leetCode每日一题(每日更新)
时间:2022-09-18 17:14
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null) return list2;
if(list2==null) return list1;
if(list1.val<list2.val){
list1.next=mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}else{
list2.next=mergeTwoLists(list2.next,list1);
return list2;
}
}
}
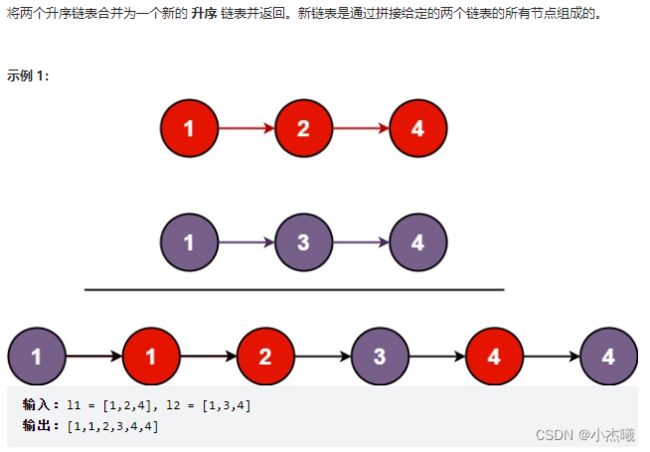
解题思路:两个链表需要按序排列合并,采用递归的方式将链表合并。首先对两个链表值判断,哪个值较小,则应该排在比较值前面,意味着要继续找最大的值。将最大值排在最后直到找到返回给前一个。递归结束后链表合并完成。
时间:2022-09-17 20:05
class Solution {
public int maxLengthBetweenEqualCharacters(String s) {
int res=-1;
int n=s.length();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int j=i+1;
for(;j<n;j++){
if(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j)){
res=Math.max(res,j-i-1);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
解题思路:采用双指针方式,依次遍历对比,记录下标差-1为中间字符数量。每次与前一个最大中间字符数量对比,赋值给res。
时间:2022-09-16 19:50
class Solution {
public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
int n = s1.length(), m = s2.length();
if (n > m) {
return false;
}
int[] cnt1 = new int[26];
int[] cnt2 = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
++cnt1[s1.charAt(i) - 'a'];
++cnt2[s2.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
if (Arrays.equals(cnt1, cnt2)) {
return true;
}
for (int i = n; i < m; ++i) {
++cnt2[s2.charAt(i) - 'a'];
--cnt2[s2.charAt(i - n) - 'a'];
if (Arrays.equals(cnt1, cnt2)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
解题思路:
首先需要判断s1与s2是否一致,采用字符ascII码表示下标,并给数组+1;这样s1的字符数组就出来了,首先判断下与s2是否一致,一致则返回true,不一致则继续判断。现在需要判断的是s2中第三个字符(s2 是否包含 s1 的排列意味着s1的字符在s2也是相邻的。那么我们知道s2字串长度是s1的长度。)之前我们的count2已经有n个字符了,如果指针继续向第三个字符滑动一位,那么最前面的一个数字就必须退出这个s1长度区间,要不然会超出s1的长度,这就有了–(++,–表示的是数组中元素内容+1、-1,new元素的时候数组默认全为0。)然后进行对比,直到对比成功。
时间:2022-09-15 19:23
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int single = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
single ^= num;
}
return single;
}
}
解题思路:采用线性空间,也就是空间复杂度为O(1)。所以不能采用hash表,解法一:暴力遍历,解法二,快速排序,解法三,异或运算。
异或运算:0与任何数字异或是数字本身,任何数字与数字本身异或是0。
时间:2022-09-14 09:51
class Solution {
public double trimMean(int[] arr) {
int n=arr.length;
int num=n*5/100;
Arrays.sort(arr);
//删除元素
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
arr[i]=0;
arr[n-i-1]=0;
}
int sum=0;
for(int a:arr){
sum+=a;
}
return (double) sum/(n-2*num);
}
}
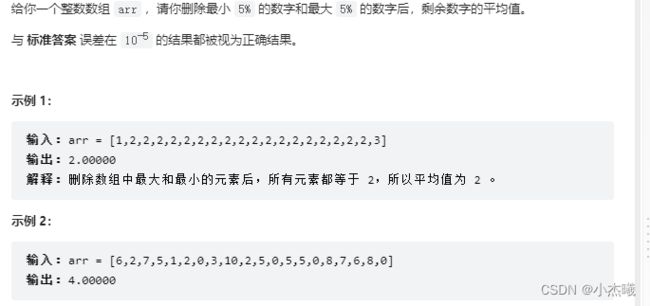
解题思路:删除最小5%,最大5%,首先对数组进行排序,java数组中无法进行长度修改,则将数组下标对应数字改为0。获取前5%数字个数采用先×5再÷100方式得到一个int类型数字。再通过下标赋值方式将数字置为0。最后获得平均数。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
//首先判断链表有多少个结点。
int count=getLength(head);
//判断删除的结点前一个位置
int delete=count-n+1;
//定义一个伪结点
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0,head);
//定义一个要被删除的当前结点
ListNode cur=dummy;
//找到要被删除结点的位置前一个(因为dummy前加了一个0,表示0是头节点,那么新结点长度+1,删除节点位置前一个则变成了L-n+1位置)
for(int i=1;i<delete;++i){
//cur.next是要被删除结点。
cur= cur.next;
}
//现在cur是被删除结点,需要将被删除结点指向的下一个结点的下一个结点与下一个结点交换位置。
cur.next=cur.next.next;
//最后返回伪结点指向的头结点的下一个结点。
return dummy.next;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head){
