Spring中的AOP(理解、在事务中的应用)
Spring中的AOP
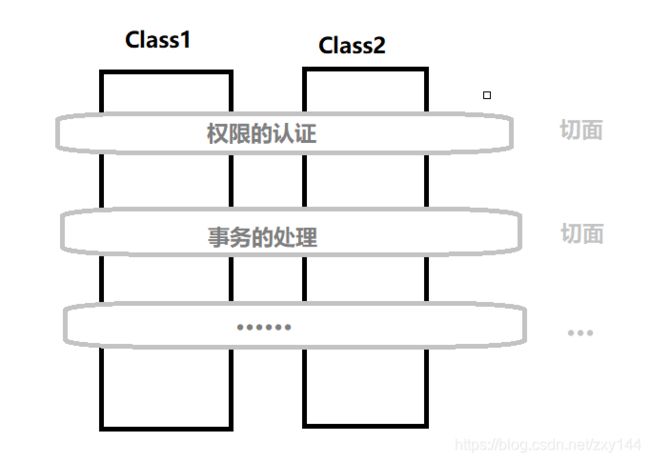
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程。
通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术
AOP是OOP(面向对象编程)的补充。
AOP可以将我们重复的代码抽取出来,在需要执行的时候,使用动态代理技术,在不修改源代码的基础上,对我们的方法进行增强
通俗的讲:将通用的功能(权限、日志、事务···)封装起来,作为一个切面,在类的执行中,找一个合适的时机,将我们的切面切入到执行流程中。
AOP中的名词和通知
SpringAOP的名词
- 切面(Aspect):被抽取的公共模块,可能会横切多个对象。 在Spring AOP中,切面可以使用通用类(基于模式的风格) 或者在普通类中以 @AspectJ 注解来实现。
- 连接点(Join point):指方法,在Spring AOP中,一个连接点 总是 代表一个方法的执行。
- 通知(Advice):在切面的某个特定的连接点(Join point)上执行的动作。通知有各种类型,其中包括“around”、“before”和“after”等通知。许多AOP框架,包括Spring,都是以拦截器做通知模型, 并维护一个以连接点为中心的拦截器链。
- 切点(Pointcut):切入点是指 我们要对哪些连接点(Join point)进行拦截的定义。通过切入点表达式,指定拦截的方法,比如指定拦截add、search。
- 引入(Introduction):(也被称为内部类型声明(inter-type declaration))。声明额外的方法或者某个类型的字段。Spring允许引入新的接口(以及一个对应的实现)到任何被代理的对象。例如,你可以使用一个引入来使bean实现 IsModified 接口,以便简化缓存机制。
- 织入(Weaving):指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。Spring是在运行时完成织入。
- 目标对象(Target Object): 被一个或者多个切面(aspect)所通知(advise)的对象。也有人把它叫做 被通知(adviced) 对象。 既然Spring AOP是通过运行时代理实现的,这个对象永远是一个 被代理(proxied) 对象。
切入点(pointcut)和连接点(join point)匹配的概念是AOP的关键,这使得AOP不同于其它仅仅提供拦截功能的旧技术。 切入点使得定位通知(advice)可独立于OO层次。 例如,一个提供声明式事务管理的around通知可以被应用到一组横跨多个对象中的方法上(例如服务层的所有业务操作)。
Spring中通知的类型
-
前置通知(Before advice):在某连接点(join point)之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行(除非它抛出一个异常)。
-
返回后通知(After returning advice):在某连接点(join point)正常完成后执行的通知:例如,一个方法没有抛出任何异常,正常返回。
-
抛出异常后通知(After throwing advice):在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。
-
后置通知(After (finally) advice):当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
-
环绕通知(Around Advice):包围一个连接点(join point)的通知,就是将目标方法封装起来。这是最强大的一种通知类型。 环绕通知可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为。它也会选择是否继续执行连接点或直接返回它们自己的返回值或抛出异常来结束执行。 环绕通知是最常用的一种通知类型。大部分基于拦截的AOP框架,例如Nanning和JBoss4,都只提供环绕通知。
切入点表达式
execution:匹配连接点的执行方法
语法:
execution([修饰符] 返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表))
- 修饰符可以省略
- 使用*表示任意类型
- 参数列表使用 .. 表示任意参数类型,有参无参都可以
举例:
execution(* com.zxy.service.impl.*.*(..))
// 任意修饰符 com.zxy.service.impl包下的 任意子包 下的 任意参数列表的任意方法
(Spring AOP还支持很多的AspectJ 切点指示器,自行了解,本篇就使用了一个execution)
AOP的使用示例:
了解了基本的基础知识后,就到了AOP的使用
(AOP最常见的使用场景就是日志、事务等)
根据上一篇的学习(动态代理两种实现),我们使用自己写的动态代理来完成了事务的处理。现在使用spring的aop就可以用更简单的方式完成事务的处理
添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
<version>1.9.6version>
dependency>
准备一个事务的切面类
package com.zxy.aspect;
import com.zxy.tx.MyTransactionManager;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author ZXY
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020/12/19 17:32
* 日志切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class TransactionAspect {
@Autowired
private MyTransactionManager transactionManager;// 引入自定义事务类
// 配置切入点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zxy.service.impl.*.*(..))")
private void pointcut(){}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("**************** 开启事务!***************");
transactionManager.begin();
}
@AfterReturning("pointcut()")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("**************** 提交事务***************");
transactionManager.commit();
}
@AfterThrowing("pointcut()")
public void afterThrowing(){
System.out.println("**************** 回滚事务***************");
transactionManager.rollback();
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("**************** 释放资源!***************");
transactionManager.close();
}
}
为启动类添加注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy开启Spring对AOP的支持:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.zxy"})
@Import({MybatisConfig.class,DataSourceConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {}
测试:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration( classes = {SpringConfig.class})
public class Test1 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountServiceImpl")
private IAccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test1(){
// 张三转账给李四1000元
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",1000.0);
}
}
正常情况:
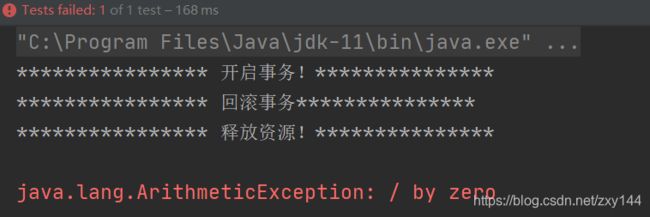
发生异常,事务回滚:
使用xml配置文件的方式配置aop:
引入约束:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
beans>
aop配置:
<bean id="loggerAspect" class="com.zxy.aspect.TransactionAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="lAspect" ref="loggerAspect">
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut1" expression="execution(* com.zxy.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after method="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
环绕通知
它是Spring框架为我们提供的一种可以在代码中手动控制增强代码功能的执行方式。能够全面的控制连接点,甚至可以控制是否执行连接点
环绕通知需要再添加一个依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrtartifactId>
<version>1.9.6version>
dependency>
Spring提供了一个接口ProceedingJoinPoint:他可以作为环绕通知方法的参数,在环绕通知执行时,可以通过该接口的实例获取目标类的对象,直接执行目标类中的方法。
我们需要调用ProceedingJoinPoint类中的proceed()方法来执行被代理的方法。(如果没有这步操作,就会导致通知得到执行而目标方法不会得到执行)
然后就可以在在目标方法的执行前后执行我们的其他增强操作
(使用环绕通知时,目标方法的返回值只能是引用类型(基本数据类型要使用对应的包装类))
使用这一个方法即可完成前面四个方法的任务:
@Around("pointcut()")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("**************** 开启事务!***************");
transactionManager.begin();
try {
joinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("**************** 提交事务***************");
transactionManager.commit();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("**************** 回滚事务***************");
transactionManager.rollback();
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("**************** 释放资源!***************");
transactionManager.close();
}
}
使用xml配置(不使用@Around注解):
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="lAspect" ref="loggerAspect">
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut1" expression="execution(* com.zxy.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:around method="aroundAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
学习到这里,我们已经使用自己的多种方式手动的完成了事务的控制,在Spring框架中,还有更简单的方式来完成我们对事务的需求,下一篇 Spring中的事务控制 ※