栈(stack)入门详解之C语言版
一、栈
1)基本概念
栈(Stack):是一种受限的线性表,即限制在表的一端进行插入和删除操作。栈也称为后进先出LIFO (Last In First Out)或先进后出FILO (First In Last Out)线性表。
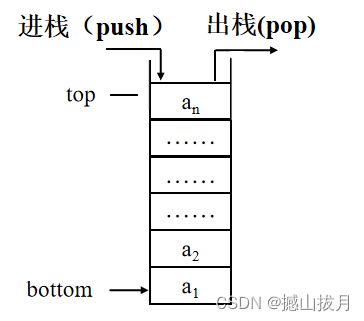
栈顶(top):允许进行插入、删除操作的一端称为栈的栈顶(top),也称为表尾。
栈底(bottom):固定不动的一端,称为栈底(bottom),也称为表头。
2)栈的示意图如下:
3)进栈和出栈的示意图:
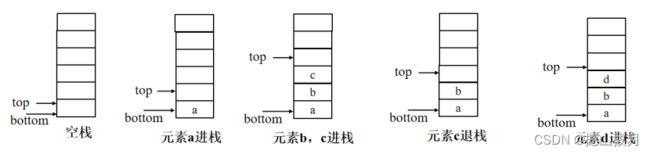
当元素进栈时,栈顶指针指向第一个为空的元素地址。
当元素出栈时,栈顶指针向下移动一个存储单元。
4)进栈和出栈序列
如果序列{1,2,3}依次进栈,则出栈的全部可能序列为:
{3,2,1}、
{2,3,1}、{2,1,3}
{1,2,3}、{1,3,2}
当进栈序列为1,2,…,n时,出栈序列的个数为尤.卡塔南数:
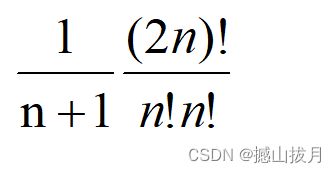
二、动态栈的基本操作
1、栈的类型定义:
typedef int ElemType ;
typedef struct stack
{
ElemType *bottom; //栈底指针
ElemType *top; //栈顶指针
int stacksize ; //当前栈的容量
}Stack ;
2、栈的初始化
假设初始时给栈分配存储空间大小为STACK_SIZE,栈的容量也赋值为STACK_SIZE。
栈初始化算法的主要过程:
1)为栈分配存储空间(也就是给栈底指针分配空间,这是因为栈底是固定不动的);
2)让栈顶指针指向栈底(表示栈是空的)。
Status Init_Stack( Stack &S )
{
S.bottom=(ElemType *)malloc(STACK_SIZE *sizeof(ElemType));
if ( !S.bottom ) //判断分配空间是否成功,如果失败则返回错误
return ERROR;
S.top = S.bottom ; //初始化时让栈顶指针指向栈底
S. stacksize = STACK_SIZE; //初始化时
return OK ;
}//Init_Stack
3、进栈(也称压栈、入栈)
元素进栈算法的主要过程:
1)首先判断栈的容量是否已经达到最大,如果达到,则追加存储空间,并重新定位栈顶指针的位置(其实就是指向实际的栈顶),然后更新栈的容量;
2)把入栈元素存入栈顶;
3)栈顶指针指向新栈顶。
Status Push(Stack &S , ElemType e)
{
//如果栈满,则使用realloc追加存储空间
if( S.top-S.bottom >= S. stacksize-1 )
{
S.bottom=(ElemType *)realloc( S.bottom, (S.stacksize+STACK_SIZE) * sizeof(ElemType));
if( !S.bottom )//如果重新分配存储空间失败,则返回错误
return ERROR;
S.top = S.bottom + S.stacksize;//重新定位栈顶
S.stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;//更新栈的容量
}
*S.top = e;//把元素存入栈顶
S.top++; //栈顶指针加1(即向上移动一个存储单元),e成为新的栈顶
return OK;
}//Push
4、出栈(也称弹栈)
元素出栈算法的主要过程:
1)判断栈是否是控制,如果是则返回出栈失败;
2)栈顶指针下移一个存储单元;
3)把栈顶指针指向位置的元素存入到目标变量中。
Status Pop( Stack &S, ElemType &e )
{
if( S.top == S.bottom ) //栈空,返回失败
return ERROR ;
S.top--;//栈顶下移
e = *S.top;//用e缓存栈顶元素
return OK;
}// Pop
5、取栈顶元素
取栈顶元素的主要步骤:
1)判断栈是否为空,为空则返回失败
2)取栈顶元素并存储到相应的变量中,需要注意的是栈顶元素实际存储在栈顶指针的下一个存储空间中。
Status GetTopElement( Stack S, ElemType &e )
{
if ( S.top == S.bottom ) //如果栈为空,则返回失败
return ERROR ;
e = *(S. top – 1) ; //用e缓存栈顶元素
return OK ;
}//GetTopElement
6、把栈置为空栈
把栈置为空栈的主要步骤:
1)把栈顶指针指向栈底即可。
Status ClearStack( Stack &S )
{
S.top = S.bottom;
return OK ;
}// ClearStack
7、销毁栈
销毁栈的主要步骤:
1)释放栈底指针(因为栈的存储空间是通过给栈底指针分配空间得到的)
2)把栈底指针和栈顶指针均赋值为NULL
3)把栈的容量赋值为0
Status DestroyStack( Stack &S )
{
free( S.bottom );
S.top = NULL;
S.bottom = NULL;
S. stacksize = 0;
