tomcat的Session和Cookie
从tomcat的session周期分析常用的缓存失效机制
-
- 前言
- 1. session和cookie的创建
- 2. Cookie被解析的过程
- 3. 通过URL传参jsessionid
- 4. 时序梳理
- 最后总结
- 参考资料
前言
http本身是无状态的协议,session和cookie恰好补充了这个状态。通过了解tomact的seesion和cookie的原理,可以在此基础上搞明白session共享和SSO单点。
1. session和cookie的创建
本文使用的tomcat代码是springboot-2.2.6.RELEASE版本内嵌的tomcat-embed-core-9.0.33版本。
下面是一个获取session的示例:
@GetMapping("test")
public String test(){
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("test","1223456");
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if(session!=null){
System.out.println(session.getId());
}
return "test";
}
request.getSession()方法的实现是org.apache.catalina.connector.Request类,该类实现了HttpServletRequest接口。
@Override
public HttpSession getSession() {
Session session = doGetSession(true);//默认是创建方法
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
return session.getSession();
}
继续看doGetSession(boolean create)方法,
protected Session doGetSession(boolean create) {
// There cannot be a session if no context has been assigned yet
Context context = getContext();
if (context == null) {
return null;
}
// Return the current session if it exists and is valid
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {//检查session是否过期
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
// Return the requested session if it exists and is valid
Manager manager = context.getManager();//获取session管理器
if (manager == null) {
return null; // Sessions are not supported
}
if (requestedSessionId != null) {//requestedSessionId比较关键,当cookie包含JSESSIONID的时候,该值等于JSESSIONID值,当URL中包含jsessionid,该值等于jsessionid
try {
session = manager.findSession(requestedSessionId);
} catch (IOException e) {
session = null;
}
if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) {
session = null;
}
if (session != null) {
session.access();
return session;
}
}
// Create a new session if requested and the response is not committed
if (!create) {
return null;
}
boolean trackModesIncludesCookie =
context.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE);
if (trackModesIncludesCookie && response.getResponse().isCommitted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("coyoteRequest.sessionCreateCommitted"));
}
// Re-use session IDs provided by the client in very limited
// circumstances.
String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();//再次获取requestedSessionId
if (requestedSessionSSL) {
// If the session ID has been obtained from the SSL handshake then
// use it.
} else if (("/".equals(context.getSessionCookiePath())
&& isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie())) {
/* This is the common(ish) use case: using the same session ID with
* multiple web applications on the same host. Typically this is
* used by Portlet implementations. It only works if sessions are
* tracked via cookies. The cookie must have a path of "/" else it
* won't be provided for requests to all web applications.
*
* Any session ID provided by the client should be for a session
* that already exists somewhere on the host. Check if the context
* is configured for this to be confirmed.
*/
if (context.getValidateClientProvidedNewSessionId()) {
boolean found = false;
for (Container container : getHost().findChildren()) {
Manager m = ((Context) container).getManager();
if (m != null) {
try {
if (m.findSession(sessionId) != null) {
found = true;
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore. Problems with this manager will be
// handled elsewhere.
}
}
}
if (!found) {
sessionId = null;
}
}
} else {
sessionId = null;
}
session = manager.createSession(sessionId);//创建seesion
// Creating a new session cookie based on that session
if (session != null && trackModesIncludesCookie) {
Cookie cookie = ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.createSessionCookie(
context, session.getIdInternal(), isSecure());//这里创建cookie,并将cookie返回到response
response.addSessionCookieInternal(cookie);
}
if (session == null) {
return null;
}
session.access();
return session;
}
Tomcat里的Cookie结构:

org.apache.catalina.connector.Response类实现了HttpServletResponse接口,Response#addSessionCookieInternal方法,
public void addSessionCookieInternal(final Cookie cookie) {
if (isCommitted()) {
return;
}
String name = cookie.getName();
final String headername = "Set-Cookie";
final String startsWith = name + "=";
String header = generateCookieString(cookie);//只获取了value值
boolean set = false;
MimeHeaders headers = getCoyoteResponse().getMimeHeaders();
int n = headers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (headers.getName(i).toString().equals(headername)) {
if (headers.getValue(i).toString().startsWith(startsWith)) {
headers.getValue(i).setString(header);
set = true;
}
}
}
if (!set) {
addHeader(headername, header);
}
}
可以看到在响应头里将sessionId作为value值添加了Header里Set-Cookie键里。
在Chrome浏览器查看如下:
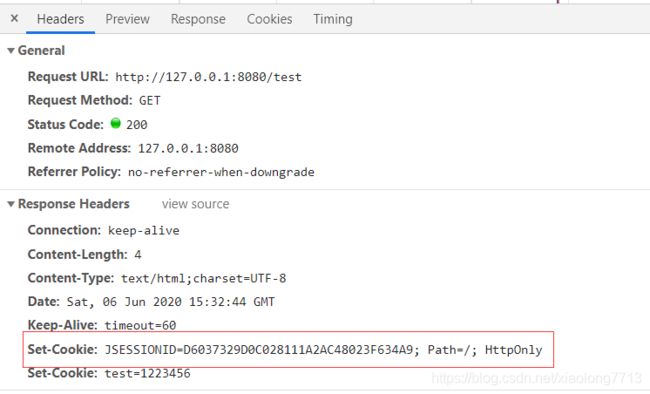
如果浏览器开启了Cookie缓存,下一次Request的请求会将Cookie带上。
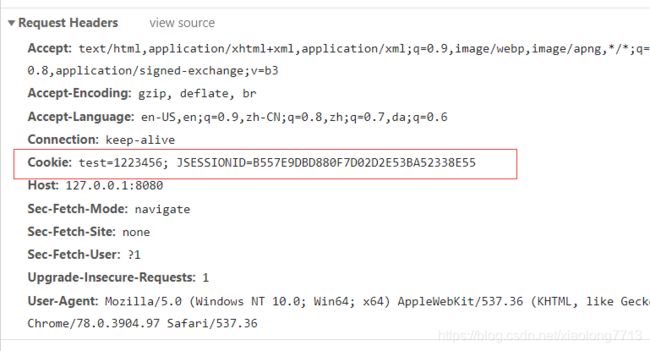
2. Cookie被解析的过程
Cookie信息是在Request Headers里,在tomcat中org.apache.coyote.Request#headers属性中,header的解析方法在Http11InputBuffer类中。
/**
* Parse the HTTP headers.
*/
boolean parseHeaders() throws IOException {
if (!parsingHeader) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("iib.parseheaders.ise.error"));
}
HeaderParseStatus status = HeaderParseStatus.HAVE_MORE_HEADERS;
do {
status = parseHeader();//解析Request的header信息
// Checking that
// (1) Headers plus request line size does not exceed its limit
// (2) There are enough bytes to avoid expanding the buffer when
// reading body
// Technically, (2) is technical limitation, (1) is logical
// limitation to enforce the meaning of headerBufferSize
// From the way how buf is allocated and how blank lines are being
// read, it should be enough to check (1) only.
if (byteBuffer.position() > headerBufferSize || byteBuffer.capacity() - byteBuffer.position() < socketReadBufferSize) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("iib.requestheadertoolarge.error"));
}
} while (status == HeaderParseStatus.HAVE_MORE_HEADERS);
if (status == HeaderParseStatus.DONE) {
parsingHeader = false;
end = byteBuffer.position();
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
解析Cookie中的JSESSIONID,CoyoteAdapter#parseSessionCookiesId,将sessionId赋值给org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#requestedSessionId
protected void parseSessionCookiesId(Request request) {
// If session tracking via cookies has been disabled for the current
// context, don't go looking for a session ID in a cookie as a cookie
// from a parent context with a session ID may be present which would
// overwrite the valid session ID encoded in the URL
Context context = request.getMappingData().context;
if (context != null && !context.getServletContext()
.getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(
SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)) {
return;
}
// Parse session id from cookies
ServerCookies serverCookies = request.getServerCookies();
int count = serverCookies.getCookieCount();
if (count <= 0) {
return;
}
String sessionCookieName = SessionConfig.getSessionCookieName(context);//这里DEFAULT_SESSION_COOKIE_NAME=JSESSIONID
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
ServerCookie scookie = serverCookies.getCookie(i);
if (scookie.getName().equals(sessionCookieName)) {
// Override anything requested in the URL
if (!request.isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie()) {
// Accept only the first session id cookie
convertMB(scookie.getValue());
request.setRequestedSessionId
(scookie.getValue().toString());//设置requestedSessionId
request.setRequestedSessionCookie(true);
request.setRequestedSessionURL(false);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Requested cookie session id is " +
request.getRequestedSessionId());
}
} else {
if (!request.isRequestedSessionIdValid()) {
// Replace the session id until one is valid
convertMB(scookie.getValue());
request.setRequestedSessionId
(scookie.getValue().toString());
}
}
}
}
}
3. 通过URL传参jsessionid
如果浏览器设置了禁止保存Cookie,此时Request请求当中没有Cookie信息,Tomcat提供了从URL中传参jsessionid,然后自动解析的机制。
实际上如果设置禁止保存Cookie,很多需要登录的网站都会报错或者登录失效,实测淘宝网报了如下的错误:

当使用URL传参时需要注意:
- jsessionid必须要小写,大写的是Cookie中的key
- 传参中需要用分号分隔,如
http://127.0.0.1:8080/test;jsessionid=FBE20C3B102FA66D924E169B108AE581;bb=FBE20C3B102FA66D924E169B108AE581
解析后的信息保存org.apache.coyote.Request#pathParameters中,解析的代码在CoyoteAdapter#parsePathParameters中,从第一个“;”处解析。
多个参数保存的数据如图所示,

URL传参解析和Cookie解析的顺序,CoyoteAdapter#postParseRequest
String sessionID;
if (request.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes()
.contains(SessionTrackingMode.URL)) {
// Get the session ID if there was one
sessionID = request.getPathParameter(
SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName(
request.getContext()));//默认为DEFAULT_SESSION_PARAMETER_NAME = "jsessionid"
if (sessionID != null) {
request.setRequestedSessionId(sessionID);
request.setRequestedSessionURL(true);
}
}
// Look for session ID in cookies and SSL session
try {
parseSessionCookiesId(request);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Too many cookies
if (!response.isError()) {
response.setError();
response.sendError(400);
}
return true;
}
parseSessionSslId(request);//解析SSL SessionId
sessionID = request.getRequestedSessionId();
可以看到先解析URL当中的jsessionid,后面的Cookie解析出requestedSessionId会覆盖,优先级较高的还是Cookie。
值得注意的是,如果是redirect跳转的话,会将seesionid加到URL后面,这一点在一些SSO单点中很有用。
MessageBytes redirectPathMB = request.getMappingData().redirectPath;
if (!redirectPathMB.isNull()) {
String redirectPath = URLEncoder.DEFAULT.encode(
redirectPathMB.toString(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String query = request.getQueryString();
if (request.isRequestedSessionIdFromURL()) {
// This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it
// shouldn't matter
redirectPath = redirectPath + ";" +
SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName(
request.getContext()) +
"=" + request.getRequestedSessionId();
}//携带SeesionId
if (query != null) {
// This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it
// shouldn't matter
redirectPath = redirectPath + "?" + query;
}
response.sendRedirect(redirectPath);
request.getContext().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);
return false;
}
4. 时序梳理
设置sessionID 的时序,
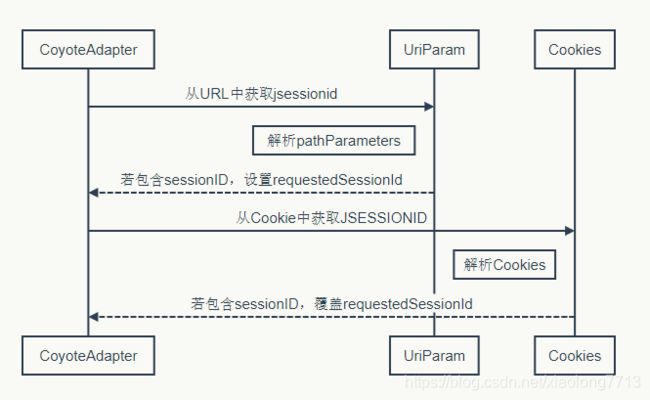
获取到sessionID并设置requestedSessionId,在org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#doGetSession(boolean create)方法中,会优先用requestedSessionId在StandardManager获取session,从而保证不同的请求获取的是同一个session。
最后总结
分析了tomcat的Session的获取方式,从Cookie里或者URL中去解析,可以清晰理解用户登录之后浏览器中免登陆的方式和页面跳转携带信息的原理。Session和Cookie机制是对HTTP无状态协议的很好的补充,这样的设计方式很值得在实际业务中去运用。
参考资料
- https://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2012/08/what-is-jsessionid-in-j2ee-web.html
- 深入Tomcat(中文版)