300. Longest Increasing Subsequence 674. Longest Continuous Increasing Subsequence 718. Maximum Len
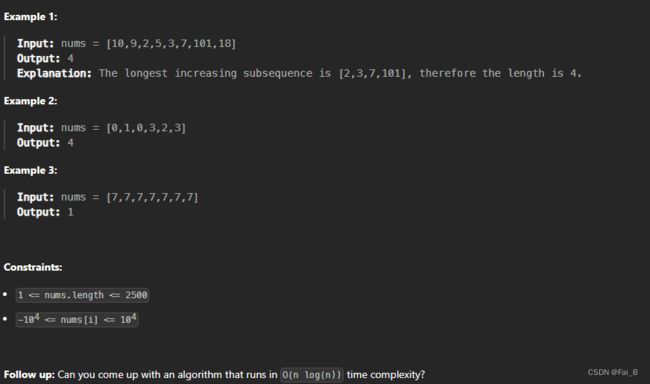
300. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Given an integer array nums, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
dp[i] : the length of the longest increasing subsequence ending in nums[i] before and including i
DP:
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution:
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) <= 1:
return len(nums)
dp = [1] * len(nums)
result = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
for j in range(0, i):
if nums[i] > nums[j]:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
result = max(result, dp[i]) #取长的子序列
return resultgreedy + Dichotomy:
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution:
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) <= 1:
return len(nums)
tails = [nums[0]] # 存储递增子序列的尾部元素
for num in nums[1:]:
if num > tails[-1]:
tails.append(num) # 如果当前元素大于递增子序列的最后一个元素,直接加入到子序列末尾
else:
# 使用二分查找找到当前元素在递增子序列中的位置,并替换对应位置的元素
left, right = 0, len(tails) - 1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if tails[mid] < num:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid
tails[left] = num
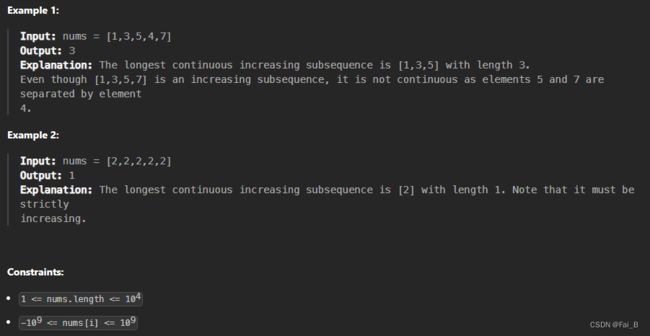
return len(tails) # 返回递增子序列的长度674. Longest Continuous Increasing Subsequence
Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the length of the longest continuous increasing subsequence (i.e. subarray). The subsequence must be strictly increasing.
A continuous increasing subsequence is defined by two indices l and r (l < r) such that it is [nums[l], nums[l + 1], ..., nums[r - 1], nums[r]] and for each l <= i < r, nums[i] < nums[i + 1].
DP:
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution:
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
result = 1
dp = [1] * len(nums)
for i in range(1, len(nums)-1):
if nums[i] > nums[i - 1]: #连续记录
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1
result = max(result, dp[i])
return result # max(dp)greedy:
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution:
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
result = 1 #连续子序列最少也是1
count = 1
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录
count += 1
else: #不连续,count从头开始
count = 1
result = max(result, count)
return result718. Maximum Length of Repeated Subarray
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return the maximum length of a subarray that appears in both arrays.
1. dp[i][j] : A ended by subscript i - 1, and B ended by subscript j - 1, with the length of the longest repeating subarray being dp[i][j].
2. When A[i - 1] and B[j - 1] are equal dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
3. Note the size of the array and the boundaries of the loop
2-dimensional DP:
Time complexity: O(m x n)
Space complexity: O(m x n)
class Solution:
def findLength(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [[0] * (len(nums2) + 1) for _ in range(len(nums1) + 1)] #cuz dp[i][j] corresponds to nums1[i - 1]&nums2[j - 1]
result = 0
for i in range(1, len(nums1) + 1):
for j in range(1, len(nums2) + 1):
if nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
if dp[i][j] > result: #do not using max(result, dp[i][j]), it takes too long
result = dp[i][j]
return result1-dimensional DP:
Time complexity: O(m x n)
Space complexity: O(m)
class Solution:
def findLength(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
# 创建一个一维数组 dp,用于存储最长公共子数组的长度
dp = [0] * (len(nums2) + 1)
# 记录最长公共子数组的长度
result = 0
# 遍历数组 nums1
for i in range(1, len(nums1) + 1):
# 用于保存上一个位置的值
prev = 0
# 遍历数组 nums2
for j in range(1, len(nums2) + 1):
# 保存当前位置的值,因为会在后面被更新
current = dp[j]
# 如果 nums1[i-1] 和 nums2[j-1] 相等
if nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]:
# 在当前位置上的最长公共子数组长度为上一个位置的长度加一
dp[j] = prev + 1
# 更新最长公共子数组的长度
if dp[j] > result:
result = dp[j]
else:
# 如果不相等,将当前位置的值置为零
dp[j] = 0
# 更新 prev 变量为当前位置的值,供下一次迭代使用
prev = current
# 返回最长公共子数组的长度
return result