; i--) {
if (i == index) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.preNode;
}
}
return null;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
return;
} else if (map.size() == cap) { //若达到缓存上限则将距今最久的缓存删
//从map中删除
map.remove(head.key);
//从链表中删除第一个
Node afterNode = getIndexNode(1);
head.nexNode = null;
afterNode.preNode = null;
head = afterNode;
size--;
}
add(key, value);
map.put(key, tail);
}
/**
* 从缓存中获取值,缓存中没有则返回null
*/
public V get(K key) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = map.get(key);
V value = node.value;
remove(key);
//将该节点增加到结尾
add(key, value);
map.put(key, tail);
return value;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 清空缓存和链表
*/
public void clear() {
map.clear();
// 将底层数组所有元素赋为null
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
/**
* 判断是包含
*/
public boolean contains(K key) {
return map.containsKey(key);
}
/**
* 删除指定缓存(从map和链表中删除)
*/
public void remove(K key) {
if (contains(key)) {
Node node = map.get(key);
//删除该节点
map.remove(key);
Node beforeNode = node.preNode;
Node afterNode = node.nexNode;
node.nexNode = null;
node.preNode = null;
if (null != beforeNode) {
beforeNode.nexNode = afterNode;
} else {
head = afterNode;
}
if (null != afterNode) {
afterNode.preNode = beforeNode;
} else {
tail = beforeNode;
}
size--;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String[] array = new String[size];
Node currentNode = head;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = String.valueOf(currentNode.value);
currentNode = currentNode.nexNode;
}
return Arrays.toString(array);
}
}
测试:
LRUCache<String,String> lruCache = new LRUCache<String,String>(4);
lruCache.put("a","a");
lruCache.put("b","b");
lruCache.put("c","c");
lruCache.put("d","d");
System.out.println("values:"+lruCache.toString());
System.out.println(lruCache.size);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//a将被淘汰
lruCache.put("e","e");
System.out.println("淘汰a后values:"+lruCache.toString());
System.out.println(lruCache.size);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//获取缓存c
System.out.println(lruCache.get("c"));
System.out.println("获取缓存c后values:"+lruCache.toString());
System.out.println(lruCache.size);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//删除缓存c
lruCache.remove("c");
System.out.println("删除c后values:"+lruCache.toString());
System.out.println(lruCache.size);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//判断是否包含缓存d
System.out.println("判断是否包含缓存d:"+lruCache.contains("d"));
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//清空所有缓存
lruCache.clear();
System.out.println("清空所有缓存后values:"+lruCache.toString());
System.out.println(lruCache.size);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
输出:
values:[a, b, c, d]
4
------------------------------
淘汰a后values:[b, c, d, e]
4
------------------------------
c
获取缓存c后values:[b, d, e, c]
4
------------------------------
删除c后values:[b, d, e]
3
------------------------------
判断是否包含缓存d:true
------------------------------
清空所有缓存后values:[]
0
------------------------------
三、HashMap+LinkedHashSet实现
代码如下:
import java.util.*;
public class LRUCache {
int cap;//最大缓存的数量
Map<String, String> values;//缓存
Set<String> position;//缓存的key,按照存入的顺序存储
public LRUCache(int cap) {
this.cap = cap;
values = new HashMap<>(cap);
position = new LinkedHashSet<>(cap);
}
/**
* 从缓存中获取值,缓存中没有则返回null
*/
public String get(String key) {
String value = null;
if (values.containsKey(key)) {
value = values.get(key);
position.remove(key);
position.add(key);
}
return value;
}
/**
* 将值放入缓存中
*/
public void put(String key, String value) {
if (position.size() == cap) {
//若达到缓存上限则将距今最久的缓存删除
String firstKey = position.iterator().next();
position.remove(firstKey);
values.remove(firstKey);
}
position.add(key);
values.put(key, value);
}
public Map<String, String> getValues() {
return values;
}
public Set<String> getPosition() {
return position;
}
}
测试:
LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache(4);
lruCache.put("a","a");
lruCache.put("b","b");
lruCache.put("c","c");
lruCache.put("d","d");
System.out.println("position:"+lruCache.getPosition());
System.out.println("values:"+lruCache.getValues());
//a将被淘汰
lruCache.put("e","e");
System.out.println("position:"+lruCache.getPosition());
System.out.println("values:"+lruCache.getValues());
输出:
position:[a, b, c, d]
values:{a=a, b=b, c=c, d=d}
position:[b, c, d, e]
values:{b=b, c=c, d=d, e=e}