Retrofit中的注解
一、Retrofit中的注解有那些?
- 方法注解:@GET ,@POST,@PUT,@DELETE,@PATH,@HEAD,@OPTIONS,@HTTP
- 标记注解:@FormUrlEncoded,@Multpart,@Streaming
- 参数注解:@Query,@QueryMap,@Body,@Field,@FieldMap,@Part,@PartMap
- 其他注解:@path,@Header,@Headers,@Uri
二、了解方法注解@HTTP
@HTTP注解的作用是可以让我们自己自定义这次接口的请求方式。
@HTTP(method = "GET", path = "get", hasBody = false)
@FormUrlEncoded
Call http(@Field("userName") String userName, @Field("password") String pwd); 参数method:使用http注解时必须要指定method,method如果是POST就会执行http方法执行post请求,method如果指定GET就会执行http方法执行get请求。
参数书path:指定path,就需要把指定请求的接口的地址传入
参数hasBody:指定hasBody,就是请求体。post请求有请求体就指定hasBody = true。get请求没有请求体就指定haBody = false。
三、了解参数注解@Body
使用@Body注解在接口类对象中的定义
@POST("post")
Call postBody(@Body RequestBody body);//自己指定requestBody 测试代码
public class AnnotationUnitTest {
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl("http://www.httpbin.org/").build();//创建retrofit对象
HttpbinService httpbinService = retrofit.create(HttpbinService.class);//创建接口类对象,并且设置为全局变量。
@Test
public void bodyTest()throws IOException {
FormBody formBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("a", "1").add("b", "2").build();
Response response = httpbinService.postBody(formBody).execute();
System.out.println(response.body().string());
}
} 测试结果
四、其他注解中的@path注解
在接口类对象中的使用
@POST("{id}")
Call pathInPath(@Path("id") String path);//@path注解作用于参数部分,意思是id=path帮我们替换掉@POST注解里面的参数 @path注解作用于参数部分,意思是{id}里面是id会被@path中的id替换掉替换成参数path
测试代码:
@Test
public void pathTest() throws IOException {
//实际上请求到的是https://www。httpbin.org/post
Response response = httpbinService.pathInPath("post").execute();
System.out.println(response.body().string());
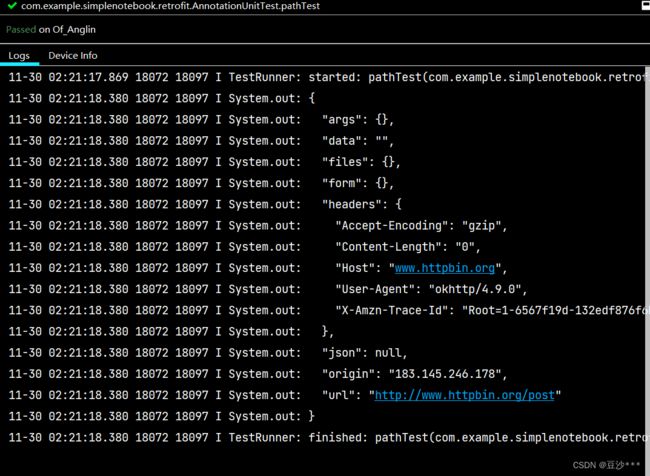
} 测试结果:
可以看到请求的url是http://www.httpbin.org/post,使用的是post请求
