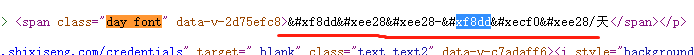文本混淆章节
1. 文本混淆简介
简单而言就是利用前端技术干扰,页面可以正常展示,而使用爬虫下载后无法提取正常的数据。
1.1 常见的干扰方式
- 字体反爬
2. 字体反爬
2.1 字体反爬简介
在 CSS3 之前,Web 开发者必须使用用户计算机上已有的字体。目前的技术开发者可以使用@font-face为网页指定字体,开发者可将心仪的字体文件放在 Web 服务器上,并在 CSS 样式中使用它。用户使用浏览器访问 Web应用时,对应的字体会被浏览器下载到用户的计算机上。
注:使用自动化selenium也无法获取正常的数据
3. 某习字体反爬实践
3.1 逆向目标
- 首页:https://www.shixiseng.com/
- 目标:https://www.shixiseng.com/interns?keyword=产品&city=全国&type=intern&from=menu
- 逆向:薪酬字体
3.2 逆向分析
3.2.1 网页分析
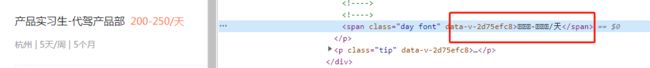
- 打开网站可以发现,价格的字体是乱码
3.2.2 页面处理
- 在页面源代码中搜索
font-face关键字,可以发现字体文件在网页源代码中
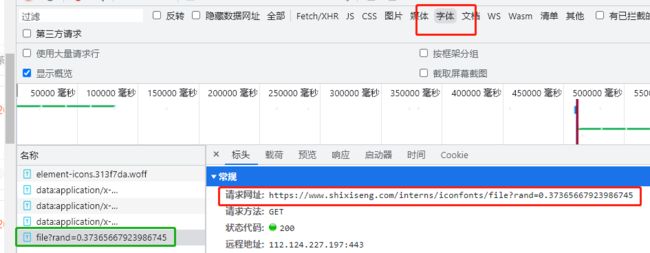
- 可以在网络抓包里面进行筛选,可以发现这里面有对应的字体文件加载地址,由后端返回
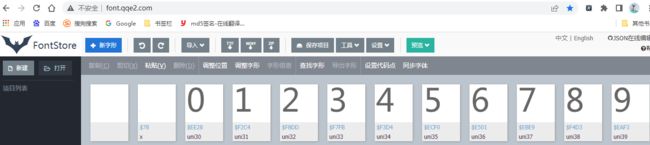
- 对于字体文件,可以直接使用工具解析
- 在线地址:http://font.qqe2.com/
- 使用方式:
- 下载字体文件到本地目录
- 访问在线工具网站,点击左上角打开,找到本地目录字体文件即可
- 使用方式:
- 在线地址:http://font.qqe2.com/
3.3.3 字体分析
- 下载后的页面元素
- 解析的字体文件
woff文件转化成xml文件进行分析cmap是关键 原来是unicode码
3.3 逆向结果
3.3.1 完整code
class Sxs():
def __init__(self):
self.headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.96 Safari/537.36"
}
def get_html(self):
# 第1步:获取html,且存为html文件以便后面研究使用
url = 'https://www.shixiseng.com/interns?keyword=%E4%BA%A7%E5%93%81&city=%E5%85%A8%E5%9B%BD&type=intern&from=menu'
ret = requests.get(url=url, headers=self.headers).text
with open('index.html', 'w', encoding='utf8') as f:
f.write(ret)
return ret
def get_font(self,ret):
# 第2步:下载html配套的ttf文件
font_url = re.findall('src: url\((.*?)\);', ret)
f_url = 'https://www.shixiseng.com' + font_url[0] if font_url else font_url
font_data = requests.get(f_url)
with open('file.woff', 'wb') as f:
f.write(font_data.content)
def get_font_data(self,ttf):
font_dict = {}
# font = TTFont("file.woff")
font = TTFont(ttf)
cmap = font.get("cmap").getBestCmap()
for k, v in cmap.items():
if v[3:]:
content = "\\u00" + v[3:] if len(v[3:]) == 2 else "\\u" + v[3:]
real_content = content.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')
k_hex = hex(k)
# 网页返回的字体是以&#x开头 ,换成以这个开头,下面代码就是直接替换
real_k = k_hex.replace("0x", "&#x")
font_dict[real_k] = real_content
return font_dict
def put_html(self,ttf_dict):
with open("index.html", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
html = f.read()
for k, v in ttf_dict.items():
html = html.replace(k, v)
return html
def get_data(self,html):
html = etree.HTML(html)
