金三银四精选面试题系列
Java中有哪几种方式来创建线程执行任务?
1. 继承Thread类
public class ZhouyuThread extends Thread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZhouyuThread thread = new ZhouyuThread();
thread.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello zhouyu");
}
}总结:重写的是run()方法,而不是start()方法,但是占用了继承的名额,Java中的类是单继承的。
讲到单继承,我们应该注意,java中的接口是可以多继承的
2. 实现Runnable接口
/**
* 作者:周瑜大都督
*/
public class ZhouyuThread implements Runnable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new ZhouyuThread());
thread.start();
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello zhouyu");
}
}总结:实现Runnable接口,实现run()方法,使用依然要用到Thread,这种方式更常用
有时候,我们会直接使用匿名内部类的方式或者Lambda表达式的方式:
public class ZhouyuThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello zhouyu");
}
});
thread.start();
}
}public class ZhouyuThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("hello zhouyu"));
thread.start();
}
}3. 实现Callable接口
public class ZhouyuThread implements Callable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new ZhouyuThread());
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
String result = futureTask.get();
System.out.println(result);
}
public String call() {
return "hello zhouyu";
}
} 总结:实现Callable接口,实现call()方法,得使用Thread+FutureTask配合,这种方式支持拿到异步执行任务的结果
4. 利用线程池来创建线程
/**
* 作者:周瑜大都督
*/
public class ZhouyuThread implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
executorService.execute(new ZhouyuThread());
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello zhouyu");
}
}总结:实现Callable接口或者Runnable接口都可以,由ExecutorService来创建线程
注意,工作中不建议使用Executors来创建线程池
总结
以上几种方式,底层都是基于Runnable。
为什么不建议使用Executors来创建线程池?
1. FixedThreadPool
当我们使用Executors创建FixedThreadPool时,对应的构造方法为:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
} 发现创建的队列为LinkedBlockingQueue,是一个无界阻塞队列,如果使用该线程池执行任务,如果任务过多就会不断的添加到队列中,任务越多占用的内存就越多,最终可能耗尽内存,导致OOM。
2. SingleThreadExecutor
当我们使用Executors创建SingleThreadExecutor时,对应的构造方法为:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue()));
} 也是LinkedBlockingQueue,所以同样可能会耗尽内存。
总结
除开有可能造成OOM之外,我们使用Executors来创建线程池也不能自定义线程的名字,不利于排查问题,所以建议直接使用ThreadPoolExecutor来定义线程池,这样可以灵活控制。
线程池有哪几种状态?每种状态分别表示什么?
1. RUNNING
Accept new tasks and process queued tasks
表示线程池正常运行,既能接受新任务,也会正常处理队列中的任务
2. SHUTDOWN
Don't accept new tasks, but process queued tasks
当调用线程池的shutdown()方法时,线程池就进入SHUTDOWN状态,表示线程池处于正在关闭状态,此状态下线程池不会接受新任务,但是会继续把队列中的任务处理完
3. STOP
Don't accept new tasks, don't process queued tasks, and interrupt in-progress tasks
当调用线程池的shutdownnow()方法时,线程池就进入STOP状态,表示线程池处于正在停止状态,此状态下线程池既不会接受新任务了,也不会处理队列中的任务,并且正在运行的线程也会被中断
4. TIDYING
All tasks have terminated, workerCount is zero, the thread transitioning to state TIDYING will run the terminated() hook method
线程池中没有线程在运行后,线程池的状态就会自动变为TIDYING,并且会调用terminated(),该方法是空方法,留给程序员进行扩展。
5. TERMINATED
terminated() has completed
terminated()方法执行完之后,线程池状态就会变为TERMINATED
Sychronized和ReentrantLock有哪些不同点?
| sychronized |
ReentrantLock |
| Java中的一个关键字 |
JDK提供的一个类 |
| 自动加锁与释放锁 |
需要手动加锁与释放锁 |
| JVM层面的锁 |
API层面的锁 |
| 非公平锁 |
公平锁或非公平锁 |
| 锁的是对象,锁信息保存在对象头中 |
int类型的state标识来标识锁的状态 |
| 底层有锁升级过程 |
没有锁升级过程 |
你的应用突然出现了OOM异常,你会如何排查?
对于还在正常运行的系统:
- 可以使用jmap来查看JVM中各个区域的使用情况
- 可以通过jstack来查看线程的运行情况,比如哪些线程阻塞、是否出现了死锁
- 可以通过jstat命令来查看垃圾回收的情况,特别是fullgc,如果发现fullgc比较频繁,那么就得进行调优了
- 通过各个命令的结果,或者jvisualvm等工具来进行分析
- 首先,初步猜测频繁发送fullgc的原因,如果频繁发生fullgc但是又一直没有出现内存溢出,那么表示fullgc实际上是回收了很多对象了,所以这些对象最好能在younggc过程中就直接回收掉,避免这些对象进入到老年代,对于这种情况,就要考虑这些存活时间不长的对象是不是比较大,导致年轻代放不下,直接进入到了老年代,尝试加大年轻代的大小,如果改完之后,fullgc减少,则证明修改有效
- 同时,还可以找到占用CPU最多的线程,定位到具体的方法,优化这个方法的执行,看是否能避免某些对象的创建,从而节省内存
对于已经发生了OOM的系统:
- 一般生产系统中都会设置当系统发生了OOM时,生成当时的dump文件(-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/usr/local/base)
- 我们可以利用jvisualvm等工具来分析dump文件
- 根据dump文件找到异常的实例对象,和异常的线程(占用CPU高),定位到具体的代码
- 然后再进行详细的分析和调试
ThreadLocal有哪些应用场景?它底层是如何实现的?
- ThreadLocal是Java中所提供的线程本地存储机制,可以利用该机制将数据缓存在某个线程内部,该线程可以在任意时刻、任意方法中获取缓存的数据
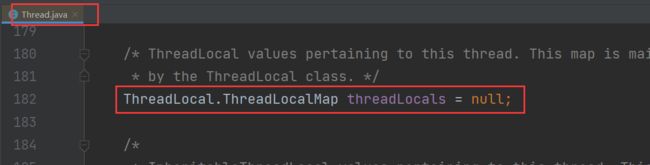
- ThreadLocal底层是通过ThreadLocalMap来实现的,每个Thread对象(注意不是ThreadLocal对象)中都存在一个ThreadLocalMap,Map的key为ThreadLocal对象,Map的value为需要缓存的值
- 如果在线程池中使用ThreadLocal会造成内存泄漏,因为当ThreadLocal对象使用完之后,应该要把设置的key,value,也就是Entry对象进行回收,但线程池中的线程不会回收,而线程对象是通过强引用指向ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap也是通过强引用指向Entry对象,线程不被回收,Entry对象也就不会被回收,从而出现内存泄漏,解决办法是,在使用了ThreadLocal对象之后,手动调用ThreadLocal的remove方法,手动清楚Entry对象
- ThreadLocal经典的应用场景就是连接管理(一个线程持有一个连接,该连接对象可以在不同的方法之间进行传递,线程之间不共享同一个连接)
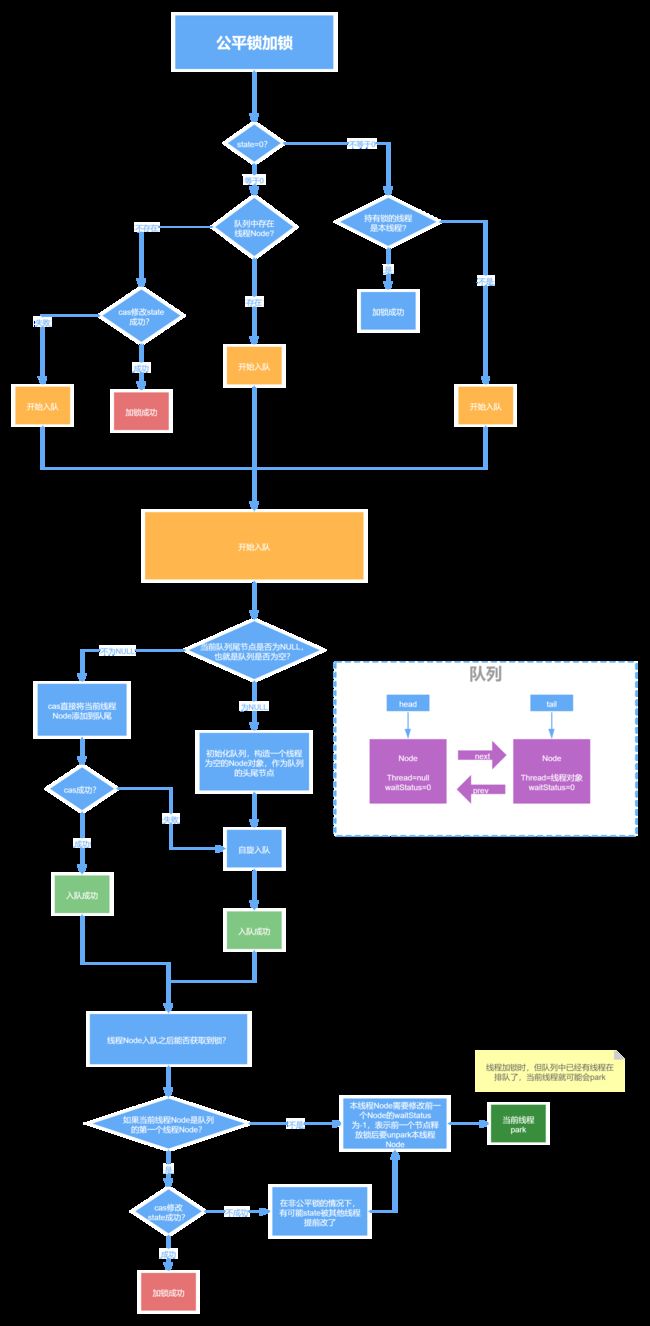
ReentrantLock分为公平锁和非公平锁,那底层分别是如何实现的?
首先不管是公平锁和非公平锁,它们的底层实现都会使用AQS来进行排队,它们的区别在于线程在使用lock()方法加锁时:
- 如果是公平锁,会先检查AQS队列中是否存在线程在排队,如果有线程在排队,则当前线程也进行排队
- 如果是非公平锁,则不会去检查是否有线程在排队,而是直接竞争锁。
公平锁的底层执行流程:
非公平锁的底层执行流程:
另外,不管是公平锁还是非公平锁,一旦没竞争到锁,都会进行排队,当锁释放时,都是唤醒排在最前面的线程,所以非公平锁只是体现在了线程加锁阶段,而没有体现在线程被唤醒阶段,ReentrantLock是可重入锁,不管是公平锁还是非公平锁都是可重入的。
Sychronized的锁升级过程是怎样的?
- 偏向锁:在锁对象的对象头中记录一下当前获取到该锁的线程ID,该线程下次如果又来获取该锁就可以直接获取到了,也就是支持锁重入
- 轻量级锁:由偏向锁升级而来,当一个线程获取到锁后,此时这把锁是偏向锁,此时如果有第二个线程来竞争锁,偏向锁就会升级为轻量级锁,之所以叫轻量级锁,是为了和重量级锁区分开来,轻量级锁底层是通过自旋来实现的,并不会阻塞线程
- 如果自旋次数过多仍然没有获取到锁,则会升级为重量级锁,重量级锁会导致线程阻塞
- 自旋锁:自旋锁就是线程在获取锁的过程中,不会去阻塞线程,也就无所谓唤醒线程,阻塞和唤醒这两个步骤都是需要操作系统去进行的,比较消耗时间,自旋锁是线程通过CAS获取预期的一个标记,如果没有获取到,则继续循环获取,如果获取到了则表示获取到了锁,这个过程线程一直在运行中,相对而言没有使用太多的操作系统资源,比较轻量。
Tomcat中为什么要使用自定义类加载器?
一个Tomcat中可以部署多个应用,而每个应用中都存在很多类,并且各个应用中的类是独立的,全类名是可以相同的,比如一个订单系统中可能存在com.zhouyu.User类,一个库存系统中可能也存在com.zhouyu.User类,一个Tomcat,不管内部部署了多少应用,Tomcat启动之后就是一个Java进程,也就是一个JVM,所以如果Tomcat中只存在一个类加载器,比如默认的AppClassLoader,那么就只能加载一个com.zhouyu.User类,这是有问题的,而在Tomcat中,会为部署的每个应用都生成一个类加载器实例,名字叫做WebAppClassLoader,这样Tomcat中每个应用就可以使用自己的类加载器去加载自己的类,从而达到应用之间的类隔离,不出现冲突。另外Tomcat还利用自定义加载器实现了热加载功能。
Mysql中九种索引失效场景分析
表数据:
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
a int primary key,
b int ,
c int ,
d int ,
e varchar(20)
) ENGINE=InnoDB ;
insert into t1 values(4,3,1,1,'d');
insert into t1 values(1,1,1,1,'a');
insert into t1 values(8,8,8,8,'h');
insert into t1 values(2,2,2,2,'b');
insert into t1 values(5,2,3,5,'e');
insert into t1 values(3,3,2,2,'c');
insert into t1 values(7,4,5,5,'g');
insert into t1 values(6,6,4,4,'f');索引情况:
a字段是主键,对应主键索引,bcd三个字段组成一个联合索引,e字段一个索引
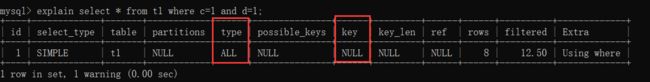
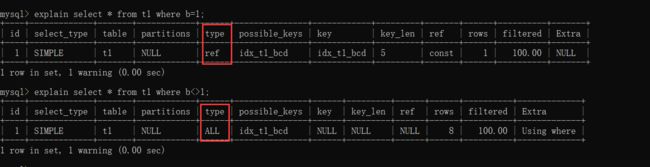
1. 不符合最左匹配原则
去掉b=1的条件就不符合最左匹配原则了,导致所有失效
2. 不正确的Like查询
不用like能走索引:
正常使用like:
不正确使用like:
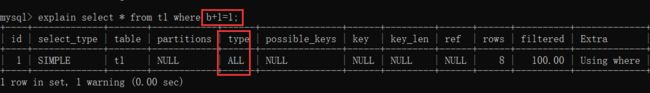
3. 对索引列进行了计算或使用了函数
4. 索引列进行了类型转换
e字段的类型是vachar,下面这个sql需要把e字段中的字符转换成数字,会导致索引失效
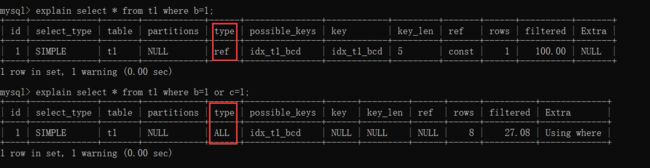
5. <>不等于导致索引失效
b=1可以走索引,b<>1就不能走索引
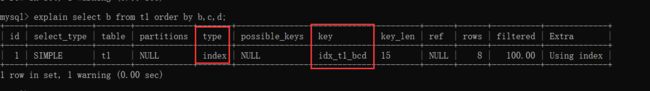
6. order by导致索引失效
就算利用索引,但是由于是select * 所以需要回表,而且回表成本比较高,所以不会走索引。
如果是select b就需要回表了,就会选择走索引
7. 使用or导致索引失效
8. select * 导致索引失效
9. 范围查询数据量过多导致索引失效
新增一些数据:
insert into t1 values(10,3,1,1,'d');
insert into t1 values(20,1,1,1,'a');
insert into t1 values(15,8,8,8,'h');
insert into t1 values(18,2,2,2,'b');
insert into t1 values(14,2,3,5,'e');
insert into t1 values(13,3,2,2,'c');
insert into t1 values(17,4,5,5,'g');
insert into t1 values(22,6,4,4,'f');SpringBoot的四种Handler类型
1、@Controller+@RequestMapping
@RestController
public class ZhouyuController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return "zhouyu";
}
}2、Controller接口
/**
* 作者:周瑜大都督
*/
@Component("/beanNameController")
public class ZhouyuBeanNameController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
response.getWriter().println("ZhouyuBeanNameController");
return null;
}
}3、HttpRequestHandler
/**
* 作者:周瑜大都督
*/
@Component("/beanNameHandler")
public class ZhouyuBeanNameHandler implements HttpRequestHandler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.getWriter().println("ZhouyuBeanNameHandler");
}
}4、RouterFunction
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
@Bean
public RouterFunction routerFunction(){
return route()
.GET("/getUserName", request -> ServerResponse.ok().body("zhouyu"))
.GET("/getUserAge", request -> ServerResponse.ok().body("88"))
.build();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class);
}
}