return OK ;
}// DestroyStack
三、利用动态栈实现进制转换
问题描述:将十进制整数n分别转换为16进制数、8进制数、2进制数。
算法主要步骤( base表示进制):
1、初始化栈
2、当n大于0时:
1)求n对base求余数
2)将余数压入栈
3)更新n为n/base
3、当栈非空时:
1)栈顶元素出栈
2)输出栈顶元素
对应的代码:
void BaseConversion( unsigned n, unsigned base )
{
Stack S;
int k, e;
InitStack( S );
while( n > 0 )
{
k = n % base;
Push( S, k );
n = n / base;
}
while( S.top != S.bottom )
{
Pop( S, e );
char format[3]={ '%' };
if( base == 16 )
{
format[1] = 'x';
}
else
{
format[1] = 'u';
}
printf( format, e );
}
free( S.bottom );
}
完整的测试代码:
//利用栈实现进制转换
#include"stdio.h"
#include"malloc.h"
#include"String.h"
#define OK 0
#define ERROR 1
#define STACKSIZE 100
#define STACKINCREMENT 10
typedef int Status;
typedef int Etype;
typedef struct stack
{
Etype *bottom; //栈底指针
Etype *top; //栈顶指针
int stacksize; //当前栈的容量
}Stack;
Status InitStack( Stack &S );
Status Push( Stack &S , Etype e );
Status Pop( Stack &S, Etype &e );
void BaseConversion( unsigned n, unsigned base );
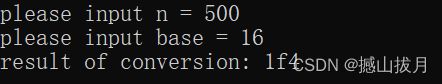
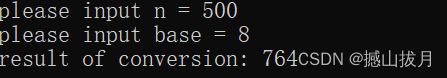
int main()
{
unsigned n, base;
printf( "please input n = " );
scanf( "%ud", &n );
printf( "please input base = " );
scanf( "%ud", &base );
printf( "result of conversion: " );
BaseConversion( n, base );
}
//栈的初始化
Status InitStack( Stack &S )
{
S.bottom=(Etype *)malloc(STACKSIZE *sizeof(Etype));
if ( !S.bottom ) //判断分配空间是否成功,如果失败则返回错误
{
return ERROR;
}
S.top = S.bottom ; //初始化时让栈顶指针指向栈底
S.stacksize = STACKSIZE; //初始化时
return OK ;
}//InitStack
//压栈(进栈、入栈)
Status Push( Stack &S , Etype e )
{
//如果栈满,则使用realloc追加存储空间
if( S.top - S.bottom >= S.stacksize-1 )
{
S.bottom=(Etype *)realloc( S.bottom, (S.stacksize+STACKSIZE) * sizeof(Etype) );
if( !S.bottom )//如果重新分配存储空间失败,则返回错误
{
return ERROR;
}
S.top = S.bottom + S.stacksize;//重新定位栈顶
S.stacksize += STACKINCREMENT;//更新栈的容量
}
*S.top = e;//把元素存入栈顶
S.top++; //栈顶指针加1(即向上移动一个存储单元),e成为新的栈顶
return OK;
}//Push
Status Pop( Stack &S, Etype &e )
{
if( S.top == S.bottom ) //栈空,返回失败
{
return ERROR;
}
S.top--; //栈顶下移
e = *S.top;//用e缓存栈顶元素
return OK;
}// Pop
void BaseConversion( unsigned n, unsigned base )
{
Stack S;
int k, e;
InitStack( S );
while( n > 0 )
{
k = n % base;
Push( S, k );
n = n / base;
}
while( S.top != S.bottom )
{
Pop( S, e );
char format[3]={ '%' };
if( base == 16 )
{
format[1] = 'x';
}
else
{
format[1] = 'u';
}
printf( format, e );
}
free( S.bottom );
}
运行结果: