pytorch 搭建GoogLeNet
目录
1. 介绍
Inception 结构
Auxiliary Classifier 辅助分类器
2. 搭建 GoodLeNet 网络
3. 训练部分
4. 预测部分
5. 训练过程
1. 介绍
GoodLeNet 网络中的亮点有:
- 引入了Inception 结构,在网络在横向上有深度,融合了不同尺度的特征信息
- 使用了 1*1 的卷积核进行降维处理
- 添加了两个辅助分类器帮助训练
- 丢弃全连接层,使用平均池化层,大大减少了模型的参数
下面是GoodLeNet 的网络结构图
每层网络的参数为:
后面的参数代表Inception 结构的配置
Inception 结构
Inception 结构出现了并行的结构,然后将这四个结构拼接在一块。右面 1*1 的卷积核存在的目的是为了降维,如图:
Auxiliary Classifier 辅助分类器
如图:
- 辅助分类器的第一层是一个平均池化下采样层,size 是 5*5,stride 是 3
两个辅助分类器的结构是一样的,分别来自有Inception 4a和Inception 4d
根据公式计算为第一个辅助分类器的输出是out = (14 - 3 + 2*0)/ 3 + 1 = 4
因此,第一个辅助分类器的输出是:4*4*512
- 1*1 的卷积核进行降维处理,然后是ReLU的激活函数
2. 搭建 GoodLeNet 网络
首先定义一个卷积的模板,因为卷积层后面接的是ReLU激活函数,这里将它们放到一块
然后,定义Inception 结构
- 这里padding 的作用是为了保证输入的 宽高 等于输出的 宽高,因为观察维度可以发现,Inception 结构的输出和输入的维度中,只有channels 变了
- 网络中需要的参数是对应图上卷积核的个数
最后定义前向传播就行了
最后定义的是辅助分类器的部分:
完整的代码段为:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, aux_logits=True):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits # 辅助分类器
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # True 小数的时候向上取整
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
if self.aux_logits: # 辅助分类器
self.aux1 = InceptionAux(512, num_classes)
self.aux2 = InceptionAux(528, num_classes)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # 不用限制原始输入224*244的图像
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.conv1(x)
# N x 64 x 112 x 112
x = self.maxpool1(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv2(x)
# N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv3(x)
# N x 192 x 56 x 56
x = self.maxpool2(x)
# N x 192 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3a(x)
# N x 256 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3b(x)
# N x 480 x 28 x 28
x = self.maxpool3(x)
# N x 480 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4a(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4c(x)
# N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4d(x)
# N x 528 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x)
# N x 832 x 14 x 14
x = self.maxpool4(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5a(x)
# N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5b(x)
# N x 1024 x 7 x 7
x = self.avgpool(x)
# N x 1024 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
# N x 1024
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
# N x 1000 (num_classes)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
# Inception 结构
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch5x5red, ch5x5, pool_proj): # 参数对应Inception所需要的卷积核个数
super(Inception, self).__init__()
# 第一个分支 1*1 卷积
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1) # 不改变size
# 第二个分支 1*1卷积 + 3*3卷积
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1), # 不改变size
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # padding 保证输出大小等于输入大小
) # out = (in - 3 + 2*1)/1 + 1 = in
# 第三个分支 1*1卷积 + 5*5卷积
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch5x5red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch5x5red, ch5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2) # padding 保证输出大小等于输入大小
) # out = (in - 5 + 2*2)/1 + 1 = in
# 第四个分支 3*3max pooling + 1*1卷积
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), # o = (i - 3 + 2*1)/1 + 1 = i
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x): # 定义前向传播
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1) # 在 channels 维度进行拼接
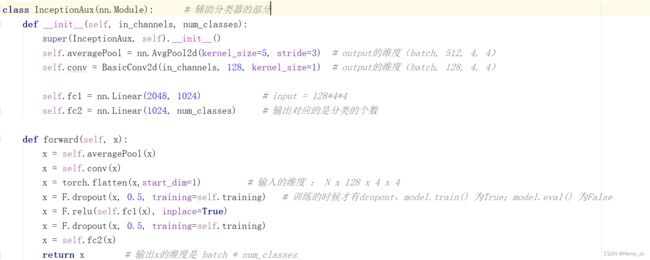
class InceptionAux(nn.Module): # 辅助分类器的部分
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.averagePool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3) # output的维度(batch, 512, 4, 4)
self.conv = BasicConv2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output的维度(batch, 128, 4, 4)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024) # input = 128*4*4
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes) # 输出对应的是分类的个数
def forward(self, x):
# 辅助分类器输入维度:1.n*512*14*14 2.n*528*14*14
x = self.averagePool(x) # 1.n*512*4*4 2.n*528*4*4
x = self.conv(x) # out = n*128*4*4 (1*1卷积核不改变size,只改变channel)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training) # 训练的时候才有dropout,model.train() 为True;model.eval() 为False
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x # 输出x的维度是 batch * num_classes
# 将卷积层+ReLU 层打包到一块,形成一个卷积模板
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
3. 训练部分
代码为:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import torch.optim as optim
from model import GoogLeNet
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tqdm import tqdm
DEVICE = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
data_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# 训练集
trainset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=False, transform=data_transform)
trainloader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
# 测试集
testset = datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=False, transform=data_transform)
testloader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=16, shuffle=False)
# 样本的个数
num_trainset = len(trainset) # 50000
num_testset = len(testset) # 10000
# 构建网络
net = GoogLeNet(num_classes=10, aux_logits=True) # 定义网络分类十个类别,且打开辅助分类器
net.to(DEVICE)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0003)
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './GoogLeNet.pth'
for epoch in range(5):
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for data in tqdm(trainloader):
images, labels = data
images,labels = images.to(DEVICE),labels.to(DEVICE)
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = net(images) # 总共有三个输出
loss0 = loss_function(logits, labels) # 计算损失
loss1 = loss_function(aux_logits1, labels)
loss2 = loss_function(aux_logits2, labels)
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3 # 将三个输出相加
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
# test
net.eval()
acc = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
for test_data in tqdm(testloader):
test_images, test_labels = test_data
test_images,test_labels = test_images.to(DEVICE),test_labels.to(DEVICE)
outputs = net(test_images) # eval模式下,辅助分类器会被设为False
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += (predict_y == test_labels).sum().item()
accurate = acc / num_testset
train_loss = running_loss / num_trainset
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, train_loss, accurate))
if accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
4. 预测部分
代码:
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from model import GoogLeNet
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
# load image
img = Image.open("./OIP-C.jpg")
img = data_transform(img)
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# 加载网络
net = GoogLeNet(num_classes=10, aux_logits=False) # 预测不需要辅助分类器
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = net.load_state_dict(torch.load("./GoogLeNet.pth"),
strict=False) # strict 设置为False 不会精确同步网络结构
net.cuda()
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = net(img.cuda())
predict = torch.max(output, dim=1)[1].data.cpu().numpy()
print(classes[int(predict)])
5. 训练过程
预测图像:
输出结果: