Android RecyclerView源码分析
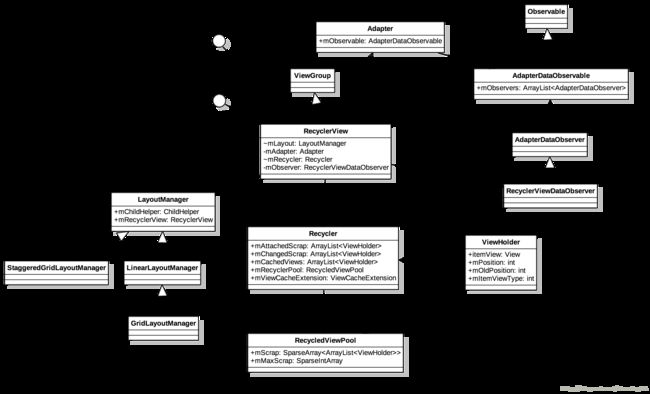
RecyclerView及相关类类图
首先从构造函数开始
public RecyclerView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
......
setScrollContainer(true);
setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
final int version = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
mPostUpdatesOnAnimation = version >= 16;
final ViewConfiguration vc = ViewConfiguration.get(context);
mTouchSlop = vc.getScaledTouchSlop();
mMinFlingVelocity = vc.getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity();
mMaxFlingVelocity = vc.getScaledMaximumFlingVelocity();
setWillNotDraw(getOverScrollMode() == View.OVER_SCROLL_NEVER);
mItemAnimator.setListener(mItemAnimatorListener);
initAdapterManager();
initChildrenHelper();
......
if (attrs != null) {
int defStyleRes = 0;
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.RecyclerView,
defStyle, defStyleRes);
String layoutManagerName = a.getString(R.styleable.RecyclerView_layoutManager);
int descendantFocusability = a.getInt(
R.styleable.RecyclerView_android_descendantFocusability, -1);
if (descendantFocusability == -1) {
setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
}
a.recycle();
createLayoutManager(context, layoutManagerName, attrs, defStyle, defStyleRes);
.....
} else {
setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
}
// Re-set whether nested scrolling is enabled so that it is set on all API levels
setNestedScrollingEnabled(nestedScrollingEnabled);
}其中的initAdapterManager,initChildrenHelper分别初始化了AdapterHelper和ChildHelper。
通过反射创建LayoutManager
private void createLayoutManager(Context context, String className, AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
if (className != null) {
className = className.trim();
if (className.length() != 0) { // Can't use isEmpty since it was added in API 9.
className = getFullClassName(context, className);
try {
ClassLoader classLoader;
if (isInEditMode()) {
// Stupid layoutlib cannot handle simple class loaders.
classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
} else {
classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
}
Class layoutManagerClass =
classLoader.loadClass(className).asSubclass(LayoutManager.class);
Constructorextends LayoutManager> constructor;
Object[] constructorArgs = null;
try {
constructor = layoutManagerClass
.getConstructor(LAYOUT_MANAGER_CONSTRUCTOR_SIGNATURE);
constructorArgs = new Object[]{context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes};
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
try {
constructor = layoutManagerClass.getConstructor();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e1) {
e1.initCause(e);
throw new IllegalStateException(attrs.getPositionDescription() +
": Error creating LayoutManager " + className, e1);
}
}
constructor.setAccessible(true);
setLayoutManager(constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs));
}
......
}
}
}创建完成后会调用setLayoutManager将其赋值给mLayout,并通过mLayout.setRecyclerView(this);与RecyclerView互相引用
public void setLayoutManager(LayoutManager layout) {
if (layout == mLayout) {
return;
}
......
mLayout = layout;
if (layout != null) {
if (layout.mRecyclerView != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("LayoutManager " + layout +
" is already attached to a RecyclerView: " + layout.mRecyclerView);
}
mLayout.setRecyclerView(this);
if (mIsAttached) {
mLayout.dispatchAttachedToWindow(this);
}
}
requestLayout();
}
初始化LayoutManager后,开始重要的一步setAdapter
public void setAdapter(Adapter adapter) {
// bail out if layout is frozen
setLayoutFrozen(false);
setAdapterInternal(adapter, false, true);
requestLayout();
}首先解除frozen状态。
其次通过setAdapterInternal重置mAdapter。
private void setAdapterInternal(Adapter adapter, boolean compatibleWithPrevious,
boolean removeAndRecycleViews) {
if (mAdapter != null) {
mAdapter.unregisterAdapterDataObserver(mObserver);
mAdapter.onDetachedFromRecyclerView(this);
}
......
mAdapterHelper.reset();
final Adapter oldAdapter = mAdapter;
mAdapter = adapter;
if (adapter != null) {
adapter.registerAdapterDataObserver(mObserver);
adapter.onAttachedToRecyclerView(this);
}
if (mLayout != null) {
mLayout.onAdapterChanged(oldAdapter, mAdapter);
}
mRecycler.onAdapterChanged(oldAdapter, mAdapter, compatibleWithPrevious);
mState.mStructureChanged = true;
markKnownViewsInvalid();
}- 取消对mObserver的订阅,并回调onDetachedFromRecyclerView方法
- 清除原有数据
- 重新给mAdapter赋值并订阅mObserver的通知,并调用相应回调
调用requestLayout进行重新布局后setAdapter完成。
Adapter
抽象类Adapter中关联了类型为AdapterDataObservable的对象mObservable,以及定义了抽象方法onCreateViewHolder,onBindViewHolder,getItemCount需子类进行实现。Adapter中的notify系列方法最终将事件转发到mObservable进行回调。
AdapterDataObservable
继承自Observable并实现了用于通知订阅者数据变化的一系列方法,如notifyChanged,notifyItemRangeChanged等.
