手写promis(2)-- 链式编程篇
目录
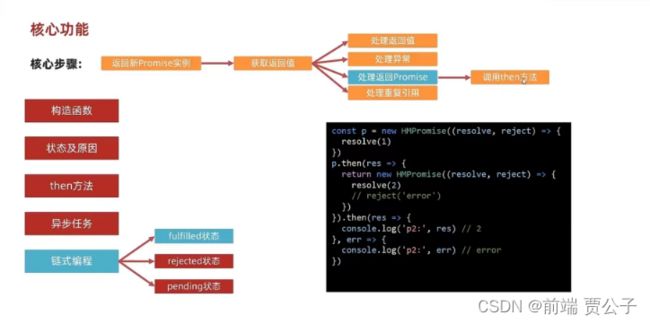
链式编程 处理异常 和普通内容
链式编程---处理返回promise
链式编程---处理重复引用
链式编程--rejected
链式编程--处理padding状态
链式编程 处理异常 和普通内容
- 1.返回promise实例:在原本then方法里边创建新promise
- 2.获取返回值:把原本的then的逻辑迁移到新promise中 是同步执行的不受影响(方便传递给新创建的promise)
- 3.处理返回值 调用新promise的 resolve
- 4.处理异常 try catch 捕获异常 调用新promise的 reject
function runAsyncTask(callback) {
if (typeof queueMicrotask === "function") {
queueMicrotask(callback);
} else if (typeof MutationObserver == "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback);
const divNode = document.createElement("div");
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true });
divNode.innerHTML = "贾公子";
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0);
}
}
/**链式编程 处理异常 和普通内容
* 1.返回promise实例
* 2.获取返回值
* 2.1处理返回值
* 2.2处理异常
*
*
*/
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MyPromise {
state = PENDING;
result = undefined;
#handlers = [];
constructor(func) {
const resolve = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
}
};
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onRejected }) => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
}
};
func(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : (x) => x;
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === "function"
? onRejected
: (x) => {
throw x;
};
// 1.返回promise实例
const p2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
// 2.获取返回值
const x = onFulfilled(this.result);
// 2.1处理返回值
resolve(x);
// 2.2处理异常
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
} else if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
},
onRejected: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
},
});
}
});
return p2;
}
}
// 测试代码
const p = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("1");
// reject("error");
});
p.then((result) => {
console.log("p1", result);
throw new Error("异常");
// return 2;
}).then(
(result) => {
console.log("p2", result);
},
(err) => {
console.log("p2", err);
}
);
链式编程---处理返回promise
1.使用 instanceof判断返回值是否为 MyPromise实例
2.如果是代表传递的返回值是promise 调用传递的promise的then方法
3.在成功回调中调用resolve,失败回调中传递reject,把结果传递
function runAsyncTask(callback) {
if (typeof queueMicrotask === "function") {
queueMicrotask(callback);
} else if (typeof MutationObserver == "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback);
const divNode = document.createElement("div");
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true });
divNode.innerHTML = "贾公子";
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0);
}
}
/**
*
*/
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MyPromise {
state = PENDING;
result = undefined;
#handlers = [];
constructor(func) {
const resolve = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
}
};
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onRejected }) => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
}
};
func(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : (x) => x;
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === "function"
? onRejected
: (x) => {
throw x;
};
const p2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.result);
// 1.处理返回promise
if (x instanceof MyPromise) {
// 2.调用then方法
x.then(
(res) => {
resolve(res);
},
(err) => {
reject(err);
}
);
} else {
resolve(x);
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
} else if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
},
onRejected: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
},
});
}
});
return p2;
}
}
// 测试代码
const p = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("1");
});
p.then((result) => {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(2);
// reject("err");
});
}).then(
(result) => {
console.log("p2", result);
},
(err) => {
console.log("p2", err);
}
);
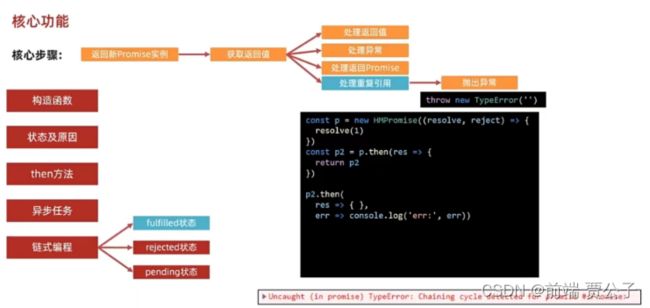
链式编程---处理重复引用
在then的回调函数中直接把then的结果返回了会抛出重复引用的问题
1.x就是then回调函数的返回值,then方法返回的promise就是p2
2.比较x跟p2是否全等 是就抛出异常
function runAsyncTask(callback) {
if (typeof queueMicrotask === "function") {
queueMicrotask(callback);
} else if (typeof MutationObserver == "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback);
const divNode = document.createElement("div");
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true });
divNode.innerHTML = "贾公子";
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0);
}
}
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MyPromise {
state = PENDING;
result = undefined;
#handlers = [];
constructor(func) {
const resolve = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
}
};
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onRejected }) => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
}
};
func(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : (x) => x;
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === "function"
? onRejected
: (x) => {
throw x;
};
const p2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.result);
// 1.处理重复的引用
if (x === p2) {
console.log("----");
throw new TypeError(
"Chaining cycle detected for promise #"
);
}
if (x instanceof MyPromise) {
x.then(
(res) => {
resolve(res);
},
(err) => {
reject(err);
}
);
} else {
resolve(x);
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
} else if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
},
onRejected: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
},
});
}
});
return p2;
}
}
// 测试代码
const p = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("1");
});
const p2 = p.then((res) => {
return p2;
});
p2.then(
(res) => {},
(err) => {
console.log(err);
}
);
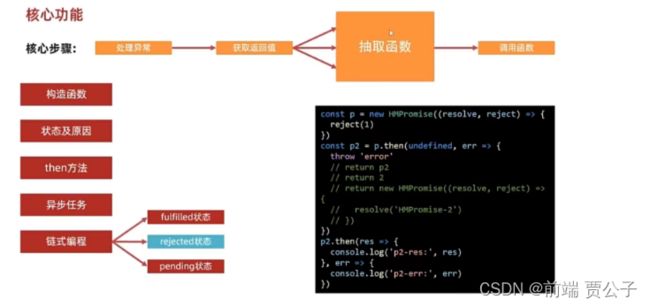
链式编程--rejected
完成链式第一步要返回promise 处理Fulfilled时候已完成
通过trycatch 处理异常
抽离函数 resolvePromise 处理 重复引用 以及返回promise的情况
调用函数测试状态
function runAsyncTask(callback) {
if (typeof queueMicrotask === "function") {
queueMicrotask(callback);
} else if (typeof MutationObserver == "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback);
const divNode = document.createElement("div");
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true });
divNode.innerHTML = "贾公子";
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0);
}
}
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MyPromise {
state = PENDING;
result = undefined;
#handlers = [];
constructor(func) {
const resolve = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
}
};
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onRejected }) => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
}
};
func(resolve, reject);
}
/**
*处理异常
*/
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : (x) => x;
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === "function"
? onRejected
: (x) => {
throw x;
};
const p2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.result);
resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
// 1.处理异常
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
// 2.获取返回值
const x = onRejected(this.result);
// 4.调用函数
resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
},
onRejected: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
},
});
}
});
return p2;
}
}
// 3.抽取函数
function resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject) {
if (x === p2) {
throw new TypeError("Chaining cycle detected for promise #");
}
if (x instanceof MyPromise) {
x.then(
(res) => {
resolve(res);
},
(err) => {
reject(err);
}
);
} else {
resolve(x);
}
}
// 测试代码
const p = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("1");
});
const p2 = p.then(undefined, (err) => {
// throw "error";
// return p2;
// return 2;
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("OK");
reject("ERROR");
});
});
p2.then(
(res) => {
console.log("p2--res", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("p2--err", err);
}
);
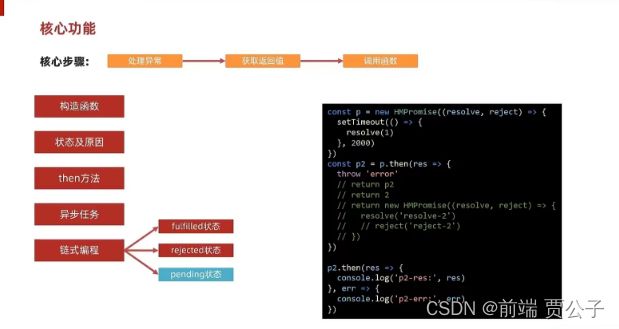
链式编程--处理padding状态
PENDING状态要根据异步执行的结果存储到handlers数组中不同的函数(onFulfilled || onRejected)两个处理链式编程的逻辑完全一样
* 处理异常 trycatch捕获异常
* 获取返回值 获取第一个promise的返回值
* 调用函数 处理 重复引用以及 返回promise的情况
function runAsyncTask(callback) {
if (typeof queueMicrotask === "function") {
queueMicrotask(callback);
} else if (typeof MutationObserver == "function") {
const obs = new MutationObserver(callback);
const divNode = document.createElement("div");
obs.observe(divNode, { childList: true });
divNode.innerHTML = "贾公子";
} else {
setTimeout(callback, 0);
}
}
function resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject) {
if (x === p2) {
throw new TypeError("Chaining cycle detected for promise #");
}
if (x instanceof MyPromise) {
x.then(
(res) => {
resolve(res);
},
(err) => {
reject(err);
}
);
} else {
resolve(x);
}
}
const PENDING = "pending";
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MyPromise {
state = PENDING;
result = undefined;
#handlers = [];
constructor(func) {
const resolve = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onFulfilled }) => {
onFulfilled(this.result);
});
}
};
const reject = (result) => {
if (this.state == PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED;
this.result = result;
this.#handlers.forEach(({ onRejected }) => {
onRejected(this.result);
});
}
};
func(resolve, reject);
}
/**
* 处理异常
* 获取返回值
* 调用函数
*/
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : (x) => x;
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === "function"
? onRejected
: (x) => {
throw x;
};
const p2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
const x = onFulfilled(this.result);
resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === REJECTED) {
runAsyncTask(() => {
try {
const x = onRejected(this.result);
resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
} else if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.#handlers.push({
onFulfilled: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
// 处理异常
try {
// 获取返回值
const x = onFulfilled(this.result);
// 调用函数
resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
},
onRejected: () => {
runAsyncTask(() => {
// 处理异常
try {
// 获取返回值
const x = onRejected(this.result);
// 调用函数
resolvePromise(p2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
},
});
}
});
return p2;
}
}
// 测试代码
const p = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("1");
}, 2000);
});
const p2 = p.then((res) => {
// throw "error";
// return p2;
// return 2;
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("OK");
}, 2000);
// reject("ERROR");
});
});
p2.then(
(res) => {
console.log("p2--res", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("p2--err", err);
}
);