int count=0;
while(head!=null){
count++;
head=head.next;
}
return count;
}
}
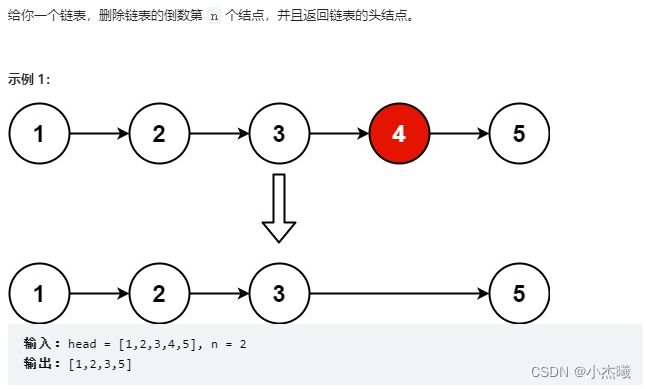
解题思路:删除结点中倒数结点,可以采用多种方法,本解题过程采用了链表计算长度,反向推出删除结点位置,然后对删除结点位置进行指向修改,首先需要找到被删除结点位于链表中位置,然后使用伪结点将原链表加头节点,找到需要被删除结点的前一个结点,然后将被删除结点赋值给当前结点,找到被删除结点指向下一个结点的指针,赋值给被删除前一个结点的指针。返回伪结点的下一个指针指向的链表。
时间:2022-09-13 10:33
class Solution {
public int maximumSwap(int num) {
char[] charArray = String.valueOf(num).toCharArray();
int maxNum=num;
int n=charArray.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
swap(charArray,i,j);
maxNum=Math.max(maxNum,Integer.parseInt(new String(charArray)));
swap(charArray,i,j);
}
}
return maxNum;
}
public void swap(char[] charArray,int i,int j){
char temp=charArray[i];
charArray[i]=charArray[j];
charArray[j]=temp;
}
}
解题思路:数字交换位置需要将数字转换为字符数组,利用下标进行位置交换。采用双指针方式将数字进行交换,每次交换后与当前最大数对比,再赋值给当前最大数,然后将数字交换回来。交换到最后则可以取得当前数字交换一次后最大值。
时间:2022-09-12 08:48
class Solution {
public int specialArray(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int res=-1;
for(int i=Math.min(n,nums[n-1]);i>=0;i--){
int count=0;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(nums[j]>=i){count++;}
}
if(count==i) {res=count;break;}
}
return res;
}
}
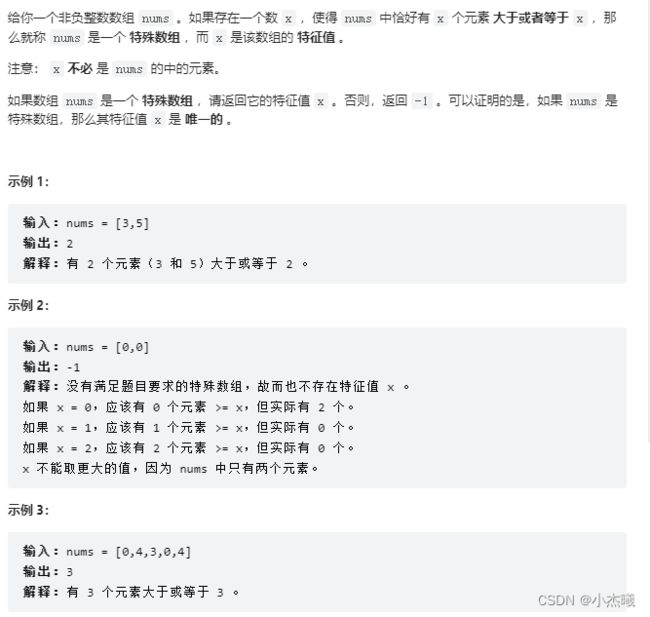
解题思路:本题求特殊值x,x值可能不在数组中,x的值要和数组中大于x值的数字个数相等。例如【3,5】结果是"2"。这个数组中最大数为5,长度为2。可知x的值必须取小于等于2的值。进一步缩短查询范围。计数器和x值相等则退出循环,并将结果赋值给res。
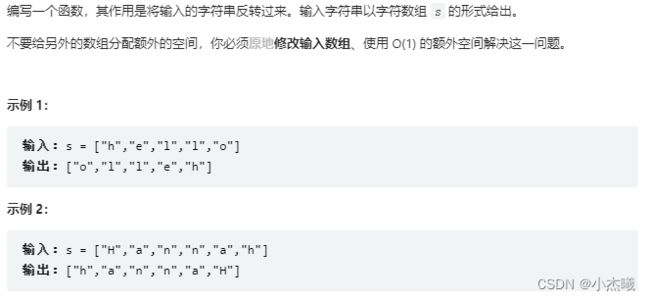
class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int n=s.length;
for(int i=0;i<n/2;i++){
char temp=s[i];
s[i]=s[n-1-i];
s[n-1-i]=temp;
}
}
}
解题思路:
双指针,首尾交换。
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuffer res=new StringBuffer();
String[] ss=s.split(" ");
for(String s1:ss){
for(int i=s1.length()-1;i>=0;i--){
res.append(s1.charAt(i));
}
if(s1!=ss[ss.length-1])res.append(" ");
}
return res.toString();
}
}
解题思路:
首先取巧采用了split函数,如果要降低时间复杂度需要采用charAt判断空,采用双指针将单词划出,再反转单词,append到结果中。这里简化了单词拆分,然后将单词进行反转,String反转有三种方法,方法一:charAt进行反转,方法二:使用StringBuffer的reverse()方法。方法三:将String字符串转化为Char字符数组,进行反转。
时间:2022-09-11 10:47
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int n=numbers.length;
int left=0,right=n-1;
while(left<right){
int sum=numbers[left]+numbers[right];
if(sum==target){
return new int[]{left+1,right+1};
}else if(sum<target){
left++;
}else{
right--;
}
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
}
解题思路:本题采用双指针策略,将左指针指向首,右指针指向末尾,判断两个数字和与目标大小关系,如果数字小了,则代表第一位数字不够大(这是一个非递减排序,最后一个数字一定是最大的),需要左指针后移,相反,如果数字太大了则是最后一位数字过大,需要右指针前移。不需要担心错过数字组合,这样做的好处是可以缩减搜索的空间,避免时间复杂度为O(n2)。
时间:2022-09-010 20:49
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans[(i + k) % n] = nums[i];
}
System.arraycopy(ans, 0, nums, 0, n);
}
解题思路:观察给出范例,新数组下标对应数值为当前下标+轮转次数,求他们的取模值,如1,2,3,4,5,6,7中1位置应该在下标3处,利用当前下标+轮转=0+3,取模后为3。则新下标为3。赋值给新数组,其他数字按规则进行。最后将新数组复制到旧数组。
时间:2022-09-09 10:59
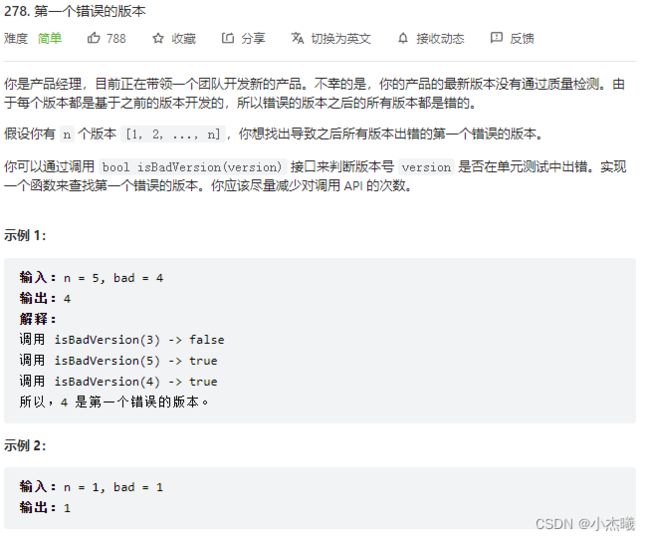
/* The isBadVersion API is defined in the parent class VersionControl.