RecyclerViewDataObserver继承自AdapterDataObservable,当setAdapter时也需将其实例注册到新的Adapter中以监听数据变化。
onViewRecycled(VH holder)
当ViewHolder被回收时调用,在此方法中可用来清理类似Bitmap等对象及时释放内存
register/unregister AdapterDataObserver(AdapterDataObserver observer)
Register/Unregister对于数据变化的监听
ViewHolder
ViewHolder中保存了列表元素的itemView、position等信息并定义了一些列FLAG。
其中的mOwnerRecyclerView变量保存RecyclerView的引用,getAdapterPosition()方法直接从中获取数据。
getAdapterPosition,getLayoutPosition
从注解的说明中可知其差别主要在于从元素添加到Adapter到重新layout之间会有一些偏差
getAdapterPosition获取的是当前holder在Adapter中的position,而getLayoutPosition返回的是当前holder在最后一次布局完成后所处的adapter的位置。
个人理解是getAdapterPosition是获取实时数据,与当前AdapterHelper中的数据相符。而getLayoutPosition是获取mPreLayoutPosition的值,与目前显示相符。大多数情况下使用getLayoutPosition。
Recycler
Recycler用来管理和复用scrapped或detached状态的元素。Recycler的核心工作即为通过多级缓存,存取holder.
Recycler中的缓存分为以下几级:
ArrayList mChangedScrap
ArrayList mAttachedScrap
ArrayList mCachedViews
ViewCacheExtension mViewCacheExtension(optional)
RecycledViewPool mRecyclerPool
Recycler中的getViewForPosition为用来查找指定position对应的View的根方法,查找view的过程其实就是查找ViewHolder的过程。
其中从第二步以后,就需要使用Adapter的getItemViewType方法得到ViewType,并根据type联合查询对应的holder。
各缓存的调用级别如下:
1.如果PreLayout中,查找mChangedScrap中是否含有指定位置的holder
if (mState.isPreLayout()) {
holder = getChangedScrapViewForPosition(position);
fromScrap = holder != null;
}2.从mAttachedScrap、mCachedViews中查找是否有指定位置的holder
if (holder == null) {
holder = getScrapViewForPosition(position, INVALID_TYPE, dryRun);
......
}3.如果设置的了ItemId,依然从mAttachedScrap、mCachedViews中获取数据,通过ItemId和type
if (mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
holder = getScrapViewForId(mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition), type, dryRun);
....
}4.若mViewCacheExtension不为null,通过position和type尝试从其中获取View,并找到对应holder
if (holder == null && mViewCacheExtension != null) {
// We are NOT sending the offsetPosition because LayoutManager does not
// know it.
final View view = mViewCacheExtension
.getViewForPositionAndType(this, position, type);
if (view != null) {
holder = getChildViewHolder(view);
......
}
}5.从RecycledViewPool中根据type查找是否有对应holder
if (holder == null) { // fallback to recycler
......
holder = getRecycledViewPool().getRecycledView(type);
if (holder != null) {
holder.resetInternal();
if (FORCE_INVALIDATE_DISPLAY_LIST) {
invalidateDisplayListInt(holder);
}
}
}6.若当前各级缓存中都没有合适的holder,调用Adapter的createViewHolder进行创建
if (holder == null) {
holder = mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type);
}RecycledViewPool
RecycledViewPool可以通过RecyclerView的setRecycledViewPool(RecycledViewPool)让多个RecyclerView共享同一个RecycledViewPool以达到更好的资源复用
其中保存ViewHolder的方式是通过ViewType与ArrayList一一对应。
即在其中每个ViewType可以存储max个该类型的ViewHolder,max默认为5,也可由用户设置
LayoutManager
LayoutManager负责计算各个View并进行布局,当View的可见状态变化时处理资源的回收和再利用。
系统提供了3个实现类分别为GridLayoutManager,LinearLayoutManager,StaggeredGridLayoutManager。
ItemDecoration
列表元素的装饰类,通过RecyclerView#addItemDecoration(ItemDecoration decor)添加。使用了装饰模式,通过重写onDraw和onDrawOver方法,在Item的绘制前和绘制后添加自定义内容绘制到Canvas上.
RecyclerView中draw,onDraw源码
@Override
public void draw(Canvas c) {
super.draw(c);
final int count = mItemDecorations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mItemDecorations.get(i).onDrawOver(c, this, mState);
}
......
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c) {
super.onDraw(c);
final int count = mItemDecorations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mItemDecorations.get(i).onDraw(c, this, mState);
}
}
总结、优化
RecyclerView通过良好的结构定义实现了高度的可定制化列表。多级缓存以及ViewPool都是可以针对业务优化的点。
- 最基本的多个RecyclerView实例共用一个RecycledViewPool即可一定程度复用已有元素。
- 通过setItemViewCacheSize调整缓存元素的个数,即空间换时间
- 创建自定义ViewCacheExtension,其调用时机在RecycledViewPool之前。