JAVA大数据-Week4-DAY6-JDBC
文章目录
- 前言
- 第五章-数据库MySql必备技能-第5节-JDBC
-
- JDBC简介
- JDBC体系结构
- JDBC组件
- SQL复习
- JDBC操作步骤-1
- JDBC操作步骤-2
- JDBC操作步骤回顾
- SQL注入
- 预状态通道
- 多表操作之一对多
- 多表关系之多对一
- 多表关系之双向一对一
- 多表关系之多对多
- 事务
- 事务案例-转账
- 批处理
- 反射处理结果集
- 封装工具类
- 属性文件
- 自定义连接池
- DBCP
- C3P0
- 德鲁伊
- 总结
- 总结
前言
第五章-数据库MySql必备技能-第5节-JDBC
JDBC简介
JAVA代码操作数据库
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多
种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。JDBC提供了一种基准,据此可以构建更高级的工具和接口,使数据库开发人员能够编写数据库应用程序
Java 具有坚固、安全、易于使用、易于理解和可从网络上自动下载等特性,是编写数据库应用程序的杰
出语言。所需要的只是 Java应用程序与各种不同数据库之间进行对话的方法。
JDBC可以在各种平台上使用Java,如Windows,Mac OS和各种版本的UNIX。
JDBC库包括通常与数据库使用相关的下面提到的每个任务的API。
- 连接数据库。
- 创建SQL或MySQL语句。
- 在数据库中执行SQL或MySQL查询。
- 查看和修改生成的记录。
JDBC体系结构
JDBC API支持用于数据库访问的两层和三层处理模型,但通常,JDBC体系结构由两层组成:
- JDBC API**:**这提供了应用程序到JDBC管理器连接。
- JDBC驱动程序API**:**这支持JDBC管理器到驱动程序连接。
JDBC API使用驱动程序管理器和特定于数据库的驱动程序来提供与异构数据库的透明连接。
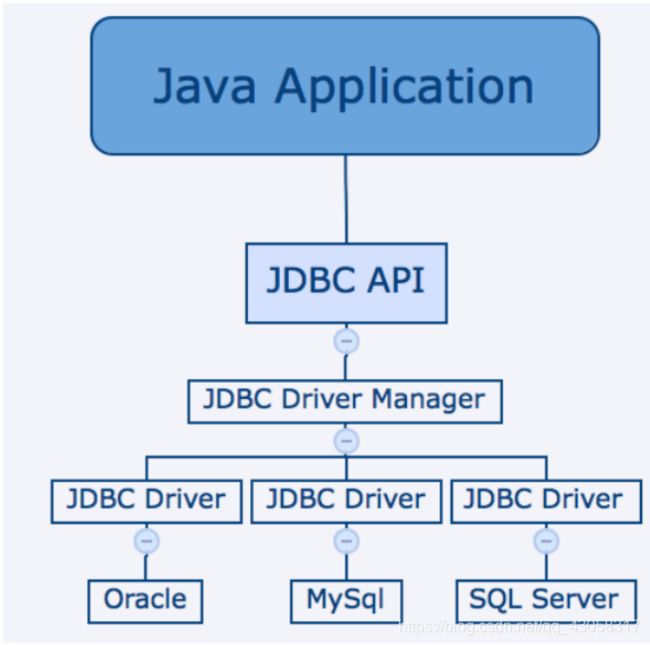
JDBC组件
3 JDBC****核心组件
**DriverManager****:** 此类管理数据库驱动程序列表。使用通信子协议将来自java应用程序的连接请求与适当的数据库驱动程序匹配。
**Driver**:此接口处理与数据库服务器的通信,我们很少会直接与Driver对象进行交互。而是使用
DriverManager对象来管理这种类型的对象。
**Connection****:**该界面具有用于联系数据库的所有方法。连接对象表示通信上下文,即,与数据库的所有通信仅通过连接对象。
**Statement**:使用从此接口创建的对象将SQL语句提交到数据库。除了执行存储过程之外,一些派
生接口还接受参数。
**ResultSet****:**在使用Statement对象执行SQL查询后,这些对象保存从数据库检索的数据。它作为一
个迭代器,允许我们移动其数据。
**SQLException****:**此类处理数据库应用程序中发生的任何错误
SQL复习
4 CRUD****语法介绍
SQL 是一种标准化的语言,它允许你在数据库上执行操作,如创建项目,查询内容,更新内容,并
删除条目等操作。
Create, Read, Update, and Delete 通常称为CRUD操作。
CREATE DATABASE语句用于创建新的数据库:
SQL> CREATE DATABASE DATABASE_NAME;
DROP DATABASE语句用于删除现有数据库:
SQL> DROP DATABASE DATABASE_NAME;
CREATE TABLE语句用于创建新表。语法是
SQL> CREATE TABLE Employees (
id INT NOT NULL,
age INT NOT NULL,
first VARCHAR(255),
last VARCHAR(255),
PRIMARY KEY ( id )
);
DROP TABLE语句用于删除现有表。
SQL> DROP TABLE table_name;
INSERT的语法类似于以下内容,其中column1,column2等表示要显示在相应列中的新数据
SQL> INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (column1, column2, ...);
SELECT语句用于从数据库中检索数据。SELECT的语法是 -
SQL> SELECT column_name, column_name, ... FROM table_name WHERE conditions;
WHERE子句可以使用比较运算符,例如=,!=,<,>,<=和> =,以及BETWEEN和LIKE运算符。
UPDATE语句用于更新数据。
SQL> UPDATE table_name
SET column_name = value, column_name = value, ...
WHERE conditions;
WHERE子句可以使用比较运算符,例如=,!=,<,>,<=和> =,以及BETWEEN和LIKE运算符。
DELETE语句用于从表中删除数据。
SQL> DELETE FROM table_name WHERE conditions;
WHERE子句可以使用比较运算符,例如=,!=,<,>,<=和> =,以及BETWEEN和LIKE运算符。
JDBC操作步骤-1
构建JDBC应用程序涉及以下六个步骤:
- **导入包:需要包含包含数据库编程所需的JDBC类的包。大多数情况下,使用import java.sql.***就足够
了。
- **注册JDBC驱动程序:**要求您初始化驱动程序,以便您可以打开与数据库的通信通道。
- 打开连接:需要使用DriverManager.getConnection**()**方法创建一个Connection对象,该对象表
示与数据库的物理连接。
- **执行查询:**需要使用类型为Statement的对象来构建和提交SQL语句到数据库。
- 从结果集中提取数据:需要使用相应的ResultSet.getXXX**()**方法从结果集中检索数据。
- **释放资源:**需要明确地关闭所有数据库资源,而不依赖于JVM的垃圾收集。
注册
https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/download-thanks.html?platform=windows
绑定
https://www.jetbrains.com/store/redeem/
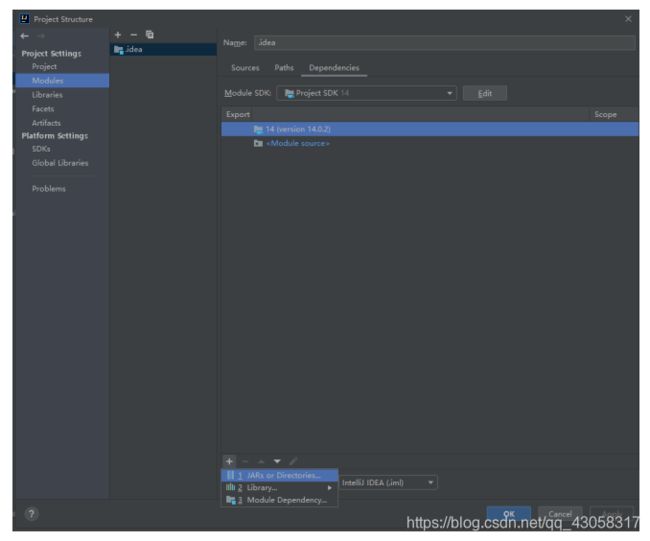
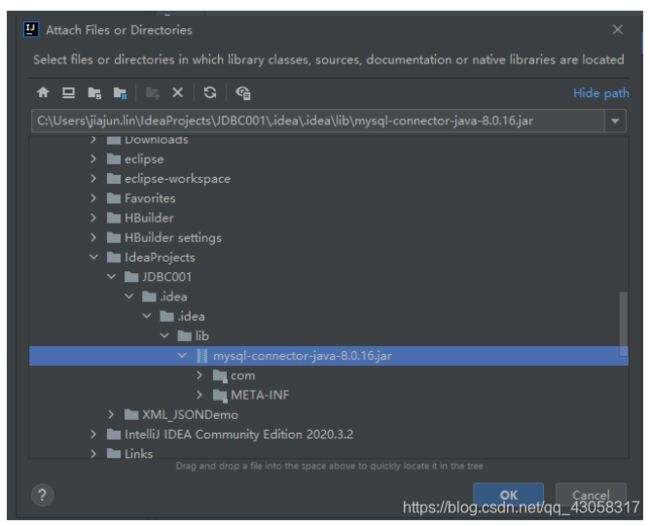
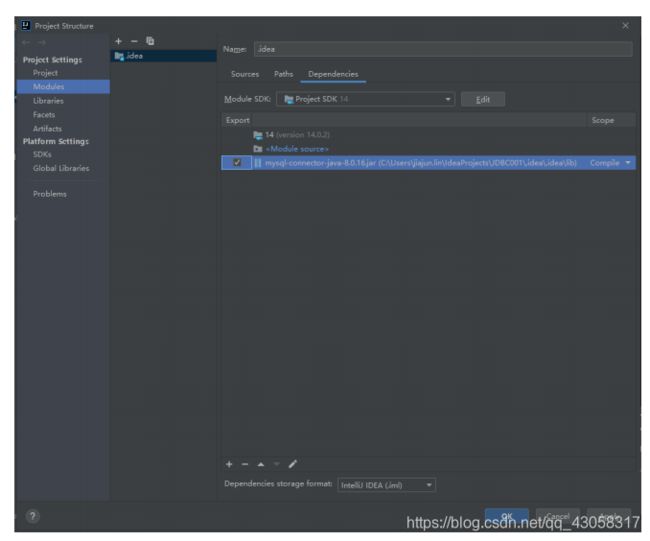
(1)驱动包
(2)
(3)
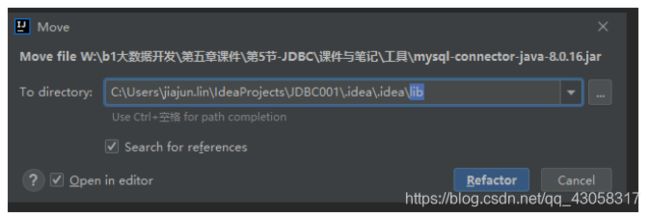
(4)将封装好的工具类拉进去
(5)将这个java包添加到程序里面
新版本
OK
(6)编写JAVA代码
(7)
(8)这里很重要ctrl+alt+shift+s
Apply
11.0 versiion
package com;
import java.sql.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
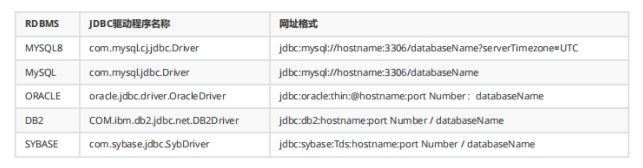
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from emp2");//executeQuery(sql) 执行查询
//4.取出结果集信息
while (resultSet.next()) { //判断是否有下一条数据
//取出数据: resultSet.getxxx("列名"); xxx表示数据类型
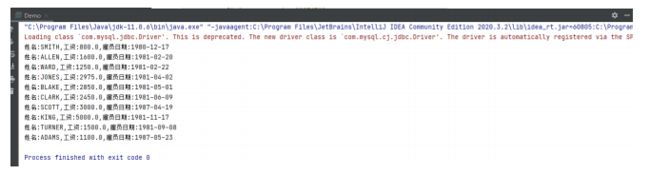
System.out.println("姓名:" + resultSet.getString("ename") + ",工资:" + resultSet.getDouble("sal") + ",雇员日期:" + resultSet.getDate("hiredate"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
JDBC操作步骤-2
做增删改
package com;
import java.sql.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
statement = connection.createStatement();
int result = statement.executeQuery("insert into emp2(ename,hiredate,sal) values('aa','2020-1-1',2000)");//executeQuery(sql) 执行查询
//4.取出结果集信息
if (result>0) {
System.out.println("执行成功");
}else {
System.out.println("执行失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
6 JDBC****连接步骤
建立JDBC连接所涉及的编程相当简单。这是简单的四个步骤
- *导入JDBC包:将Java语言的import***语句添加到Java代码中导入所需的类。
- **注册JDBC驱动程序:**此步骤将使JVM将所需的驱动程序实现加载到内存中,以便它可以满足您的JDBC
请求。
- **数据库URL配置:**这是为了创建一个格式正确的地址,指向要连接到的数据库。
- 创建连接对象:最后,调用DriverManager对象的**getConnection****()**方法来建立实际的数据库连
接。
Class.forName();
注册驱动程序最常见的方法是使用Java的**Class.forName()**方法,将驱动程序的类文件动态加载到内存
中,并将其自动注册
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
}catch(ClassNotFoundException ex) {
System.out.println("Error: unable to load driver class!");
System.exit(1);
}
DriverManager.registerDriver()
第二种方法是使用静态**DriverManager.registerDriver****()**方法。
try {
Driver myDriver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver( myDriver );
}catch(ClassNotFoundException ex) {
System.out.println("Error: unable to load driver class!");
System.exit(1);
}
数据库URL配置
加载驱动程序后,可以使用**DriverManager.getConnection****()**方法建立连接。为了方便参考,让我
列出三个重载的DriverManager.getConnection()方法 -
- getConnection(String url)
- getConnection(String url,Properties prop)
- getConnection(String url,String user,String password)
创建数据库连接对象
String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp2?serverTimezone=UTC";
String USER = "username";
String PASS = "password"
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASS);
完整的连接地址:
版本1:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名? useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
版本2:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp2?serverTimezone=UTC
使用数据库URL和属性对象
DriverManager.getConnection()方法的第三种形式需要一个数据库URL和一个Properties对象 -
DriverManager.getConnection(String url, Properties info);
import java.util.*;
String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp2?serverTimezone=UTC";
Properties info = new Properties( );
info.put( "user", "username" );
info.put( "password", "password" );
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, info);
关闭数据库连接
为确保连接关闭,您可以在代码中提供一个“fifinally”块。一个fifinally块总是执行,不管是否发生异常。要关闭上面打开的连接,你应该调用close()方法如下 -
conn.close();
JDBC操作步骤回顾
6.1 JDBC执行SQL****语句
一旦获得了连接,我们可以与数据库进行交互。JDBC Statement和PreparedStatement接口定义了使
您能够发送SQL命令并从数据库接收数据的方法和属性。
| 接口 | 推荐使用 |
| ------------------ | ---------------------------------------- |
| 声明 | 用于对数据库进行通用访问。在运行时使用静态SQL语句时很有用。Statement接口不能
接受参数。 |
| PreparedStatement的 | 当您计划多次使用SQL语句时使用。PreparedStatement接口在运行时接受
输入参数。 |
6.2 Statement
创建语句对象
在使用Statement对象执行SQL语句之前,需要使用Connection对象的createStatement()方法创建
一个,如下例所示:
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement( );
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
. . .
