Spring IoC&DI入门
一:Spring IoC&DI概念
(1)Spring概念
Spring是包含了众多工具方法的IoC容器,是一个开源框架,让我们的开发更加简单
Spring的两大核心和特点:IoC和AOP
(2)IoC的介绍
1.概念
IoC: InversionofControl (控制反转),即Spring是⼀个能装对象的"控制反转"的容器
(IoC是Spring的核心思想,也是常见的面试题)
①控制反转:即控制权反转,指创建对象的过程被反转了;把创建对象的控制权交给了Spring,由Spring进行管理对象,既可以存对象,也可以取出来
例:当需要某个对象时,传统开发模式中需要自己通过new创建对象,现在不需要再进行创建,把创建对象的任务交给容器,程序中只需要依赖注入(DependencyInjection,DI)就可以了,此时让容器来进行一系列操作
②举例:
(1)比如自动驾驶;传统驾驶方式,车辆的横向和纵向驾驶控制权由驾驶员来控制,现在交给了驾驶自动化系统来控制
(2)在类上面添加@RestController和@Controller注解,就是把这个对象交给Spring管理,Spring框架启动时就会加载该类,把对象交给Spring管理,也属于是IoC思想
2.作用
①资源集中管理:资源不由使用资源的双方管理,而由不使用资源的第三方管理;即IoC容器会帮我们管理⼀些资源(对象等),我们需要使用时,只需要从IoC容器中去取就可以了
②降低耦合度:我们在创建实例的时候不需要了解其中的细节,降低了使用资源双方的依赖程度,也就是我们说的耦合度
(3)DI的介绍
1.概念
DI: DependencyInjection(依赖注入)
容器在运行期间,动态的为应用程序提供运行时所依赖的资源,称之为依赖注入
2.DI与IoC的关系
IoC是个思想,而思想只是一种指导原则,最终还要有可行的落地方案,而DI就属于具体的实现;所以也可说DI是IoC的一种实现
(4)IoC&DI实现方式
①IoC:把对象创建控制权交给Spring,即存东西
②DI:把依赖对象取出来,并赋值给该对象的属性,即取东西
(5)Bean
1.Bean的概念
Spring是一个容器,存的是对象,而对象这个词在Spring的范畴内称为Bean
2.Bean的命名约定
①五大类注解的命名约定
(1)默认情况:Bean名称为首字母小写
(2)特殊情况:Bean名称为类名;当前两个字符都是大写的情况下
②@Bean方法注解的命名约定
Bean名称为@Bean方法注解下的方法名
二:IoC注解详解
(1)注解分类
①类注解:@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration
(这五大注解只能加在类上,并且只能加在自己的代码中;不能把第三方包给Spring管理)
②方法注解:@Bean
(如果加入了一些第三方jar包也想给Spring管理,就可以使用@Bean)
(2)应用分层
三层架构
代码分层逻辑和调用先后:先由Controller去调用Service,然后Service去调用Dao
①Controller(表现层):接受请求,返回结果
②Service(业务逻辑层):主要处理业务相关逻辑
③Dao(数据层):处理数据的,包含数据的存储,增删改查
(3)类注解-@Controller(控制器存储)
1.作用
Spring框架启动加载时,把这个对象交给Spring容器管理;等到需要时再从容器里拿
当包是Controller时,这个包里的类就用@Controller来存储Bean(对象)
(包是Controller表示是表现层,用于接收请求返回结果)
2.使用代码观察结果
①初谈DemoApplication运行类
其中,SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args)这一行代码的run就表示Spring这个应用开始启动,启动之后返回的就是上文说到的IoC容器
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
②ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext用来接收返回的IoC容器
(此时的IoC容器就存放了很多由Spring管理的对象)
即获取Spring上下文;这里的上下文指的就是Spring运行环境
ApplicationContext翻译过来就是:Spring上下文;因为对象都交给Spring管理了,所以获取对象要从Spring中获取,那么就得先得到Spring的上下文
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
③getBean方法
getBean方法即从Spring上下文中获取对象
(上文说过Bean就是Spring范畴里对象的意思)
主要的三个getBean方法
(1)String s:表示Bean的名称
(根据名称来获取Bean,要强制类型转换才能调用方法)
(2)Class
aClass:表示Bean的类型;可以加泛型参数的指定 (根据名称来获取Bean,可直接调用方法)
④尝试运行观察结果
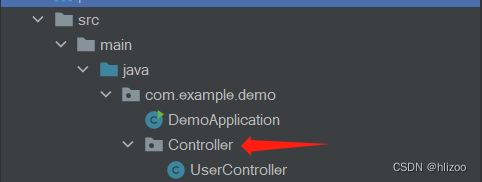
1.先在com.example.demo目录下创建一个Controller包,然后创建一个UserController类
(@Controller这个注解十分重要,没有它就不会把UserController对象交给Spring管理)
package com.example.demo.Controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller //这个@Controller至关重要 public class UserController { public void doController(){ System.out.println("do Controller....."); } }
2.再在DemoApplication类中获取对象且执行方法
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //从Spring上下文中获取对象 //根据类来获取UserController对象 UserController bean = context.getBean(UserController.class); //执行doController的方法 bean.doController(); } }
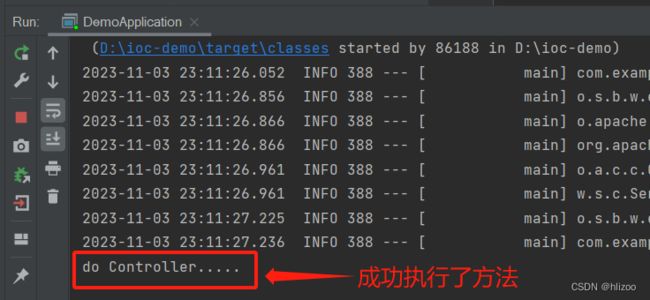
3.运行并观察结果
4.去掉UserController类中的@Controller注解再次运行
(4)类注解-@Service(服务存储)
1.作用
Spring框架启动加载时,把这个对象交给Spring容器管理;等到需要时再从容器里拿
当包是Service时,这个包里的类就用@Service来存储Bean(对象)
