Redis数据库——键空间
一.服务器中的数据库
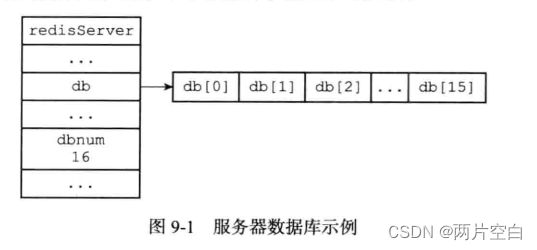
Redis服务器将所有数据库都保存在服务器状态redis.h/redisServer结构的db数组中,db数组的每一个项都是一个redis.h/redisDb结构,每一个RedisDb结构代表一个数据库。
在初始化服务器时,程序会根据服务器状态的dbnum属性来决定应该创建多少个数据库。
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
struct redisServer {
/* General */
pid_t pid; /* Main process pid. */
pthread_t main_thread_id; /* Main thread id */
char *configfile; /* Absolute config file path, or NULL */
char *executable; /* Absolute executable file path. */
char **exec_argv; /* Executable argv vector (copy). */
int dynamic_hz; /* Change hz value depending on # of clients. */
int config_hz; /* Configured HZ value. May be different than
the actual 'hz' field value if dynamic-hz
is enabled. */
mode_t umask; /* The umask value of the process on startup */
int hz; /* serverCron() calls frequency in hertz */
int in_fork_child; /* indication that this is a fork child */
//数据库数组
redisDb *db;
...
...
int dbnum; /* Total number of configured DBs */
...
...
};dbnum属性的值有服务器配置的database选项决定,默认情况下该选项的值为16,所以Redis服务器默认会创建16个数据库。
二. 切换数据库
每一个Redis客户端都有自己的目标数据库,每当客户端执行数据库写命令或者数据库读命令的时候,目标数据库就会成为这些命令的操作对象。
默认情况下,Redis客户端的目标数据库为0号数据库,但客户端可以通过执行select命令来切换目标数据库。
在服务器内部,客户端的状态client结构的db属性记录了客户端当前的目标数据库,这个属性是指向redisServer.redisDb结构的指针。
typedef struct client {
uint64_t id; /* Client incremental unique ID. */
connection *conn;
int resp; /* RESP protocol version. Can be 2 or 3. */
//记录当前正在使用的数据库
redisDb *db; /* Pointer to currently SELECTed DB. */
...
...
}client;client.db指针指向redisServer.db数组的其中一个元素,而被指向的元素就是客户端的目标数据库。
select的实现原理:通过修改client.db指针,让它指向服务器不同的数据库,从而实现切换目标数据库的功能。
目前,Redis仍然没有可以返回客户端目标数据库的命令,虽然redis-cli客户端在输入符旁边提示当前所使用的目标数据库。
但是,你在其他语言的客户端中执行redis命令,并且该客户端好像没有向redis-cli那样显示目标数据库的号码,在多次切换数据库之后,你可能会忘记当前使用的哪个数据库。
为了避免误操作,在执行Redis命令,特别向FLUSHDB这样的危险命令前,最好先执行一个select命令,显示的切换到指定数据库,然后再执行别的命令。
三.数据库的键空间
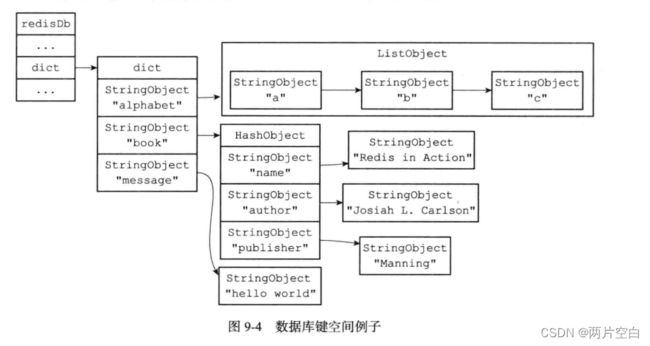
Redis是一个键值对数据库服务器,服务器中的每一个数据库是由一个redis.h/redisDb结构表示。其中redisDb结构中的dict字典保存了数据库中的所有键值对,我们简称这个字典为键空间。
typedef struct redisDb {
//键空间
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;键空间和用户所见到的数据库是直接对应的:
- 键空间的键也就是数据库的键,每一个键都是一个字符串对象。
- 键空间的值也就是数据库的值,每一个值可以是字符串对象,列表对象,哈希表对象,集合对象和有序集合对象中的任意一种Redis对象。
举个例子:
127.0.0.1:6379> set message "hello world"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush alphabet "a" "b" "c"