}
创建Statement对象后,您可以使用它来执行一个SQL语句,其中有三个执行方法之一。
- boolean execute**(String SQL)**:如果可以检索到ResultSet对象,则返回一个布尔值true; 否则返
回false。使用此方法执行SQL DDL语句或需要使用真正的动态SQL时。
- int executeUpdate**(String SQL)**:返回受SQL语句执行影响的行数。使用此方法执行预期会影响
多个行的SQL语句,例如INSERT,UPDATE或DELETE语句。
- ResultSet executeQuery**(String SQL)**:返回一个ResultSet对象。当您希望获得结果集时,请使
用此方法,就像使用SELECT语句一样。
关闭Statement对象
就像我们关闭一个Connection对象以保存数据库资源一样,由于同样的原因,还应该关闭Statement对
象。
一个简单的调用close()方法将执行该作业。如果先关闭Connection对象,它也会关闭Statement对
象。但是,应始终显式关闭Statement对象,以确保正确清理。
Statement stmt = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement( );
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
stmt.close();
}
SQL注入
就是通过把SQL命令插入到Web表单提交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执
行恶意的SQL命令。具体来说,它是利用现有应用程序,将(恶意的)SQL命令注入到后台数据库引擎
执行的能力,它可以通过在Web表单中输入(恶意)SQL语句得到一个存在安全漏洞的网站上的数据
库,而不是按照设计者意图去执行SQL语句。比如先前的很多影视网站泄露VIP会员密码大多就是通过
WEB表单递交查询字符暴出的,这类表单特别容易受到SQL注入式攻击。
String username ="admin";
String password=" 'abc' or 1=1 ";
String sql="select * from users where username= '"+username+"' and password= "+password;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
String path = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName(path);
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
statement = connection.createStatement();
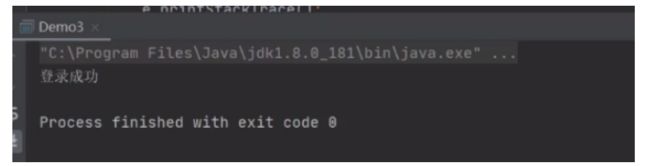
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from users2 where username='a' and password='11'");//executeQuery(sql) 执行查询
//4.取出结果集信息
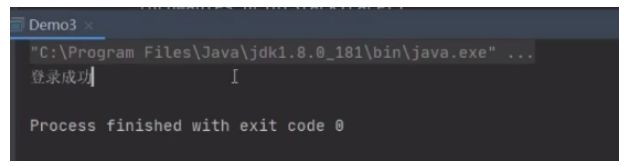
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
密码改为111
uname=‘aa’;pass=‘111’;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
String path = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName(path);
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
statement = connection.createStatement();
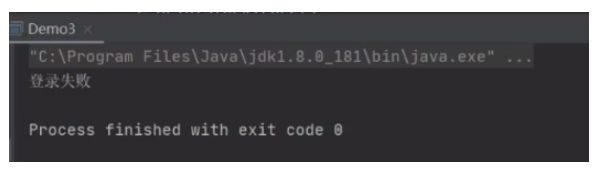
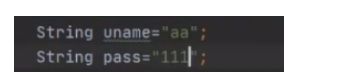
String uname = 'aa';
String pass = '111';
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from users2 where username='"+uname+"' and password='+pass);//executeQuery(sql) 执行查询
//4.取出结果集信息
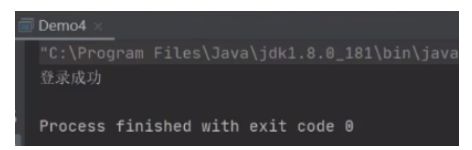
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
加粗样式
SQL注入的精妙之处
就是写一个恒成立的条件
String uname = 'abcd';
String pass = " '' or 1=1 ";
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
String path = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName(path);
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
statement = connection.createStatement();
String uname = "abcd";
String pass = " '' or 1=1 ";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from users2 where username='"+uname+"' and password='+pass);//executeQuery(sql) 执行查询
//4.取出结果集信息
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
怎么解决这个问题?
使用预状态通道
预状态通道
?表示占位
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pps = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
String path = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName(path);
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
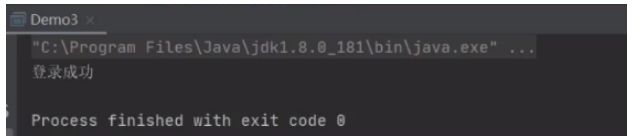
String sql = "select * from users where username=? and password=?";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
String uname = "abcd";
String pass = " '' or 1=1 ";
//给展位符赋值 (下标,数值内容)
pps.setString(1,uname);
pps.setString(2,pass);
resultSet = pps.executeQuery();//executeQuery(sql) 执行查询
//4.取出结果集信息
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
正确的
7 PreparedStatement(预状态通道)
该PreparedStatement****的接口扩展了Statement接口,它为您提供了一个通用的Statement对象有两
个优点附加功能。
此语句使您可以动态地提供参数。
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
String SQL = "Update Employees SET age = ? WHERE id = ?";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(SQL);
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
. . .
}
JDBC中的所有参数都由?符号,这被称为参数标记。在执行SQL****语句之前,必须为每个参数提供值。
所述的setXXX()方法将值绑定到所述参数,其中XXX代表要绑定到输入参数的值的Java数据类型。如果
忘记提供值,将收到一个SQLException。
每个参数标记由其顺序位置引用。第一个标记表示位置1,下一个位置2等等。该方法与Java数组索引不
同,从0开始。
关闭PreparedStatement对象
就像关闭Statement对象一样,由于同样的原因,还应该关闭PreparedStatement对象。
一个简单的调用close()方法将执行该作业。如果先关闭Connection对象,它也会关闭
PreparedStatement对象。但是,应始终显式关闭PreparedStatement对象,以确保正确清理。
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
String SQL = "Update Employees SET age = ? WHERE id = ?";
pstmt = conn.preparedStatement(SQL);
. . .
}
catch (SQLException e) {
. . .
}
finally {
pstmt.close();
}
对比statement和PreparedStatement;
(1)statement属于状态通道,PreparedStatement属于预状态通道
(2)预状态通道会先编译sql语句,再去执行,比statement执行效率高
(3)预状态通道支持占位符?,给占位符赋值的时候,位置从1开始
(4)预状态通道可以防止sql注入,原因:预状态通道在处理值的时候以字符串的方式处理
8 ResultSet
SELECT语句是从数据库中选择行并在结果集中查看行的标准方法。该java.sql.ResultSet****中的接口表示
结果集数据库查询。
ResultSet对象维护指向结果集中当前行的游标。术语“结果集”是指包含在ResultSet对象中的行和列数
据。
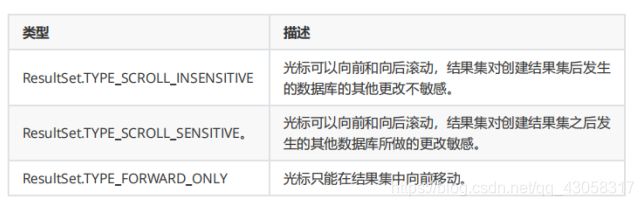
如果没有指定任何ResultSet类型,您将自动获得一个TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY。
try {
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(
ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY,
ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
}catch(Exception ex) {
....