(包是Service表示是业务逻辑层,用于主要处理业务相关逻辑)
2.使用代码观察结果
1.先在com.example.demo目录下创建一个Service包,然后创建一个UserService类
package com.example.demo.Service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service //@Service至关重要 public class UserService { public void doService(){ System.out.println("do Service....."); } }
2.再在DemoApplication类中获取对象且执行方法
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据类来获取UserService对象 UserService bean1 = context.getBean(UserService.class); //根据名称来获取UserService对象(由于根据名称来获取Bean,要强转才可调用方法) UserService bean2 = (UserService)context.getBean("userService"); //根据名称和类来获取UserService对象 UserService bean3 = context.getBean("userService",UserService.class); //执行doService的方法 bean1.doService(); bean2.doService(); bean3.doService(); } }
3.运行并观察结果
(5)类注解-@Repository(仓库存储)
1.作用
Spring框架启动加载时,把这个对象交给Spring容器管理;等到需要时再从容器里拿
当包是Dao时,这个包里的类就用@Repository来存储Bean(对象)
(包是Dao表示是数据层,用于处理数据的,包含数据的存储,增删改查)
2.使用代码观察结果
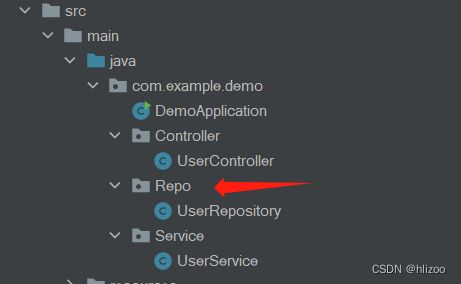
1.先在com.example.demo目录下创建一个Repo包,然后创建一个UserRepository类
package com.example.demo.Repo; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class UserRepository { public void doRepository(){ System.out.println("do Repository....."); } }
2.再在DemoApplication类中获取对象且执行方法
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Repo.UserRepository; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据类来获取UserRepository对象 UserRepository bean1 = context.getBean(UserRepository.class); //根据名称来获取UserRepository对象(由于根据名称来获取Bean,要强转才可调用方法) UserRepository bean2 = (UserRepository)context.getBean("userRepository"); //根据名称和类型来获取UserRepository对象 UserRepository bean3 = context.getBean("userRepository",UserRepository.class); //执行doRepository的方法 bean1.doRepository(); bean2.doRepository(); bean3.doRepository(); } }
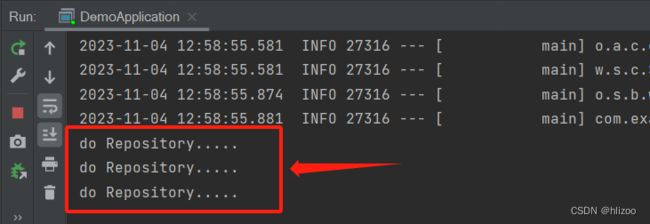
3.运行并观察结果
(6)类注解-@Component(组件存储)
1.作用
Spring框架启动加载时,把这个对象交给Spring容器管理;等到需要时再从容器里拿
Component表示除了那三个应用分层之外的代码,即不属于那三个分层的其它代码,比如一些组件等等
2.使用代码观察结果
1.先在com.example.demo目录下创建一个Component包,然后创建一个UserComponent类
package com.example.demo.Component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class UserComponent { public void doComponent(){ System.out.println("do Component....."); } }
2.再在DemoApplication类中获取对象且执行方法
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Component.UserComponent; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Repo.UserRepository; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据类来获取UserRepository对象 UserComponent bean1 = context.getBean(UserComponent.class); //根据名称来获取UserRepository对象(由于根据名称来获取Bean,要强转才可调用方法) UserComponent bean2 = (UserComponent)context.getBean("userComponent"); //根据名称和类型来获取UserRepository对象 UserComponent bean3 = context.getBean("userComponent",UserComponent.class); //执行doRepository的方法 bean1.doComponent(); bean2.doComponent(); bean3.doComponent(); } }
3.运行并观察结果
(7)类注解-@Configuration(配置存储)
1.作用
Spring框架启动加载时,把这个对象交给Spring容器管理;等到需要时再从容器里拿
Configuration表示配置层;用于处理项目中的⼀些配置信息
2.使用代码观察结果
1.先在com.example.demo目录下创建一个Configuration包,然后创建一个UserConfiguration类