boolean isBadVersion(int version); */
public class Solution extends VersionControl {
public int firstBadVersion(int n) {
int left=1,right=n;
while(left<right){
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;
if(isBadVersion(mid)){
right=mid;
}else{
left=mid+1;
}
}
return left;
}
}
解题思路:采用二分查找,当left与right相等时就是第一个版本了
时间:2022-09-08 10:40
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head ==null) return null;
ListNode curr=head;
while(curr.next!=null){
if(curr.val==curr.next.val){
curr.next=curr.next.next;
}else{
curr=curr.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
解题思路:首先判断head是否为空,其次取curr作为当前节点,从head开始,当curr的下一个next不存在时,循环结束。判断当curr的值与curr的next的值相等时,将curr.next.next赋值给curr.next,表示将当前节点的指针指向下一个节点的下一个节点。如果不相等,则正常指向下一个节点,并将当前节点转换为下一个节点。循环结束后,将原head返回,就是有序列表。
时间:2022-09-07 10:50
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = reorderSpaces(" practice makes perfect");
System.out.println(s);
}
public static String reorderSpaces(String text) {
int n = text.length();
//空格数量
int blank=0;
//单词集合
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n;) {
if(text.charAt(i)==' ' && ++i >=0 && blank++ >=0) continue;
int j=i;
while (j<n && text.charAt(j) != ' ') j++;
list.add(text.substring(i,j));
i=j;
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int wordNum=list.size(),gap=blank/Math.max(wordNum-1,1);
String k="";
while (gap-->0) k+=" ";
for (int i = 0; i < wordNum; i++) {
sb.append(list.get(i));
if(i!=wordNum-1){
sb.append(k);
}
}
while (sb.length()!=n) sb.append(" ");
return sb.toString();
}
解题思路:采用双指针,在遍历当前字符串的同时,将空格以及单词个数进行统计,单词统计采用双指针进行分割保存,并记录个数。根据单词个数以及空格数进行判断间隔大小,中间空格符字符串k。重新开始排列,单词在前,空格在后,最后一个字符不加空格。末尾判断新排列字符串是否与原字符串一致大小。不一致则末尾新增空格。
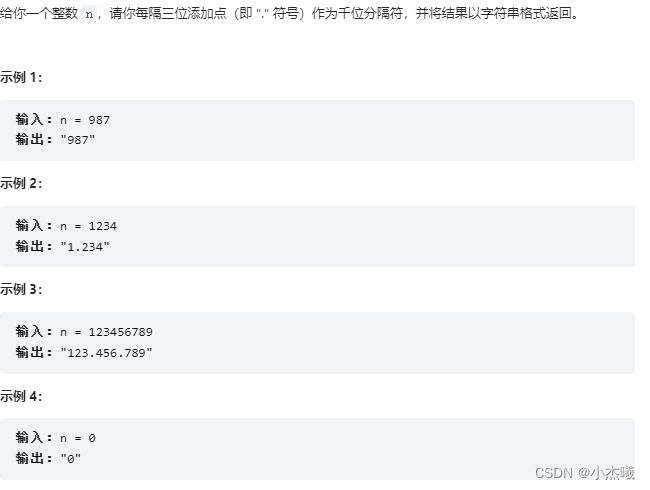
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = thousandSeparator(1);
System.out.println(s);
}
public static String thousandSeparator(int n) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String ns = String.valueOf(n);
int length = ns.length();
for (int i = length,j=0; i >0; i--,j++) {
if(j==3){
sb.append(".");
j=0;
}
sb.append(ns.charAt(i-1));
}
sb.reverse();
return sb.toString();
}
解题思路:首先将n转换为字符串,采用末尾字符划分,每三个数字加一个分隔符。最后将字符串反转。
时间:2022-09-06 14:31
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = climbStairs(5);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int climbStairs(int n) {
int pre=0,curr=0,res=1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
pre =curr;
curr=res;
res=pre+curr;
}
return res;
}
解题思路:本题从字面意思看是一道最多路线选择的题目。考虑采用动态规划的方式进行,假设有f(x)的路线方案,每次只能1阶或者2阶,那么路线方案必定最后一个是f(x-1)或f(x-2),那么可以得到式子:f(x)=f(x-1)+f(x-2)。x-1阶的方案加上x-2阶的方案就是x的方案数量。考虑边界值,f(1)=f(0)-f(-1),f(2)=f(1)-f(0)。f(1)=1。所以f(1)=1,f(2)=2不参与计算,单独作为初始值。f(3)=f(2)+f(1)=1+2=3。多次验证发现计算结果无误,采用滚筒加法,使用pre标记前两个阶级方案书,curr为前一个方案数,res作为当前方案数。
时间:2022-09-05 10:22
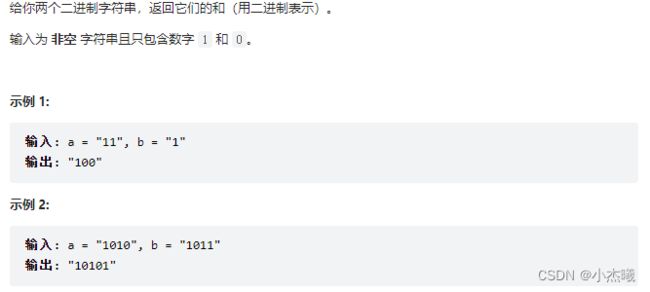
class Solution {
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
int n = Math.max(a.length(), b.length()), carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
carry += i < a.length() ? (a.charAt(a.length() - 1 - i) - '0') : 0;
carry += i < b.length() ? (b.charAt(b.length() - 1 - i) - '0') : 0;
ans.append((char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
carry /= 2;
}
if (carry > 0) {
ans.append('1');
}
ans.reverse();
return ans.toString();
}
}
解题思路:首先获取两个字符串大小对比,使用最大的作为循环次数。二进制是逢二进一,从最后一个个字符计算并加进carry。再将carry追加进ans中,最好判断carry/2是否>0,是则在ans里面追加1。最后将ans反转,就能得到二进制和。
时间:2022-09-04 10:22
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] nums = new int[][]{
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0}
};
int i = numSpecial(nums);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int numSpecial(int[][] mat) {
int res = 0;
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
int[] rowSum = new int[m];
int[] colSum = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
rowSum[j] += mat[i][j];
colSum[i] += mat[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1 && rowSum[j] == 1 && colSum[i] == 1) {
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
解题思路:矩阵的特殊位置必须采用一维数组嵌套一维数组进行建立,因为只有数字0和1,采用每行,每列单独相加的方式判断当前行,当前列是否只有一个1。并用两个一维数组记录。再对矩阵中每个位置进行判断,判断当前位置数字是否为1,且当前行值大小是否也为1,当前列大小是否也为1。
时间:2022-09-03 10:41
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();
inorders(root,res);
return res;
}
public void inorders(TreeNode root,List<Integer> res){
if(root==null){
return;
}
inorders(root.left,res);
res.add(root.val);
inorders(root.right,res);
}
}
中序遍历:左中右
方法一:采用递归方式,递归方法中优先遍历左节点。再遍历右节点。
方法二:采用迭代方式:暂时不会
方法三:采用mirrors遍历方式:暂时不会
时间:2022-09–02 11:15
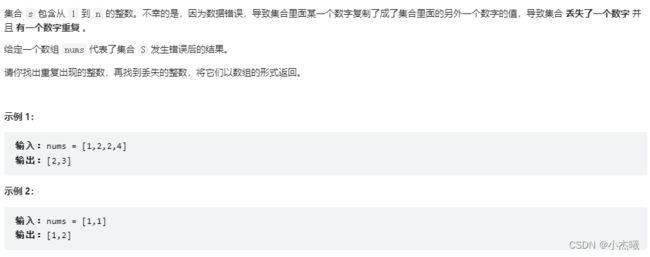
645. 错误的集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {1,2,3,3,4};
int[] prices = findErrorNums(ints);
for (int price : prices) {
System.out.println(price);
}
}
public static int[] findErrorNums(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int[] res = new int[2];
int pre=0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int cur=nums[i];
if(cur==pre){
res[0]=pre;
}else if(cur-pre>1){
res[1]=pre+1;
}
pre=cur;
}
if(nums[nums.length-1] != nums.length){
res[1]= nums.length;
}
return res;
}
代码思路:题目要求是1-n个整数,首先对这个数组进行排序,因为从1开始,所以设置pre从0开始,表示当前数的前一位数。for循环中的if语句判断当前值与前一个值是否相等,相等则重复,不相等则走else-if,判断当前数字与前一个数字大小关系,如果大于1则表明中间还存在一个数字,则pre+1。然后将当前值赋值给前一位,继续循环。循环外的if语句则判断数组最后一位数是否与数组长度一致,因为题目要求从1开始,n结束,则表明是连续的。所以最后进行判断大小与长度。不一致则表明丢失数据是数组长度n。
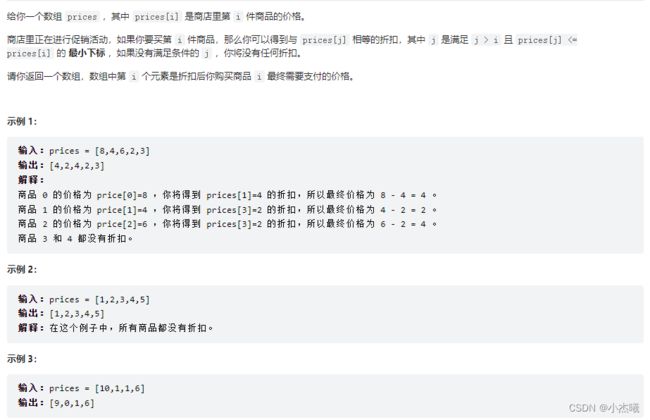
时间:2022-09–01 13:54
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {10,1,1,6};
int[] prices = finalPrices(ints);
for (int price : prices) {
System.out.println(price);
}
}
public static int[] finalPrices(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(j>i && prices[j]<=prices[i]){
prices[i] =prices[i]-prices[j];
break;
}
}
}
return prices;
}
解题思路:本题没看懂题意,但是根据题目给出的条件如果你要买第 i 件商品,那么你可以得到与 prices[j] 相等的折扣,其中 j 是满足 j > i 且 prices[j] <= prices[i] 的 最小下标 ,如果没有满足条件的 j ,你将没有任何折扣。推出条件1: j>i 以及 条件2:prices[j] <= prices[i]。
采用双循环,对每个价格都进行判断是否存在折扣,折扣的大小。满足折扣的条件则是两个条件同时成立。折扣价格后为原价-折扣价格,并将后面价格赋值给原价。最后返回价格数组。
时间:2022-08-31 19:40
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = mySqrt(8);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x==1)return 1;
if(x==0)return 0;
int left=1,right=x/2;
while (left<right){
int mid=left+(right-left+1)/2;
if(mid>x/mid){
right=mid-1;
}else {
left=mid;
}
}
return left;
}
解题思路:采用二分查找法,最大不超过x的1/2。 mid=left+(right-left+1)/2 是保证mid在赋值时不会死循环。
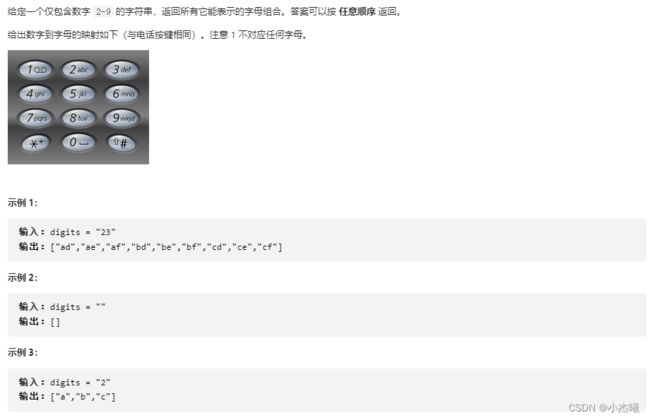
时间:2022-08-30 16:16
class Solution {
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (digits.length() == 0) {
return list;
}
HashMap<Character, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put('2', "abc");
map.put('3', "def");
map.put('4', "ghi");
map.put('5', "jkl");
map.put('6', "mno");
map.put('7', "pqrs");
map.put('8', "tuv");
map.put('9', "wxyz");
back(list, map, digits, 0, new StringBuffer());
return list;
}
public static void back(List<String> list, HashMap<Character, String> map, String digits, Integer index, StringBuffer combination) {
//当index值=digits时表示回溯完了。将combination添加进list。
if (digits.length() == index) {
list.add(combination.toString());
}else {
//获取map集合总对应的字符
String letter = map.get(digits.charAt(index));
int letterCounts = letter.length();
//根据字符长度
for (int i = 0; i < letterCounts; i++) {
//将字符追加进combination
combination.append(letter.charAt(i));
//回溯 index+1变为3对应的def。再回溯index+1=2,符合if条件,追加进list。回溯结束
back(list,map,digits,index+1,combination);
//回溯第一次结束,需要删除回溯后append的内容,进行第二次回溯
combination.deleteCharAt(index);
}
}
}
}
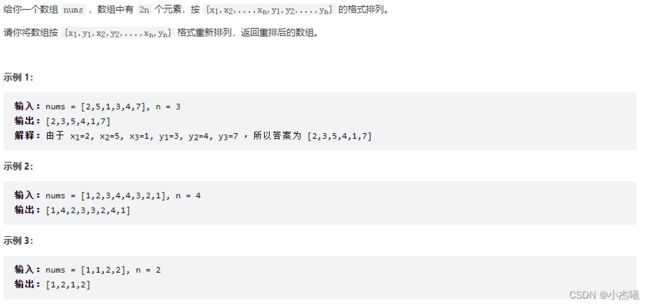
时间:2022-08-29 10:47
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums=new int[]{2,5,1,3,4,7};//251、347 235417
int[] shuffle = shuffle(nums, 3);
for (int i : shuffle) {
System.out.print(i);
}
}
public static int[] shuffle(int[] nums, int n) {
int[] ans = new int[2 * n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans[2 * i] = nums[i];
ans[2 * i + 1] = nums[i + n];
}
return ans;
}
解题思路:根据n的大小判断需要交换几次才能达到重新排列的结果。根据本题n=3判断,数组分为两组,每组三个元素。具体分割为数组下标0,1,2以及3,4,5。需要0下标不动,3下标移动到1下标,1下标移动到2下标,4下标移动到3下标,2下标移动到4下标,5下标不用动。那么总共需要移动6次(包括不动的坐标),刚好是n的2倍,那么在n的移动次数内,需要对下标进行两次移动。第一次移动。0不变则i与n的对应关系是20=0;第二次移动20+1=0+3;第三次移动21=1;第四次移动21+1=1+3;第五次移动22+1=2;第六次移动22+1=2+3。得出关系一、三、五次移动2i=i;二、四、六移动2i+1=i+n。
时间:2022-08-28 10:25
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strings = generateParenthesis(1);
strings.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
static ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
public static List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
if(n<=0) return list;
getParenthesis("",n,n);
return list;
}
public static void getParenthesis(String str,int left,int right){
//判断left和right数量
if(left==0 && right==0){
//已经没有剩余括号数量了
list.add(str);
return;
}
//判断如果left=right
if(left==right){
//下一个必须为左括号
getParenthesis(str+"(",left-1,right);
}else if (left<right){
//剩余左括号小于右括号,可以右括号,也可以左括号
if(left>0){
//如果左括号已还存在。则继续添加左括号
getParenthesis(str+"(",left-1,right);
}
getParenthesis(str+")",left,right-1);
}
}
解题思路:采用迭代方法,通过对括号的数量进行判断,完成对括号有效性的分析,通过不断迭代的方式,将完整的排列组合方式写出
时间:2022-08-27 17:43
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {5};
int target = 5;
Integer ud = search(nums, target);
System.out.println(ud);
}
public static int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
int mid=0;
while (left <= right) {
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
break;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else
left=mid+1;
}
return left>right?-1:mid;
}
解题思路:二分查找,给定的数组是有序数组,采用二分查找,left取数组最左,right取数组最右,mid取中间一个下标,利用中间下标对应数字大小与target对比,如果nums[mid]
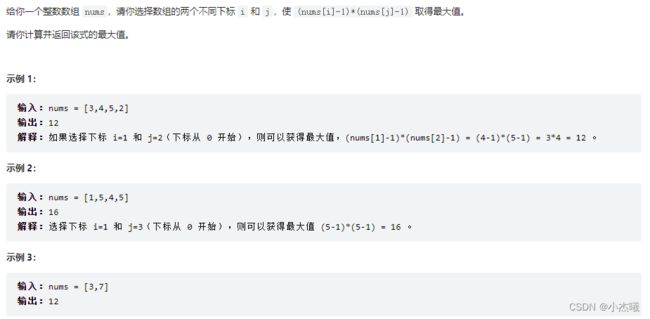
时间:2022-08-26 14:43
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {3, 4, 5, 2};
Integer ud = maxProduct(nums);
System.out.println(ud);
}
public static int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int a = nums[0], b = nums[1];
if (a < b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > a) {
b = a;
a = nums[i];
} else if (nums[i] > b) {
b = nums[i];
}
}
return (a - 1) * (b - 1);
}
解题思路:采用一次遍历,存储最大值最小值。指定第一个下标为最大值,第二个下标为次最大值。先判断是否相同,不同交换,然后从第三个数字开始循环,首先与最大值判断,满足条件则交换,并改变次最大值。不满足条件则与次最大值比较,满足则交换。
时间:2022-08-25 14:17
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean ud = judgeCircle("UD");
System.out.println(ud);
}
public static boolean judgeCircle(String moves) {
char[] chars = moves.toCharArray();
if(chars.length%2==1) return false;
int hFlag=0,vFlag=0;
for (char aChar : chars) {
if(aChar=='U'){
vFlag++;
}else if(aChar=='D'){
vFlag--;
} else if (aChar=='L'){
hFlag++;
}
else if (aChar=='R'){
hFlag--;
}
}
return hFlag==0 && vFlag==0;
}
解题思路:左右,上下必须统一消除,和括号匹配机制一致
时间:2022-08-24 15:29
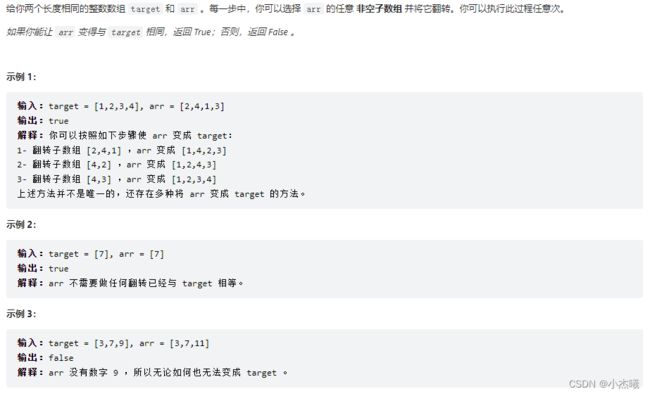
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] target = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] arr = {2,4,1,3};
boolean b = canBeEqual(target, arr);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static boolean canBeEqual(int[] target, int[] arr) {
int[] hash = new int[1001];
for (int i : target) {
hash[i]++;
}
for (int i : arr) {
if (--hash[i] < 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
解题思路:采用数组对数字的一个统计,数组中下标为目标数组或原数组数字大小,对应内容则为数字出现次数。判断出现次数小于0的话返回false;
时间:2022-08-23 22:19
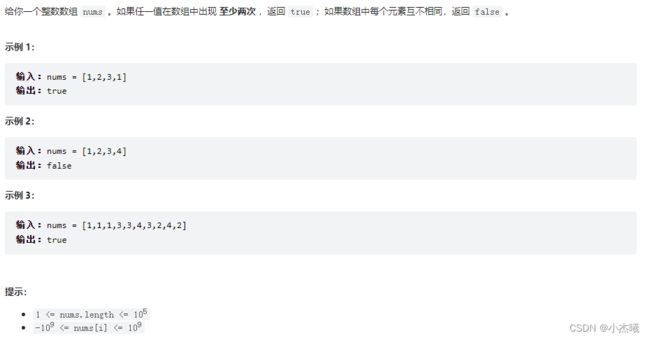
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {};
boolean b = containsDuplicate(ints);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
HashMap<Integer, Boolean> map = new HashMap<>();
Boolean flag=false;
for (int num : nums) {
if(!map.containsKey(num)){
map.put(num,false);
}else {
flag=true;
}
}
return flag;
}
解题思路:利用hashmap不重复存储相同键的原理,只要map中存在,即判断是存在重复元素,返回true,反之返回false;
//错误代码
public static boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(!map.containsKey(nums[i])){
map.put(nums[i],i);
}else {
//获取已存到map中的value
Integer j = map.get(nums[i]);
if(Math.abs(i-j)<=k){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
错误原因:没有考虑到第二个重复元素可能与后面元素相邻重复例如{1,0,1,1}.。0下标与2下标不满足要求,但是2下标与3下标满足要求,错误程序就是这里没有考虑到要将2下标覆盖0下标,导致返回结果出错
//正确代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {1,0,1,1};
boolean b = containsNearbyDuplicate(ints,1);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(nums[i]) && Math.abs(i- map.get(nums[i]))<=k){
return true;
}
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
return false;
}
解题思路:还是和上面一题一样,采用hash表来存储,这里需要考虑的是上面错误代码出现的问题,改进后代码如上所示。
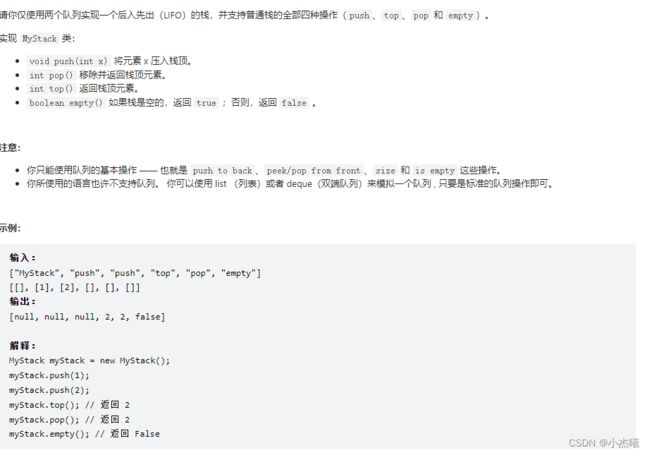
时间:2022-08-22 10:49
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1= new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
queue2= new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//将x插入到queue2队列
queue2.offer(x);
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
//在queue1不为空的前提下,将queue1的head删除,并将其插入到queue2
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
//将queue1复制一份
Queue<Integer> temp=queue1;