}finally {
....
}
多表操作之一对多
9 JAVA****操作两表关系
四种:双向一对一,一对多,多对一,多对多
多表关系处理数据
(1) 数据库通过外键建立两表关系
(2) 实体类通过属性的方式建立两表关系
实体类要求:类名**=表名,列名=**属性名
9.1 一对多(老师**->**学生)
(1)创建数据表
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`stuid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`stuname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`teacherid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`stuid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('1', 'aaa', '3');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('2', 'bb', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('3', 'cc', '3');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('4', 'dd', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('5', 'ee', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('6', 'ff', '2');
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `teacher`;
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`tid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`tname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`tid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('1', '张三老师');
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('2', '李四老师');
INSERT INTO `teacher` VALUES ('3', '王五');
select * from student;
select * from teacher;
(2)创建实体类
bean包存放实体类
数据->(数据库是主外键建立关系,类是通过集合来建立关系的)>
一方(老师)存储多方数据的集合,List studentList;
多方存储一方的ID
->生成get,set方法封装一下
->写一个调用老师的接口dao.TeacherDao interface
(public Teacher getById(int tid);)
->新建一个包 impl.TeacherDaoImpl 类实现接口
sql,
->测试
public class Teacher {
private int tid;
private String tname;
//一方存储多方数据的集合
private List list=new ArrayList();
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public int getTid() {
return tid;
}
public void setTid(int tid) {
this.tid = tid;
}
public String getTname() {
return tname;
}
public void setTname(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
}
public class Student {
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
//外键列一般不生成属性
// private int teacherid;
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
}
(3)定义dao接口
public interface TeacherDao {
//定义操作方法
//1.定义一个根据老师id查询老师信息(学生的信息)
public Teacher getById(int tid);
}
(4)定义实现类
package dao.impl;
import bean.Student;
import dao.TeacherDao;
import bean.Teacher;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TeacherDaoImpl implements TeacherDao {
@Override
public Teacher getById(int tid) {
//操作数据库
//用于连接数据库
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pps = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
String path = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName(path);
//2.获得连接
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//专门用来连接mysql8驱动地址
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yh3?serverTimezone=UTC";
//
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
String sql = "select * from student s,teacher t where s.teacherid=t.tid and t.tid=?";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//给展位符赋值 (下标,数值内容)
pps.setInt(1,tid);
//执行sql
resultSet = pps.executeQuery();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
List students = new ArrayList();
while (resultSet.next()) {
//1.取出各自的信息
teacher.setTid(resultSet.getInt("tid"));
teacher.setTname(resultSet.getString("tname"));
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuId(resultSet.getInt("stuid"));
student.setStuName(resultSet.getString("stuname"));
//2.建立学生和老师之间的关系
students.add(student);
}
teacher.setStudentList(students);
return teacher;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables ) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection !=null ) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}
(4)定义测试类
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TeacherDao dao= new TeacherDaoImpl();
Teacher teacher = dao.getById(1);
System.out.println("老师姓名:"+teacher.getTname());
List studentList = teacher.getStudentList();
for (Student student : studentList) {
System.out.println("\t studentname="+student.getStuName());
}
}
}
多表关系之多对一
数据表同上
实体类:
public class Student {
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
//外键列一般不生成属性
// private int teacherid;
//多方存储一方的数据
private Teacher teacher;
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
}
public class Teacher {
private int tid;
private String tname;
public int getTid() {
return tid;
}
public void setTid(int tid) {
this.tid = tid;
}
public String getTname() {
return tname;
}
public void setTname(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
}
接口:
//查询所有的学生(包含老师的信息)
public List getAll();
实现类:
public List getAll() {
//操作数据库
Connection connection =null;
PreparedStatement pps =null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得链接
String userName="root";
String passWord="123456";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord);
//3.定义sql,创建预状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
String sql="select * from student s,teacher t where s.teacherid=t.tid";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//执行sql resultSet = pps.executeQuery();
List students=new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
//1.取出各自的信息
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuId(resultSet.getInt("stuid"));
student.setStuName(resultSet.getString("stuname"));
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setTid(resultSet.getInt("tid"));
teacher.setTname(resultSet.getString("tname"));
//2.建立学生和老师之间的关系
student.setTeacher(teacher);
students.add(student);
}
return students;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
测试类:
public static void main(String[] args) {
TeacherDao dao= new TeacherDaoImpl();
List students = dao.getAll();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.getStuName()+","+student.getTeacher().getTname()); }
}
多表关系之双向一对一
在任一方都带有对方的对象
9.3 一对一(妻子丈夫)
数据表:
CREATE TABLE `husband` (
`husid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`husname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`husid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `husband` VALUES ('1', '邓超');
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `wife`;
CREATE TABLE `wife` (
`wifeid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`wifename` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`hid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`wifeid`),
UNIQUE KEY `uq_wife_hid` (`hid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `wife` VALUES ('1', '孙俪', '1');
实体类:
public class Husband {
private int husid;
private String husname;
private Wife wife;
public int getHusid() {
return husid;
}
public void setHusid(int husid) {
this.husid = husid;
}
public String getHusname() {
return husname;
}
public void setHusname(String husname) {
this.husname = husname;
}
public Wife getWife() {
return wife;
}
public void setWife(Wife wife) {
this.wife = wife;
}
}
public class Wife {
private int wifeid;
private String wifeName;
private Husband husband;
public int getWifeid() {
return wifeid;
}
public void setWifeid(int wifeid) {
this.wifeid = wifeid;
}
public String getWifeName() {
return wifeName;
}
public void setWifeName(String wifeName) {
this.wifeName = wifeName;
}
public Husband getHusband() {
return husband;
}
public void setHusband(Husband husband) {
this.husband = husband;
}
}
接口:
//查询妻子就应该返回妻子这个对象
//查询丈夫就应该返回丈夫 这个对象
//两者都通过ID去找
public interface WifeDao {
//查询妻子信息(包含丈夫信息)
public Wife getWife(int wid);
//查询丈夫信息(包含妻子信息)
public Husband getHus(int hid);
}
实现类:
public class WifeDaoImpl implements WifeDao {
@Override
public Wife getWife(int wid) {
//操作数据库
Connection connection =null;
PreparedStatement pps =null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得链接
String userName="root";
String passWord="123456";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord);
//3.定义sql,创建预状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
String sql="select * from wife w,husband h where w.hid=h.husid and w.wifeid=?";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pps.setInt(1,wid);
//执行sql
resultSet = pps.executeQuery();
Wife wife = new Wife();
while (resultSet.next()){
//1.取出各自的信息
wife.setWifeId(resultSet.getInt("wifeid"));
wife.setWifeName(resultSet.getString("wifename"));
Husband husband = new Husband();
husband.setHusId(resultSet.getInt("husid"));
husband.setHusName(resultSet.getString("husname"));
//2.建立妻子和丈夫之间的关系
wife.setHusband(husband);
}
return wife;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Husband getHus(int hid) {
//操作数据库
Connection connection =null;
PreparedStatement pps =null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得链接
String userName="root";
String passWord="123456";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord);
//3.定义sql,创建预状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
String sql="select * from wife w,husband h where w.hid=h.husid and h.husid=?";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pps.setInt(1,hid);
//执行sql
resultSet = pps.executeQuery();
Husband husband = new Husband();
while (resultSet.next()){
//1.取出各自的信息 Wife wife = new Wife();
wife.setWifeId(resultSet.getInt("wifeid"));
wife.setWifeName(resultSet.getString("wifename"));
husband.setHusId(resultSet.getInt("husid"));
husband.setHusName(resultSet.getString("husname"));
//2.建立妻子和丈夫之间的关系
husband.setWife(wife);
}
return husband;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}
测试类:
public static void main(String[] args) {
WifeDaoImpl wifeDao = new WifeDaoImpl();
Wife wife = wifeDao.getWife(1);
System.out.println(wife.getWifeName()+","+wife.getHusband().getHusName());
Husband hus = wifeDao.getHus(1);
System.out.println(hus.getHusName()+","+hus.getWife().getWifeName());
}
多表关系之多对多
多对多的数据表至少要有3张表
集合包含集合
9.4 多对多**(科目-学生)**
数据表:
CREATE TABLE `middle` (
`middleid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`stuid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`subid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`middleid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ---------------------------- -- Records of middle -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('1', '1', '1');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('2', '1', '2');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('3', '1', '3');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('4', '1', '5');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('5', '2', '2');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('6', '3', '2');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('7', '4', '2');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('8', '5', '2');
INSERT INTO `middle` VALUES ('9', '6', '2');
-- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for `student` -- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`stuid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`stuname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`teacherid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`stuid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ---------------------------- -- Records of student -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('1', '张三', '3');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('2', '李四', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('3', '王五', '3');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('4', '赵六', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('5', '花花', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('6', '潇潇', '2');
-- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for `subject` -- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `subject`;
CREATE TABLE `subject` (
`subid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`subname` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`subid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ---------------------------- -- Records of subject -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `subject` VALUES ('1', 'java');
INSERT INTO `subject` VALUES ('2', 'ui');
INSERT INTO `subject` VALUES ('3', 'h5');
INSERT INTO `subject` VALUES ('4', 'c');
INSERT INTO `subject` VALUES ('5', 'c++');
INSERT INTO `subject` VALUES ('6', 'c#');
实体类:
public class Subject {
private int subid;
private String subname;
private List stulist;
public int getSubid() {
return subid;
}
public void setSubid(int subid) {
this.subid = subid;
}
public String getSubname() {
return subname;
}
public void setSubname(String subname) {
this.subname = subname;
}
public List getStulist() {
return stulist;
}
public void setStulist(List stulist) {
this.stulist = stulist;
}
}
public class Student {
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
//外键列一般不生成属性
// private int teacherid;
private Teacher teacher;
private List subjects;
public List getSubjects() {
return subjects;
}
public void setSubjects(List subjects) {
this.subjects = subjects;
}
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
}
接口:
public interface SubjectDao {
//查询某个学生信息(查询出所学科目)
public Student findById(int id);
//查询某个科目以及对应的学生姓名
public Subject findBySubId(int subId);
}
实现类:
public class SubjectDaoImpl implements SubjectDao {
@Override public
Student findById(int id) {
//操作数据库
Connection connection =null;
PreparedStatement pps =null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得链接
String userName="root";
String passWord="123456";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord);
//3.定义sql,创建预状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
String sql="select * from student s,subject su,middle m where s.stuid=m.stuid and su.subid=m.subid and s.stuid=?";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pps.setInt(1,id);
//执行sql
resultSet = pps.executeQuery();
Student student = new Student();
List subjects=new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
//1.取出各自的信息
student.setStuId(resultSet.getInt("stuid"));
student.setStuName(resultSet.getString("stuname"));
Subject subject = new Subject();
subject.setSubId(resultSet.getInt("subid"));
subject.setSubName(resultSet.getString("subname"));
subjects.add(subject);
}
//2.建立学生和科目之间的关系
student.setSubjects(subjects);
return student;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Subject findBySubId(int subId) {
//操作数据库 Connection connection =null;
PreparedStatement pps =null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得链接
String userName="root";
String passWord="123456";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, passWord);
//3.定义sql,创建预状态通道(进行sql语句的发送)
String sql="select * from student s,subject su,middle m where s.stuid=m.stuid and su.subid=m.subid and su.subid=?";
pps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); pps.setInt(1,subId);
//执行sql
resultSet = pps.executeQuery();
Subject subject = new Subject();
List studentList=new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
//1.取出各自的信息
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuId(resultSet.getInt("stuid"));
student.setStuName(resultSet.getString("stuname"));
studentList.add(student);
subject.setSubId(resultSet.getInt("subid"));
subject.setSubName(resultSet.getString("subname"));
}
//2.建立学生和科目之间的关系
subject.setStudentList(studentList);
return subject;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}
测试类***
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubjectDaoImpl subjectDao = new SubjectDaoImpl();
/* Student student = subjectDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(student.getStuName());
List subjects = student.getSubjects();
for (Subject subject : subjects) {
System.out.println("\t"+subject.getSubName());
}
*/
/*某一科目*/
Subject subject = subjectDao.findBySubId(2);
System.out.println(subject.getSubName());
List studentList = subject.getStudentList();
for (Student student : studentList) {
System.out.println("\t"+student.getStuName());
}
}
//思考题:学生中又想包含老师的集合
事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
package test;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
Savepoint abc = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得连接
String userName = "root";
String password = "123456";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yh3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行线sql访问的发送
statement = connection.createStatement();
//返回结果为影响的行数
int result = statement.executeUpdate("insert into emp2(ename,hiredate,sal) values('a','2020-1-1',2000)");
abc = connection.setSavepoint("abc");
int result2 = statement.executeUpdate("insert into emp2(ename,hiredate,sal) values('b','2020-1-1',2000)");
System.out.println(5/0);
//代码方式提交事务
connection.commit();
if (result > 0) {
System.out.println("执行成功");
} else {
System.out.println("执行失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
//connection.rollback();
connection.rollback(abc);
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
10 数据库事务
-> 一组要么同时执行成功,要么同时执行失败的SQL语句。是数据库操作的一个执行单元。
10.1 事务概述
数据库事务(Database Transaction) ,是指作为单个逻辑工作单元执行的一系列操作,要么完全地执
行,要么完全地不执行。 事务处理可以确保除非事务性单元内的所有操作都成功完成,否则不会永久更新面向数据的资源。通过将一组相关操作组合为一个要么全部成功要么全部失败的单元,可以简化错误恢复并使应用程序更加可靠。一个逻辑工作单元要成为事务,必须满足所谓的ACID(原子性、一致性、隔离性和持久性)属性。事务是数据库运行中的逻辑工作单位,由DBMS中的事务管理子系统负责事务的处理。
事务开始于
- 连接到数据库上,并执行一条DML语句insert、update或delete
- 前一个事务结束后,又输入了另一条DML语句
事务结束于
- 执行commit或rollback语句。
- 执行一条DDL语句,例如create table语句,在这种情况下,会自动执行commit语句。
- 执行一条DDL语句,例如grant语句,在这种情况下,会自动执行commit。
- 断开与数据库的连接
- 执行了一条DML语句,该语句却失败了,在这种情况中,会为这个无效的DML语句执行rollback语
句。
10.2 事务的四大特点
(ACID)
- actomicity(原子性)
表示一个事务内的所有操作是一个整体,要么全部成功,要么全部失败
- consistency(一致性)
表示一个事务内有一个操作失败时,所有的更改过的数据都必须回滚到修改前状态
- isolation(隔离性)
事务查看数据时数据所处的状态,要么是另一并发事务修改它之前的状态,要么是另一事务修
改它之后的状态,事务不会查看中间状态的数据。
- durability(持久性)
持久性事务完成之后,它对于系统的影响是永久性的。
10.3 JDBC****中事务应用
如果JDBC连接处于自动提交模式,默认情况下,则每个SQL语句在完成后都会提交到数据库。
事务使您能够控制是否和何时更改应用于数据库。它将单个SQL语句或一组SQL语句视为一个逻辑单
元,如果任何语句失败,则整个事务将失败。
要启用手动事务支持,而不是JDBC驱动程序默认使用的自动提交模式,请使用Connection对象的
setAutoCommit**()**方法。如果将boolean false传递给setAutoCommit(),则关闭自动提交。我
们可以传递一个布尔值true来重新打开它。
10.4 事务的提交和回滚
完成更改后,我们要提交更改,然后在连接对象上调用**commit****()**方法,如下所示:
conn.commit( );
否则,要使用连接名为conn的数据库回滚更新,请使用以下代码 -
conn.rollback( );
try{
//Assume a valid connection object conn
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
String SQL = "INSERT INTO Employees values (106, 20, 'Rita', 'Tez')";
stmt.executeUpdate(SQL);
//Submit a malformed SQL statement that breaks
String SQL = "INSERTED IN Employees VALUES (107, 22, 'Sita', 'Singh')";
stmt.executeUpdate(SQL);
// If there is no error.