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class UserConfiguration { public void doConfiguration(){ System.out.println("do Configuration....."); } }
2.再在DemoApplication类中获取对象且执行方法
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Component.UserComponent; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserConfiguration; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Repo.UserRepository; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据类来获取UserRepository对象 UserConfiguration bean1 = context.getBean(UserConfiguration.class); //根据名称来获取UserRepository对象(由于根据名称来获取Bean,要强转才可调用方法) UserConfiguration bean2 = (UserConfiguration)context.getBean("userConfiguration"); //根据名称和类型来获取UserRepository对象 UserConfiguration bean3 = context.getBean("userConfiguration",UserConfiguration.class); //执行doRepository的方法 bean1.doConfiguration(); bean2.doConfiguration(); bean3.doConfiguration(); } }
3.运行并观察结果
(8)为什么要这么多类注解
与应用分层相关;用不同的注解就可以区分不同层次
@Controller:控制层;接收请求,对请求进行处理,并进行响应
@Servie:业务逻辑层;处理具体的业务逻辑
@Repository:数据访问层,也称为持久层;负责数据访问操作
@Configuration:配置层;处理项目中的⼀些配置信息
(9)类注解之间的关系
@Controller、@Servie、@Repository、@Configuration,它们本身就是属于@Component的衍生类,也可以理解为"子类"
(10)方法注解-@Bean
1.应用场景
①@Bean注解可以在使用外部包里的类
(类注解不能加在外部包里的类,此时就需要@Bean注解)
②⼀个类,需要定义多个不同的对象时,此时就需要@Bean注解
比如说数据库操作可能需要多个数据源
(如果使用类注解,得到的对象是一模一样的;只有使用方法注解才可以获得不同的对象)
2.方法注解要结合类注解使用
1.方法
@Bean要配合类注解才能将对象正常的存储到Spring容器中
2.代码演示
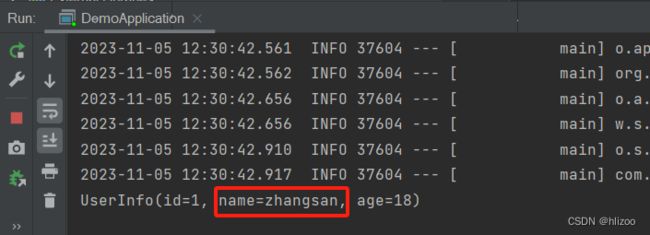
①场景演示:假设UserInfo类是外部包的类,此时我需要用它定义对象
②先在Configuration包下创建一个UserInfo类
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import lombok.Data; @Data public class UserInfo { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; }
③再在Configuration包下创建一个BeanConfiguration类,我们用它来创建UserInfo对象
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //@Bean方法注解要结合类注解才能拿到对象,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(){ UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName("zhangsan"); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } }
④最后在DemoApplication获取UserInfo对象package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Component.UserComponent; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserConfiguration; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Repo.UserRepository; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //获取外部包里的UserConfiguration UserInfo userInfo = context.getBean(UserInfo.class); System.out.println(userInfo); } }
⑤观察运行结果
3.定义多个对象
1.方法
@Bean可以针对同⼀个类, 定义多个对象
此时我们需要通过Bean的名称来获取不同对象,Bean的名称就是就是@Bean注解下的方法名
2.代码演示
①场景演示:假设UserInfo类是外部包的类,此时我需要用它定义多个对象
②跟前面一样,如果创建了UserInfo类就不用创建了
③在BeanConfiguration类创建两个对象,模拟多对象
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //类注解结合@Bean方法注解才能拿到,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(){ //第一个对象 UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName("zhangsan"); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo2(){ //第二个对象 UserInfo userInfo2 = new UserInfo(); userInfo2.setId(2); userInfo2.setName("lisi"); userInfo2.setAge(28); return userInfo2; } }
