Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Problem
Given the head of a linked list, reverse the nodes of the list k at a time, and return the modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
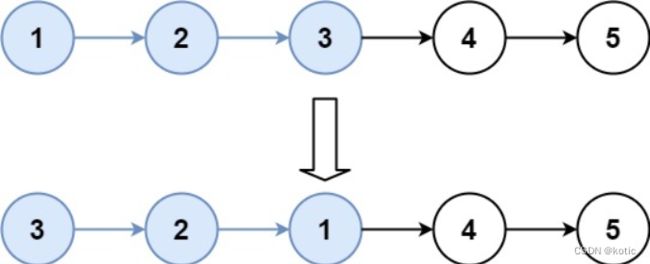
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Intuition
The goal is to reverse the nodes of the linked list in groups of size k. We need to keep track of the start and end of each group and reverse the nodes within each group. The challenge is to handle the edge case when the number of remaining nodes is less than k, in which case those nodes should be left as they are.
Approach
- Initialization: Set pointers
current,end,he(head), andguardto the head of the linked list. - Loop through the Linked List:
- Use a loop to iterate through the linked list in groups of size
k. - Update the
endpointer to thek-th node in the current group.
- Use a loop to iterate through the linked list in groups of size
- Reverse Nodes within Group:
- Reverse the nodes within the identified group using the
prevpointer. - Update the
prev,current, andnxtpointers accordingly.
- Reverse the nodes within the identified group using the
- Update Pointers:
- Update pointers to maintain connections between reversed groups:
- If it's the first reversed group (
countloop == 1), update the head of the linked list (head = current). - Otherwise, connect the reversed group to the previous group using the
guard.nextpointer. - Update the
guardpointer to the end of the reversed group.
- If it's the first reversed group (
- Reset
prev,current,end, andhepointers for the next iteration.
- Update pointers to maintain connections between reversed groups:
- Continue Until End:
- Continue the loop until the end of the linked list is reached.
Complexity
- Time complexity:
The time complexity of this solution is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. In each iteration of the loop, we reverse a group of size k, and we traverse each node exactly once.
- Space complexity:
The space complexity is O(1) since we are using a constant amount of extra space, regardless of the size of the input linked list. We are not using any additional data structures that scale with the input size.
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
count, countloop = 1, 0
current = end = he = guard = head
if k == 1:
return head
while end:
if count < k:
end = end.next
count += 1
else:
count = 1
prev = None
while current != end:
nxt = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = nxt
countloop += 1
if countloop == 1:
head = current
nxt = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = nxt
end = nxt
he.next = current
he = current
else:
nxt = current.next
current.next = prev
guard.next = current
while guard.next:
guard = guard.next
prev = None
current = nxt
end = nxt
he.next = current
he = current
return head