conn.commit();
}catch(SQLException se){
// If there is any error.
conn.rollback();
}
10.5 Savepoints
新的JDBC 3.0 Savepoint接口为您提供了额外的事务控制。
设置保存点时,可以在事务中定义逻辑回滚点。如果通过保存点发生错误,则可以使用回滚方法来撤消
所有更改或仅保存在保存点之后所做的更改。
Connection对象有两种新的方法来帮助您管理保存点 -
- setSavepoint**(String savepointName):**定义新的保存点。它还返回一个Savepoint对象。
- releaseSavepoint**(Savepoint savepointName):**删除保存点。请注意,它需要一个Savepoint
对象作为参数。此对象通常是由setSavepoint()方法生成的保存点。
try{
//Assume a valid connection object conn
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
Savepoint savepoint1 = conn.setSavepoint("Savepoint1");
String SQL = "INSERT INTO Employees VALUES (106, 20, 'Rita', 'Tez')";
stmt.executeUpdate(SQL);
String SQL = "INSERTED IN Employees VALUES (107, 22, 'Sita', 'Tez')";
stmt.executeUpdate(SQL);
conn.commit();
}catch(SQLException se){
conn.rollback(savepoint1);
}
1、要取消掉JDBC的自动提交:void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit)
2、执行各个SQL语句,加入到批处理之中
3、如果所有语句执行成功,则提交事务 commit();如果出现了错误,则回滚:rollback()
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
add(connection);
// int i = 1/0;
sub(connection);
System.out.println("===============");
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("---------------");
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
以上就是java代码利用jdbc操作数据库的最简单版本,数据库事务通常要借助补捉异常语句
事务案例-转账
package test;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
Savepoint abc = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得连接
String userName = "root";
String password = "123456";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yh3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行线sql访问的发送
statement = connection.createStatement();
//返回结果为影响的行数
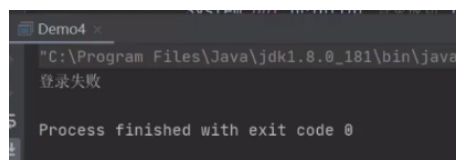
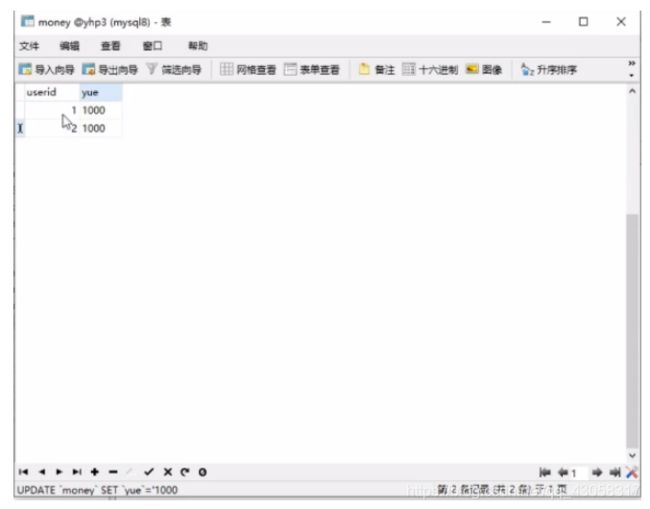
int result = statement.executeUpdate("update money set yue=yue-100 where userid=1");
abc = connection.setSavepoint("abc");
int result2 = statement.executeUpdate("update money set yue=yue+100 where userid=2");
//代码方式提交事务
connection.commit();
if (result2 > 0) {
System.out.println("执行成功");
} else {
System.out.println("执行失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
connection.rollback();
}catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
批处理
package test;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
Savepoint abc = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得连接
String userName = "root";
String password = "123456";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yh3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//设置成手动提交
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行线sql访问的发送
statement = connection.createStatement();
//4.定义sql
String sql1 = "insert into teacher(tname) values('张三a')";
statement.addBatch(sql1);
String sql2 = "insert into teacher(tname) values('张三b')";
statement.addBatch(sql2);
String sql3 = "insert into teacher(tname) values('张三c')";
statement.addBatch(sql3);
String sql4 = "insert into teacher(tname) values('张三d')";
statement.addBatch(sql4);
int[] ints = statement.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.println("anInt:"+anInt);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
connection.rollback();
}catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package test;
import com.mysql.cj.x.protobuf.MysqlxPrepare;
import java.sql.*;
public class PreparedStatementBatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pps = null;
Savepoint abc = null;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得连接
String userName = "root";
String password = "123456";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yh3?serverTimezone=UTC";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//设置成手动提交
//3.定义sql,创建状态通道(进行线sql访问的发送
pps = connection.prepareStatement("insert into teacher(tname) values(?)");
//4.赋值
pps.setString(1,"李四A");
pps.addBatch();//无参方法
pps.setString(1,"李四B");
pps.addBatch();//无参方法
pps.setString(1,"李四C");
pps.addBatch();//无参方法
pps.setString(1,"李四D");
pps.addBatch();//无参方法
int[] ints = pps.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.println("anInt:"+anInt);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
connection.rollback();
}catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
//5.关闭资源
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
11.JDBC****批处理
批量处理允许您将相关的SQL语句分组到批处理中,并通过对数据库的一次调用提交它们。
当您一次向数据库发送多个SQL语句时,可以减少连接数据库的开销,从而提高性能。
11.1 Statement****批处理
以下是使用语句对象的批处理的典型步骤序列
- 使用**createStatement****()**方法创建Statement对象。
- 使用**setAutoCommit****()**将auto-commit设置为false 。
- 使用**addBatch****()**方法在创建的语句对象上添加您喜欢的SQL语句到批处理中。
- 在创建的语句对象上使用**executeBatch****()**方法执行所有SQL语句。
- 最后,使用**commit****()**方法提交所有更改。
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//sql1
String SQL = "INSERT INTO Employees (id, first, last, age) VALUES(200,'Zia', 'Ali', 30)";
stmt.addBatch(SQL);
//sql2
tring SQL = "INSERT INTO Employees (id, first, last, age) VALUES(201,'Raj', 'Kumar', 35)";
stmt.addBatch(SQL);
//sql3
String SQL = "UPDATE Employees SET age = 35 WHERE id = 100";
stmt.addBatch(SQL);
int[] count = stmt.executeBatch();
conn.commit();
11.2 PreparedStatement****批处理
\1. 使用占位符创建SQL语句。
\2. 使用prepareStatement****() 方法创建PrepareStatement对象。
\3. 使用**setAutoCommit****()**将auto-commit设置为false 。
\4. 使用**addBatch****()**方法在创建的语句对象上添加您喜欢的SQL语句到批处理中。
\5. 在创建的语句对象上使用**executeBatch****()**方法执行所有SQL语句。
\6. 最后,使用**commit****()**方法提交所有更改。
String SQL = "INSERT INTO Employees (id, first, last, age) VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?)"; PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(SQL);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// Set the variables
pstmt.setInt( 1, 400 );
pstmt.setString( 2, "Pappu" );
pstmt.setString( 3, "Singh" );
pstmt.setInt( 4, 33 );
// Add it to the batch
pstmt.addBatch();
// Set the variables
pstmt.setInt( 1, 401 );
pstmt.setString( 2, "Pawan" );
pstmt.setString( 3, "Singh" );
pstmt.setInt( 4, 31 );
// Add it to the batch
pstmt.addBatch();
//add more batches
//Create an int[] to hold returned values
int[] count = stmt.executeBatch();
//Explicitly commit statements to apply changes
conn.commit();
反射处理结果集
太多的结果集
接口:
//查询所有的学生信息
public List findallstudent(Class cla);
实现类:
@Override public List findallstudent(Class cla) {
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pps = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp", "root", "123456");
List list=new ArrayList();
String sqla = "select * from student";
pps = con.prepareStatement(sqla);
rs = pps.executeQuery();
//得到数据库中的所有的列有哪些?
ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
//返回数据库中的相关信息
int count=metaData.getColumnCount();
//得到列数 String[]
columnnames=new String[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// System.out.println(metaData.getColumnName(i+1));
//列的位置从1开始
columnnames[i]=metaData.getColumnName(i+1);
}
//得到实体类中的所有的方法
Method[] methods =cla.getDeclaredMethods();
while(rs.next()){
Object s=cla.newInstance();
//调取无参构造创建对象
for (String columnname : columnnames) {
String name="set"+columnname;
//setstuid
for (Method method : methods) {
if(method.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(name)){
method.invoke(s,rs.getObject(columnname));
//执行了对应的 set方法
break;
}
}
}
list.add(s);
}
System.out.println("执行成功");
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (pps != null) {
pps.close();
}
if (con != null) {
con.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
封装工具类
建一个包:util
DBUtils
public class DbUtils {
//1.定义需要的工具类对象
protected Connection connection=null;
protected PreparedStatement pps=null;
protected ResultSet rs=null;
protected int k=0;//受影响的行数
private String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp";
private String username="root";
private String password="123456";
//2.加载驱动
static{
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//3.获得连接
protected Connection getConnection(){
try {
connection=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
//4.创建通道
protected PreparedStatement getPps(String sql){
try {
getConnection();//insert into users values(?,?,?,?,)
pps=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return pps;
}
//5.给占位符赋值 list中保存的是给占位符所赋的值
private void setParams(List list){
try {
if(list!=null&&list.size()>0){
for (int i=0;i属性文件
13.1 properties文件保存数据库信息-特点:key-value****存储方式
db.properties 放src下
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yhp
user=root
password=123456
工具类中读取属性文件
方式 1 :
DBUtils.java
private static String userName;
private static String userPass;
private static String url;
private static String driverName;
//2.加载驱动s
static {
try {
InputStream inputStream = 当前类名.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
dirverName = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
userName = properties.getProperty("user");
userPass = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverName);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
方式2:
static{
//参数只写属性文件名即可,不需要写后缀
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");
driverName = bundle.getString("driver");
url = bundle.getString("url");
userName = bundle.getString("user");
userPass = bundle.getString("password");
}
说明:
使用ResourceBundle访问本地资源
在设计时,我们往往需要访问一些适合本地修改的配置信息,如果作为静态变量,那么每次修改都
需要重新编译一个class,.confifig保存此类信息并不适合,这时我们需要ResourceBundle。
通过ResourceBundle,我们需要访问位于/WEB-INF/classes目录下的一个后缀名为properties的文本
类型文件,从里面读取我们需要的值。
自定义连接池
**14.**连接池
**1.**自定义连接池
数据连接池原理
连接池基本的思想是在系统初始化的时候,将数据库连接作为对象存储在内存中,当用户需要访问数
据库时,并非建立一个新的连接,而是从连接池中取出一个已建立的空闲连接对象。使用完毕后,用户
也并非将连接关闭,而是将连接放回连接池中,以供下一个请求访问使用。而连接的建立、断开都由连
接池自身来管理。同时,还可以通过设置连接池的参数来控制连接池中的初始连接数、连接的上下限数
以及每个连接的最大使用次数、最大空闲时间等等,也可以通过其自身的管理机制来监视数据库连接的
数量、使用情况等。
1.1 自定义连接池
我们可以通过自定义的方式实现连接池!分析连接池类应该包含特定的属性和方法!
属性: 集合 放置Connection
方法: 获取连接方法
回收连接方法
具体实现代码:
public class Pool{
static LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//初始化10个连接
static{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.newInstance().getConnection();
list.add(connection);
}
}
/**
* 从连接池子中获取连接的方式
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
if (list.isEmpty()) {
//JDBCUtils类是自定义类,封装了连接数据库的信息代码
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.newInstance().getConnection();
list.addLast(connection);
}
Connection conn = list.removeFirst();
return conn;
}
/**
* 返回到连接池子中 回收
*/
public static void addBack(Connection conn){
if (list.size() >= 10) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
list.addLast(conn); //10
}
}
/**
* 获取连接池子中连接数量的方法
*/
public static int getSize(){
return list.size();
}
}
1.2 java****规范实现连接池
Java为连接池实现提供了一个规范(接口),规范的写法,我们需要实现DataSource接口!
但是实现DataSource接口有一个弊端,没有提供回收链接方法!这里我们将使用装饰者模式!
装饰Connection!具体实现代码如下:
\1. 创建装饰Connection
public class MyConnection implements Connection{
//将被装饰者导入
private Connection conn;
private LinkedList list;
public MyConnection(Connection conn, LinkedList list) {
super();
this.conn = conn;
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return conn.unwrap(iface);
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return conn.isWrapperFor(iface);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return conn.createStatement();
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException { }
@Override
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
conn.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
conn.rollback();
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
list.addLast(conn);
}
...