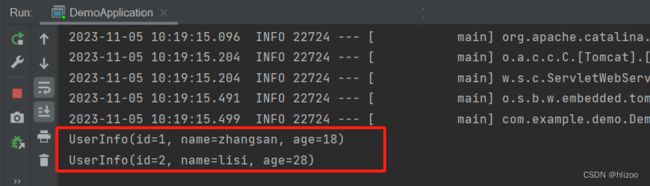
④最后在DemoApplication获取这两个UserInfo对象
(此时就需要用到根据Bean的名称获取对象,Bean的名称就是@Bean注解下的方法名)
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Component.UserComponent; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserConfiguration; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Repo.UserRepository; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据Bean名称获取不同的UserInfo对象 //Bean的名称就是@Bean注解下的方法名 UserInfo userInfo1 = (UserInfo) context.getBean("userInfo1"); UserInfo userInfo2 = (UserInfo) context.getBean("userInfo2"); System.out.println(userInfo1); System.out.println(userInfo2); } }
⑤观察运行结果
4.传递方法参数
1.方法
给形参也写个方法,方法的数据类型与参数类型对应,并且加上@Bean注解
2.代码演示
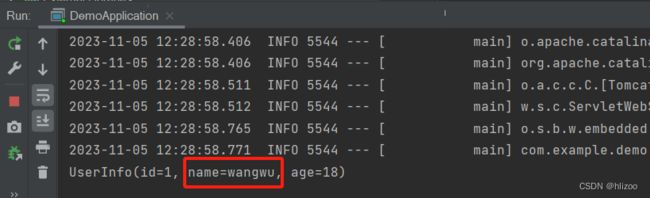
①同样还是用到UserInfo类,只不过在BeanConfiguration类给userInfo1加个形参,此时就说明userInfo1需要一个String类型的Bean
(注意这里我写了个方法并加上@Bean注解,此时也就有了一个String类型的Bean)package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //类注解结合@Bean方法注解才能拿到,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public String name(){ return "wangwu"; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(String name){ //第一个对象 UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName(name); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo2(){ //第二个对象 UserInfo userInfo2 = new UserInfo(); userInfo2.setId(2); userInfo2.setName("lisi"); userInfo2.setAge(28); return userInfo2; } }
②获取对象并观察运行结果
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Component.UserComponent; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserConfiguration; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Repo.UserRepository; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据Bean名称获取不同的UserInfo对象 //Bean的名称就是@Bean注解下的方法名 UserInfo userInfo1 = (UserInfo) context.getBean("userInfo1"); System.out.println(userInfo1); } }
5.Bean的存储方式
1.原则
①如果需要的Bean类型,它的对象只有一个时,就直接赋值了
②如果需要的Bean类型,它的对象有多个时,就根据名字进行匹配,优先使用同名的
2.代码演示
①当我在加两个形参方法时,一个name,一个name2
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //类注解结合@Bean方法注解才能拿到,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public String name(){ return "wangwu"; } @Bean public String name2(){ return "zhangsan"; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(String name){ //第一个对象 UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName(name); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo2(){ //第二个对象 UserInfo userInfo2 = new UserInfo(); userInfo2.setId(2); userInfo2.setName("lisi"); userInfo2.setAge(28); return userInfo2; } }
②userInfo1会优先调用相同名字的,即调用第一个方法,因为名字都为name
③当我删除了name,只保留一个name2,此时不管名字是否相同都直接赋值
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration //类注解结合@Bean方法注解才能拿到,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public String name2(){ return "zhangsan"; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(String name){ //第一个对象 UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName(name); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo2(){ //第二个对象 UserInfo userInfo2 = new UserInfo(); userInfo2.setId(2); userInfo2.setName("lisi"); userInfo2.setAge(28); return userInfo2; } }
6.Bean的重命名
当你给Bean的形参加上一个字符串,这个字符串就是你指定的Bean名,后续就通过它来获取对象
①name={} 可以省略
②只有⼀个名称时,{}也可以省略
(11)路径扫描
1.特点
默认扫描DemoApplication启动类所在的目录
2.推荐做法
把启动类放在我们希望扫描的包的路径下, 这样我们定义的Bean(对象)就都可以被扫描到
3.@ComponentScan
①作用
指定根目录,使得根目录下的所有子目录都可以被启动类扫描到
②演示
Ⅰ.当你把启动类放在了Controller包下,启动类就只能扫描到Controller下的Bean
Ⅱ.当你试图去获取Service包下的Bean时,启动类就会扫描不到
Ⅲ.此时就可以在启动类加上@ComponentScan注解,指定它的扫描路径,最后运行成功
三:DI注解详解
(1)DI注解作用
提供IoC容器在创建Bean时所依赖的对象,即注入依赖的对象
把对象取出来放到某个类的属性中
(2)DI依赖注入的三种方式
①属性注入(Field Injection)
(1)优点:
简洁,使用方便
(2)缺点:
1.只能用于IoC容器,如果是非IoC容器不可用,并且只有在使用的时候才会出现NPE(空指针异常)
2.不能注入⼀个Final修饰的属性
②构造方法注入(Constructor Injection)
(1)优点:
1.可以注入final修饰的属性
2.注入的对象不会被修改
3.依赖对象在使用前⼀定会被完全初始化,因为依赖是在类的构造方法中执行的,而构造方 法是在类加载阶段就会执行的方法
4. 通用性好, 构造方法是JDK支持的,所以更换任何框架,他都是适用的
(2)缺点:
注入多个对象时,代码会比较繁琐
③Setter注入(Setter Injection)
(1)优点:
方便在类实例之后, 重新对该对象进行配置或者注入
(2)缺点:
1.不能注入⼀个Final修饰的属性
2.注入对象可能会被改变, 因为setter方法可能会被多次调用, 就有被修改的风险
(3)属性注入
1.注解
使用@Autowired注解,给类的属性中实现注入,让Spring帮我们自动创建对象
(即把当前类依赖的属性通过@Autowired注入到当前类中)
属性注入和类型相匹配,与注入的属性名称无关
(与类型相关,与名称无关)
如果一个类型存在多个对象,会优先进行名称匹配,即相同名字的,如果没有同名则报错
(下文@Autowired存在问题的原因)
2.代码演示
①此时UserController是依赖UserService的,我们通过@Atuowired来给UserController注入依赖的UserService对象,此时不用我们自己创建UserService对象,就可以直接使用UserService的方法了
package com.example.demo.Controller; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; public void doController(){ userService.doService(); System.out.println("do Controller....."); } }
②运行启动类并观察结果
(预期结果:当调用doController时就会调用到doService)
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据类来获取UserController对象 UserController bean1 = context.getBean(UserController.class); //执行doController的方法 bean1.doController(); } }
(4)构造方法注入
1.注解
使用@Autowired注解,在类的构造方法中实现注入
如果类只有一个构造方法,那么@Autowired注解可以省略
如果类中有多个构造方法,那么需要加上@Autowired来明确指定到底使用哪个构造方法
2.代码演示
如下所示,给带一个参数的构造方法带上@Autowired,就表示告诉Spring说要调用这个带一个参数的构造方法
package com.example.demo.Controller; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller public class UserController { private UserService userService; private UserInfo userInfo; @Autowired public UserController(UserService userService){ this.userService = userService; } public UserController(UserService userService,UserInfo userInfo){ this.userService = userService; this.userInfo = userInfo; } public void doController(){ userService.doService(); System.out.println("do Controller....."); } }
(5)Setter方法注入
1.注解
在设置set方法的时候需要加上@Autowired注解
2.代码演示
package com.example.demo.Controller; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller public class UserController { private UserService userService; @Autowired public void setUserService(UserService userService){ this.userService = userService; } public void doController(){ userService.doService(); System.out.println("do Controller....."); } }
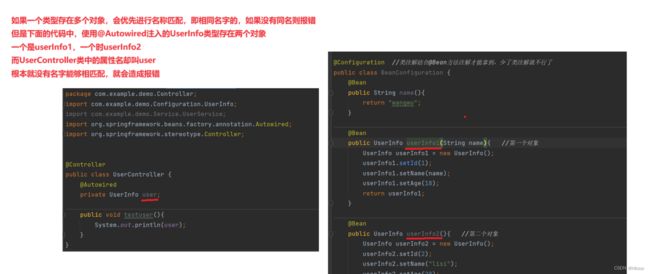
(6)@Autowired存在的问题
1.问题描述
当同⼀类型存在多个bean时,使用@Autowired会存在问题
涉及到了上述的属性注入;因为属性注入时,如果一个类型存在多个对象,会优先进行名称匹配,即相同名字的,如果没有同名则报错,此时使用@Autowired会存在问题
2.代码演示
3.解决办法
①@Autowired下的属性名和需要使用的对象名保持一致
②@Primary
③@Qualifier
④@Resource
(下文细说)
(7)@Primary
1.作用
当存在多个相同类型的Bean注入时,加上@Primary注解,来确定默认的实现
即在对象中,加上@Primary,此时就默认这个为运行时的对象
2.代码演示
①BeanConfiguration类的代码
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; @Configuration //类注解结合@Bean方法注解才能拿到,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public String name(){ return "wangwu"; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(String name){ //第一个对象 UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName(name); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo2(){ //第二个对象 UserInfo userInfo2 = new UserInfo(); userInfo2.setId(2); userInfo2.setName("lisi"); userInfo2.setAge(28); return userInfo2; } }
②UserController类的代码
(注意此时我的属性名没有一个是和我的对象名是一致的,userInfo≠userInfo1≠userInfo2)
package com.example.demo.Controller; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller public class UserController { @Autowired private UserInfo userInfo; public void testuser(){ System.out.println(userInfo); } }
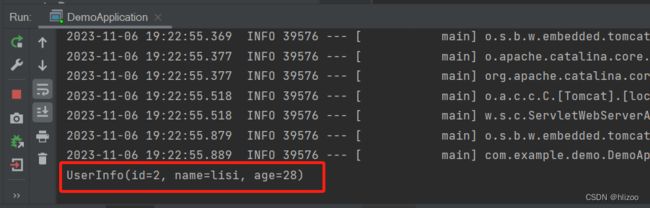
③运行DemoApplication启动类代码观察结果
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.Controller.UserController; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring上下文 ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); //根据类来获取UserController对象 UserController bean1 = context.getBean(UserController.class); //执行doController的方法 bean1.testuser(); } }
(8)@Qualifier
1.作用
指定当前要注入的Bean对象;在@Qualifier的value属性中,指定注入的Bean的名称
@Qualifier注解不能单独用,必须配合@Autowired使用;一般是写在@Autowired上方
2.代码演示
①BeanConfiguration类的代码
package com.example.demo.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; @Configuration //类注解结合@Bean方法注解才能拿到,少了类注解就不行了 public class BeanConfiguration { @Bean public String name(){ return "wangwu"; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo1(String name){ //第一个对象 UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); userInfo1.setId(1); userInfo1.setName(name); userInfo1.setAge(18); return userInfo1; } @Bean public UserInfo userInfo2(){ //第二个对象 UserInfo userInfo2 = new UserInfo(); userInfo2.setId(2); userInfo2.setName("lisi"); userInfo2.setAge(28); return userInfo2; } }
②UserController类的代码
(注意@Qualifier;此时我指定了使用名为userInfo2的对象)
package com.example.demo.Controller; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller public class UserController { @Qualifier("userInfo2") @Autowired private UserInfo userInfo; public void testuser(){ System.out.println(userInfo); } }
③运行DemoApplication启动类代码观察结果
(代码同上,就不重复了)
(9)@Resource
1.作用
按照Bean的名称进行注入;通过name属性指定要注入的Bean的名称
加了@Resource就不需要同时加@AutoWired了
2.代码演示
①BeanConfiguration类的代码
(代码同上,就不重复了)
②UserController类的代码
(注意没有了@AutoWired,我使用了@Resource指定了使用名为userInfo2的对象)
package com.example.demo.Controller; import com.example.demo.Configuration.UserInfo; import com.example.demo.Service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import javax.annotation.Resource; @Controller public class UserController { @Resource(name = "userInfo2") private UserInfo userInfo; public void testuser(){ System.out.println(userInfo); } }
③运行DemoApplication启动类代码观察结果
(代码同上,就不重复了)
(10)常见面试题
使用@Autowired和@Resource是最多的