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> hset book name "Redis in Action"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> hset book author "Josiah L. Carlson" publisher "Manning"
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> - messge是一个字符串键,键的名字是一个包含字符串messge的字符串对象,键的值是一个包含字符串"hello world"的字符串对象。
- alphabet是一个列表键,键的名字是一个包含字符串alphabet的字符串对象,键的值是一个包含三个元素的列表对象。
- book是一个哈希键,键的名字是一个包含字符串book的字符串对象,键的值是一个包含三个键值对的哈希表对象。
3.1 数据库的增删查改
因为数据库的键是一个字典,所以对数据库的增删查改,实际是对字典的增删查改。
3.1.1添加新建
添加一个新的键值对到数据库,实际上就是将一个新键值对添加到键空间字典中,其中键为字符串对象,而值为Redis任意一种类型的Redis对象。
比如:
127.0.0.1:6379> set date "2023.12.1"
OK添加一个新键值对,键是一个值为date字符串的字符串对象,键的值为2023.12.1字符串的字符串对象。
3.1.2 删除键
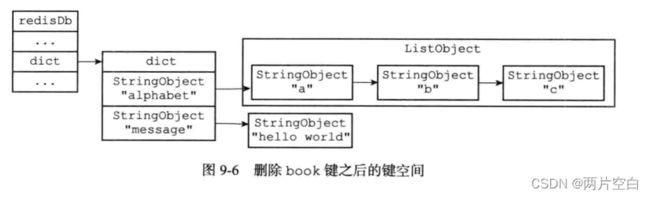
删除数据库中的一个键,实际上就是在键空间里面删除键所对应的键值对对象。就是删除字典中的一个节点。
127.0.0.1:6379> del book
(integer) 13.1.3 更新键
对一个数据库键进行更新,实际上就是对键空间里面键对应的值对象进行更新,根据值对象的类型不同,更新的具体方法也会不同。
127.0.0.1:6379> get message
"hello world"
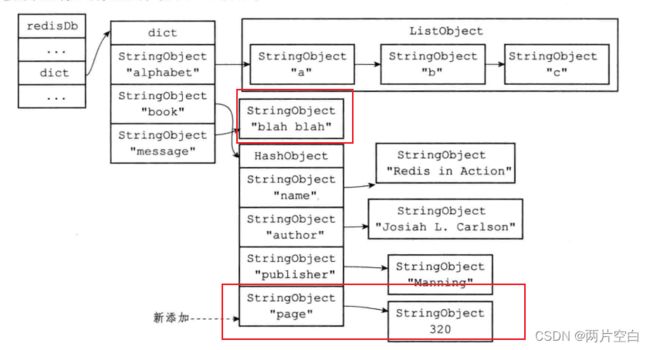
127.0.0.1:6379> set message "blah blah"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get message
"blah blah"上面是对数据库键message对应的值"hello world"字符串修改成了"blah blah"字符串。
127.0.0.1:6379> hset book page 320
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> 上面是修改数据库键book对应的值哈希对象,新加一个节点键为page,值为320。
3.1.4 对键取值
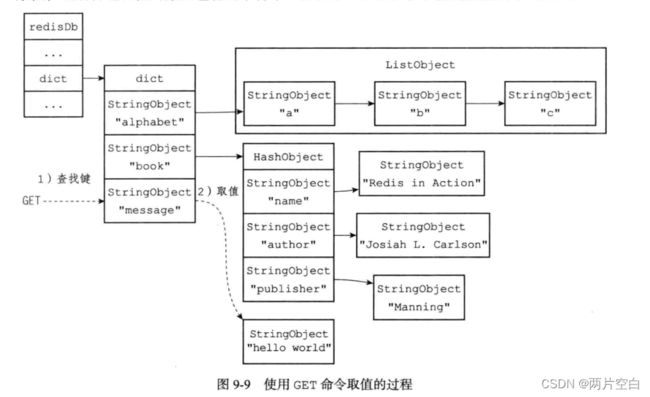
对一个数据库键进行取值,实际上就是对键空间里面取出键所对应的值对象,根据值对象的类型不同,更新的具体方法也会不同。
127.0.0.1:6379> get message
"hello world"get命令首先在键空间(client.db)中查找键message,找到键后,去到该键对应的字符串对象,之后返回值对象所包含的字符串"hello world"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange alphabet 0 -1
1) "a"
2) "b"
3) "c"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange命令首先在键空间(client.db)中查找键alphabet,找到键后,去到该键对应的列表对象值,之后返回列表对象中包含的三个字符串对象的值。
3.1.5 其他键空间操作
除了增删查改操作外,还有针对数据库本身的Redis命令, 也是通过键空间进行处理完成的。
- FLUSHDB:通过删除键空间的所有键值对实现的
- RANDOMKEY:通过在键空间随机返回一个键实现的
- DSSIZE:返回键空间中包含的键值对的数量
其他命令exits,rename,keys等,都是通过对键空间进行操作来实现的。
3.1.6 读写键空间的维护操作
当使用Redis命令对数据库进行读写时,服务器不仅会对键空间执行指定的读写操作,还会执行额外的维护操作。
- 在读取一个键时(读操作和写操作都会对键进行读取),服务器会更具键是否存在来更新服务器的键的空间命中(hit)次数或键的空间不命中次数,可以通过命令info stats命令的keyspace_hits属性和keyspce_misses属性查看。
- 在读取一个键后。服务器会更新一个键的LRU(最后一次使用)时间,这个值可以用于计算键的闲置时间。使用OBJECT IDLETIME
命令来查看键key的闲置时间。 - 如果服务器在读取一个键发现该键已经过期,那么服务器会先删除这个过期键,然后执行余下操作。
- 如果客户端使用watch监视一个键,当服务器对监视的键进行修改后,会把这个键标记为脏(dirty),从而让事务注意到这个键已经被修改过。
- 服务器每修改一个键之后,都会对脏(dirty)键计数器的值增1。这个计数器会触发服务器的持久化以及复制操作
- 如果服务器开启了数据库通知功能,那么在对键进行修改后,服务器将按配置发送相应的数据库通知。