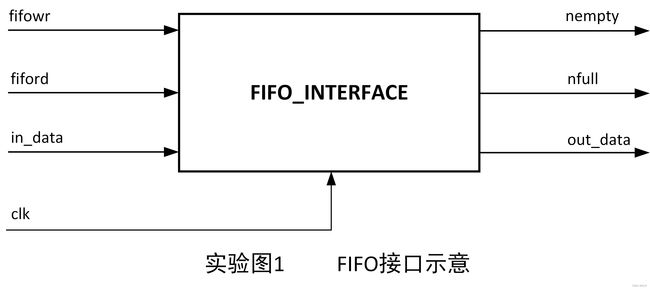
练习十二:利用SRAM设计一个FIFO
利用SRAM设计一个FIFO
-
-
- 1,任务目的
- 2,设计要求
- 3,FIFO接口的设计思路
- 4,FIFO接口的测试,top.v
- 5,FIFO接口的参考设计,fifo_interface.v
- 6,SRAM模型,sram.v代码
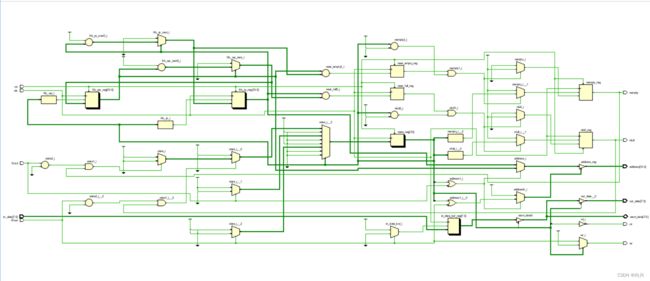
- 7,vivado生成的RTL原理图
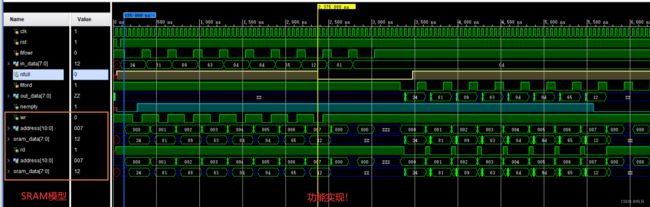
- 8,波形图
-
- 8.1,波形全图
- 8.2,波形细化
- 9,
-
1,任务目的
(1)学习和掌握存取队列管理的状态机设计的基本方法;
(2)了解并掌握用存储器构成FIFO的接口设计的基本技术;
(3)用工程概念来编写完整的测试模块,达到完整测试覆盖;
在本练习中,要求利用练习十一中提供的SRAM模型,设计SRAM读写控制逻辑,使SRAM的行为对用户表现为一个FIFO(先进先出存储器)。
2,设计要求
本练习要求同学设计的FIFO 是
同步FIFO,即对FIFO的读/写使用同一个时钟。该FIFO应当提供用户读使能(fiford)和写使能(fifowr)输入控制信号,并输出指示FIFO状态的非空(nempty)和非满(nfull)信号,FIFO的输入、输出数据使用各自的数据总线:in_data和out_data。
3,FIFO接口的设计思路
4,FIFO接口的测试,top.v
在完成一个设计后,需要进行测试以确认设计的正确性和完整性。而要进行测试,就需要编写测试激励和结果检查程序,即测试平台(testbench)。在某些情况下,如果设计的接口能够预先确定,测试平台的编写也可以在设计完成之前就进行,
这样做的好处:在设计测试平台的同时也在更进一步深入了解设计要求,有助于理清设计思路,及时发现设计方案的错误。
编写测试激励时,除了注意对实际可能存在的各种情况的覆盖外,还要有意针对非正常情况下的操作进行测试。在本练习中,就应当进行在FIFO读空后继续读取,FIFO写满后继续写入和FIFO复位后马上读取等操作的测试。
测试激励中通常会有一些复杂操作需要反复进行,如本练习中对FIFO的读写操作。这时可以将这些复杂操作纳入到几个task中,即减少了激励编写的工作量,也使得程序的可读性更好。
下面的测试程序作为一个参考,先用这段程序测试所设计的FIFO接口,然后编写更全面的测试程序。
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 2023/12/04 16:18:41
// Design Name:
// Module Name: test_fifo
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool Versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
// 测试信号
`define FIFO_SIZE 8
// `include "sram.v" // 所有的仿真工具不需要加这句,只要 sram.v 模块编译就可以了
`timescale 1ns/ 1ns
module test_fifo;
reg [7:0] in_data; // FIFO 数据总线
reg fiford, fifowr; // FIFO 控制信号
wire [7:0] out_data;
wire nfull, nempty; // FIFO 状态信号
reg clk, rst;
wire [7:0] sram_data; // SRAM 数据总线
wire [10:0] address; // SRAM 地址总线
wire rd, wr; // SRAM 读写控制信号
reg [7:0] data_buf [`FIFO_SIZE:0]; // 数据缓存,用于结果检查
integer index;
// 系统时钟
initial clk = 0;
always #25 clk = ~clk;
// 测试激励序列
initial begin
fiford = 1;
fifowr = 1;
rst = 1;
#40 rst = 0;
#42 rst = 1;
if(nempty) $display($time, "Error: FIFO be empty, nempty should be low. \n");
// 连续写 FIFO
index = 0;
repeat(`FIFO_SIZE) begin
data_buf[index] = $random;
write_fifo(data_buf[index]);
index = index + 1;
end
if(nfull) $display($time, "Error: FIFO full, nfull should be low. \n");
repeat(2) write_fifo($random);
#200
// 连续读FIFO
index = 0;
read_fifo_compare(data_buf[index]);
if(~nfull) $display($time, "Error: FIFO not full, nfull should be high. \n");
repeat(`FIFO_SIZE - 1) begin
index = index + 1;
read_fifo_compare(data_buf[index]);
end
if(nempty) $display($time, "Error: FIFO be empty, nempty should be low. \n");
repeat(2) read_fifo_compare(8'bx);
reset_fifo;
// 写后续 FIFO
repeat(`FIFO_SIZE * 2) begin
data_buf[0] = $random;
write_fifo(data_buf[0]);
read_fifo_compare(data_buf[0]);
end
// 异常操作
reset_fifo;
read_fifo_compare(8'bx);
write_fifo(data_buf[0]);
read_fifo_compare(data_buf[0]);
