MyBatis
Mabatis连接方式是连接池,采取了事务管理方式。将自动提交取消改为手动提交,所以在做增删改操作时需要commit().
Mybatis-config
Mapper
将下划线映射为驼峰
查询单个
<select id="selectById" resultMap="ProdResultMap">
select * from prod where prod_id=#{id};
select>
#{id} 相当于preparestatement预编译 可以防止注入
还有一种写法是${id} 是拼进去的参数 不能防止注入
条件 < 在xml 文件中不被识别 解决方式:转义字符:< 或 data区 CD回车 data区中写入小于号
多表联查
多对一
对1的那一方新建对象属性
查询到信息方法1:起别名(resultMap)级联查询
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="bean.EmpMapper">
<resultMap id="empAndDeptMap" type="entity.Emp">
<result column="DNAME" property="dept.dname"/>
<result column="LOC" property="dept.loc"/>
resultMap>
<select id="selectEmpAndDept" resultMap="empAndDeptMap">
SELECT e.*,d.DNAME,d.LOC
FROM emp e,dept d
WHERE e.deptno=d.DEPTNO
select>
mapper>
方法二 association
association:处理多对一关系的属性(处理对象)
设置属性:javatype
找到对应的属性用association进行设置,对属性中的属性使与数据库字段对应

<resultMap id="empAndDeptMap" type="entity.Emp">
<association property="dept" javaType="entity.Dept">
<id column="DEPTNO" property="deptno"/>
<result column="DNAME" property="dname"/>
<result column="LOC" property="loc"/>
association>
resultMap>
一对多
collection:处理一对多关系的属性(处理集合)
设置类型:oftype
模糊分页查询
<select id="findByPage" resultType="entity.Emp">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE ENAME LIKE concat('%',#{aaa.ename},'%') AND JOB LIKE concat('%',#{aaa.job},'%') LIMIT #{bbb},#{ccc}
select>
传入的条件字段名对应不上
解决方式1:加注解@param(设置的参数名)
<select id="selectByPage" resultType="entity.Emp">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE ename LIKE concat('%',#{ename},'%') LIMIT #{page},#{pageSize}
select>
List<Emp> selectByPage(@Param("ename") String name, @Param("page") int page, @Param("pageSize")int pageSize);
解决方式2:把要传的参数装到Map集合中,键是自己拼的#{},值是传进去的参数
@Test
public void t4() throws IOException {
InputStream ra = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory build = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(ra);
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> m = new HashMap<>(16);
m.put("ename","M");
m.put("page",0);
m.put("pageSize",2);
List<Emp> l = mapper.selectByPage2(m);
for (Emp emp : l) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
关于参数
模糊查询和插入记录的时候当传进来的是实体类对象时,xml中查询的参数必须和属性名相同,因为需要借助反射,用名字调用get/set方法往属性里给值。传多个参时要用@param注解起别名,要和xml文件中参数名相同
关于返回值
返回多个时,接口代理里需要用List接收,而xml配置文件中则需要放List泛型里的内容,简言之,xml文件的返回值类型可以是String.Date,Integer.Double,Boolean,实体类本身,绝对不写list
resultType可选值:表示的把数据库的单行记录封装的目标类型:实体对象,简单类型
当只想返回数据库表中的某些字段(实体类部分属性)时,我们可以选择用Map集合来接收,键为字段名,值为数据库取出的值。这种方法也可以处理多表联查的返回数据
<select id="nameMgr" resultType="map">
select ENAME,MGR from emp
select>
List<Map<String,Object>> nameMgr();
增删改
由于mabatis采取事务管理,将自动提交关掉,所以在执行增删改操作时,需要手动commit()
增删改不需要返回值类型,但是可以获得数据库最后一次新增的id号,用到的关键字是useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id",在后台使用这个自增id的方法是通过获得当前对象的id属性
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
INSERT INTO product(id,prod_name,prod_price,prod_store,prod_desc) VALUES(null,#{prodName},#{prodPrice},#{prodStore},#{prodDesc})
insert>
@Test
public void t8() throws IOException {
InputStream ra = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactory build = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(ra);
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession();
ProductMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ProductMapper.class);
Product p = new Product();
p.setProdPrice(400);
p.setProdName("床");
p.setProdStore(20);
p.setProdDesc("好");
System.out.println(mapper.insert(p));
//增删改需要提交
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
System.out.println(p.getId());
sqlSession.close();
}
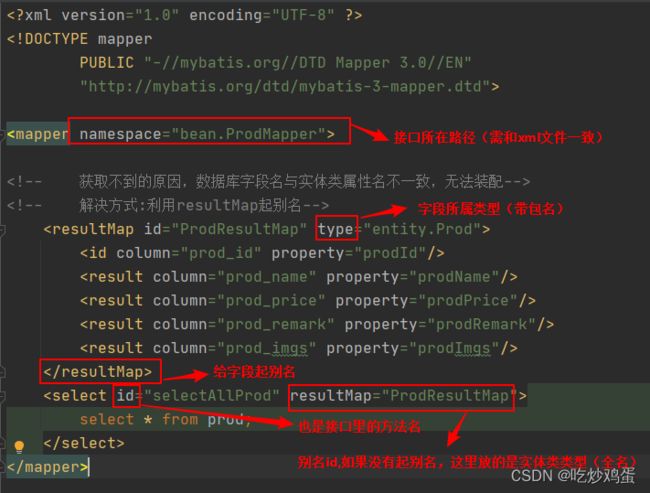
resultMap
将字段名设置为属性名
一对多重新总结
三种方法
1.手动查两次,获得每个员工部门编号,再利用部门编号查询部门信息,最后装配
<select id="getByNo" resultType="entity.Dept">
SELECT * FROM dept WHERE DEPTNO=#{deptno}
select>
<sql id="allfields">
EMPNO,ENAME,JOB,MGR,HIREDATE,SAL,COMM,DEPTNO
sql>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="again">
select
<include refid="allfields">include>
from emp;
select>
@Test
public void t13() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory s = SqlSessionUtil.getS();
SqlSession sqlSession = s.openSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
DeptMapper mapper1 = sqlSession.getMapper(DeptMapper.class);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.selectAll();
for (Emp emp : emps) {
Dept byNo = mapper1.getByNo(emp.getDeptno());
emp.setDept(byNo);
}
emps.forEach(new Consumer<Emp>() {
@Override
public void accept(Emp emp) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
});
sqlSession.close();
}
2.利用标签查,只查一次用户信息,返回的部门编号作为条件直接在标签中进行二次查询
<resultMap id="again" type="entity.Emp">
<id column="EMPNO" property="empno"/>
<result column="ENAME" property="ename"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="entity.Dept" column="DEPTNO" select="dao.DeptMapper.getByNo">
association>
resultMap>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="again">
select
<include refid="allfields">include>
from emp;
select>
@Test
public void t11() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory s = SqlSessionUtil.getS();
SqlSession sqlSession = s.openSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.selectAll();
for (Emp emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
3.直接用sql语句多表联查,查到所有信息,需要在resultMap中用association重新装配属性中的属性,使用这种方法需要在resultMap中映射所有属性和列名,不然返回null值
<resultMap id="fields2" type="entity.Emp">
<id column="EMPNO" property="empno"/>
<result column="ENAME" property="ename"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="entity.Dept">
<result column="DNAME" property="dname"/>
<result column="LOC" property="loc"/>
<result column="DEPTNO" property="deptno"/>
association>
resultMap>
<select id="empAndDept" resultMap="fields2">
SELECT * FROM emp e,dept d WHERE e.DEPTNO=d.DEPTNO
select>
动态sql
自动生成where并忽略紧跟其后的and 或者 or
<select id="findByPage" resultType="entity.Emp">
SELECT * FROM emp
<where>
<if test="ename!=null and ename!=''">
and ENAME LIKE concat('%',#{ename},'%')
if>
<if test="job != null and job != ''">
AND JOB LIKE concat('%',#{job},'%')
if>
where>
select>
条件判断,有test属性;
注意:test条件表达式中的写法与{}完全一致
自动生成set,并会忽略掉最后的逗号
<update id="updateMsg">
# ENAME='SUEY',JOB='SALSMAN' WHERE EMPNO=7500
UPDATE emp
<set>
<if test="ename!=null and ename != ''">
ENAME=#{ename},
if>
<if test="job!=null and job != ''">
JOB=#{job},
if>
set>
where empno=#{empno}
update>
属性:
open:以...开始
close:以...结束
separate:分隔符,以...分隔
item:用来遍历数组/集合的变量名
collection:集合类型,底层实际上是一个Map集合,键是是集合类型,值是集合内容
List: put("list",ids)
Array: put("array",ids);
Collection:put("collection",ids);
@Param put("ids",ids)
批量查询(list)
<select id="selectSomeEmps" resultType="entity.Emp">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE EMPNO IN
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="i">
#{i}
foreach>
select>
批量增加(array)
<insert id="insertEmps">
INSERT INTO emp(EMPNO,ENAME) VALUES
<foreach collection="array" item="i" separator=",">
(#{i.empno},#{i.ename})
foreach>
insert>
批量删除(如果用了注解,那么循环类型就要是注解中的参数名)
<delete id="deleteEmps">
DELETE FROM emp WHERE EMPNO in
<foreach collection="dt" item="i" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{i}
foreach>
delete>
代理模式
静态代理
代理人帮忙做了一点事,也做了一点自己的事,但是总的来说我们做的是一样的事
1.实现同一个接口
2.代理持有被代理对象,在实例化代理的同时把被代理对象当作构造器参数传过去(也可以持有接口,这样代理对象之间可以实现相互嵌套(多态))
3.不需要改动的方法交给被代理对象去做,需要改动的方法,代理人在自己的方法里改(类似套了一个套子)
//接口
public interface Move {
void move();
}
//被代理对象
public class Car implements Move{
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.println("我可以移动");
}
}
//代理人
public class MyProxy implements Move{
Move m;
public MyProxy(Move m) {
this.m = m;
}
@Override
public void move() {
m.move();
System.out.println("我在代理层被默默的修改了");
}
}
//实现类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c = new Car();
MyProxy mp = new MyProxy(c);
mp.move();
}
}