}
基于规范实现的连接池
/**
* 创建一个规范的连接池子
*/
public class DataSourcePool implements DataSource{
static LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
static{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.newInstance().getConnection();
list.add(connection);
}
}
public static int getSize(){
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = list.removeFirst();
MyConnection conn1 = new MyConnection(conn, list);
return conn1;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException { }
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException { }
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public T unwrap(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
最小连接数:
是数据库一直保持的数据库连接数,所以如果应用程序对数据库连接的使用量不大,将有大量的数据库
资源被浪费。
初始化连接数:
连接池启动时创建的初始化数据库连接数量。
最大连接数:
是连接池能申请的最大连接数,如果数据库连接请求超过此数,后面的数据库连接请求被加入到等待队
列中。
最大等待时间:
当没有可用连接时,连接池等待连接被归还的最大时间,超过时间则抛出异常,可设置参数为0或者负
数使得无限等待(根据不同连接池配置)。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-R6CjZyEb-1616891709172)(C:\Users\jiajun.lin\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210328001937492.png)]
注****1:在DBCP连接池的配置中,还有一个maxIdle的属性,表示最大空闲连接数,超过的空闲连接将被释放,默认值为8。对应的该属性在Druid连接池已不再使用,配置了也没有效果,c3p0连接池则没有对应的属性。
注****2:数据库连接池在初始化的时候会创建initialSize个连接,当有数据库操作时,会从池中取出一个连接。如果当前池中正在使用的连接数等于maxActive,则会等待一段时间,等待其他操作释放掉某一个连接,如果这个等待时间超过了maxWait,则会报错;如果当前正在使用的连接数没有达到
maxActive,则判断当前是否空闲连接,如果有则直接使用空闲连接,如果没有则新建立一个连接。在
连接使用完毕后,不是将其物理连接关闭,而是将其放入池中等待其他操作复用。
DBCP
2.DBCP****连接池
> DBCP是一个依赖Jakarta commons-pool对象池机制的数据库连接池.DBCP可以直接的在应用程序中
使用,Tomcat的数据源使用的就是DBCP。
2.1 DBCP****连接池的使用
2.1.1 导入相应jar包
mysql-jdbc.jar
commons-dbcp.jar
commons-pool.jar
2.1.2 硬编码使用DBCP
> 所谓的硬编码方式就是在代码中添加配置
@Test
public void testHard() throws SQLException{
// 硬编码 使用DBCP连接池子
BasicDataSource source = new BasicDataSource();
//设置连接的信息
source.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
source.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day2");
source.setUsername("root");
source.setPassword("111");
Connection connection = source.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from student";
Statement createStatement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet executeQuery = createStatement.executeQuery(sql);
while (executeQuery.next()) {
System.out.println(executeQuery.getString(2));
}
connection.close(); //回收
}
2.1.4 软编码使用DBCP
> 所谓的软编码,就是在项目中添加配置文件,这样就不需要每次代码中添加配合!
\1. 项目中添加配置
文件名称: info.properties
文件位置: src下
#连接设置
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day2
username=root password=111
#
initialSize=10
#最大连接数量
maxActive=50
#
maxIdle=20
#
minIdle=5
#
maxWait=6000
1.DButils工具类 代码实现
//1.创建dbcp的工具类对象
static BasicDataSource datasource=new BasicDataSource();
//2.加载驱动
static {
try {
//加载属性文件
//1.使用工具类 ,参数是属性文件的文件名(不要加后缀)
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");
driverClass = bundle.getString("driverclass");
url = bundle.getString("url");
username = bundle.getString("uname");
password = bundle.getString("upass");
init=bundle.getString("initsize");
//2.将驱动地址等信息传递给dbcp
datasource.setDriverClassName(driverClass);
datasource.setUrl(url);
datasource.setUsername(username);
datasource.setPassword(password);
datasource.setInitialSize(Integer.parseInt(init));
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//3.获得连接
public static Connection getConn() {
try {
con= datasource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
C3P0
3 C3P0****连接池
> c3p0是一个开放源代码的JDBC连接池,它在lib目录中与Hibernate一起发布,包括了实现jdbc3和
jdbc2扩展规范说明的Connection 和Statement 池的DataSources 对象。
c3p0与dbcp区别
dbcp没有自动回收空闲连接的功能
c3p0有自动回收空闲连接功能
dbcp需要手动设置配置文件
c3p0不需要手动设置
3.1 实现方式
1 .手动设置 ComboPooledDataSource
2 加载配置文件方式
src/c3p0-config.xml(文件名固定)
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
加载 文件中 中的配置
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource("aaa");
加载 中的配置
3.2 实现步骤
3.1.1 导入jar包
c3p0-0.9.1.2.jar
mysql-connector-java-5.0.8.jar
3.1.2.添加配置文件
> c3p0是在外部添加配置文件,工具直接进行应用,因为直接引用,所以要求固定的命名和文件位置
文件位置: src
文件命名:c3p0-confifig.xml/c3p0-confifig.properties
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day2
root
111
30000
30
10
30
100
10
200
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day2
root
111
5
20
10
40
20
5
注意*** c3p0的配置文件内部可以包含命名配置文件和默认配置文件!默认是选择默认配置!如果需要切换
命名配置可以在创建c3p0连接池的时候填入命名即可!
3.1.3.定义代码
Connection con=null;
ComboPooledDataSource db=new ComboPooledDataSource("abc");
public Connection getCon(){
try {con=db.getConnection();
System.out.println("初始化的链接数量:"+db.getInitialPoolSize());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
德鲁伊
**4 Druid(德鲁伊)**连接池
阿里出品,淘宝和支付宝专用数据库连接池,但它不仅仅是一个数据库连接池,它还包含一个
ProxyDriver(代理驱动),一系列内置的JDBC组件库,一个SQL Parser(sql解析器)。支持所有JDBC兼
容的数据库,包括Oracle、MySql、Derby、Postgresql、SQL Server、H2等等。
Druid针对Oracle和MySql做了特别优化,比如Oracle的PS Cache内存占用优化,MySql的ping检测优
化。
Druid提供了MySql、Oracle、Postgresql、SQL-92的SQL的完整支持,这是一个手写的高性能SQL
Parser,支持Visitor模式,使得分析SQL的抽象语法树很方便。
简单SQL语句用时10微秒以内,复杂SQL用时30微秒。
通过Druid提供的SQL Parser可以在JDBC层拦截SQL做相应处理,比如说分库分表、审计等。Druid防
御SQL注入攻击的WallFilter就是通过Druid的SQL Parser分析语义实现的。
Druid 是目前比较流行的高性能的,分布式列存储的OLAP框架(具体来说是MOLAP)。它有如下几个特
点:
一. 亚秒级查询
druid提供了快速的聚合能力以及亚秒级的OLAP查询能力,多租户的设计,是面向用户分析应用的理
想方式。
二.实时数据注入
druid支持流数据的注入,并提供了数据的事件驱动,保证在实时和离线环境下事件的实效性和统一性
三.可扩展的PB级存储
druid集群可以很方便的扩容到PB的数据量,每秒百 万级别的数据注入。即便在加大数据规模的情况
下,也能保证时其效性
四.多环境部署
druid既可以运行在商业的硬件上,也可以运行在云上。它可以从多种数据系统中注入数据,包括
hadoop,spark,kafka,storm和samza等
五.丰富的社区
druid拥有丰富的社区,供大家学习
4.1 使用步骤
4.1.1 导入jar包
4.1.2 编写工具类
/**
* 阿里的数据库连接池
* 性能最好的
* Druid
* */
public class DruidUtils {
//声明连接池对象
private static DruidDataSource ds;
static{
///实例化数据库连接池对象
ds=new DruidDataSource();
//实例化配置对象
Properties properties=new Properties();
try {
//加载配置文件内容
properties.load(DruidUtils.class.getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties"));
//设置驱动类全称
ds.setDriverClassName(properties.getProperty("driverClassName"));
//设置连接的数据库
ds.setUrl(properties.getProperty("url"));
//设置用户名
ds.setUsername(properties.getProperty("username"));
//设置密码
ds.setPassword(properties.getProperty("password"));
//设置最大连接数量
ds.setMaxActive(Integer.parseInt(properties.getProperty("maxActive")));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取连接对象
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return ds.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
注:在Druid连接池的配置中,driverClassName可配可不配,如果不配置会根据url自动识别dbType(数
据库类型),然后选择相应的driverClassName。