力扣 437. 路径总和 III(中等)
题目
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 targetSum ,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于 targetSum 的 路径 的数目。
路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
示例 1:
 、
、
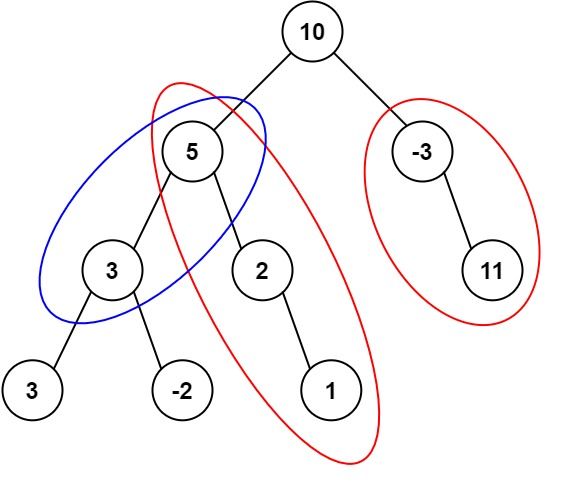
输入:root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8
输出:3
解释:和等于 8 的路径有 3 条,如图所示。
示例 2:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:3
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [0,1000]
- − 1 0 9 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1 0 9 -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9 −109<=Node.val<=109
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
题解
方法一:深度优先搜索
首先拿到题目肯定要想到这题目要用到深度优先搜索来计算路径和,那么首先想到的解法就是穷举每一个节点作为根节点,来计算根节点往下的路径和。递归遍历每一个节点的所有可能的路径,然后将这些路径数目加起来即为返回结果。
那么这里有两种方法:双重递归或者层序遍历+递归。
(1)自己写的层序遍历+递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int res = 0;
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cnt = queue.poll();
res += dfs(cnt, targetSum);
if(cnt.left != null) queue.offer(cnt.left);
if(cnt.right != null) queue.offer(cnt.right);
}
return res;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
int res = 0;
if(root != null){
if(root.val == targetSum) res++; // 如果符合要求 res++
res += dfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val);
res += dfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
return res;
}
}
(2)双重递归
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int res = rootSum(root, targetSum);
res += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);
res += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
return res;
}
public int rootSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
int res = 0;
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.val == targetSum) res++;
res += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val);
res += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
return res;
}
}
方法二: 前缀和
定义节点的前缀和为:由根结点到当前结点的路径上所有节点的和。
使用哈希表来存储当前路径上的前缀和的数量。
利用前缀和只需遍历一次二叉树即可,时间复杂度为O(N)。
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> prefix = new HashMap<>();
prefix.put(0, 1);
return dfs(root, prefix, 0, targetSum);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, Map<Integer, Integer> prefix, int curr, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ret = 0;
curr += root.val;
ret = prefix.getOrDefault(curr - targetSum, 0);
prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) + 1);
ret += dfs(root.left, prefix, curr, targetSum);
ret += dfs(root.right, prefix, curr, targetSum);
prefix.put(curr, prefix.getOrDefault(curr, 0) - 1);
return ret;
}
}