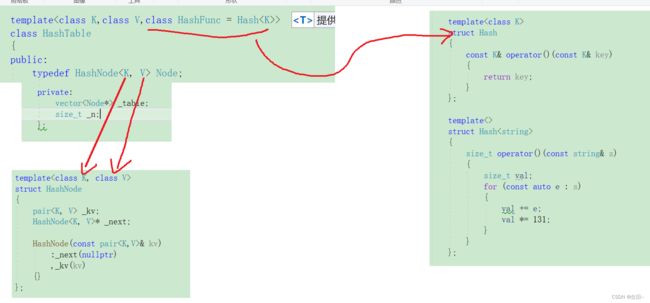
哈希的模拟实现和封装unorder_map和unorder_set
1, 哈希的概念
哈希也叫散列。它的本质就是映射。我们说的哈希表就是一个数组。
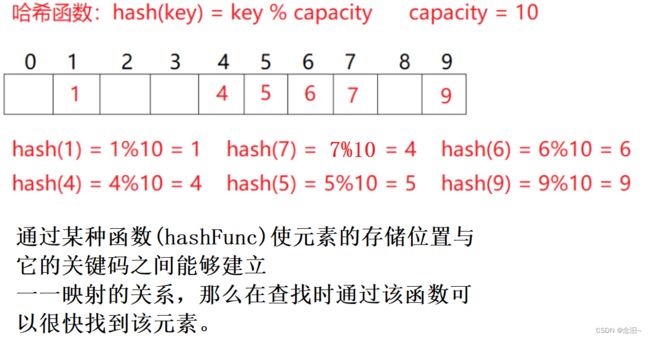
常见的哈希函数
1,直接定址法(重要)
优点:每个值都有一个唯一位置,效率很高,每个数都是一次都能找到。
缺点:适用场景比较局限,通常要求数据是整数,范围集中。
2,除留余数法(重要)
开辟固定的一块空间, 用key % size() 算出映射位置。
优点:适用常见广,不受限制。
缺点:存在哈希冲突,并且哈希冲突越多,效率越低。(什么是哈希冲突,就是不同的元素根据相同的哈希哈数算出相同的位置)
如何解决哈希冲突呢?
3, 平方取中法(了解)
4,折叠法(了解)
5,随机数法(了解)
6,数学分析法(了解)
如何解决哈希冲突呢?
1,闭散列------开放定址法(线性探测 ,二次探测)
线性探测: 算出的位置如果有值,继续向后找空位置, + i (i = 1, 2, 3, 4,)
二次探测:算出的位置如果有元素,也是继续向后找空位置 + i ^ 2 (i = 1, 2 ,3 ,4 ,5).
随着冲突的越多,我们需要扩容。什么时候需要扩容呢? 当负载因子大于0.7的时候。
负载因子 = 当前存储的元素个数 / 空间大小(size())。
2,开散列-----哈希桶/拉链法。数组中存放节点的指针,如果位置相同,则挂在后面

如何去控制负载因子呢?
1,负载因子越小,冲突的概率越低,效率越高,但是浪费的空间越多。
反之, 高, 低, 少。
实际中,哈希桶这种结构更加实用。
原因在于: 1,空间利用率高
2,极端情况下可以应对(数据不多,但是全部冲突)。
闭散列解决方案的具体实现
插入函数:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
HashFunc hf;
if (Find(kv.first)) //为什么这里不用hf(kv。first)呢? 因为查找的时候不需要转换成int类型
{
return false;
}
if (_table.size() == 0)
{
_table.resize(10);
}
else if ((_n * 10) / _table.size() > 7) //负载因子大于0.7就扩容处理
{
//需要扩容处理
HashTable newHash;
newHash._table.resize(_table.size() * 2);
for (const auto& e : _table)
{
newHash.Insert(e._kv);
}
_table.swap(newHash._table);
}
size_t start = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
size_t i = 1,index = start;
while (_table[index]._state == EXITS)
{
index += i; //如果是二次探测,只需要改为 index += i^2;
index %= _table.size();
i++;
}
_table[index]._kv = kv;
_table[index]._state = EXITS;
_n++;
return true;
}
查找
HashDate<K,V>* Find(const K& key)
{
HashFunc hf;
if (_table.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
size_t start = hf(key) % _table.size();
size_t index = start, i = 1;
while (_table[index]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_table[index]._state == EXITS
&& _table[index]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_table[index];
}
index += i;
i++;
index %= _table.size();
}
return nullptr;
}
删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashFunc hf;
HashDate<K, V>* ret = Find(hf(key));
if (ret == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
ret->_state = DELETE;
_n--;
return true;
}
2,开散列
插入函数
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
HashFunc hf;
if (_table.size() == 0)
{
_table.resize(10);
}
else if (_n / _table.size() >= 1)
{
//扩容处理
HashTable<K, V, HashFunc> newht;
newht._table.resize(_table.size() * 2);
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
if (_table[i])
{
while (cur)
{
//只要是获取位置的时候都要用hf去获取对应的整形,因为int可以直接使用,但是string就要进行转换
size_t index = hf(cur->_kv.first) % newht._table.size();
cur->_next = newht._table[index]; //头插
newht._table[index] = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
newht._n++;
}
}
}
_table.swap(newht._table);
}
size_t index = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = newnode;
_n++;
return true;
}
查找函数
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
HashFunc hf;
if (_table.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
size_t i = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
删除函数
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashFunc hf;
size_t i = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[i];
Node* pre = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (pre == nullptr)
{
_table[i] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
pre->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
用哈希桶来封装unordered_set和unordered_map
这个和用红黑树封装map和set类似。
哈希桶封装unordered_set 和unordered_map的时候,如何只用一份代码去封装呢?
改装后的hashtable---->主要就是利用仿函数来获得map和set各自的key,并且模拟实现的迭代器。
namespace openHash
{
//templateunordered_set
#include "Hash.h"
namespace chen
{
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{ struct SetOfKey
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename openHash::HashTable<K, K, SetOfKey>::iterator iterator;
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
private:
openHash::HashTable<K, K, SetOfKey> _ht;
};
}
unorder_map
#include "Hash.h"
namespace chen
{
template <class K, class V>
class unordered_map
{
public:
struct MapOfKey
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& data)
{
return data.first;
}
};
typedef typename openHash::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapOfKey>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
private:
openHash::HashTable<K, pair<K, V>, MapOfKey> _ht;
};
}