深入浅出 Linux 中的 ARM IOMMU SMMU II
SMMU 驱动中的系统 I/O 设备探测
要使系统 I/O 设备的 DMA 内存访问能通过 IOMMU,需要将系统 I/O 设备和 IOMMU 设备绑定起来,也就是执行 SMMU 驱动中的系统 I/O 设备探测。总线发现系统 I/O 设备并和对应的驱动程序绑定,与 IOMMU 设备驱动程序注册并为 IOMMU 设备执行探测初始化的相对顺序不固定,可能系统 I/O 设备先被发现并和对应的驱动程序绑定,也可能 IOMMU 设备驱动程序注册及为 IOMMU 设备执行探测初始化先进行。
SMMU 驱动中的系统 I/O 设备探测有两个时机:
-
如果系统 I/O 设备发现并和对应的驱动程序绑定先执行,在为 IOMMU 设备执行探测初始化时,调用
bus_set_iommu()函数为总线类型设置 IOMMU 回调,此时会遍历总线类型上已经发现的设备列表,并尝试执行 SMMU 驱动中的系统 I/O 设备探测及连接。 -
如果为 IOMMU 设备执行探测初始化先进行,则总线在发现及添加设备,并和对应的设备驱动程序绑定时,调用
of_dma_configure()之类的函数尝试执行 SMMU 驱动中的系统 I/O 设备探测。
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序 probe 时执行系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测
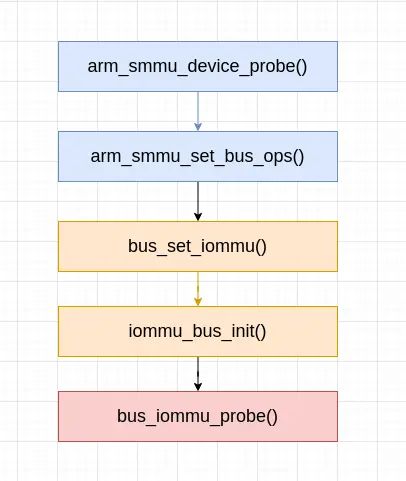
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序 probe 时,通过如下这样的调用链:
一路调到 bus_iommu_probe() 函数,bus_iommu_probe() 函数执行对总线类型上已经添加的系统 I/O 设备的探测。bus_iommu_probe() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
int bus_iommu_probe(struct bus_type *bus)
{
struct iommu_group *group, *next;
LIST_HEAD(group_list);
int ret;
/*
* This code-path does not allocate the default domain when
* creating the iommu group, so do it after the groups are
* created.
*/
ret = bus_for_each_dev(bus, NULL, &group_list, probe_iommu_group);
if (ret)
return ret;
list_for_each_entry_safe(group, next, &group_list, entry) {
/* Remove item from the list */
list_del_init(&group->entry);
mutex_lock(&group->mutex);
/* Try to allocate default domain */
probe_alloc_default_domain(bus, group);
if (!group->default_domain) {
mutex_unlock(&group->mutex);
continue;
}
iommu_group_create_direct_mappings(group);
ret = __iommu_group_dma_attach(group);
mutex_unlock(&group->mutex);
if (ret)
break;
__iommu_group_dma_finalize(group);
}
return ret;
}
bus_iommu_probe() 函数主要做了这样一些事情:
-
遍历总线类型上的所有设备,针对每个设备执行 IOMMU 探测,获得或创建每个设备的
struct iommu_group,这些struct iommu_group放进一个链表中,由一个传出参数返回。各个设备的 IOMMU 探测主要由probe_iommu_group()函数完成。 -
遍历前 1 步中找到的所有
struct iommu_group,针对其中的每一个执行:- 将其从
struct iommu_group链表中移除; - 为 IOMMU group 分配默认的 domain,这主要通过
probe_alloc_default_domain()函数完成; - 为 IOMMU group 分配默认的 domain 失败,则检查下一个
struct iommu_group,否则继续执行; - 创建设备直接映射,这主要通过
iommu_group_create_direct_mappings()函数完成; - 连接设备和 IOMMU domain,这主要通过
__iommu_group_dma_attach()函数完成; - 完成系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测,这主要通过
__iommu_group_dma_finalize()函数完成。
- 将其从
probe_iommu_group() 函数为每个系统 I/O 设备执行 IOMMU 探测,该函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static struct dev_iommu *dev_iommu_get(struct device *dev)
{
struct dev_iommu *param = dev->iommu;
if (param)
return param;
param = kzalloc(sizeof(*param), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!param)
return NULL;
mutex_init(¶m->lock);
dev->iommu = param;
return param;
}
static void dev_iommu_free(struct device *dev)
{
struct dev_iommu *param = dev->iommu;
dev->iommu = NULL;
if (param->fwspec) {
fwnode_handle_put(param->fwspec->iommu_fwnode);
kfree(param->fwspec);
}
kfree(param);
}
static int __iommu_probe_device(struct device *dev, struct list_head *group_list)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
struct iommu_device *iommu_dev;
struct iommu_group *group;
int ret;
if (!ops)
return -ENODEV;
if (!dev_iommu_get(dev))
return -ENOMEM;
if (!try_module_get(ops->owner)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err_free;
}
iommu_dev = ops->probe_device(dev);
if (IS_ERR(iommu_dev)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(iommu_dev);
goto out_module_put;
}
dev->iommu->iommu_dev = iommu_dev;
group = iommu_group_get_for_dev(dev);
if (IS_ERR(group)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(group);
goto out_release;
}
iommu_group_put(group);
if (group_list && !group->default_domain && list_empty(&group->entry))
list_add_tail(&group->entry, group_list);
iommu_device_link(iommu_dev, dev);
return 0;
out_release:
ops->release_device(dev);
out_module_put:
module_put(ops->owner);
err_free:
dev_iommu_free(dev);
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static bool iommu_is_attach_deferred(struct iommu_domain *domain,
struct device *dev)
{
if (domain->ops->is_attach_deferred)
return domain->ops->is_attach_deferred(domain, dev);
return false;
}
/**
* iommu_group_add_device - add a device to an iommu group
* @group: the group into which to add the device (reference should be held)
* @dev: the device
*
* This function is called by an iommu driver to add a device into a
* group. Adding a device increments the group reference count.
*/
int iommu_group_add_device(struct iommu_group *group, struct device *dev)
{
int ret, i = 0;
struct group_device *device;
device = kzalloc(sizeof(*device), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!device)
return -ENOMEM;
device->dev = dev;
ret = sysfs_create_link(&dev->kobj, &group->kobj, "iommu_group");
if (ret)
goto err_free_device;
device->name = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "%s", kobject_name(&dev->kobj));
rename:
if (!device->name) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_remove_link;
}
ret = sysfs_create_link_nowarn(group->devices_kobj,
&dev->kobj, device->name);
if (ret) {
if (ret == -EEXIST && i >= 0) {
/*
* Account for the slim chance of collision
* and append an instance to the name.
*/
kfree(device->name);
device->name = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "%s.%d",
kobject_name(&dev->kobj), i++);
goto rename;
}
goto err_free_name;
}
kobject_get(group->devices_kobj);
dev->iommu_group = group;
mutex_lock(&group->mutex);
list_add_tail(&device->list, &group->devices);
if (group->domain && !iommu_is_attach_deferred(group->domain, dev))
ret = __iommu_attach_device(group->domain, dev);
mutex_unlock(&group->mutex);
if (ret)
goto err_put_group;
/* Notify any listeners about change to group. */
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&group->notifier,
IOMMU_GROUP_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);
trace_add_device_to_group(group->id, dev);
dev_info(dev, "Adding to iommu group %d\n", group->id);
return 0;
err_put_group:
mutex_lock(&group->mutex);
list_del(&device->list);
mutex_unlock(&group->mutex);
dev->iommu_group = NULL;
kobject_put(group->devices_kobj);
sysfs_remove_link(group->devices_kobj, device->name);
err_free_name:
kfree(device->name);
err_remove_link:
sysfs_remove_link(&dev->kobj, "iommu_group");
err_free_device:
kfree(device);
dev_err(dev, "Failed to add to iommu group %d: %d\n", group->id, ret);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_group_add_device);
. . . . . .
struct iommu_group *iommu_group_get(struct device *dev)
{
struct iommu_group *group = dev->iommu_group;
if (group)
kobject_get(group->devices_kobj);
return group;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_group_get);
/**
* iommu_group_ref_get - Increment reference on a group
* @group: the group to use, must not be NULL
*
* This function is called by iommu drivers to take additional references on an
* existing group. Returns the given group for convenience.
*/
struct iommu_group *iommu_group_ref_get(struct iommu_group *group)
{
kobject_get(group->devices_kobj);
return group;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_group_ref_get);
/**
* iommu_group_put - Decrement group reference
* @group: the group to use
*
* This function is called by iommu drivers and users to release the
* iommu group. Once the reference count is zero, the group is released.
*/
void iommu_group_put(struct iommu_group *group)
{
if (group)
kobject_put(group->devices_kobj);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_group_put);
. . . . . .
static struct iommu_group *iommu_group_get_for_dev(struct device *dev)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
struct iommu_group *group;
int ret;
group = iommu_group_get(dev);
if (group)
return group;
if (!ops)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
group = ops->device_group(dev);
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(group == NULL))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if (IS_ERR(group))
return group;
ret = iommu_group_add_device(group, dev);
if (ret)
goto out_put_group;
return group;
out_put_group:
iommu_group_put(group);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
. . . . . .
static int probe_iommu_group(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
struct list_head *group_list = data;
struct iommu_group *group;
int ret;
/* Device is probed already if in a group */
group = iommu_group_get(dev);
if (group) {
iommu_group_put(group);
return 0;
}
ret = __iommu_probe_device(dev, group_list);
if (ret == -ENODEV)
ret = 0;
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static int __iommu_attach_device(struct iommu_domain *domain,
struct device *dev)
{
int ret;
if (unlikely(domain->ops->attach_dev == NULL))
return -ENODEV;
ret = domain->ops->attach_dev(domain, dev);
if (!ret)
trace_attach_device_to_domain(dev);
return ret;
}
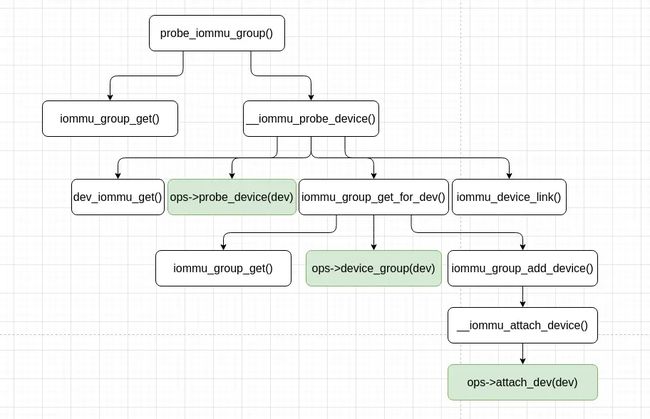
probe_iommu_group() 函数首先尝试从设备 (由 struct device 表示) 获得它的 IOMMU group,如果获得成功,就返回,否则调用 __iommu_probe_device() 函数为系统 I/O 设备执行 IOMMU 的探测。
__iommu_probe_device() 函数的主要执行过程如下:
-
通过
dev_iommu_get()获得设备 (由struct device表示) 的dev_iommu。前面我们提到,在 IOMMU 子系统中,struct dev_iommu对象表示一个连接到 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备。在dev_iommu_get()函数中,首先尝试获得设备的dev_iommu,如果失败,会为设备创建struct dev_iommu对象。 -
调用 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
probe_device()回调,添加设备到 IOMMU 设备驱动程序处理。SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的probe_device()回调检查设备是否与 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序匹配。probe_device()回调成功时,为系统 I/O 设备返回它连接的 IOMMU 设备 (由struct iommu_device表示),失败时返回退出。 -
调用
iommu_group_get_for_dev()函数为设备查找或创建 IOMMU group。- 尝试从设备获得它的 IOMMU group,如果获得成功,就返回,否则继续执行。
- 调用 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
device_group()回调为设备查找或创建 IOMMU group,不同系统 I/O 设备间共享及创建 IOMMU group 的规则,由 IOMMU 设备驱动程序确定。 - 将设备添加进 IOMMU group 的设备列表中。如果 IOMMU group 的 domain 已经存在,且设备不需要延迟连接,则会调用
__iommu_attach_device()函数连接系统 I/O 设备和 IOMMU 设备,并会通知监听者 IOMMU group 添加了设备。
-
将获得的 IOMMU group 添加进传入的 IOMMU group 链表中。只有 IOMMU group 是新创建的会执行这个动作。
-
创建系统 I/O 设备和 IOMMU 设备间的链接。指示设备由给定的 IOMMU 管理。在 sysfs 中,IOMMU 设备的 “devices” 目录中将创建一个到该设备的链接,并在被链接的设备下创建一个指向 IOMMU 设备的 “IOMMU” 链接。
probe_iommu_group() 函数的执行过程总结如下图:
probe_iommu_group()/__iommu_probe_device() 函数为设备创建了如下对象:
- 表示一个连接到 IOMMU 的系统 I/O 设备的
struct dev_iommu对象; - SMMUv3 设备驱动程序内部表示系统 I/O 设备的
struct arm_smmu_master对象,在 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的probe_device()回调中; - IOMMU group。
probe_alloc_default_domain() 函数为各个 IOMMU group 分配默认的 domain,该函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int __iommu_group_for_each_dev(struct iommu_group *group, void *data,
int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
{
struct group_device *device;
int ret = 0;
list_for_each_entry(device, &group->devices, list) {
ret = fn(device->dev, data);
if (ret)
break;
}
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static int iommu_group_alloc_default_domain(struct bus_type *bus,
struct iommu_group *group,
unsigned int type)
{
struct iommu_domain *dom;
dom = __iommu_domain_alloc(bus, type);
if (!dom && type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA) {
dom = __iommu_domain_alloc(bus, IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA);
if (dom)
pr_warn("Failed to allocate default IOMMU domain of type %u for group %s - Falling back to IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA",
type, group->name);
}
if (!dom)
return -ENOMEM;
group->default_domain = dom;
if (!group->domain)
group->domain = dom;
if (!iommu_dma_strict) {
int attr = 1;
iommu_domain_set_attr(dom,
DOMAIN_ATTR_DMA_USE_FLUSH_QUEUE,
&attr);
}
return 0;
}
. . . . . .
static int probe_get_default_domain_type(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
struct __group_domain_type *gtype = data;
unsigned int type = 0;
if (ops->def_domain_type)
type = ops->def_domain_type(dev);
if (type) {
if (gtype->type && gtype->type != type) {
dev_warn(dev, "Device needs domain type %s, but device %s in the same iommu group requires type %s - using default\n",
iommu_domain_type_str(type),
dev_name(gtype->dev),
iommu_domain_type_str(gtype->type));
gtype->type = 0;
}
if (!gtype->dev) {
gtype->dev = dev;
gtype->type = type;
}
}
return 0;
}
static void probe_alloc_default_domain(struct bus_type *bus,
struct iommu_group *group)
{
struct __group_domain_type gtype;
memset(>ype, 0, sizeof(gtype));
/* Ask for default domain requirements of all devices in the group */
__iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, >ype,
probe_get_default_domain_type);
if (!gtype.type)
gtype.type = iommu_def_domain_type;
iommu_group_alloc_default_domain(bus, group, gtype.type);
}
. . . . . .
static struct iommu_domain *__iommu_domain_alloc(struct bus_type *bus,
unsigned type)
{
struct iommu_domain *domain;
if (bus == NULL || bus->iommu_ops == NULL)
return NULL;
domain = bus->iommu_ops->domain_alloc(type);
if (!domain)
return NULL;
domain->ops = bus->iommu_ops;
domain->type = type;
/* Assume all sizes by default; the driver may override this later */
domain->pgsize_bitmap = bus->iommu_ops->pgsize_bitmap;
mutex_init(&domain->switch_log_lock);
return domain;
}
probe_alloc_default_domain() 函数:
-
遍历 IOMMU group 中的所有系统 I/O 设备,通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
def_domain_type()回调为系统 I/O 设备获得默认的 domain 类型,这分为几种情况来处理:- IOMMU 设备驱动程序不支持为系统 I/O 设备获得默认 domain 类型的操作,或者通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序为所有系统 I/O 设备获得的默认 domain 类型都为 0,则采用定义的全局默认 domain 类型;
- IOMMU 设备驱动程序为部分系统 I/O 设备定义了默认 domain 类型,且所有这些系统 I/O 设备的默认 domain 类型相同,则采用这个默认的 domain 类型;
- IOMMU 设备驱动程序为部分系统 I/O 设备定义了默认 domain 类型,但所有这些系统 I/O 设备的默认 domain 类型不完全相同,则采用定义的全局默认 domain 类型。
-
根据获得的默认 domain 类型,通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
domain_alloc()回调为 IOMMU group 分配默认的 domain。如果分配传入的 domain 类型的 domain 失败,还会尝试分配IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMAdomain 类型的 domain。
iommu_group_create_direct_mappings() 函数为各个 IOMMU group 中的各个系统 I/O 设备创建直接映射,该函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int iommu_create_device_direct_mappings(struct iommu_group *group,
struct device *dev)
{
struct iommu_domain *domain = group->default_domain;
struct iommu_resv_region *entry;
struct list_head mappings;
unsigned long pg_size;
int ret = 0;
if (!domain || domain->type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA)
return 0;
BUG_ON(!domain->pgsize_bitmap);
pg_size = 1UL << __ffs(domain->pgsize_bitmap);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&mappings);
iommu_get_resv_regions(dev, &mappings);
/* We need to consider overlapping regions for different devices */
list_for_each_entry(entry, &mappings, list) {
dma_addr_t start, end, addr;
if (domain->ops->apply_resv_region)
domain->ops->apply_resv_region(dev, domain, entry);
start = ALIGN(entry->start, pg_size);
end = ALIGN(entry->start + entry->length, pg_size);
if (entry->type != IOMMU_RESV_DIRECT &&
entry->type != IOMMU_RESV_DIRECT_RELAXABLE)
continue;
for (addr = start; addr < end; addr += pg_size) {
phys_addr_t phys_addr;
phys_addr = iommu_iova_to_phys(domain, addr);
if (phys_addr)
continue;
ret = iommu_map(domain, addr, addr, pg_size, entry->prot);
if (ret)
goto out;
}
}
iommu_flush_iotlb_all(domain);
out:
iommu_put_resv_regions(dev, &mappings);
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static int iommu_do_create_direct_mappings(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
struct iommu_group *group = data;
iommu_create_device_direct_mappings(group, dev);
return 0;
}
static int iommu_group_create_direct_mappings(struct iommu_group *group)
{
return __iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group,
iommu_do_create_direct_mappings);
}
. . . . . .
phys_addr_t iommu_iova_to_phys(struct iommu_domain *domain, dma_addr_t iova)
{
if (unlikely(domain->ops->iova_to_phys == NULL))
return 0;
return domain->ops->iova_to_phys(domain, iova);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_iova_to_phys);
size_t iommu_pgsize(struct iommu_domain *domain,
unsigned long addr_merge, size_t size)
{
unsigned int pgsize_idx;
size_t pgsize;
/* Max page size that still fits into 'size' */
pgsize_idx = __fls(size);
/* need to consider alignment requirements ? */
if (likely(addr_merge)) {
/* Max page size allowed by address */
unsigned int align_pgsize_idx = __ffs(addr_merge);
pgsize_idx = min(pgsize_idx, align_pgsize_idx);
}
/* build a mask of acceptable page sizes */
pgsize = (1UL << (pgsize_idx + 1)) - 1;
/* throw away page sizes not supported by the hardware */
pgsize &= domain->pgsize_bitmap;
/* make sure we're still sane */
BUG_ON(!pgsize);
/* pick the biggest page */
pgsize_idx = __fls(pgsize);
pgsize = 1UL << pgsize_idx;
return pgsize;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_pgsize);
static int __iommu_map(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,
phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int prot, gfp_t gfp)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = domain->ops;
unsigned long orig_iova = iova;
unsigned int min_pagesz;
size_t orig_size = size;
phys_addr_t orig_paddr = paddr;
int ret = 0;
if (unlikely(ops->map == NULL ||
domain->pgsize_bitmap == 0UL))
return -ENODEV;
if (unlikely(!(domain->type & __IOMMU_DOMAIN_PAGING)))
return -EINVAL;
/* find out the minimum page size supported */
min_pagesz = 1 << __ffs(domain->pgsize_bitmap);
/*
* both the virtual address and the physical one, as well as
* the size of the mapping, must be aligned (at least) to the
* size of the smallest page supported by the hardware
*/
if (!IS_ALIGNED(iova | paddr | size, min_pagesz)) {
pr_err("unaligned: iova 0x%lx pa %pa size 0x%zx min_pagesz 0x%x\n",
iova, &paddr, size, min_pagesz);
return -EINVAL;
}
pr_debug("map: iova 0x%lx pa %pa size 0x%zx\n", iova, &paddr, size);
while (size) {
size_t pgsize = iommu_pgsize(domain, iova | paddr, size);
pr_debug("mapping: iova 0x%lx pa %pa pgsize 0x%zx\n",
iova, &paddr, pgsize);
ret = ops->map(domain, iova, paddr, pgsize, prot, gfp);
if (ret)
break;
iova += pgsize;
paddr += pgsize;
size -= pgsize;
}
/* unroll mapping in case something went wrong */
if (ret)
iommu_unmap(domain, orig_iova, orig_size - size);
else
trace_map(orig_iova, orig_paddr, orig_size);
return ret;
}
static int _iommu_map(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,
phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int prot, gfp_t gfp)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = domain->ops;
int ret;
ret = __iommu_map(domain, iova, paddr, size, prot, gfp);
if (ret == 0 && ops->iotlb_sync_map)
ops->iotlb_sync_map(domain, iova, size);
return ret;
}
int iommu_map(struct iommu_domain *domain, unsigned long iova,
phys_addr_t paddr, size_t size, int prot)
{
might_sleep();
return _iommu_map(domain, iova, paddr, size, prot, GFP_KERNEL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_map);
. . . . . .
