javascript实现Stack(栈)数据结构
上一篇文章我们理解了List这种数据结构,知道了它的特点和一些使用场景,这篇文章我们就来看一下栈这种数据结构,这里的栈可不是客栈哦,哈哈
栈其实和List非常像,使用javascript实现都是基于数组来实现
尝试理解Stack
1.栈只能在栈顶进行入栈和出栈( 我们可以尝试把栈想象成一个瓶子,瓶子只有一个瓶口,所有的东西都只能从瓶口塞进去,丛瓶口拿出来)
2. 栈是一种后进先出的数据结构(LIFO,last-in-first-out)(最后塞进瓶子的东西一定最先从瓶子里面拿出来)
3. 栈也有自己的属性和方法(瓶子里面可以塞很多东西,我们也可以取出瓶子里的东西,或清空整个瓶子)
代码实现
function Stack () {
// 当前栈的数据
this.data = [];
// 栈顶位置
this.top = 0
// 向栈中压入一个元素
this.push = function (elem) {
this.data[this.top++] = elem
}
// 从栈中弹出(删除)栈顶元素并返回
this.pop = function() {
return this.data[--this.top]
}
// 仅返回栈顶元素,不删除
this.peek = function() {
return this.data[this.top-1]
}
// 返回栈中的元素个数
this.length = function() {
return this.top
}
// 清空栈
this.clear = function() {
this.top = 0
}
}
测试一下
const s = new Stack();
s.push("David");
s.push("Raymond");
s.push("Bryan");
console.log('当前栈长度length:', s.length());
console.log('当前栈顶元素为:', s.peek());
const popped = s.pop()
console.log('被弹出的栈顶元素为:', popped);
console.log('当前栈顶元素为:', s.peek());
s.push("Cynthia");
console.log('当前栈顶元素为:', s.peek());
s.clear()
console.log('执行了清空栈');
console.log('当前栈长度length:', s.length());
console.log('当前栈顶元素为:', s.peek());
s.push("Clayton");
console.log('当前栈顶元素为:', s.peek());
实际应用
- 进制转换
/**
* 进制转换
* @param num
* @param base
*/
function mulBase(num, base) {
const s = new Stack()
do {
s.push(num%base)
num = Math.floor(num/base)
} while (num > 0)
let converted = ''
while(s.length() > 0) {
converted += s.pop()
}
return converted
}
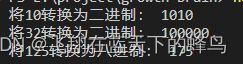
console.log('将10转换为二进制:', mulBase(10, 2))
console.log('将32转换为二进制:', mulBase(32, 2))
console.log('将125转换为八进制:', mulBase(125, 8))
/**
* 判断一个字符串是否回文字符串
* @param word 需要判断的字符串
*/
function isPalindrome(word) {
const s = new Stack()
for(let i = 0; i < word.length; i ++) {
s.push(word[i])
}
let rword = ''
while(s.length() > 0) {
rword += s.pop()
}
if(word === rword) return true
return false
}
const word = "hello";
if (isPalindrome(word)) {
console.log(word + " 是回文字符串");
}
else {
console.log(word + " 不是回文字符串");
}
const word1 = "racecar"
if (isPalindrome(word1)) {
console.log(word1 + " 是回文字符串");
}
else {
console.log(word1 + " 不是回文字符串");
}
/**
* 使用栈模拟递归过程,返回n的阶乘 n!
* @param n
* @returns
*/
function fact(n) {
const s = new Stack()
while (n > 1) {
s.push(n--)
}
let product = 1
while(s.length() > 0) {
product *= s.pop()
}
return product
}
console.log('5的阶乘为:', fact(5))
- 表达式括号匹配问题
/**
* 计算某个表达式中的括号是否匹配
* @param str 表达式
* @returns 匹配情况
*/
function isMatch (str) {
const match = {
match: true,
position: -1
}
const left = new Stack()
const right = new Stack()
const ml = ['(', '[', '{']
const mr = [ ')', ']', '}']
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i ++) {
if (ml.includes(str[i])) {
left.push({
value: str[i],
position: i
})
}
if (mr.includes(str[i])) {
right.push({
value: str[i],
position: i
})
}
}
while (left.length() || right.length()) {
const l = left.pop()
const r = right.pop()
let index
if (l) index = ml.findIndex((item) => item === l.value)
else index = mr.findIndex((item) => item === r.value)
if (mr[index] !== r?.value || ml[index] !== l?.value) {
match.match = false
match.position = l ? l.position : r.positon
return match
}
}
return match
}
const string = '2.3 + 23/12 + (3.14159 * 0.24'
if (!isMatch(string).match) {
console.log(`表达式${string}括号不匹配,不匹配位置为:`, isMatch(string).position)
} else {
console.log(`表达式${string}括号匹配成功`)
}
const string1 = '({ab}(c)ccc['
if (!isMatch(string1).match) {
console.log(`表达式${string1}括号不匹配,不匹配位置为:`, isMatch(string1).position)
} else {
console.log(`表达式${string1}括号匹配成功`)
}
![]()
好了,文章就到这里了,大家如果想了解更多就去看《数据结构与算法javascript描述》这本书吧,希望大家都能有所收获~