//将插入好的queue2重新赋值给queue1
queue1=queue2;
//将新插入元素后的queue1赋值给queue2
queue2=temp;
}
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
解题思路一:通过两个队列,完成栈的先进后出操作,需要考虑队列操作是先进先出。那么栈顶与之对应的就是队列的head。插入操作时,将插入元素放入新队列,再复制queue1队列元素到queue2中。queue2则是插入后的新队列。将其赋值给queue1队列。通过中间变量,将queue2重新置空。
class MyStack {
ArrayDeque<Integer> queue1;
public MyStack() {
queue1= new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
queue1.addFirst(x);
}
public int pop() {
return queue1.removeFirst();
}
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
解题思路二:使用ArrayDeque对象中的addFirst(E)方法,直接将插入元素置为head。
时间:2022-08-21 15:54
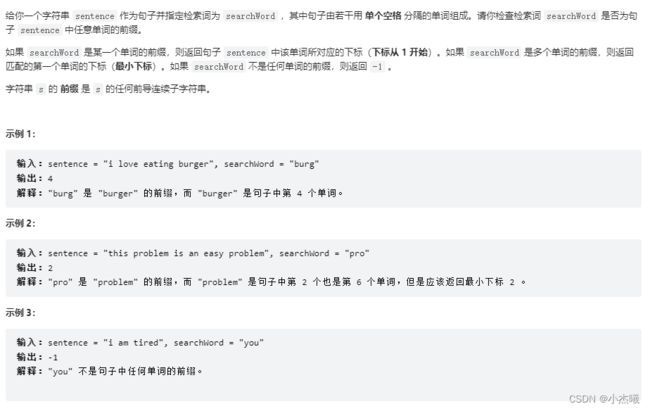
public static void main(String[] args) {
int res = isPrefixOfWord("i love eating burger", "burger");
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int isPrefixOfWord(String sentence, String searchWord) {
String[] sne = sentence.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < sne.length; i++) {
if(sne[i].startsWith(searchWord)){
return i+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
解题思路:首先分割字符串,对每个字符串进行前缀判断,判断前缀一致则返回下标+1;
时间:2022-08-20 15:54
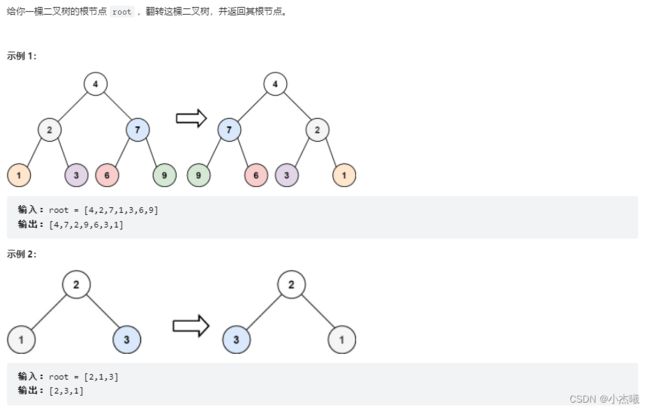
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root ==null) return null;
TreeNode left=invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right=invertTree(root.right);
root.left=right;
root.right=left;
return root;
}
解题思路:
1、遇到二叉树问题,首先想到得是采用递归得方式,找到二叉树最底下的叶子,进行一个交换,这样才能保证对叶子的父节点指向不出问题。通过递归,获取父节点的最左节点、最右节点。接下来对节点进行一个交换就能完成二叉树的翻转了。
时间:2022-08-19 18:19
public static void main(String[] args) {
int res = busyStudent(new int[]{9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, new int[]{10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10}, 5);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int busyStudent(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int queryTime) {
int res=0;
if (startTime==null || endTime==null) return res;
for (int i = 0; i < startTime.length; i++) {
if (startTime[i]<=queryTime && endTime[i]>=queryTime){
++res;
}
}
return res;
}
解题思路:
1、查询时间一定位于开始时间和结束时间中间,只需要判断是否在两个数字之间即可,然后做一个边界值判断。
时间:2022-08-18 20:21
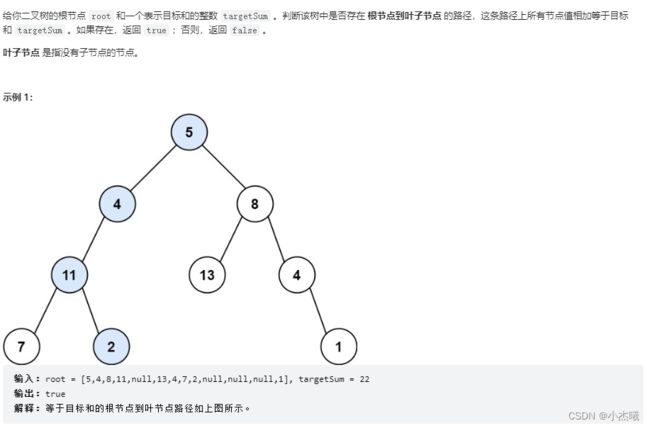
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root ==null) return false;
if(root.left ==null && root.right==null){
return targetSum==root.val;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum-root.val);
}
解题思路:
1、采用递归的思路,本题叶子节点结束计算。
2、首先判断节点是否为空,如果是空的则直接返回false。
3、判断当前节点的叶子节点是否存在,如果存在则表明没有走到树的末端叶子。如果不存在则将目标值与叶子值对比,返回Boolean值。
4、如果存在叶子节点,继续将右叶子,左叶子节点与目标相差值传入递归函数,直到返回了Boolean值,进行判断。
时间:2022-08-14 08:21
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="011101";
int maxScore = maxScore(s);
System.out.println(maxScore);
}
public static int maxScore(String s) {
int addSum=0;
//分割次数
int splitNum = s.length() - 1;
//转换为数组
for (int i = 0; i < splitNum; i++) {
String left = s.substring(0,i+1);
String right = s.substring(i+1);
//计算left中0的数量;
int sumZero=0;
int i1=left.indexOf("0");
while (i1!=-1){
i1=left.indexOf("0",i1+1);
sumZero++;
}
//计算right中1的数量;
int sumOne=0;
int i2=right.indexOf("1");
while (i2!=-1){
i2=right.indexOf("1",i2+1);
sumOne++;
}
addSum = Math.max(addSum, sumOne+sumZero);
}
return addSum;
}
解题思路:确定切割次数,每次切割都是比上次多切割一个字符,分成左和右,采用substring方式切割,对左右两边的字符串处理,判断是否含0,1。并通过indexOf确定是否存在,记录次数。通过Math.max,获取最大和。
时间:2022-08-13 10:44
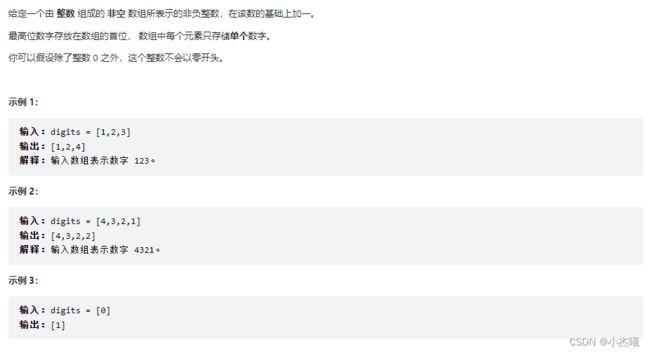
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {1,2,9};
int[] res = plusOne(ints);
for (int re : res) {
System.out.println(re);
}
}
public static int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
int n = digits.length;
//逆序找出9
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
//判断如果末尾不是9,进入if
if (digits[i] != 9) {
//末尾++;
++digits[i];
//如果末尾数字不处理
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
digits[j] = 0;
System.out.println(j);
}
return digits;
}
}
// digits 中所有的元素均为 9
int[] ans = new int[n + 1];
ans[0] = 1;
return ans;
}
解题思路:通过逆序找出末尾数字,如果数字是9则不做任何处理,处理倒数第二个数字。处理判断是否为9,不是则++。再判断j大小,j表示当前修改数字位置,只要不是末尾,基本上都要修改。所以符合逢9进1。
时间:2022-08-12 11:22
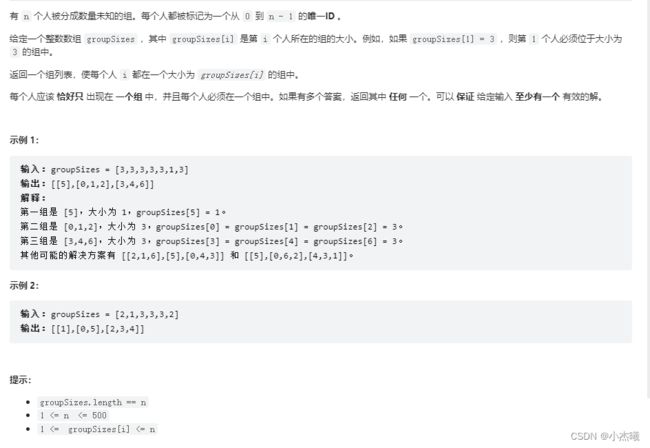
1282. 用户分组
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3};
List<List<Integer>> res = groupThePeople(ints);
System.out.println(res.toString());
}