$stop;
end
fifo_interface fifo_mk(
.in_data (in_data ),
.out_data (out_data ),
.fiford (fiford ),
.fifowr (fifowr ),
.nfull (nfull ),
.nempty (nempty ),
.address (address ),
.sram_data (sram_data ),
.rd (rd ),
.wr (wr ),
.clk (clk ),
.rst (rst )
);
sram m1(
.Address (address ),
.Data (sram_data ),
.SRG (rd ), // SRAM 读使能
.SRE (1'b0 ), // SRAM 片选,低有效
.SRW (wr ) // SRAM 写使能
);
task write_fifo;
input [7:0] data;
begin
in_data = data;
#50 fifowr = 0; // 往 SRAM 中写数
#200 fifowr = 1;
#50;
end
endtask
task read_fifo_compare;
input [7:0] data;
begin
#50 fiford = 0; // 从 SRAM 中读数
#200 fiford = 1;
if(out_data != data)
$display($time, "Error: Data retrieved (%h) not match the one stored(%h) .\n", out_data, data);
#50;
end
endtask
task reset_fifo;
begin
#40 rst = 0;
#40 rst = 1;
end
endtask
endmodule
5,FIFO接口的参考设计,fifo_interface.v
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 2023/12/04 16:14:09
// Design Name:
// Module Name: fifo_interface
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool Versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
// FIFO接口的参考设计
`define SRAM_SIZE 8 // 为减少对 FIFO 控制器的测试工作量,置 SRAM 空间为 8 字节
// `timescale 1ns/ 1ns
module fifo_interface(
in_data, // 用户的输入数据总线
out_data, // 用户的输出数据总线
fiford, // FIFO读控制信号,低电平有效
fifowr, // FIFO写控制信号,低电平有效
nfull, //
nempty, //
address, // 到 SRAM 的地址总线
sram_data, // 到 SRAM 的双向数据总线
rd, // SRAM 读使能,低电平有效
wr, // SRAM 写使能,低电平有效
clk, // 系统时钟信号
rst // 全局复位信号,低电平有效
);
// 来自用户的控制输入信号
input fiford, fifowr, clk, rst;
// 来自用户的数据信号
input [7:0] in_data;
output [7:0] out_data;
reg [7:0] in_data_buf; // 输入数据缓冲区
reg [7:0] out_data_buf; // 输出数据缓冲区
// 输出到用户的状态指示信号
output nfull, nempty;
reg nfull, nempty;
// 输出到 SRAM 的控制信号
output rd, wr;
// 到 SRAM 的双向数据总线
inout [7:0] sram_data;
// 输出到 SRAM 的地址总线
output [10:0] address;
reg [10:0] address;
// internal register
reg [10:0] fifo_wp; // FIFO写指针
reg [10:0] fifo_rp; // FIFO读指针
reg [10:0] fifo_wp_next; // fifo_wp 的下一个值
reg [10:0] fifo_rp_next; // fifo_rp 的下一个值
reg near_full, near_empty;
reg [3:0] state; // SRAM 操作状态机寄存器
parameter idle = 4'b0000;
parameter read_ready = 4'b0100;
parameter read = 4'b0101;
parameter read_over = 4'b0111;
parameter write_ready = 4'b1000;
parameter write = 4'b1001;
parameter write_over = 4'b1011;
// SRAM 操作状态机
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
state <= idle;
else
case(state)
idle: // 等待 FIFO 的操作控制信号
if(fifowr == 0 && nfull) // 用户发出写 FIFO 申请,且 FIFO 未满
state <= write_ready;
else if(fiford == 0 && nempty) // 用户发出读 FIFO 申请,且 FIFO 未空
state <= read_ready;
else
state <= idle; // 没有对 FIFO 操作的申请
read_ready: // 建立 SRAM 操作所需地址和数据
state <= read;
read: // 等待用户结束当前读操作
if(fiford == 1)
state <= read_over;
else
state <= read;
read_over: // 继续给出 SRAM 地址以保证数据稳定
state <= idle;
write_ready: // 建立 SRAM 操作所需地址和数据
