【Leetcode合集】1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
代码仓库地址: https://github.com/slience-me/Leetcode
个人博客 :https://slienceme.xyz
-
给你一棵二叉树,每个节点的值为 1 到 9 。我们称二叉树中的一条路径是 「伪回文」的,当它满足:路径经过的所有节点值的排列中,存在一个回文序列。
请你返回从根到叶子节点的所有路径中 伪回文 路径的数目。
示例 1:
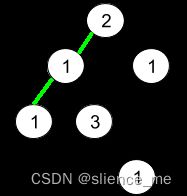
输入:root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1]
输出:2
解释:上图为给定的二叉树。总共有 3 条从根到叶子的路径:红色路径 [2,3,3] ,绿色路径 [2,1,1] 和路径 [2,3,1] 。
在这些路径中,只有红色和绿色的路径是伪回文路径,因为红色路径 [2,3,3] 存在回文排列 [3,2,3] ,绿色路径 [2,1,1] 存在回文排列 [1,2,1] 。
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1]
输出:1
解释:上图为给定二叉树。总共有 3 条从根到叶子的路径:绿色路径 [2,1,1] ,路径 [2,1,3,1] 和路径 [2,1] 。
这些路径中只有绿色路径是伪回文路径,因为 [2,1,1] 存在回文排列 [1,2,1] 。
示例 3:
输入:root = [9]
输出:1
提示:
- 给定二叉树的节点数目在范围 [1, 105]内
1 <= Node.val <= 9
方案1:递归方法
伪回文数:N个对数+1个单数
采用vector给1-9的数字计数,定义变量count
为叶子结点时,判断计数count的各个数字的计数是否满足条件
然后递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countPseudoPalindromic(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &count) {
// 该结点为空则返回0
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
// 值计数+1
count[root->val]++;
// 判定叶子结点
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
// 到达叶子节点时检查路径的伪回文性质
int oddCount = 0; //记录伪路径数
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) {
if (count[i] % 2 != 0) { //存在奇数 233->323(1+0) yes 1232(1+0+1) no
oddCount++;
}
}
count[root->val]--;//返还个数
return oddCount <= 1 ? 1 : 0;//N个对数+1个单数
}
int leftCount = countPseudoPalindromic(root->left, count);
int rightCount = countPseudoPalindromic(root->right, count);
count[root->val]--;
return leftCount + rightCount;
}
int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> count(10, 0); // 存储节点值的出现次数
return countPseudoPalindromic(root, count);
}
};
执行用时分布 268ms 击败93.50%使用 C++ 的用户
消耗内存分布177.11MB 击败32.00%使用 C++ 的用户
方案2:初次优化
代码优化有限,vector变为原生数组,基本没有太大效果
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countPseudoPalindromic(TreeNode *root, int count[]) {
// 该结点为空则返回0
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
// 值计数+1
count[root->val]++;
// 判定叶子结点
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
// 到达叶子节点时检查路径的伪回文性质
int oddCount = 0; //记录伪路径数
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) {
if (count[i] % 2 != 0) { //存在奇数 233->323(1+0) yes 1232(1+0+1) no
oddCount++;
}
}
count[root->val]--;//返还个数
return oddCount <= 1 ? 1 : 0;//N个对数+1个单数
}
int leftCount = countPseudoPalindromic(root->left, count);
int rightCount = countPseudoPalindromic(root->right, count);
count[root->val]--;
return leftCount + rightCount;
}
int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode *root) {
int count[10]= {0};
return countPseudoPalindromic(root, count);
}
};
执行用时分布 260ms 击败98%使用 C++ 的用户
消耗内存分布176.33MB 击败39.50%使用 C++ 的用户
方案3:代码简化
效率没有提高
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void judgement() {
int oddCount = 0; //记录伪路径数
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) { // N个对数+1个单数
if (counts[i] % 2 != 0) { //==1 存在奇数且是3 233->323(1+0) yes 1232(1+0+1) no
oddCount++; //记录单个数的个数
}
}
res+= (oddCount <= 1) ? 1 : 0;//N个对数+1个单数
}
void countPseudoPalindromic(TreeNode *root) {
// 空结点情况
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 叶子结点情况
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
counts[root->val]++; // 值计数+1
judgement();
counts[root->val]--;//返还个数
return;
}
// 普通结点情况
counts[root->val]++;
countPseudoPalindromic(root->left);
countPseudoPalindromic(root->right);
counts[root->val]--;
}
int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode *root) {
counts.resize(10);//修改大小
countPseudoPalindromic(root);
return res;
}
private:
vector<int> counts;
int res=0;
};
执行用时分布 296ms 击败56.50%使用 C++ 的用户
消耗内存分布175.59MB 击败56.00%使用 C++ 的用户