五、那么我们尝试使用@path注解调用post请求,并且传递用户名和密码两个参数
在接口类对象中的使用
@POST("{id}")
@FormUrlEncoded
Call pathInPath(@Path("id") String path,@Field("userName") String userName, @Field("password") String pwd);//@path注解作用于参数部分,意思是id=path帮我们替换掉@POST注解里面的参数
测试代码
@Test
public void pathTest() throws IOException {
//实际上请求到的是https://www。httpbin.org/post
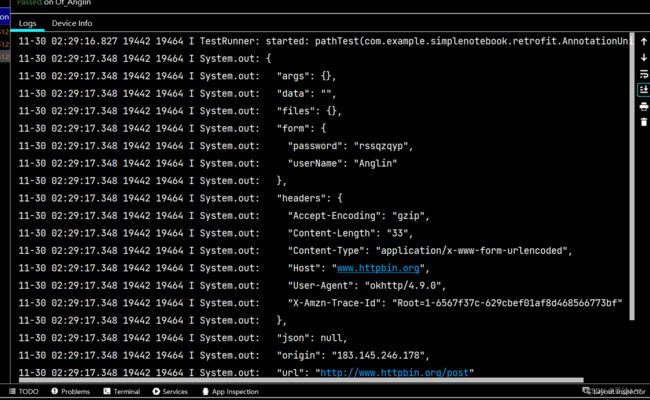
Response response = httpbinService.pathInPath("post","Anglin","rssqzqyp").execute();
System.out.println(response.body().string());
} 测试结果
六、其他注解中的@Header注解
@Header是用来设置请求头的
在接口类对象中的使用
@POST("{id}")
@FormUrlEncoded
Call pathInPath(@Path("id") String path, @Header("os")String os, @Field("userName") String userName, @Field("password") String pwd);//@path注解作用于参数部分,意思是id=path帮我们替换掉@POST注解里面的参数
测试代码
@Test
public void pathTest() throws IOException {
//实际上请求到的是https://www。httpbin.org/post
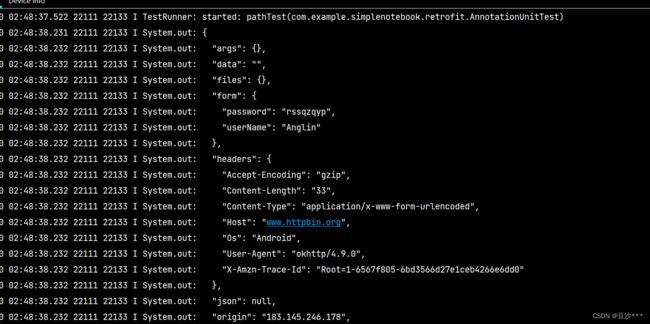
Response response = httpbinService.pathInPath("post","Android","Anglin","rssqzqyp").execute();
System.out.println(response.body().string());
} 运行结果
七、其他注解中的@Headers注解
@Headers是添加多个请求头或者写一个请求头都可以,写多个要用花括号{}
在接口类对象中的使用
@Headers({"os:amdroid","version:1.0"})
@POST("post")
Call postWithHeaders(); 测试代码
@Test
public void headersTest() throws IOException {
Call reponse = httpbinService.postWithHeaders();
System.out.println(reponse.execute().body().string());
} 测试结果
可以看到我们已经成功添加了请求头平台和版本号。
八、其他注解中的@Url
@url注解作用于参数中,作用是指定完整的http地址,不像之前的注解还要自己进行拼接。
在接口类对象中的使用
@POST
Call postUrl(@Url String url); 测试代码
@Test
public void urlTest() throws IOException {
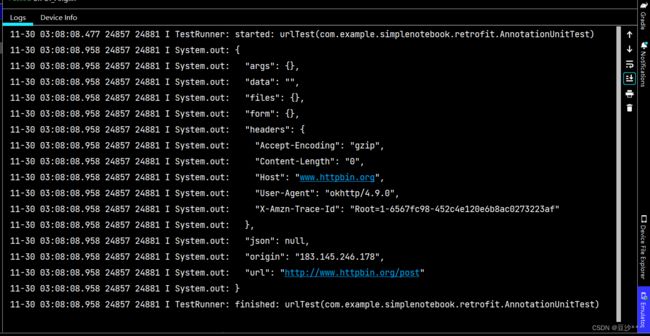
Response response = httpbinService.postUrl("http://www.httpbin.org/post").execute();
System.out.println(response.body().string());
} 测试结果