void iommu_get_resv_regions(struct device *dev, struct list_head *list)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
if (ops && ops->get_resv_regions)
ops->get_resv_regions(dev, list);
}
void iommu_put_resv_regions(struct device *dev, struct list_head *list)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
if (ops && ops->put_resv_regions)
ops->put_resv_regions(dev, list);
}
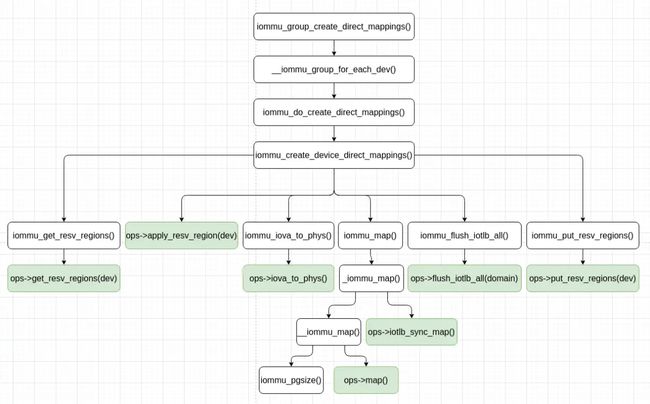
iommu_group_create_direct_mappings() 函数遍历 IOMMU group 中的各个系统 I/O 设备,通过 iommu_do_create_direct_mappings()/iommu_create_device_direct_mappings()函数为每个设备创建设备的直接映射,直接映射针对设备的保留内存区域,且 domain type 为 DMA。
iommu_create_device_direct_mappings() 的执行过程如下:
- 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
get_resv_regions()回调获得设备的所有保留内存映射区域,没开启 IOMMU 时,保留内存映射区域的地址是物理内存地址,开启 IOMMU 时,保留内存映射区域的地址是 IO 虚拟地址。 - 针对设备的每个保留内存映射区域:
- 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
apply_resv_region()回调,应用保留内存映射区域; - 将内存映射区域的起始地址对齐到页大小;
- 针对内存映射区域内的每个内存页:
- 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
iova_to_phys()回调获得内存页的物理地址,用于判断是否可以映射; - 通过
iommu_map()/_iommu_map()函数映射一个内存页。
- 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
- 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
- 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
flush_iotlb_all()回调刷新 domain 的 IO TLB。 - 通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
put_resv_regions()回调释放获得的设备的所有保留内存映射区域。
iommu_create_device_direct_mappings() 函数的执行过程总结如下图:
__iommu_group_dma_attach() 函数为各个 IOMMU group 中的各个系统 I/O 设备建立与 IOMMU 设备的连接,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int iommu_group_do_dma_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
struct iommu_domain *domain = data;
int ret = 0;
if (!iommu_is_attach_deferred(domain, dev))
ret = __iommu_attach_device(domain, dev);
return ret;
}
static int __iommu_group_dma_attach(struct iommu_group *group)
{
return __iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group->default_domain,
iommu_group_do_dma_attach);
}
__iommu_group_dma_attach() 函数遍历 IOMMU group 中的各个系统 I/O 设备,通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的 is_attach_deferred() 回调判断系统 I/O 设备是否需要延迟连接,如果不需要,则会调用 __iommu_attach_device() 函数,通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的 attach_dev() 回调连接系统 I/O 设备和 IOMMU 设备。由于前面的步骤,此时可以确保 IOMMU group 的 domain 是存在的,因而不需要像前面在将设备添加到 IOMMU group 中那样检查 domain。
__iommu_group_dma_finalize() 函数为各个 IOMMU group 中的各个系统 I/O 设备结束 IOMMU 探测,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int iommu_group_do_probe_finalize(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
struct iommu_domain *domain = data;
if (domain->ops->probe_finalize)
domain->ops->probe_finalize(dev);
return 0;
}
static void __iommu_group_dma_finalize(struct iommu_group *group)
{
__iommu_group_for_each_dev(group, group->default_domain,
iommu_group_do_probe_finalize);
}
__iommu_group_dma_finalize() 函数遍历 IOMMU group 中的各个系统 I/O 设备,通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的 probe_finalize() 回调为系统 I/O 设备结束 IOMMU 探测。
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序 probe 时执行系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测的整体过程大概如下图所示:
系统 I/O 设备和其对应的驱动程序绑定时执行系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测
系统 I/O 设备和其对应的驱动程序绑定时执行系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测,入口是 of_dma_configure()/of_dma_configure_id() 函数,它们用于建立 DMA 配置。of_dma_configure() 函数定义 (位于 include/linux/of_device.h 文件中) 如下:
int of_dma_configure_id(struct device *dev,
struct device_node *np,
bool force_dma, const u32 *id);
static inline int of_dma_configure(struct device *dev,
struct device_node *np,
bool force_dma)
{
return of_dma_configure_id(dev, np, force_dma, NULL);
}
系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测的调用链大概像下面这样:
[ 19.147047] iommu_probe_device+0x28/0x1c0
[ 19.152700] of_iommu_configure+0xd8/0x1e0
[ 19.158358] of_dma_configure_id+0x1c8/0x2a4
[ 19.164266] platform_dma_configure+0x20/0x90
[ 19.170186] really_probe+0xa0/0x4c0
[ 19.175083] driver_probe_device+0x58/0xc0
[ 19.180657] device_driver_attach+0xc0/0xd0
[ 19.186342] __driver_attach+0x84/0x124
[ 19.191559] bus_for_each_dev+0x70/0xd0
[ 19.196795] driver_attach+0x24/0x30
[ 19.201686] bus_add_driver+0x108/0x1fc
[ 19.206928] driver_register+0x78/0x130
[ 19.212189] __platform_driver_register+0x4c/0x60
of_dma_configure_id() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/of/device.c 文件中) 如下:
int of_dma_configure_id(struct device *dev, struct device_node *np,
bool force_dma, const u32 *id)
{
const struct iommu_ops *iommu;
const struct bus_dma_region *map = NULL;
u64 dma_start = 0;
u64 mask, end, size = 0;
bool coherent;
int ret;
ret = of_dma_get_range(np, &map);
if (ret < 0) {
/*
* For legacy reasons, we have to assume some devices need
* DMA configuration regardless of whether "dma-ranges" is
* correctly specified or not.
*/
if (!force_dma)
return ret == -ENODEV ? 0 : ret;
} else {
const struct bus_dma_region *r = map;
u64 dma_end = 0;
/* Determine the overall bounds of all DMA regions */
for (dma_start = ~0; r->size; r++) {
/* Take lower and upper limits */
if (r->dma_start < dma_start)
dma_start = r->dma_start;
if (r->dma_start + r->size > dma_end)
dma_end = r->dma_start + r->size;
}
size = dma_end - dma_start;
/*
* Add a work around to treat the size as mask + 1 in case
* it is defined in DT as a mask.
*/
if (size & 1) {
dev_warn(dev, "Invalid size 0x%llx for dma-range(s)\n",
size);
size = size + 1;
}
if (!size) {
dev_err(dev, "Adjusted size 0x%llx invalid\n", size);
kfree(map);
return -EINVAL;
}
}
/*
* If @dev is expected to be DMA-capable then the bus code that created
* it should have initialised its dma_mask pointer by this point. For
* now, we'll continue the legacy behaviour of coercing it to the
* coherent mask if not, but we'll no longer do so quietly.
*/
if (!dev->dma_mask) {
dev_warn(dev, "DMA mask not set\n");
dev->dma_mask = &dev->coherent_dma_mask;
}
if (!size && dev->coherent_dma_mask)
size = max(dev->coherent_dma_mask, dev->coherent_dma_mask + 1);
else if (!size)
size = 1ULL << 32;
/*
* Limit coherent and dma mask based on size and default mask
* set by the driver.
*/
end = dma_start + size - 1;
mask = DMA_BIT_MASK(ilog2(end) + 1);
dev->coherent_dma_mask &= mask;
*dev->dma_mask &= mask;
/* ...but only set bus limit and range map if we found valid dma-ranges earlier */
if (!ret) {
dev->bus_dma_limit = end;
dev->dma_range_map = map;
}
coherent = of_dma_is_coherent(np);
dev_dbg(dev, "device is%sdma coherent\n",
coherent ? " " : " not ");
iommu = of_iommu_configure(dev, np, id);
if (PTR_ERR(iommu) == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
/* Don't touch range map if it wasn't set from a valid dma-ranges */
if (!ret)
dev->dma_range_map = NULL;
kfree(map);
return -EPROBE_DEFER;
}
dev_dbg(dev, "device is%sbehind an iommu\n",
iommu ? " " : " not ");
arch_setup_dma_ops(dev, dma_start, size, iommu, coherent);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(of_dma_configure_id);
of_dma_configure_id() 函数做了如下几件事情:
- 调用
of_dma_get_range()函数获得设备的 DMA 范围信息,并把它们放进一个 map 数组中。设备的 DMA 范围信息在设备树文件中,由设备节点的 “dma-ranges” 属性定义,像下面 (位于 arch/arm64/boot/dts/apm/apm-storm.dtsi 文件中) 这样:
pcie0: pcie@1f2b0000 {
. . . . . .
dma-ranges = <0x42000000 0x80 0x00000000 0x80 0x00000000 0x00 0x80000000
0x42000000 0x00 0x00000000 0x00 0x00000000 0x80 0x00000000>;
. . . . . .
};
of_dma_get_range() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/of/address.c 文件中) 如下:
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_DMA
/**
* of_dma_get_range - Get DMA range info and put it into a map array
* @np: device node to get DMA range info
* @map: dma range structure to return
*
* Look in bottom up direction for the first "dma-ranges" property
* and parse it. Put the information into a DMA offset map array.
*
* dma-ranges format:
* DMA addr (dma_addr) : naddr cells
* CPU addr (phys_addr_t) : pna cells
* size : nsize cells
*
* It returns -ENODEV if "dma-ranges" property was not found for this
* device in the DT.
*/
int of_dma_get_range(struct device_node *np, const struct bus_dma_region **map)
{
struct device_node *node = of_node_get(np);
const __be32 *ranges = NULL;
bool found_dma_ranges = false;
struct of_range_parser parser;
struct of_range range;
struct bus_dma_region *r;
int len, num_ranges = 0;
int ret = 0;
while (node) {
ranges = of_get_property(node, "dma-ranges", &len);
/* Ignore empty ranges, they imply no translation required */
if (ranges && len > 0)
break;
/* Once we find 'dma-ranges', then a missing one is an error */
if (found_dma_ranges && !ranges) {
ret = -ENODEV;
goto out;
}
found_dma_ranges = true;
node = of_get_next_dma_parent(node);
}
if (!node || !ranges) {
pr_debug("no dma-ranges found for node(%pOF)\n", np);
ret = -ENODEV;
goto out;
}
of_dma_range_parser_init(&parser, node);
for_each_of_range(&parser, &range)
num_ranges++;
r = kcalloc(num_ranges + 1, sizeof(*r), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!r) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
/*
* Record all info in the generic DMA ranges array for struct device.
*/
*map = r;
of_dma_range_parser_init(&parser, node);
for_each_of_range(&parser, &range) {
pr_debug("dma_addr(%llx) cpu_addr(%llx) size(%llx)\n",
range.bus_addr, range.cpu_addr, range.size);
if (range.cpu_addr == OF_BAD_ADDR) {
pr_err("translation of DMA address(%llx) to CPU address failed node(%pOF)\n",
range.bus_addr, node);
continue;
}
r->cpu_start = range.cpu_addr;
r->dma_start = range.bus_addr;
r->size = range.size;
r->offset = range.cpu_addr - range.bus_addr;
r++;
}
out:
of_node_put(node);
return ret;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_HAS_DMA */
- 计算所有 DMA 区域整体的边界和大小。
- 初始化设备的
dma_mask,及总线 DMA 限制。 - 调用
of_iommu_configure()函数为设备执行 IOMMU 配置。 - 调用
arch_setup_dma_ops()函数为设备设置 DMA 操作回调。
of_iommu_configure() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/of_iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static int of_iommu_xlate(struct device *dev,
struct of_phandle_args *iommu_spec)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops;
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode = &iommu_spec->np->fwnode;
int ret;
ops = iommu_ops_from_fwnode(fwnode);
if ((ops && !ops->of_xlate) ||
!of_device_is_available(iommu_spec->np))
return NO_IOMMU;
ret = iommu_fwspec_init(dev, &iommu_spec->np->fwnode, ops);
if (ret)
return ret;
/*
* The otherwise-empty fwspec handily serves to indicate the specific
* IOMMU device we're waiting for, which will be useful if we ever get
* a proper probe-ordering dependency mechanism in future.
*/
if (!ops)
return driver_deferred_probe_check_state(dev);
if (!try_module_get(ops->owner))
return -ENODEV;
ret = ops->of_xlate(dev, iommu_spec);
module_put(ops->owner);
return ret;
}
static int of_iommu_configure_dev_id(struct device_node *master_np,
struct device *dev,
const u32 *id)
{
struct of_phandle_args iommu_spec = { .args_count = 1 };
int err;
err = of_map_id(master_np, *id, "iommu-map",
"iommu-map-mask", &iommu_spec.np,
iommu_spec.args);
if (err)
return err == -ENODEV ? NO_IOMMU : err;
err = of_iommu_xlate(dev, &iommu_spec);
of_node_put(iommu_spec.np);
return err;
}
static int of_iommu_configure_dev(struct device_node *master_np,
struct device *dev)
{
struct of_phandle_args iommu_spec;
int err = NO_IOMMU, idx = 0;
while (!of_parse_phandle_with_args(master_np, "iommus",
"#iommu-cells",
idx, &iommu_spec)) {
err = of_iommu_xlate(dev, &iommu_spec);
of_node_put(iommu_spec.np);
idx++;
if (err)
break;
}
return err;
}
. . . . . .
static int of_iommu_configure_device(struct device_node *master_np,
struct device *dev, const u32 *id)
{
return (id) ? of_iommu_configure_dev_id(master_np, dev, id) :
of_iommu_configure_dev(master_np, dev);
}
. . . . . .
const struct iommu_ops *of_iommu_configure(struct device *dev,
struct device_node *master_np,
const u32 *id)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = NULL;
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev);
int err = NO_IOMMU;
if (!master_np)
return NULL;
if (fwspec) {
if (fwspec->ops)
return fwspec->ops;
/* In the deferred case, start again from scratch */
iommu_fwspec_free(dev);
}
/*
* We don't currently walk up the tree looking for a parent IOMMU.
* See the `Notes:' section of
* Documentation/devicetree/bindings/iommu/iommu.txt
*/
if (dev_is_pci(dev)) {
struct of_pci_iommu_alias_info info = {
.dev = dev,
.np = master_np,
};
pci_request_acs();
err = pci_for_each_dma_alias(to_pci_dev(dev),
of_pci_iommu_init, &info);
of_pci_check_device_ats(dev, master_np);
} else {
err = of_iommu_configure_device(master_np, dev, id);
}
/*
* Two success conditions can be represented by non-negative err here:
* >0 : there is no IOMMU, or one was unavailable for non-fatal reasons
* 0 : we found an IOMMU, and dev->fwspec is initialised appropriately
* <0 : any actual error
*/
if (!err) {
/* The fwspec pointer changed, read it again */
fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev);
ops = fwspec->ops;
}
/*
* If we have reason to believe the IOMMU driver missed the initial
* probe for dev, replay it to get things in order.
*/
if (!err && dev->bus && !device_iommu_mapped(dev))
err = iommu_probe_device(dev);
/* Ignore all other errors apart from EPROBE_DEFER */
if (err == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
ops = ERR_PTR(err);
} else if (err < 0) {
dev_dbg(dev, "Adding to IOMMU failed: %d\n", err);
ops = NULL;
}
return ops;
}
这里主要关注非 PCIe 设备的情况。struct iommu_fwspec 对象包含每设备的 IOMMU 实例数据。of_iommu_configure() 函数执行过程如下:
- 尝试从系统 I/O 设备获得它的
struct iommu_fwspec对象。dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev)函数定义 (位于 include/linux/iommu.h 文件中) 如下:
static inline struct iommu_fwspec *dev_iommu_fwspec_get(struct device *dev)
{
if (dev->iommu)
return dev->iommu->fwspec;
else
return NULL;
}
static inline void dev_iommu_fwspec_set(struct device *dev,
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec)
{
dev->iommu->fwspec = fwspec;
}
dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev) 函数通过系统 I/O 设备的 struct dev_iommu *iommu 获得其 struct iommu_fwspec 对象,但系统 I/O 设备的 struct dev_iommu *iommu 在 IOMMU 配置设备时,或系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测时创建。如果这里成功获得了系统 I/O 设备的 struct iommu_fwspec 对象,且其 IOMMU 回调有效,则直接返回其 IOMMU 回调。为系统 I/O 设备调用 of_dma_configure_id() 函数时,已经对系统 I/O 设备执行过了 IOMMU 初始化时,会发生这种情况。如果这里成功获得了系统 I/O 设备的 struct iommu_fwspec 对象,但其 IOMMU 回调无效,struct iommu_fwspec 对象会被先释放掉。
- 通过
of_iommu_configure_device()函数,从设备树的设备节点中获得它连接的 IOMMU 设备的句柄,并为系统 I/O 设备调用of_iommu_xlate()函数执行 iommu xlate 操作。of_iommu_xlate()函数执行过程如下:- 在 IOMMU 子系统的所有 IOMMU 设备列表中查找与获得的 IOMMU 设备句柄匹配的 IOMMU 设备的 IOMMU 回调。这通过
iommu_ops_from_fwnode()函数完成。 - 调用
iommu_fwspec_init()函数为设备创建struct iommu_fwspec对象。当系统 I/O 设备的 dev_iommu 不存在时,iommu_fwspec_init()函数会创建它。 - 通过找到的 IOMMU 设备的 IOMMU 设备驱动程序的
of_xlate()回调,将 OF master ID 添加到 IOMMU 组。
- 在 IOMMU 子系统的所有 IOMMU 设备列表中查找与获得的 IOMMU 设备句柄匹配的 IOMMU 设备的 IOMMU 回调。这通过
iommu_ops_from_fwnode() 函数和 iommu_fwspec_init() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops_from_fwnode(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = NULL;
struct iommu_device *iommu;
spin_lock(&iommu_device_lock);
list_for_each_entry(iommu, &iommu_device_list, list)
if (iommu->fwnode == fwnode) {
ops = iommu->ops;
break;
}
spin_unlock(&iommu_device_lock);
return ops;
}
int iommu_fwspec_init(struct device *dev, struct fwnode_handle *iommu_fwnode,
const struct iommu_ops *ops)
{
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev);
if (fwspec)
return ops == fwspec->ops ? 0 : -EINVAL;
if (!dev_iommu_get(dev))
return -ENOMEM;
/* Preallocate for the overwhelmingly common case of 1 ID */
fwspec = kzalloc(struct_size(fwspec, ids, 1), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!fwspec)
return -ENOMEM;
of_node_get(to_of_node(iommu_fwnode));
fwspec->iommu_fwnode = iommu_fwnode;
fwspec->ops = ops;
dev_iommu_fwspec_set(dev, fwspec);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_fwspec_init);
- 通过
iommu_probe_device()函数执行系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测。
iommu_probe_device() 函数与 bus_iommu_probe() 函数做的事情类似,差别在于前者针对单个系统 I/O 设备,后者则针对总线类型上存在的许多系统 I/O 设备。iommu_probe_device() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
int iommu_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
struct iommu_group *group;
int ret;
ret = __iommu_probe_device(dev, NULL);
if (ret)
goto err_out;
group = iommu_group_get(dev);
if (!group)
goto err_release;
/*
* Try to allocate a default domain - needs support from the
* IOMMU driver. There are still some drivers which don't
* support default domains, so the return value is not yet
* checked.
*/
iommu_alloc_default_domain(group, dev);
if (group->default_domain) {
ret = __iommu_attach_device(group->default_domain, dev);
if (ret) {
iommu_group_put(group);
goto err_release;
}
}
iommu_create_device_direct_mappings(group, dev);
iommu_group_put(group);
if (ops->probe_finalize)
ops->probe_finalize(dev);
return 0;
err_release:
iommu_release_device(dev);
err_out:
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static int iommu_get_def_domain_type(struct device *dev)
{
const struct iommu_ops *ops = dev->bus->iommu_ops;
unsigned int type = 0;
if (ops->def_domain_type)
type = ops->def_domain_type(dev);
return (type == 0) ? iommu_def_domain_type : type;
}
. . . . . .
static int iommu_alloc_default_domain(struct iommu_group *group,
struct device *dev)
{
unsigned int type;
if (group->default_domain)
return 0;
type = iommu_get_def_domain_type(dev);
return iommu_group_alloc_default_domain(dev->bus, group, type);
}
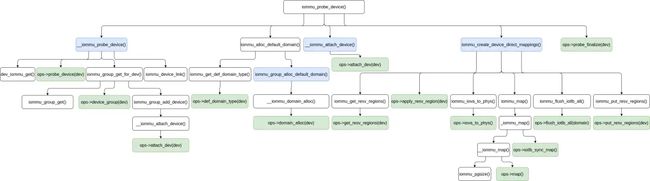
iommu_probe_device() 函数主要做了这样一些事情:
-
通过
__iommu_probe_device()函数为系统 I/O 设备执行 IOMMU 探测,获得或创建设备的struct iommu_group。 -
为 IOMMU group 分配默认的 domain,这主要通过
iommu_alloc_default_domain()函数完成。iommu_alloc_default_domain()函数首先通过iommu_get_def_domain_type()函数获得系统 I/O 设备默认的 domain 的类型,然后通过iommu_group_alloc_default_domain()函数分配默认的 domain。 -
连接系统 I/O 设备和 IOMMU domain,这主要通过
__iommu_attach_device()函数完成。 -
创建设备直接映射,这主要通过
iommu_create_device_direct_mappings()函数完成。 -
完成系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测,这主要通过 IOMMU 设备驱动程序提供的
probe_finalize()回调完成。
iommu_probe_device() 函数整体的执行过程大概如下图所示:
of_dma_configure()/of_dma_configure_id() 函数整体的执行过程 (iommu_probe_device() 函数的部分调用关系简略表示) 大概如下图所示:
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序中的系统 I/O 设备探测
如上所述,系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测过程中,有多个 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序提供的 IOMMU 回调,出于不同的目的被调用。系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测过程可以分为几个阶段,每个阶段会有不同的 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序 IOMMU 回调被调用:
-
OF IOMMU 配置设备,
struct iommu_fwspec对象创建及初始化:- of_xlate()/arm_smmu_of_xlate()
-
IOMMU 探测设备:
- probe_device()/arm_smmu_probe_device()
- device_group()/arm_smmu_device_group()
-
分配默认的 domain:
- def_domain_type()/arm_smmu_device_domain_type()
- domain_alloc()/arm_smmu_domain_alloc()
-
连接系统 I/O 设备和 SMMUv3 设备:
- attach_dev()/arm_smmu_attach_dev()
-
创建设备直接区域映射:
- get_resv_regions()/arm_smmu_get_resv_regions()
- apply_resv_region()/*,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序未实现
- iova_to_phys()/arm_smmu_iova_to_phys()
- map()/arm_smmu_map()
- iotlb_sync_map()/*,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序未实现
- flush_iotlb_all()/arm_smmu_flush_iotlb_all()
- put_resv_regions()/generic_iommu_put_resv_regions()
-
结束系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测:
- probe_finalize()/*,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序未实现
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序定义的所有 IOMMU 回调都位于 drivers/iommu/arm/arm-smmu-v3/arm-smmu-v3.c 文件中。
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的 of_xlate() 回调 arm_smmu_of_xlate() 将从设备树文件中解析获得的系统 I/O 设备的 StreamID 添加进它的 struct iommu_fwspec 对象,这个函数定义如下:
static int arm_smmu_of_xlate(struct device *dev, struct of_phandle_args *args)
{
return iommu_fwspec_add_ids(dev, args->args, 1);
}
arm_smmu_of_xlate() 函数调用 iommu_fwspec_add_ids() 函数添加 1 个 StreamID。iommu_fwspec_add_ids() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
int iommu_fwspec_add_ids(struct device *dev, u32 *ids, int num_ids)
{
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev);
int i, new_num;
if (!fwspec)
return -EINVAL;
new_num = fwspec->num_ids + num_ids;
if (new_num > 1) {
fwspec = krealloc(fwspec, struct_size(fwspec, ids, new_num),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!fwspec)
return -ENOMEM;
dev_iommu_fwspec_set(dev, fwspec);
}
for (i = 0; i < num_ids; i++)
fwspec->ids[fwspec->num_ids + i] = ids[i];
fwspec->num_ids = new_num;
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_fwspec_add_ids);
iommu_fwspec_add_ids() 函数确保 struct iommu_fwspec 对象中有足够的空间来存放要添加的 StreamID,如果空间不足,会先重新分配并初始化 struct iommu_fwspec 对象,之后将要添加的 StreamID 放进 struct iommu_fwspec 对象。
在 IOMMU 探测设备阶段,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的 probe_device() 回调 arm_smmu_probe_device() 执行系统 I/O 设备的 IOMMU 探测。这个函数定义如下::
static void
arm_smmu_write_strtab_l1_desc(__le64 *dst, struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc *desc)
{
u64 val = 0;
val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_L1_DESC_SPAN, desc->span);
val |= desc->l2ptr_dma & STRTAB_L1_DESC_L2PTR_MASK;
/* See comment in arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc() */
WRITE_ONCE(*dst, cpu_to_le64(val));
}
. . . . . .