state <= write;
write: // 等待用户结束当前写操作
if(fifowr == 1)
state <= write_over;
else
state <= write;
write_over: // 继续给出 SRAM 地址和写入数据以保证数据稳定
state <= idle;
default:
state <= idle;
endcase
// 产生 SRAM 操作相关信号
assign rd = ~state[2]; // state 为 read_ready 或 read 或 read_over
assign wr = (state == write) ? fifowr : 1'b1;
always@(posedge clk)
if(~fifowr)
in_data_buf <= in_data;
assign sram_data = (state[3])? in_data_buf : 8'hzz;
// state 为 write_ready 或 write 或 write_over
always@(state or fiford or fifowr or fifo_wp or fifo_rp)
if(state[2] || ~fiford)
address = fifo_rp;
else if(state[3] || ~fifowr)
address = fifo_wp;
else
address = 'bz;
// 产生 FIFO 数据
assign out_data = (state[2]) ? sram_data : 8'bz;
always@(posedge clk)
if(state == read)
out_data_buf <= sram_data;
// 计算 FIFO 读写指针
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
fifo_rp <= 0;
else if(state == read_over)
fifo_rp <= fifo_rp_next;
always@(fifo_rp)
if(fifo_rp == `SRAM_SIZE - 1)
fifo_rp_next = 0;
else
fifo_rp_next = fifo_rp + 1;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
fifo_wp <= 0;
else if(state == write_over)
fifo_wp <= fifo_wp_next;
always@(fifo_wp)
if(fifo_wp == `SRAM_SIZE - 1)
fifo_wp_next = 0;
else
fifo_wp_next = fifo_wp + 1;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
near_empty <= 1'b0;
else if(fifo_wp == fifo_rp_next)
near_empty <= 1'b1;
else
near_empty <= 1'b0;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
nempty <= 1'b0;
else if(near_empty && state == read)
nempty <= 1'b0;
else if(state == write)
nempty <= 1'b1;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
near_full <= 1'b0;
else if(fifo_rp == fifo_wp_next)
near_full <= 1'b1;
else
near_full <= 1'b0;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(~rst)
nfull <= 1'b1;
else if(near_full && state == write)
nfull <= 1'b0;
else if(state == read)
nfull <= 1'b1;
// // 调用 SRAM
// sram m1(
// .Address (address ),
// .Data (sram_data ),
// .SRG (rd ), // SRAM 读使能
// .SRE (1'b0 ), // SRAM 片选,低有效
// .SRW (wr ) // SRAM 写使能
// );
endmodule
6,SRAM模型,sram.v代码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 2023/12/04 16:18:04
// Design Name:
// Module Name: sram
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool Versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 2023/12/01 17:38:38
// Design Name:
// Module Name: sram
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool Versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
/* sram is Verilog HDL model for HM - 65162, 2K*8 bit Asynchronous(异步) CMOS
Static RAM. It is used in simulation to substitute the real RAM to verify whether
the writing or reading of the RAM is OK.
This module is a behavioral model for simulation only, not synthesizable. It's
writing and reading function are verified.
*/
module sram(
Address, Data, SRG, SRE, SRW
);
input [10:0] Address;
input SRG; // output enable
input SRE; // chip enable
input SRW; // write enable
inout [7:0] Data; // Bus
wire [10:0] Addr = Address;
reg [7:0] RdData;
reg [7:0] SramMem [0:'h7ff];
reg RdSramDly, RdFlip;
wire [7:0] FlpData;
wire [7:0] Data;
reg WR_flag; // to judge the signals according to the specification of
// HM-65162
integer i;
wire RdSram = ~SRG & ~SRE;
wire WrSram = ~SRW & ~SRE;
reg [10:0] DelayAddr;
reg [7:0] DelayData;
reg WrSramDly;
integer file;
assign FlpData = (RdFlip) ? ~RdData : RdData;
assign Data = (RdSramDly) ? FlpData : 'hz;
/*
parameters of read circle
*/
// 参数序号、最大或最小、参数含义
parameter TAVQV = 90, // 2, max, address access time
TELQV = 90, // 3, max, chip enable access time
TELQX = 5, // 4, min, chip enable output enable time
TGLQV = 65, // 5, max, output enable access tiem
TGLQX = 5, // 6, min, output enable output enable time
TEHQZ = 50, // 7, max, chip enable output disable time
TGHQZ = 40, // 8, max, output enable output disable time
TAVQX = 5; // 9, min, output hold from address change
parameter TAVWL = 10, // 12, min, address setup time
TWLWH = 55, // 13, min, chip enable pulse setup time,
// write enable pluse width,
TWHAX = 15, // 14, min10, write enable read setup time,
// 读上升沿后地址保留时间
TWLQZ = 50, // 16, max, write enable output disable time
TDVWH = 30, // 17, min, data setup time
TWHDX = 20, // 18, min15, data hold time
TWHQX = 20, // 19, min0, write enable output enable time, 0
TWLEH = 55, // 20, min, write enable pulse setup time
TDVEH = 30, // 21, min, chip enable data setup time
TAVWH = 70; // 22, min65, address valid to end of write
initial begin
file = $fopen("ramlow.txt");
if(!file) begin
$display("Could not open the file.");
$stop;
end
end
initial begin
for(i = 0; i < 'h7ff; i = i + 1)
SramMem[i] = i;
// monitor($time, "DelayAddr = %h, DelayData = %h", DelayAddr, DelayData);
end
initial RdSramDly = 0;
initial WR_flag = 1;
// READ CIRCLE
always@(posedge RdSram) #TGLQX RdSramDly = RdSram;
always@(posedge SRW) #TWHQX RdSramDly = RdSram;
always@(Addr) begin
#TAVQX;
RdFlip = 1;
#(TGLQV - TAVQX); // address access time
if(RdSram)
RdFlip = 0;
end
always@(posedge RdSram) begin
RdFlip = 1;
#TAVQV; // output enable access time
if(RdSram)
RdFlip = 0;
end
always@(Addr) #TAVQX RdFlip = 1;
always@(posedge SRG) #TEHQZ RdSramDly = RdSram;
always@(posedge SRE) #TGHQZ RdSramDly = RdSram;
always@(negedge SRW) #TWLQZ RdSramDly = 0;
always@(negedge WrSramDly or posedge RdSramDly) RdData = SramMem[Addr];
// WRITE CIRCLE
always@(Addr) #TAVWL DelayAddr = Addr; // Address setup
always@(Data) #TDVWH DelayData = Data; // Data setup
always@(WrSram) #5 WrSramDly = WrSram;
always@(Addr or Data or WrSram) WR_flag = 1;
always@(negedge SRW) begin
#TWLWH; // Write enable pulse width
if(SRW) begin
WR_flag = 0;
$display("ERROR! Can't write! Write enable time(W) is too short!");
end
end
always@(negedge SRW) begin
#TWLEH; // Write enable pulse setup time
if(SRE) begin
WR_flag = 0;
$display("ERROR! Can't write! write enable pulse setup time(E) is too short!");
end
end
always@(posedge SRW) begin
#TWHAX; // Write enable read setup time
if(DelayAddr !== Addr) begin
WR_flag = 0;
$display("ERROR! Can't write! Write enable read setup time is too short!");
end
end
always@(Data)
if(WrSram) begin
#TDVEH; // chip enable data setup time
if(SRE) begin
WR_flag = 0;
$display("ERROR! Can't write! chip enable data setup time is too short!");
end
end
always@(Data)
if(WrSram) begin
#TDVEH;
if(SRW) begin
WR_flag = 0;
$display("ERROR! Can't write! chip enable data setup time is too short!");
end
end
always@(posedge SRW) begin
#TWHDX; // Data hold time
if(DelayData !== Data)
$display("Warning! Data hold time is too short!");
end
always@(DelayAddr or DelayData or WrSramDly)
if(WrSram && WR_flag) begin
if(!Addr[5]) begin
#15 SramMem[Addr] = Data;
// $display("mem[%h] = %h", Addr, Data);
$fwrite(file, "mem[%h] = %h", Addr, Data);
if(Addr[0] && Addr[1]) $fwrite(file, "\n");
end
else begin
$fclose(file);
$display("Please check the txt.");
$stop;
end
end
endmodule