public static List<List<Integer>> groupThePeople(int[] groupSizes) {
int length = groupSizes.length;
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (!map.containsKey(groupSizes[i])) {
map.put(groupSizes[i], 1);
} else {
map.put(groupSizes[i], map.get(groupSizes[i]) + 1);
}
}
Set<Integer> set = map.keySet();
for (Integer integer : set) {
for (int i = 0; i < map.get(integer) / integer; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<>(integer);
int addSum = 0;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < length; i1++) {
if (groupSizes[i1] == integer && addSum < integer) {
++addSum;
groupSizes[i1] = 0;
l1.add(i1);
}
}
res.add(l1);
}
}
return res;
}
解题思路:
1、首先数组中存在多个重复元素,元素内容是几,存数据的新数组长度就是多少,那么先将原数组中元素进行区分,采用hash表,将元素大小,以及元素个数进行统计,再根据元素个数/元素大小,确定当前元素大小需要拆分多少个组出来。并将原数组中已经使用过的元素置为0。将已经完成的列表add进最终列表。结果出现。
时间:2022-08-11 09:42
public static void main(String[] args) {
String equation="covid2019";
String res = reformat(equation);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static String reformat(String s) {
int n = s.length();
char[] split = s.toCharArray();
ArrayDeque<Character> numQue = new ArrayDeque<>();
ArrayDeque<Character> stringQue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(Character.isDigit(split[i])){
numQue.push(split[i]);
}else {
stringQue.push(split[i]);
}
}
if(Math.abs(numQue.size() - stringQue.size()) > 1) return "";
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < n/2+1; i++) {
if(!numQue.isEmpty() && numQue.size() >=stringQue.size()){
buffer.append(numQue.pop());
}
if(!stringQue.isEmpty()){
buffer.append(stringQue.pop());
}
}
return buffer.toString();
}
解题思路:采用双栈方式将数字和字符串进行提取,然后新建StringBuffer 将数字和字符apeend进去。需要考虑的边界问题较多。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String equation = "covid2019";
String res = reformat(equation);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static String reformat(String s) {
int n = s.length();
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int sumDigit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (Character.isDigit(chars[i])) sumDigit++;
}
int sumAlpha = n - sumDigit;
if (Math.abs(sumAlpha - sumDigit) > 1) return "";
boolean flag = sumDigit > sumAlpha;
for (int i = 0, j = 1; i < n; i += 2) {
if (Character.isDigit(chars[i]) != flag) {
while (Character.isDigit(chars[j]) != flag){
j += 2;
}
swap(chars,i,j);
}
}
return new String(chars);
}
public static void swap(char[] arr,int i,int j){
char c=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=c;
}
解题思路:采用双指针方式,先判断数字和字符数量,满足|sumAlpha - sumDigit| >1 则返回空字符串;判断数字和字符数量,如果数字大则第一位应该是数字,反之亦然。循环内取首字符,判断是否满足前置条件Character.isDigit(chars[i]) != flag,满足则进入第二个判断Character.isDigit(chars[j]) != flag。首先第一个前置条件不满足,则i+2;直到找到满足条件的数字,第二步则判断j=1时,是否为不同类型,不同类型则进入循环j+=2;知道满足条件退出循环,将两者进行交换。核心思想为:不断向右寻找正确的字符,然后交换,知道数组尾端。
时间:2022-08-10 09:57
解题思路:1、java字符分割方式,按照空格进行分割。代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String equation="luffy is still word";
int res = lengthOfLastWord(equation);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
String[] split = s.split(" ");
String s1 = split[split.length- 1];
return s1.length();
}
2、使用从后往前的双指针来判断最后一个字符串的长度。最后j-i则是字符长度。j是最后一个字符串末尾位置,i是最后一个字符串首位置。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String equation="luffy is still word";
int res = lengthOfLastWord(equation);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
int n=s.length();
int j=n-1;
while (j>=0 && s.charAt(j)==' '){
j--;
}
int i=j;
while (i>=0 && s.charAt(i)!=' '){
i--;
}
return j-i;
}
时间:2022-08-09 09:38
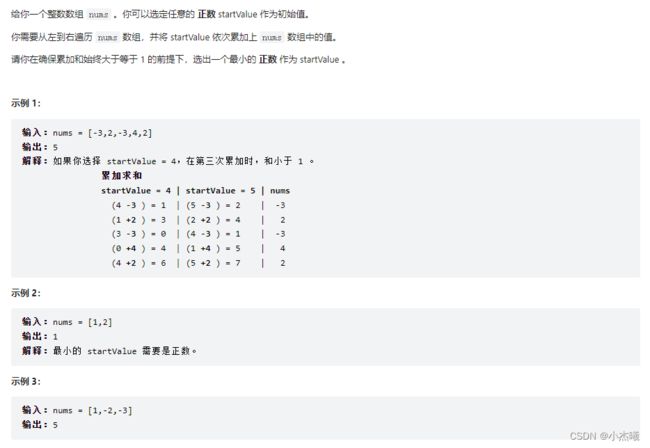
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {-3,2,-3,4,2};
int i = minStartValue(ints);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int minStartValue(int[] nums) {
int accSum =0;
int accSumMin =0;
for (int num : nums) {
accSum +=num;
accSumMin =Math.min(accSumMin,accSum);
}
return -accSumMin+1;
}
解题思路:
1、数组内部进行累加和,求出累加过程中最小值。对最小值取反+1;则为最小正整数
-3 + 0 = -3 => 最小值为-3
-3 + 2 = -1 => 最小值为-3
-1 - 3 = -4 => 最小值为-4
-4 + 4 = 0 => 最小值为-4
0 + 2 = 2 => 最小值为-4
综上所排列得出累加过程中最小的数为-4 则判断当初始值为5的时候累加值永远大于1。
时间:2022-08-08 09:53
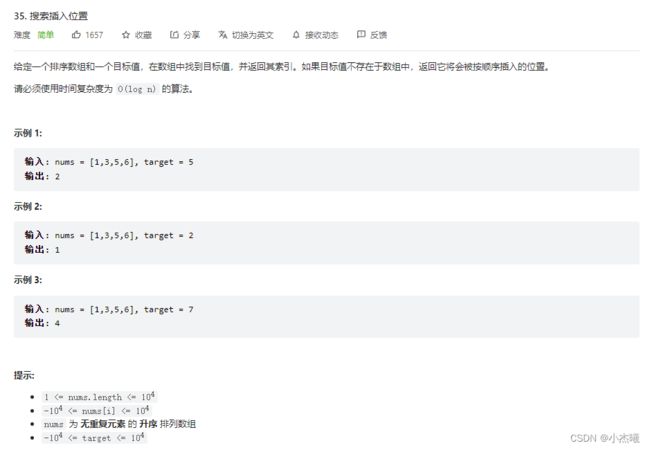
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {1, 3, 5, 6};
int target=2;
int i = searchInsert(ints, target);
System.out.println(i );
}
public static int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int n=nums.length;
int left=0,right=n-1;
while (left<=right){
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}else if(nums[mid]<target){
left=mid+1;
}else {
right=mid-1;
}
}
return left;
}
解题思路:
采用二分查找发符合条件时间复杂度O(log n)。
数组有序,设置left=0,right=nums.length-1;获取mid中间值,与目标值判断,相等则返回,如果mid值小于目标值,则目标值在mid——right中间。将left设置为mid+1。right不用动,重新获取mid。如果mid值小于目标值,则目标值在left——mid中间。将right设置为mid-1。left不用动,重新获取mid。直到left>right时还没有返回则直接返回left。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = {1,2,3,4,5};
int i = maxArea(ints);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int maxArea(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
int left=0,right=n-1;
int ans=0;
while (left<right){
int area = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right-left);
ans=Math.max(area,ans);
if(height[left]<height[right]){
left++;
}
else right--;
}
return ans;
}
解题思路
1、本题采用双指针策略,左指针指向数组下标0,右指针指向数组末端。通过公式计算面积,最短板(Math.min判断)*x轴距离(也就是右指针-左指针)。通过Math.max判断面积是否最大,全部判断完毕后输出。
时间:2022-08-07 09:16
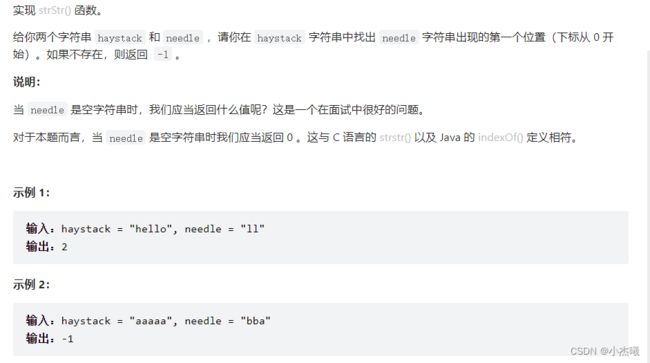
public static void main(String[] args) {
String haystack="aaaa";
String needle="ll";
int i = strStr(haystack, needle);
System.out.println(i);
}
public static int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int index=haystack.indexOf(needle);
return index;
}
解题思路:???? 简单的有点离谱了。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 2;
List<String> logs = new ArrayList<String>() {{
add("0:start:0");
add("0:start:2");
add("0:start:5");
add("1:start:7");
add("1:end:7");
add("0:end:8");
}};
int[] ints = exclusiveTime(n, logs);
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.println(anInt);
}
}
public static int[] exclusiveTime(int n, List<String> logs) {
int[] nums = new int[n];
ArrayDeque<int[]> arrayDeque = new ArrayDeque<>();
logs.forEach(log -> {
String[] split = log.split(":");
int functionId = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
String function = split[1];
int timestamp = Integer.parseInt(split[2]);
if (("start").equals(function)) {
if (!arrayDeque.isEmpty()) {
nums[arrayDeque.peek()[0]] += timestamp - arrayDeque.peek()[1];
arrayDeque.peek()[1] = timestamp;
}
arrayDeque.push(new int[]{functionId, timestamp});
} else {
int[] t = arrayDeque.pop();
nums[t[0]] += timestamp - t[1] + 1;
if (!arrayDeque.isEmpty()) {
arrayDeque.peek()[1] =timestamp+1;
}
}
});
return nums;
}
解题思路:
1、一个cpu执行函数,必须顺序执行下去。当栈中有执行函数时,则暂停当前运行的函数,计算已经执行的时间。然后将这个函数入栈。
2、当函数调用结束时,将栈顶元素弹出,计算对应的执行时间,如果存在暂停的函数,则开始运行该函数。
每个函数都存在start和end。遇到start的标志时都入栈,遇到end的时候。将栈顶出栈。记录相应的执行时间。
分别获取log日志中内容,切割分为三部分,functionId,function,timestamp。判断栈是否为空,为空则直接入栈,此时入栈元素是[0,0]。
第一条日志结束。第二条日志是[0:start:2],判断是否“start”,是则先计算相应时间【计算方式为获取栈顶元素[0,0],由第二条日志时间2-0=2 ,再加上已经执行单位时间nums[0]=0,已执行单位时间为nums[0]=2。】。修改栈顶元素时间为2,再入栈元素[0,2]。栈元素【[0,2],[0,2]】
第二条日志结束,第三条日志[0:start:5],判断是否“start”,是则计算相应时间【计算方式为获取栈顶元素[0,2],由第三条日志时间是5-2=3,再加上已经执行单位时间nums[0]=2,已执行单位时间为nums[0]=5。】。修改栈顶元素时间为5,入栈元素[0,5]。栈元素【[0,2],[0,5],[0,5]】
第三条日志结束,第四条日志[1:start:7],判断是否是"start",是则计算相应时间【计算方式为获取栈顶元素[0,5],由第四条日志时间是7-5=2,再加上已经执行单位时间nums[0]=2,已执行单位时间为nums[0]=7。】。修改栈顶元素时间为7,入栈元素[1,7]。栈元素【[0,2],[0,5],[0,7],[1,7]】
第四条日志结束,第五条日志[17],判断是否是"start“,否则出栈栈顶元素[1,7]。计算相应的时间【计算方式为(timestamp)7-(pop)7+1=1,再加上该functionId为1的已执行单位时间nums[1]=0(默认从0开始),所以nums[1]=1】,修改栈顶元素,7+1。此时栈中元素为【[0,2],[0,5],[0,8]】。
第五条日志结束,第六条日志[08],判断是否是"start",否则出栈栈顶元素[0,8]。计算相应的时间【计算方式为8-8+1=1,再加上nums[0]=7,nums[0]=8】。修改栈顶元素 8+1=9。此时栈内元素【[0,2],[0,9]】。日志结束。
nums为统计执行时间数组。nums[0],nums[1]分别统计的是functionId=0,functionId=1的已执行时间。
输出结果nums[0]=8,nums[1]=1。返回结果nums[8,1]。
时间:2022-08-06 15:49
1408. 数组中的字符串匹配
给你一个字符串数组 words ,数组中的每个字符串都可以看作是一个单词。请你按 任意 顺序返回 words 中是其他单词的子字符串的所有单词。
如果你可以删除 words[j] 最左侧和/或最右侧的若干字符得到 word[i] ,那么字符串 words[i] 就是 words[j] 的一个子字符串。

public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] strings = {"mass", "as", "hero", "superhero"};
List<String> list = stringMatching(strings);
System.out.println(list);
}
public static List<String> stringMatching(String[] words) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
for(int j=0;j<words.length;j++){
if(i==j) continue;
if(words[j].indexOf(words[i])>=0){
list.add(words[i]);
break;
}
}
}
return list;
}
解题思路:
暴力解题,时间复杂度O(m2 * n2)。
双层循环,使用indexOf获取子串是否存在,不存在返回-1。