static void arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes(__le64 *strtab, unsigned int nent)
{
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < nent; ++i) {
arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent(NULL, -1, strtab);
strtab += STRTAB_STE_DWORDS;
}
}
static int arm_smmu_init_l2_strtab(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 sid)
{
size_t size;
void *strtab;
struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg *cfg = &smmu->strtab_cfg;
struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc *desc = &cfg->l1_desc[sid >> STRTAB_SPLIT];
if (desc->l2ptr)
return 0;
size = 1 << (STRTAB_SPLIT + ilog2(STRTAB_STE_DWORDS) + 3);
strtab = &cfg->strtab[(sid >> STRTAB_SPLIT) * STRTAB_L1_DESC_DWORDS];
desc->span = STRTAB_SPLIT + 1;
desc->l2ptr = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, size, &desc->l2ptr_dma,
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!desc->l2ptr) {
dev_err(smmu->dev,
"failed to allocate l2 stream table for SID %u\n",
sid);
return -ENOMEM;
}
arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes(desc->l2ptr, 1 << STRTAB_SPLIT);
arm_smmu_write_strtab_l1_desc(strtab, desc);
return 0;
}
. . . . . .
static bool arm_smmu_sid_in_range(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 sid)
{
unsigned long limit = smmu->strtab_cfg.num_l1_ents;
if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB)
limit *= 1UL << STRTAB_SPLIT;
return sid < limit;
}
static int arm_smmu_insert_master(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu,
struct arm_smmu_master *master)
{
int i;
int ret = 0;
struct arm_smmu_stream *new_stream, *cur_stream;
struct rb_node **new_node, *parent_node = NULL;
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(master->dev);
master->streams = kcalloc(fwspec->num_ids, sizeof(*master->streams),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!master->streams)
return -ENOMEM;
master->num_streams = fwspec->num_ids;
mutex_lock(&smmu->streams_mutex);
for (i = 0; i < fwspec->num_ids; i++) {
u32 sid = fwspec->ids[i];
new_stream = &master->streams[i];
new_stream->id = sid;
new_stream->master = master;
/*
* Check the SIDs are in range of the SMMU and our stream table
*/
if (!arm_smmu_sid_in_range(smmu, sid)) {
ret = -ERANGE;
break;
}
/* Ensure l2 strtab is initialised */
if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB) {
ret = arm_smmu_init_l2_strtab(smmu, sid);
if (ret)
break;
}
/* Insert into SID tree */
new_node = &(smmu->streams.rb_node);
while (*new_node) {
cur_stream = rb_entry(*new_node, struct arm_smmu_stream,
node);
parent_node = *new_node;
if (cur_stream->id > new_stream->id) {
new_node = &((*new_node)->rb_left);
} else if (cur_stream->id < new_stream->id) {
new_node = &((*new_node)->rb_right);
} else {
dev_warn(master->dev,
"stream %u already in tree\n",
cur_stream->id);
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
}
}
if (ret)
break;
rb_link_node(&new_stream->node, parent_node, new_node);
rb_insert_color(&new_stream->node, &smmu->streams);
}
if (ret) {
for (i--; i >= 0; i--)
rb_erase(&master->streams[i].node, &smmu->streams);
kfree(master->streams);
}
mutex_unlock(&smmu->streams_mutex);
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static struct iommu_ops arm_smmu_ops;
static struct iommu_device *arm_smmu_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
int ret;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu;
struct arm_smmu_master *master;
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev);
if (!fwspec || fwspec->ops != &arm_smmu_ops)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(dev_iommu_priv_get(dev)))
return ERR_PTR(-EBUSY);
smmu = arm_smmu_get_by_fwnode(fwspec->iommu_fwnode);
if (!smmu)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
master = kzalloc(sizeof(*master), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!master)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
master->dev = dev;
master->smmu = smmu;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&master->bonds);
dev_iommu_priv_set(dev, master);
ret = arm_smmu_insert_master(smmu, master);
if (ret)
goto err_free_master;
device_property_read_u32(dev, "pasid-num-bits", &master->ssid_bits);
master->ssid_bits = min(smmu->ssid_bits, master->ssid_bits);
/*
* Note that PASID must be enabled before, and disabled after ATS:
* PCI Express Base 4.0r1.0 - 10.5.1.3 ATS Control Register
*
* Behavior is undefined if this bit is Set and the value of the PASID
* Enable, Execute Requested Enable, or Privileged Mode Requested bits
* are changed.
*/
arm_smmu_enable_pasid(master);
if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_CDTAB))
master->ssid_bits = min_t(u8, master->ssid_bits,
CTXDESC_LINEAR_CDMAX);
if ((smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALLS &&
device_property_read_bool(dev, "dma-can-stall")) ||
smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALL_FORCE)
master->stall_enabled = true;
arm_smmu_init_pri(master);
return &smmu->iommu;
err_free_master:
kfree(master);
dev_iommu_priv_set(dev, NULL);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
probe_device() 回调大概做了这样一些事情:
- 创建并初始化
struct arm_smmu_master对象。struct arm_smmu_master在 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序中表示一个连接到 SMMUv3 设备的系统 I/O 设备。struct arm_smmu_master对象通过系统 I/O 设备的 dev_iommu 的priv字段和它连接在一起,这从dev_iommu_priv_get()/dev_iommu_priv_set()函数的定义 (位于 include/linux/iommu.h 文件中) 可以看出来:
static inline void *dev_iommu_priv_get(struct device *dev)
{
if (dev->iommu)
return dev->iommu->priv;
else
return NULL;
}
static inline void dev_iommu_priv_set(struct device *dev, void *priv)
{
dev->iommu->priv = priv;
}
-
调用
arm_smmu_insert_master()函数为系统 I/O 设备创建流,并把这些流 SID 插入 SMMUv3 设备的 SID 树中:- 为流分配内存。要创建的流的数量根据系统 I/O 设备的 StreamID 的数量确定,对于大多数一般的系统 I/O 设备为 1。
- 对于每个流:
- 初始化流的 ID;
- 检查流的 ID 是否在设置的 StreamID 的范围内,如果不在则检查下一个流,否则继续执行;
- 如果使用了 2 级流表,在
arm_smmu_init_l2_strtab()函数中分配并填充第 2 级流表。arm_smmu_init_l2_strtab()函数调用arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes()函数将第 2 级流表中的所有流表项 STE 初始化为旁路 SMMU,并调用arm_smmu_write_strtab_l1_desc()函数将第 2 级流表的地址写入第 1 级流表中,对应的 L1 流表描述符中; - 将 StreamID 插入 SMMUv3 设备的 SID 树中;
- 如果针对某个流的某个操作执行失败,则移除已经为当前系统 I/O 设备添加的所有 StreamID。
-
从设备树文件中读取系统 I/O 设备的 SubstreamID 位长,并计算将采用的 SubstreamID 位长。
-
启用 PASID。仅用于 PCIe 设备。
-
不支持 2 级 CD 表时,更新 SubstreamID 位长。
-
检查是否要为系统 I/O 设备支持 Stall 模式。
-
初始化 PRI。仅用于 PCIe 设备。
在 IOMMU 探测设备阶段,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的 device_group() 回调 arm_smmu_device_group() 用于为系统 I/O 设备查找或创建 IOMMU group,这个函数定义如下:
static struct iommu_group *arm_smmu_device_group(struct device *dev)
{
struct iommu_group *group;
/*
* We don't support devices sharing stream IDs other than PCI RID
* aliases, since the necessary ID-to-device lookup becomes rather
* impractical given a potential sparse 32-bit stream ID space.
*/
if (dev_is_pci(dev))
group = pci_device_group(dev);
else
group = generic_device_group(dev);
return group;
}
arm_smmu_device_group() 函数分为 PCIe 设备和其它设备来执行。IOMMU 子系统不支持设备共享 stream ID,除了 PCI RID 别名。这里主要关注非 PCIe 设备。generic_device_group() 函数为非 PCIe 设备分配 IOMMU group,这个函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
struct iommu_group *iommu_group_alloc(void)
{
struct iommu_group *group;
int ret;
group = kzalloc(sizeof(*group), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!group)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
group->kobj.kset = iommu_group_kset;
mutex_init(&group->mutex);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&group->devices);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&group->entry);
BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&group->notifier);
ret = ida_simple_get(&iommu_group_ida, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL);
if (ret < 0) {
kfree(group);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
group->id = ret;
ret = kobject_init_and_add(&group->kobj, &iommu_group_ktype,
NULL, "%d", group->id);
if (ret) {
ida_simple_remove(&iommu_group_ida, group->id);
kobject_put(&group->kobj);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
group->devices_kobj = kobject_create_and_add("devices", &group->kobj);
if (!group->devices_kobj) {
kobject_put(&group->kobj); /* triggers .release & free */
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
}
/*
* The devices_kobj holds a reference on the group kobject, so
* as long as that exists so will the group. We can therefore
* use the devices_kobj for reference counting.
*/
kobject_put(&group->kobj);
ret = iommu_group_create_file(group,
&iommu_group_attr_reserved_regions);
if (ret)
return ERR_PTR(ret);
ret = iommu_group_create_file(group, &iommu_group_attr_type);
if (ret)
return ERR_PTR(ret);
pr_debug("Allocated group %d\n", group->id);
return group;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(iommu_group_alloc);
. . . . . .
/*
* Generic device_group call-back function. It just allocates one
* iommu-group per device.
*/
struct iommu_group *generic_device_group(struct device *dev)
{
return iommu_group_alloc();
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(generic_device_group);
generic_device_group() 函数分配一个新的 IOMMU group,它为 struct iommu_group 对象分配内存,初始化对象,获得 group ID,并创建 sysfs 文件。SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的 device_group() 回调为非 PCIe 分配新的 IOMMU group。
def_domain_type()/arm_smmu_device_domain_type() 和 domain_alloc()/arm_smmu_domain_alloc() 在分配默认的 domain 阶段配合使用,前者用于获得默认的 domain 类型,后者用于分配 domain 对象。这两个回调实现如下:
static struct iommu_domain *arm_smmu_domain_alloc(unsigned type)
{
struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain;
if (type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_UNMANAGED &&
type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA &&
type != IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY)
return NULL;
/*
* Allocate the domain and initialise some of its data structures.
* We can't really do anything meaningful until we've added a
* master.
*/
smmu_domain = kzalloc(sizeof(*smmu_domain), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!smmu_domain)
return NULL;
if (type == IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA &&
iommu_get_dma_cookie(&smmu_domain->domain)) {
kfree(smmu_domain);
return NULL;
}
mutex_init(&smmu_domain->init_mutex);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&smmu_domain->devices);
spin_lock_init(&smmu_domain->devices_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&smmu_domain->mmu_notifiers);
return &smmu_domain->domain;
}
. . . . . .
#ifdef CONFIG_SMMU_BYPASS_DEV
static int arm_smmu_device_domain_type(struct device *dev)
{
int i;
struct pci_dev *pdev;
if (!dev_is_pci(dev))
return 0;
pdev = to_pci_dev(dev);
for (i = 0; i < smmu_bypass_devices_num; i++) {
if ((smmu_bypass_devices[i].vendor == pdev->vendor) &&
(smmu_bypass_devices[i].device == pdev->device)) {
dev_info(dev, "device 0x%hx:0x%hx uses identity mapping.",
pdev->vendor, pdev->device);
return IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY;
}
}
return 0;
}
#endif
对于 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序来说, def_domain_type()/arm_smmu_device_domain_type() 回调在开启 SMMU 绕过部分系统 I/O 设备特性时可用,且仅对于 PCIe 设备可用。此时,可以通过 Linux 内核的启动参数传入要绕过 SMMU 的 PCIe 设备的 vendor id 和 device id,def_domain_type()/arm_smmu_device_domain_type() 回调为这些设备返回 domain 类型 IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY,即绕过 SMMU。对于其它情况,采用全局的默认 domain 类型。
domain_alloc()/arm_smmu_domain_alloc() 回调根据传入的 domain 类型分配 domain 对象。Linux 的 IOMMU 子系统用 struct iommu_domain 对象表示 domain,SMMUv3 设备驱动程序继承自 struct iommu_domain 定义了自己的 domain 对象,即 struct arm_smmu_domain。domain_alloc()/arm_smmu_domain_alloc() 回调为 struct arm_smmu_domain 对象分配内存,并初始化其各个字段。当 domain 类型为 IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA 时,还会为 domain 获得 dma cookie。iommu_get_dma_cookie() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/dma-iommu.c 文件中) 如下:
static struct iommu_dma_cookie *cookie_alloc(enum iommu_dma_cookie_type type)
{
struct iommu_dma_cookie *cookie;
cookie = kzalloc(sizeof(*cookie), GFP_KERNEL);
if (cookie) {
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cookie->msi_page_list);
cookie->type = type;
}
return cookie;
}
/**
* iommu_get_dma_cookie - Acquire DMA-API resources for a domain
* @domain: IOMMU domain to prepare for DMA-API usage
*
* IOMMU drivers should normally call this from their domain_alloc
* callback when domain->type == IOMMU_DOMAIN_DMA.
*/
int iommu_get_dma_cookie(struct iommu_domain *domain)
{
if (domain->iova_cookie)
return -EEXIST;
domain->iova_cookie = cookie_alloc(IOMMU_DMA_IOVA_COOKIE);
if (!domain->iova_cookie)
return -ENOMEM;
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(iommu_get_dma_cookie);
SMMUv3 设备驱动程序的 attach_dev() 回调 arm_smmu_attach_dev() 用于连接系统 I/O 设备和 SMMUv3 设备,这个回调实现如下:
static void arm_smmu_detach_dev(struct arm_smmu_master *master)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = master->domain;
if (!smmu_domain)
return;
arm_smmu_disable_ats(master);
spin_lock_irqsave(&smmu_domain->devices_lock, flags);
list_del(&master->domain_head);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&smmu_domain->devices_lock, flags);
master->domain = NULL;
master->ats_enabled = false;
arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev(master);
}
static int arm_smmu_attach_dev(struct iommu_domain *domain, struct device *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct iommu_fwspec *fwspec = dev_iommu_fwspec_get(dev);
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu;
struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = to_smmu_domain(domain);
struct arm_smmu_master *master;
if (!fwspec)
return -ENOENT;
master = dev_iommu_priv_get(dev);
smmu = master->smmu;
/*
* Checking that SVA is disabled ensures that this device isn't bound to
* any mm, and can be safely detached from its old domain. Bonds cannot
* be removed concurrently since we're holding the group mutex.
*/
if (arm_smmu_master_sva_enabled(master)) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot attach - SVA enabled\n");
return -EBUSY;
}
arm_smmu_detach_dev(master);
mutex_lock(&smmu_domain->init_mutex);
if (!smmu_domain->smmu) {
smmu_domain->smmu = smmu;
ret = arm_smmu_domain_finalise(domain, master);
if (ret) {
smmu_domain->smmu = NULL;
goto out_unlock;
}
} else if (smmu_domain->smmu != smmu) {
dev_err(dev,
"cannot attach to SMMU %s (upstream of %s)\n",
dev_name(smmu_domain->smmu->dev),
dev_name(smmu->dev));
ret = -ENXIO;
goto out_unlock;
} else if (smmu_domain->stage == ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1 &&
master->ssid_bits != smmu_domain->s1_cfg.s1cdmax) {
dev_err(dev,
"cannot attach to incompatible domain (%u SSID bits != %u)\n",
smmu_domain->s1_cfg.s1cdmax, master->ssid_bits);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_unlock;
} else if (smmu_domain->stage == ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1 &&
smmu_domain->stall_enabled != master->stall_enabled) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot attach to stall-%s domain\n",
smmu_domain->stall_enabled ? "enabled" : "disabled");
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_unlock;
} else if (smmu_domain->parent) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot attach auxiliary domain\n");
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_unlock;
}
master->domain = smmu_domain;
if (smmu_domain->stage != ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_BYPASS)
master->ats_enabled = arm_smmu_ats_supported(master);
arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev(master);
spin_lock_irqsave(&smmu_domain->devices_lock, flags);
list_add(&master->domain_head, &smmu_domain->devices);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&smmu_domain->devices_lock, flags);
arm_smmu_enable_ats(master);
out_unlock:
mutex_unlock(&smmu_domain->init_mutex);
return ret;
}
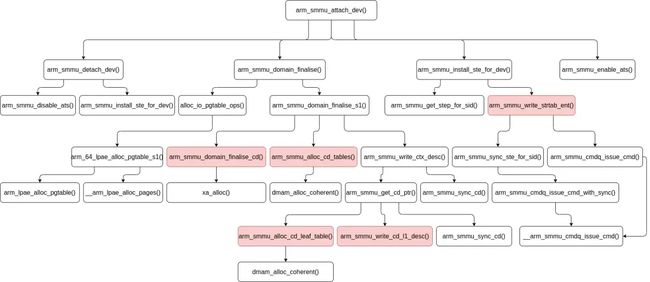
arm_smmu_attach_dev() 函数做了这样一些事情:
-
检查系统 I/O 设备的 SVA 已经被禁用,以确保它没有绑定到任何 mm,且可以从老的 domain 安全地断开连接。
-
从老的 domain 断开连接:
- 停用 ATS,仅用于 PCIe 设备;
- 将系统 I/O 设备 (在 SMMUv3 设备驱动程序中由
struct arm_smmu_master对象表示) 从 domain 的设备列表中移除; - 调用
arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev()函数为系统 I/O 设备安装流表 STE,此时系统 I/O 设备已经与 domain 断开连接,系统 I/O 设备的流表 STE 将被配置为旁路 SMMU。
-
对于非 PCIe 的一般系统 I/O 设备,每个设备都是一个独立 IOMMU group,也都有一个独立的 domain。如果 domain 没有和 SMMU 设备连接起来,则连接 domain 和 SMMU 设备,并调用
arm_smmu_domain_finalise()函数配置 SMMU domain。 -
连接系统 I/O 设备与 domain。
-
调用
arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev()函数再次为系统 I/O 设备安装流表 STE,此时系统 I/O 设备已经与 domain 连接。 -
将系统 I/O 设备添加进 domain 的设备列表中。
-
开启 ATS,仅用于 PCIe 设备。
arm_smmu_domain_finalise() 函数配置 SMMU domain,这个函数定义如下:
static int arm_smmu_domain_finalise(struct iommu_domain *domain,
struct arm_smmu_master *master)
{
int ret;
unsigned long ias, oas;
enum io_pgtable_fmt fmt;
struct io_pgtable_cfg pgtbl_cfg;
struct io_pgtable_ops *pgtbl_ops;
int (*finalise_stage_fn)(struct arm_smmu_domain *,
struct arm_smmu_master *,
struct io_pgtable_cfg *);
struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = to_smmu_domain(domain);
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;
if (domain->type == IOMMU_DOMAIN_IDENTITY) {
smmu_domain->stage = ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_BYPASS;
return 0;
}
/* Restrict the stage to what we can actually support */
if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TRANS_S1))
smmu_domain->stage = ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S2;
if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_TRANS_S2))
smmu_domain->stage = ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1;
switch (smmu_domain->stage) {
case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1:
ias = (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_VAX) ? 52 : 48;
ias = min_t(unsigned long, ias, VA_BITS);
oas = smmu->ias;
fmt = ARM_64_LPAE_S1;
if (smmu_domain->parent)
finalise_stage_fn = arm_smmu_domain_finalise_cd;
else
finalise_stage_fn = arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1;
break;
case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_NESTED:
case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S2:
ias = smmu->ias;
oas = smmu->oas;
fmt = ARM_64_LPAE_S2;
finalise_stage_fn = arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s2;
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
pgtbl_cfg = (struct io_pgtable_cfg) {
.pgsize_bitmap = smmu->pgsize_bitmap,
.ias = ias,
.oas = oas,
.coherent_walk = smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_COHERENCY,
.tlb = &arm_smmu_flush_ops,
.iommu_dev = smmu->dev,
};
if (smmu_domain->non_strict)
pgtbl_cfg.quirks |= IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_NON_STRICT;
if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HD)
pgtbl_cfg.quirks |= IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_HD;
if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BBML1)
pgtbl_cfg.quirks |= IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_BBML1;
else if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_BBML2)
pgtbl_cfg.quirks |= IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_BBML2;
pgtbl_ops = alloc_io_pgtable_ops(fmt, &pgtbl_cfg, smmu_domain);
if (!pgtbl_ops)
return -ENOMEM;
domain->pgsize_bitmap = pgtbl_cfg.pgsize_bitmap;
domain->geometry.aperture_end = (1UL << pgtbl_cfg.ias) - 1;
domain->geometry.force_aperture = true;
ret = finalise_stage_fn(smmu_domain, master, &pgtbl_cfg);
if (ret < 0) {
free_io_pgtable_ops(pgtbl_ops);
return ret;
}
smmu_domain->pgtbl_ops = pgtbl_ops;
return 0;
}
arm_smmu_domain_finalise() 函数的执行过程如下:
-
根据从 SMMUv3 设备的 SMMU_IDR* 寄存器读取的硬件特性及配置,如是否执行第 1 阶段地址转换,是否执行第 2 阶段地址转换,输入地址大小,输出地址大小等,来确定 IO 页表的格式和配置,及后面要执行的
finalise_stage_fn。对于一般的系统 I/O 设备驱动,只需要执行第 1 阶段的地址转换,IO 页表格式将是 ARM_64_LPAE_S1,后面要执行的finalise_stage_fn将是arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1()。 -
根据前面获得的 IO 页表格式和配置,调用
alloc_io_pgtable_ops()函数分配 IO 页表操作。 -
执行
finalise_stage_fn,对于一般的系统 I/O 设备驱动,即arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1()函数。 -
连接 IO 页表操作和 domain。
alloc_io_pgtable_ops() 函数定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/io-pgtable.c 文件中) 如下:
static const struct io_pgtable_init_fns *
io_pgtable_init_table[IO_PGTABLE_NUM_FMTS] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_IOMMU_IO_PGTABLE_LPAE
[ARM_32_LPAE_S1] = &io_pgtable_arm_32_lpae_s1_init_fns,
[ARM_32_LPAE_S2] = &io_pgtable_arm_32_lpae_s2_init_fns,
[ARM_64_LPAE_S1] = &io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s1_init_fns,
[ARM_64_LPAE_S2] = &io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s2_init_fns,
[ARM_MALI_LPAE] = &io_pgtable_arm_mali_lpae_init_fns,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IOMMU_IO_PGTABLE_ARMV7S
[ARM_V7S] = &io_pgtable_arm_v7s_init_fns,
#endif
};
struct io_pgtable_ops *alloc_io_pgtable_ops(enum io_pgtable_fmt fmt,
struct io_pgtable_cfg *cfg,
void *cookie)
{
struct io_pgtable *iop;
const struct io_pgtable_init_fns *fns;
if (fmt >= IO_PGTABLE_NUM_FMTS)
return NULL;
fns = io_pgtable_init_table[fmt];
if (!fns)
return NULL;
iop = fns->alloc(cfg, cookie);
if (!iop)
return NULL;
iop->fmt = fmt;
iop->cookie = cookie;
iop->cfg = *cfg;
return &iop->ops;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(alloc_io_pgtable_ops);
alloc_io_pgtable_ops() 函数根据传入的 IO 页表格式选择一组 IO 页表初始化操作,并利于 IO 页表初始化操作的分配操作分配一组 IO 页表,并将其中的 IO 页表操作返回。对于 ARM_64_LPAE_S1 格式,选中的 IO 页表初始化操作将是 io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s1_init_fns。这组 IO 页表初始化操作定义 (位于 drivers/iommu/io-pgtable-arm.c 文件中) 如下:
static void __arm_lpae_free_pgtable(struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data, int lvl,
arm_lpae_iopte *ptep)
{
arm_lpae_iopte *start, *end;
unsigned long table_size;
if (lvl == data->start_level)
table_size = ARM_LPAE_PGD_SIZE(data);
else
table_size = ARM_LPAE_GRANULE(data);
start = ptep;
/* Only leaf entries at the last level */
if (lvl == ARM_LPAE_MAX_LEVELS - 1)
end = ptep;
else
end = (void *)ptep + table_size;
while (ptep != end) {
arm_lpae_iopte pte = *ptep++;
if (!pte || iopte_leaf(pte, lvl, data->iop.fmt))
continue;
__arm_lpae_free_pgtable(data, lvl + 1, iopte_deref(pte, data));
}
__arm_lpae_free_pages(start, table_size, &data->iop.cfg);
}
static void arm_lpae_free_pgtable(struct io_pgtable *iop)
{
struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data = io_pgtable_to_data(iop);
__arm_lpae_free_pgtable(data, data->start_level, data->pgd);
kfree(data);
}
. . . . . .
static struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *
arm_lpae_alloc_pgtable(struct io_pgtable_cfg *cfg)
{
struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data;
int levels, va_bits, pg_shift;
arm_lpae_restrict_pgsizes(cfg);
if (!(cfg->pgsize_bitmap & (SZ_4K | SZ_16K | SZ_64K)))
return NULL;
if (cfg->ias > ARM_LPAE_MAX_ADDR_BITS)
return NULL;
if (cfg->oas > ARM_LPAE_MAX_ADDR_BITS)
return NULL;
data = kmalloc(sizeof(*data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data)
return NULL;
pg_shift = __ffs(cfg->pgsize_bitmap);
data->bits_per_level = pg_shift - ilog2(sizeof(arm_lpae_iopte));
va_bits = cfg->ias - pg_shift;
levels = DIV_ROUND_UP(va_bits, data->bits_per_level);
data->start_level = ARM_LPAE_MAX_LEVELS - levels;
/* Calculate the actual size of our pgd (without concatenation) */
data->pgd_bits = va_bits - (data->bits_per_level * (levels - 1));
data->iop.ops = (struct io_pgtable_ops) {
.map = arm_lpae_map,
.unmap = arm_lpae_unmap,
.iova_to_phys = arm_lpae_iova_to_phys,
.split_block = arm_lpae_split_block,
.merge_page = arm_lpae_merge_page,
.sync_dirty_log = arm_lpae_sync_dirty_log,
.clear_dirty_log = arm_lpae_clear_dirty_log,
};
return data;
}
static struct io_pgtable *
arm_64_lpae_alloc_pgtable_s1(struct io_pgtable_cfg *cfg, void *cookie)
{
u64 reg;
struct arm_lpae_io_pgtable *data;
typeof(&cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.tcr) tcr = &cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.tcr;
bool tg1;
if (cfg->quirks & ~(IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_NS |
IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_NON_STRICT |
IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_TTBR1 |
IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_HD |
IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_BBML1 |
IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_BBML2))
return NULL;
data = arm_lpae_alloc_pgtable(cfg);
if (!data)
return NULL;
/* TCR */
if (cfg->coherent_walk) {
tcr->sh = ARM_LPAE_TCR_SH_IS;
tcr->irgn = ARM_LPAE_TCR_RGN_WBWA;
tcr->orgn = ARM_LPAE_TCR_RGN_WBWA;
} else {
tcr->sh = ARM_LPAE_TCR_SH_OS;
tcr->irgn = ARM_LPAE_TCR_RGN_NC;
tcr->orgn = ARM_LPAE_TCR_RGN_NC;
}
tg1 = cfg->quirks & IO_PGTABLE_QUIRK_ARM_TTBR1;
switch (ARM_LPAE_GRANULE(data)) {
case SZ_4K:
tcr->tg = tg1 ? ARM_LPAE_TCR_TG1_4K : ARM_LPAE_TCR_TG0_4K;
break;
case SZ_16K:
tcr->tg = tg1 ? ARM_LPAE_TCR_TG1_16K : ARM_LPAE_TCR_TG0_16K;
break;
case SZ_64K:
tcr->tg = tg1 ? ARM_LPAE_TCR_TG1_64K : ARM_LPAE_TCR_TG0_64K;
break;
}
switch (cfg->oas) {
case 32:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_32_BIT;
break;
case 36:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_36_BIT;
break;
case 40:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_40_BIT;
break;
case 42:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_42_BIT;
break;
case 44:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_44_BIT;
break;
case 48:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_48_BIT;
break;
case 52:
tcr->ips = ARM_LPAE_TCR_PS_52_BIT;
break;
default:
goto out_free_data;
}
tcr->tsz = 64ULL - cfg->ias;
/* MAIRs */
reg = (ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_NC
<< ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_SHIFT(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_IDX_NC)) |
(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_WBRWA
<< ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_SHIFT(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_IDX_CACHE)) |
(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_DEVICE
<< ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_SHIFT(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_IDX_DEV)) |
(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_INC_OWBRWA
<< ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_SHIFT(ARM_LPAE_MAIR_ATTR_IDX_INC_OCACHE));
cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.mair = reg;
/* Looking good; allocate a pgd */
data->pgd = __arm_lpae_alloc_pages(ARM_LPAE_PGD_SIZE(data),
GFP_KERNEL, cfg);
if (!data->pgd)
goto out_free_data;
/* Ensure the empty pgd is visible before any actual TTBR write */
wmb();
/* TTBR */
cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.ttbr = virt_to_phys(data->pgd);
return &data->iop;
out_free_data:
kfree(data);
return NULL;
}
. . . . . .
struct io_pgtable_init_fns io_pgtable_arm_32_lpae_s1_init_fns = {
.alloc = arm_32_lpae_alloc_pgtable_s1,
.free = arm_lpae_free_pgtable,
};
io_pgtable_arm_64_lpae_s1_init_fns 的页表分配操作 arm_64_lpae_alloc_pgtable_s1(),它分两步分配 IO 页表:
-
调用
arm_lpae_alloc_pgtable()分配 IO 页表结构,初始化包括 IO 页表操作在内的各种配置。 -
分配并创建 PGD。
arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1() 函数定义如下:
static void arm_smmu_sync_cd(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain,
int ssid, bool leaf)
{
size_t i;
unsigned long flags;
struct arm_smmu_master *master;
struct arm_smmu_cmdq_batch cmds = {};
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;
struct arm_smmu_cmdq_ent cmd = {
.opcode = CMDQ_OP_CFGI_CD,
.cfgi = {
.ssid = ssid,
.leaf = leaf,
},
};
arm_smmu_preempt_disable(smmu);
spin_lock_irqsave(&smmu_domain->devices_lock, flags);
list_for_each_entry(master, &smmu_domain->devices, domain_head) {
for (i = 0; i < master->num_streams; i++) {
cmd.cfgi.sid = master->streams[i].id;
arm_smmu_cmdq_batch_add(smmu, &cmds, &cmd);
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&smmu_domain->devices_lock, flags);
arm_smmu_cmdq_batch_submit(smmu, &cmds);
arm_smmu_preempt_enable(smmu);
}
static int arm_smmu_alloc_cd_leaf_table(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu,
struct arm_smmu_l1_ctx_desc *l1_desc)
{
size_t size = CTXDESC_L2_ENTRIES * (CTXDESC_CD_DWORDS << 3);
l1_desc->l2ptr = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, size,
&l1_desc->l2ptr_dma, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!l1_desc->l2ptr) {
dev_warn(smmu->dev,
"failed to allocate context descriptor table\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
return 0;
}
static void arm_smmu_write_cd_l1_desc(__le64 *dst,
struct arm_smmu_l1_ctx_desc *l1_desc)
{
u64 val = (l1_desc->l2ptr_dma & CTXDESC_L1_DESC_L2PTR_MASK) |
CTXDESC_L1_DESC_V;
/* See comment in arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc() */
WRITE_ONCE(*dst, cpu_to_le64(val));
}
static __le64 *arm_smmu_get_cd_ptr(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain,
u32 ssid)
{
__le64 *l1ptr;
unsigned int idx;
struct arm_smmu_l1_ctx_desc *l1_desc;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;
struct arm_smmu_ctx_desc_cfg *cdcfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg.cdcfg;
if (smmu_domain->s1_cfg.s1fmt == STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT_LINEAR)
return cdcfg->cdtab + ssid * CTXDESC_CD_DWORDS;
idx = ssid >> CTXDESC_SPLIT;
l1_desc = &cdcfg->l1_desc[idx];
if (!l1_desc->l2ptr) {
if (arm_smmu_alloc_cd_leaf_table(smmu, l1_desc))
return NULL;
l1ptr = cdcfg->cdtab + idx * CTXDESC_L1_DESC_DWORDS;
arm_smmu_write_cd_l1_desc(l1ptr, l1_desc);
/* An invalid L1CD can be cached */
arm_smmu_sync_cd(smmu_domain, ssid, false);
}
idx = ssid & (CTXDESC_L2_ENTRIES - 1);
return l1_desc->l2ptr + idx * CTXDESC_CD_DWORDS;
}
int arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain, int ssid,
struct arm_smmu_ctx_desc *cd)
{
/*
* This function handles the following cases:
*
* (1) Install primary CD, for normal DMA traffic (SSID = 0).
* (2) Install a secondary CD, for SID+SSID traffic.
* (3) Update ASID of a CD. Atomically write the first 64 bits of the
* CD, then invalidate the old entry and mappings.
* (4) Quiesce the context without clearing the valid bit. Disable
* translation, and ignore any translation fault.
* (5) Remove a secondary CD.
*/
u64 val;
bool cd_live;
__le64 *cdptr;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;
if (WARN_ON(ssid >= (1 << smmu_domain->s1_cfg.s1cdmax)))
return -E2BIG;
cdptr = arm_smmu_get_cd_ptr(smmu_domain, ssid);
if (!cdptr)
return -ENOMEM;
val = le64_to_cpu(cdptr[0]);
cd_live = !!(val & CTXDESC_CD_0_V);
if (!cd) { /* (5) */
val = 0;
} else if (cd == &quiet_cd) { /* (4) */
val |= CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_EPD0;
} else if (cd_live) { /* (3) */
val &= ~CTXDESC_CD_0_ASID;
val |= FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_ASID, cd->asid);
/*
* Until CD+TLB invalidation, both ASIDs may be used for tagging
* this substream's traffic
*/
} else { /* (1) and (2) */
u64 tcr = cd->tcr;
cdptr[1] = cpu_to_le64(cd->ttbr & CTXDESC_CD_1_TTB0_MASK);
cdptr[2] = 0;
cdptr[3] = cpu_to_le64(cd->mair);
if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HD))
tcr &= ~CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_HD;
if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_HA))
tcr &= ~CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_HA;
/*
* STE is live, and the SMMU might read dwords of this CD in any
* order. Ensure that it observes valid values before reading
* V=1.
*/
arm_smmu_sync_cd(smmu_domain, ssid, true);
val = tcr |
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN
CTXDESC_CD_0_ENDI |
#endif
CTXDESC_CD_0_R | CTXDESC_CD_0_A |
(cd->mm ? 0 : CTXDESC_CD_0_ASET) |
CTXDESC_CD_0_AA64 |
FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_ASID, cd->asid) |
CTXDESC_CD_0_V;
if (smmu_domain->stall_enabled)
val |= CTXDESC_CD_0_S;
}
/*
* The SMMU accesses 64-bit values atomically. See IHI0070Ca 3.21.3
* "Configuration structures and configuration invalidation completion"
*
* The size of single-copy atomic reads made by the SMMU is
* IMPLEMENTATION DEFINED but must be at least 64 bits. Any single
* field within an aligned 64-bit span of a structure can be altered
* without first making the structure invalid.
*/
WRITE_ONCE(cdptr[0], cpu_to_le64(val));
arm_smmu_sync_cd(smmu_domain, ssid, true);
return 0;
}
static int arm_smmu_alloc_cd_tables(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain)
{
int ret;
size_t l1size;
size_t max_contexts;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;
struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;
struct arm_smmu_ctx_desc_cfg *cdcfg = &cfg->cdcfg;
max_contexts = 1 << cfg->s1cdmax;
if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_CDTAB) ||
max_contexts <= CTXDESC_L2_ENTRIES) {
cfg->s1fmt = STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT_LINEAR;
cdcfg->num_l1_ents = max_contexts;
l1size = max_contexts * (CTXDESC_CD_DWORDS << 3);
} else {
cfg->s1fmt = STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT_64K_L2;
cdcfg->num_l1_ents = DIV_ROUND_UP(max_contexts,
CTXDESC_L2_ENTRIES);
cdcfg->l1_desc = devm_kcalloc(smmu->dev, cdcfg->num_l1_ents,
sizeof(*cdcfg->l1_desc),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdcfg->l1_desc)
return -ENOMEM;
l1size = cdcfg->num_l1_ents * (CTXDESC_L1_DESC_DWORDS << 3);
}
cdcfg->cdtab = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, l1size, &cdcfg->cdtab_dma,
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdcfg->cdtab) {
dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to allocate context descriptor\n");
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_l1;
}
return 0;
err_free_l1:
if (cdcfg->l1_desc) {
devm_kfree(smmu->dev, cdcfg->l1_desc);
cdcfg->l1_desc = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
. . . . . .
static int arm_smmu_domain_finalise_cd(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain,
struct arm_smmu_master *master,
struct io_pgtable_cfg *pgtbl_cfg)
{
int ret;
u32 asid;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;
struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;
typeof(&pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.tcr) tcr = &pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.tcr;
refcount_set(&cfg->cd.refs, 1);
ret = xa_alloc(&arm_smmu_asid_xa, &asid, &cfg->cd,
XA_LIMIT(1, (1 << smmu->asid_bits) - 1), GFP_KERNEL);
if (ret)
return ret;
cfg->cd.asid = (u16)asid;
cfg->cd.ttbr = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.ttbr;
cfg->cd.tcr = FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_T0SZ, tcr->tsz) |
FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_TG0, tcr->tg) |
FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_IRGN0, tcr->irgn) |
FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_ORGN0, tcr->orgn) |
FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_SH0, tcr->sh) |
FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_IPS, tcr->ips) |
CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_HA | CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_HD |
CTXDESC_CD_0_TCR_EPD1 | CTXDESC_CD_0_AA64;
cfg->cd.mair = pgtbl_cfg->arm_lpae_s1_cfg.mair;
return 0;
}
static int arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain,
struct arm_smmu_master *master,
struct io_pgtable_cfg *pgtbl_cfg)
{
int ret;
struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;
/* Prevent SVA from modifying the ASID until it is written to the CD */
mutex_lock(&arm_smmu_asid_lock);
ret = arm_smmu_domain_finalise_cd(smmu_domain, master, pgtbl_cfg);
if (ret)
goto out_unlock;
cfg->s1cdmax = master->ssid_bits;
smmu_domain->stall_enabled = master->stall_enabled;
ret = arm_smmu_alloc_cd_tables(smmu_domain);
if (ret)
goto out_free_asid;
/*
* Note that this will end up calling arm_smmu_sync_cd() before
* the master has been added to the devices list for this domain.
* This isn't an issue because the STE hasn't been installed yet.
*/
ret = arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc(smmu_domain, 0, &cfg->cd);
if (ret)
goto out_free_cd_tables;
mutex_unlock(&arm_smmu_asid_lock);
return 0;
out_free_cd_tables:
arm_smmu_free_cd_tables(smmu_domain);
out_free_asid:
arm_smmu_free_asid(&cfg->cd);
out_unlock:
mutex_unlock(&arm_smmu_asid_lock);
return ret;
}
arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1() 函数的执行过程如下:
-
调用
arm_smmu_domain_finalise_cd()函数,为 domain 获得 ASID,并根据前面获得的 IO 页表配置等信息创建第 1 阶段转换的 CD 配置。 -
调用
arm_smmu_alloc_cd_tables()函数根据 SSID 位数计算 CD 表的项数,并分配 CD 表,分为两种情况来处理:- SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 2 级 CD 表,且 SSID 位数大于 CTXDESC_SPLIT(10),分配 L1 CD 描述符表,并分配与 L1 CD 描述符表项数相同的
struct arm_smmu_l1_ctx_desc对象数组,struct arm_smmu_l1_ctx_desc对象表示上下文描述符,但它主要由 CPU 访问,而不是 SMMUv3 硬件设备,它的内容将被以 SMMUv3 硬件设备支持的方式写入 L1 CD 描述符表的对应位置; - SMMUv3 硬件设备仅支持 1 级 CD 表,或者 SSID 位数小于 CTXDESC_SPLIT(10),直接分配 CD 表。
- SMMUv3 硬件设备支持 2 级 CD 表,且 SSID 位数大于 CTXDESC_SPLIT(10),分配 L1 CD 描述符表,并分配与 L1 CD 描述符表项数相同的
-
调用
arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc()函数将上下文描述符写入 CD 表,这里 SSID 取了 0:- 调用
arm_smmu_get_cd_ptr()函数得到 CD 指针,这可以分为两种情况:- 如果使用了 2 级 CD 表,先调用
arm_smmu_alloc_cd_leaf_table()函数分配第 2 级 CD 表,调用arm_smmu_write_cd_l1_desc()函数将 L1 CD 描述符写入 L1 CD 描述符表的对应位置,调用arm_smmu_sync_cd()函数向命令队列发送命令以同步 CD,返回第 2 级 CD 表中对应位置的 CD 项指针,两个具体位置由传入的 SSID 确定。 - 仅使用了 1 级 CD 表,返回 CD 表中对应位置的 CD 项指针,具体位置由传入的 SSID 确定。
- 如果使用了 2 级 CD 表,先调用
- 通过 CD 指针将 CD 配置写入 CD 项。
- 调用
arm_smmu_sync_cd()函数向命令队列发送命令以同步 CD。
- 调用
在 arm_smmu_attach_dev() 函数中,arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev() 函数用来最后将 CD 表配置等信息写入流表的 STE,这个函数定义如下:
static void arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent(struct arm_smmu_master *master, u32 sid,
__le64 *dst)
{
/*
* This is hideously complicated, but we only really care about
* three cases at the moment:
*
* 1. Invalid (all zero) -> bypass/fault (init)
* 2. Bypass/fault -> translation/bypass (attach)
* 3. Translation/bypass -> bypass/fault (detach)
*
* Given that we can't update the STE atomically and the SMMU
* doesn't read the thing in a defined order, that leaves us
* with the following maintenance requirements:
*
* 1. Update Config, return (init time STEs aren't live)
* 2. Write everything apart from dword 0, sync, write dword 0, sync
* 3. Update Config, sync
*/
u64 val = le64_to_cpu(dst[0]);
bool ste_live = false;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = NULL;
struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *s1_cfg = NULL;
struct arm_smmu_s2_cfg *s2_cfg = NULL;
struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain = NULL;
struct arm_smmu_cmdq_ent prefetch_cmd = {
.opcode = CMDQ_OP_PREFETCH_CFG,
.prefetch = {
.sid = sid,
},
};
if (master) {
smmu_domain = master->domain;
smmu = master->smmu;
}
if (smmu_domain) {
switch (smmu_domain->stage) {
case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S1:
s1_cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;
break;
case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_S2:
case ARM_SMMU_DOMAIN_NESTED:
s2_cfg = &smmu_domain->s2_cfg;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (val & STRTAB_STE_0_V) {
switch (FIELD_GET(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, val)) {
case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_BYPASS:
break;
case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S1_TRANS:
case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S2_TRANS:
ste_live = true;
break;
case STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_ABORT:
BUG_ON(!disable_bypass);
break;
default:
BUG(); /* STE corruption */
}
}
/* Nuke the existing STE_0 value, as we're going to rewrite it */
val = STRTAB_STE_0_V;
/* Bypass/fault */
if (!smmu_domain || !(s1_cfg || s2_cfg)) {
if (!smmu_domain && disable_bypass)
val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_ABORT);
else
val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_BYPASS);
dst[0] = cpu_to_le64(val);
dst[1] = cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_SHCFG,
STRTAB_STE_1_SHCFG_INCOMING));
dst[2] = 0; /* Nuke the VMID */
/*
* The SMMU can perform negative caching, so we must sync
* the STE regardless of whether the old value was live.
*/
if (smmu)
arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(smmu, sid);
return;
}
if (s1_cfg) {
u64 strw = smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_E2H ?
STRTAB_STE_1_STRW_EL2 : STRTAB_STE_1_STRW_NSEL1;
BUG_ON(ste_live);
dst[1] = cpu_to_le64(
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1DSS, STRTAB_STE_1_S1DSS_SSID0) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1CIR, STRTAB_STE_1_S1C_CACHE_WBRA) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1COR, STRTAB_STE_1_S1C_CACHE_WBRA) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_S1CSH, ARM_SMMU_SH_ISH) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_STRW, strw));
if (master->prg_resp_needs_ssid)
dst[1] |= cpu_to_le64(STRTAB_STE_1_PPAR);
if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_STALLS &&
!master->stall_enabled)
dst[1] |= cpu_to_le64(STRTAB_STE_1_S1STALLD);
val |= (s1_cfg->cdcfg.cdtab_dma & STRTAB_STE_0_S1CTXPTR_MASK) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S1_TRANS) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_S1CDMAX, s1_cfg->s1cdmax) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT, s1_cfg->s1fmt);
}
if (s2_cfg) {
BUG_ON(ste_live);
dst[2] = cpu_to_le64(
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_2_S2VMID, s2_cfg->vmid) |
FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_2_VTCR, s2_cfg->vtcr) |
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN
STRTAB_STE_2_S2ENDI |
#endif
STRTAB_STE_2_S2PTW | STRTAB_STE_2_S2AA64 |
STRTAB_STE_2_S2R);
dst[3] = cpu_to_le64(s2_cfg->vttbr & STRTAB_STE_3_S2TTB_MASK);
val |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_0_CFG, STRTAB_STE_0_CFG_S2_TRANS);
}
if (master->ats_enabled)
dst[1] |= cpu_to_le64(FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_STE_1_EATS,
STRTAB_STE_1_EATS_TRANS));
arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(smmu, sid);
/* See comment in arm_smmu_write_ctx_desc() */
WRITE_ONCE(dst[0], cpu_to_le64(val));
arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid(smmu, sid);
/* It's likely that we'll want to use the new STE soon */
if (!(smmu->options & ARM_SMMU_OPT_SKIP_PREFETCH))
arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd(smmu, &prefetch_cmd);
}
. . . . . .
static __le64 *arm_smmu_get_step_for_sid(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu, u32 sid)
{
__le64 *step;
struct arm_smmu_strtab_cfg *cfg = &smmu->strtab_cfg;
if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB) {
struct arm_smmu_strtab_l1_desc *l1_desc;
int idx;
/* Two-level walk */
idx = (sid >> STRTAB_SPLIT) * STRTAB_L1_DESC_DWORDS;
l1_desc = &cfg->l1_desc[idx];
idx = (sid & ((1 << STRTAB_SPLIT) - 1)) * STRTAB_STE_DWORDS;
step = &l1_desc->l2ptr[idx];
} else {
/* Simple linear lookup */
step = &cfg->strtab[sid * STRTAB_STE_DWORDS];
}
return step;
}
static void arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev(struct arm_smmu_master *master)
{
int i, j;
struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = master->smmu;
for (i = 0; i < master->num_streams; ++i) {
u32 sid = master->streams[i].id;
__le64 *step = arm_smmu_get_step_for_sid(smmu, sid);
/* Bridged PCI devices may end up with duplicated IDs */
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (master->streams[j].id == sid)
break;
if (j < i)
continue;
arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent(master, sid, step);
}
}
arm_smmu_install_ste_for_dev() 函数为系统 I/O 设备的每个流执行如下操作:
-
根据 StreamID 获得对应的 STE 指针,分为两种情况来处理:
- 使用了 2 级流表,返回第 2 级流表中对应的 STE 的指针;
- 使用了 1 级流表,返回流表中对应的 STE 的指针。
-
调用
arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent()函数写入流表 STE,这分为三种情况来处理:- 旁路 SMMU;
- 使用第 1 阶段地址转换;
- 使用第 2 阶段地址转换;
arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent()函数在写入流表 STE 后,会调用arm_smmu_sync_ste_for_sid()函数向命令队列发送命令,为流同步 STE。
arm_smmu_attach_dev() 函数的执行过程总结如下图: