技术阅读周刊第十一期
技术阅读周刊,每周更新。
历史更新
20231124:第七期
20231201:第八期
20231215:第十期
A Comprehensive guide to Spring Boot 3.2 with Java 21, Virtual Threads, Spring Security, PostgreSQL, Flyway, Caching, Micrometer, Opentelemetry, JUnit 5, RabbitMQ, Keycloak Integration, and More! (10/17) | by Jonathan Chevalier | Nov, 2023 | Medium
URL: https://medium.com/@jojoooo/exploring-a-base-spring-boot-application-with-java-21-virtual-thread-spring-security-flyway-c0fde13c1eca#551c
本文讲解了基于最新的 Spring Boot3.2 和 Java 21 所使用到的技术栈
数据库
数据库使用 Postgres15 和 flyway 来管理数据库 schema 的迁移。
异常处理
Spring6 实现了新的 RFC9457规范,实现以下接口:
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class GlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
// Process @Valid
@Override
protected ResponseEntity{
"type": "about:blank",
"title": "Bad Request",
"status": 400,
"detail": "Validation failed.",
"instance": "/management/companies",
"errors": [
{
"pointer": "name",
"reason": "must not be blank"
},
{
"pointer": "slug",
"reason": "must not be blank"
}
]
}应用异常
@Getter
public class RootException extends RuntimeException {
@Serial private static final long serialVersionUID = 6378336966214073013L;
private final HttpStatus httpStatus;
private final List errors = new ArrayList<>();
public RootException(@NonNull final HttpStatus httpStatus) {
super();
this.httpStatus = httpStatus;
}
public RootException(@NonNull final HttpStatus httpStatus, final String message) {
super(message);
this.httpStatus = httpStatus;
}
}
@ExceptionHandler(RootException.class)
public ResponseEntity rootException(final RootException ex) {
log.info(ex.getMessage(), ex);
// Uses default message, can be adapted to use ex.getMessage().
final ProblemDetail problemDetail =
this.buildProblemDetail(
ex.getHttpStatus(), API_DEFAULT_REQUEST_FAILED_MESSAGE, ex.getErrors());
return ResponseEntity.status(ex.getHttpStatus()).body(problemDetail);
}
{
"type": "about:blank",
"title": "Internal Server Error",
"status": 500,
"detail": "Request failed.",
"instance": "/back-office/hello-world"
} 异常降级
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
public ProblemDetail handleAllExceptions(final Throwable ex, final WebRequest request) {
log.warn(ex.getMessage(), ex);
this.slack.notify(format("[API] InternalServerError: %s", ex.getMessage()));
return this.buildProblemDetail(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, API_DEFAULT_ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
{
"type": "about:blank",
"title": "Internal Server Error",
"status": 500,
"detail": "Something went wrong. Please try again later or enter in contact with our service.",
"instance": "/back-office/hello-world"
}当有无法处理的异常时,就需要配置一个兜底的异常。
缓存
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
public interface CompanyRepository extends JpaRepository {
String CACHE_NAME = "company";
@NonNull
@Cacheable(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "{'byId', #id}")
@Override
Optional findById(@NonNull Long id);
@Cacheable(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "{'bySlug', #slug}")
Optional findBySlug(String slug);
@Caching(
evict = {
@CacheEvict(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "{'byId', #entity.id}"),
@CacheEvict(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "{'bySlug', #entity.slug}"),
})
@Override
@NonNull S save(@NonNull S entity);
/*
* This cache implementation is only valid if the table is not
* frequently updated since it will clear the cache at every update operation
* If you want to be more performant you can use something like https://github.com/ms100/cache-as-multi
* */
@NonNull
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = CACHE_NAME, allEntries = true)
@Override
List saveAll(@NonNull Iterable entities);
@Caching(
evict = {
@CacheEvict(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "{'byId', #entity.id}"),
@CacheEvict(value = CACHE_NAME, key = "{'bySlug', #entity.slug}"),
})
@Override
void delete(@NonNull Company entity);
/*
* This cache implementation is only valid if the table is not
* frequently updated since it will clear the cache at every delete operation
* If you want to be more performant you can use something like https://github.com/ms100/cache-as-multi
* */
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = CACHE_NAME, allEntries = true)
@Override
void deleteAll(@NonNull Iterable entities);
} Spring 提供了标准的缓存接口,即便是后续需要切换到 Redis,使用的 API 和注解都不会发生改变。
线程
Java21 后支持了虚拟线程,几乎可以无限的实现线程,在 Spring Boot 3.2 需要单独开启。
spring.threads.virtual.enabled可观测性
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
io.micrometer
micrometer-registry-prometheus
spring:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: info, health, prometheus, metrics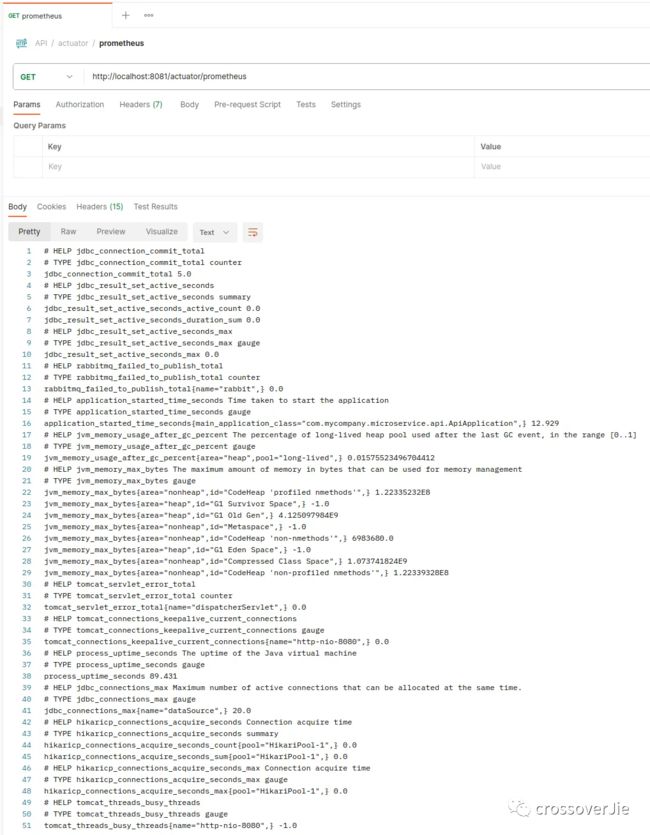 image.png
image.png
注意在生成环境不要暴露管理 API
Trace
io.micrometer
micrometer-tracing-bridge-otel
net.ttddyy.observation
datasource-micrometer-spring-boot
${datasource-micrometer.version}
io.opentelemetry
opentelemetry-exporter-otlp
${opentelemetry-exporter-otlp.version}
同步请求的时候每个请求都会带上 traceId 和 spanId ,如果是异步请求时候需要配置:spring.reactor.context-propagation=true
如果使用 @Async时:
@Configuration
public class TaskExecutorConfig {
/*
* Override default SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor to provide context propagation in @Async function
* */
@Bean
public TaskExecutor simpleAsyncTaskExecutor() {
final SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor();
taskExecutor.setTaskDecorator(new ContextPropagatingTaskDecorator());
return taskExecutor;
}
}本地测试时候可以使用 Otel Desktop Viewer
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1
otlp:
tracing:
endpoint: http://localhost:4317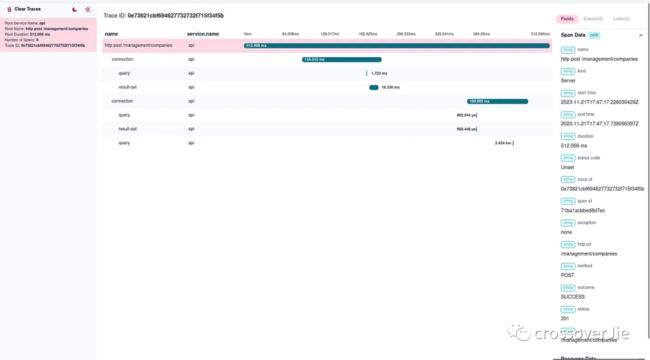 image.png
image.png
Rust Vs Go: A Hands-On Comparison
URL: https://www.shuttle.rs/blog/2023/09/27/rust-vs-go-comparison
动手比较 Rust 和 Go
 image.png
image.png
本文是通过编写一个 web 服务来进行比较的。
Go 更加简单易学,同时标准库非常强大,只需要配合 gin+sqlx 这两个第三方库就能实现一个 web 服务
Rust也可以快速的构建一个安全的 web 服务,但需要依赖许多第三方库,比如http/JSON/模板引擎/时间处理等
但 Rust 在异常处理方面心智负担更低,代码更容易阅读。
如果是一个初创小团队,使用 Go 的上手难度确实更低;
但如果团队愿意花时间投入到 Rust 中,结合他出色的错误处理,和强大的编译检查,长时间来看会得到更好的效果。
为什么要使用 Go 语言?Go 语言的优势在哪里?- 知乎
URL: https://www.zhihu.com/question/21409296/answer/1040884859
图文并茂,讲解了 G-M-P 各自之间的关系,以及调度模型。
 image.png
image.png
G: Goroutine,用户创建的协程,图中搬运的砖头。
M: Machine,OS 内核的线程的抽象,代表真正执行的资源;对应到就是图中的地鼠,地鼠不能用户直接创建;得是砖头 G 太多,地鼠 M 本身太少,同时还有空闲的小车 P,此时就会从其他地方借一些地鼠 M 过来直到把小车 P 用完为止。
P: Processor 处理器,G 只有绑定到 P 才能被调度;P 是图中的小车,由用户设置的
GoMAXPROCS决定小车的数量。
文章链接:
https://blog.canopas.com/golang-14-shorthand-tricks-you-might-not-know-8d8d21954c49
https://medium.com/@jojoooo/exploring-a-base-spring-boot-application-with-java-21-virtual-thread-spring-security-flyway-c0fde13c1eca#551c
https://www.zhihu.com/question/21409296/answer/1040884859
往期推荐
如何给开源项目发起提案
如何编写一个 Pulsar Broker Interceptor 插件
老炮新作,大一统的监控探针采集器 cprobe 开源了
五分钟 k8s 实战-滚动更新与优雅停机
点分享
点收藏
点点赞
点在看