li_list = html.xpath("//div[@class='intern-wrap intern-item']")
for li in li_list:
title = "".join(li.xpath(".//div[@class='f-l intern-detail__job']//a/text()")[0].split())
price = "".join( li.xpath(".//div[@class='f-l intern-detail__job']//span[@class='day font']/text()")[0].split())
name = li.xpath('.//a[@class="title ellipsis"]/text()')[0]
print(title, price,name)
def main(self):
# 第1步:获取html,且存为html文件以便后面研究使用
ret = self.get_html()
# 第2步:下载html配套的ttf文件
self.get_font(ret)
# 第3步:提取ttf中摄影的数据
font_dict = self.get_font_data('file.woff')
# 第4步:对下载(HTML内容)进行替换
html = self.put_html(font_dict)
# 第5步:使用xpath提取想要的数据
data = self.get_data(html)
print(data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Sxs().main()4. 字体解析工具
4.1 工具安装
pip install fontTools # 使用这个包处理字体文件4.2 字体读取
from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont
# 加载字体文件:
font = TTFont('file.woff')
# 转为xml文件:
font.saveXML('file.xml')4.3 节点读取
from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont
# 加载字体文件:
font = TTFont('file.woff')
kv = font.keys()
print(kv)字体文件不仅包含字形数据和点信息,还包括字符到字形映射、字体标题、命名和水平指标等,这些信息存在对应的表中:
| 表 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| cmap | 字符到字形映射 |
| glyf | 字形数据 |
| head | 字体标题 |
| hhea | 水平标题 |
| hmtx | 水平指标 |
| loca | 索引到位置 |
| maxp | 最大限度的 |
| name | 命名 |
| post | 后记 |
4.4 获取请求到的字体code和name的对应关系
code_name_map = font_aa.getBestCmap()4.5 获取字体坐标信息
font_aa = TTFont('file.woff')
# 获取请求到的字体形状
glyf = font_aa['glyf']
#font['glyf'][字体编码].coordinates
font_aa['glyf']['uni4E94'].coordinates5. 某车字体反爬
5.1 逆向目标
- 首页:https://www.renrenche.com/
- 目标:https://www.renrenche.com/bj/ershouche/p2/?&plog_id=838083390d4b077a45852d11065f60ad
- 逆向:标题字体
5.2 逆向分析
5.2.1 原字形还原
请求字体链接,获取字体code和name的对应关系,然后遍历,获取网页中反爬文字的真实文字。
relation_table = {"zero": "0", "one": "1", "two": "2", "three": "3", "four": "4", "five": "5", "seven": "6","eight": "7", "six": "8", "nine": "9"}
def woff_font(font_url):
'''获取字体真实对应关系'''
newmap = {}
resp = session.get(font_url) # 请求字体链接
woff_data = BytesIO(resp.content)
font = TTFont(woff_data) # 读取woff数据
cmap = font.getBestCmap() # 获取字体对应关系
font.close()
for k, v in cmap.items():
value = v
key = str(k - 48) # 获取真实的key
try:
get_real_data = relation_table[value]
except:
get_real_data = ''
if get_real_data != '':
newmap[key] = get_real_data # 将字体真实结果对应
return newmap5.3 逆向代码
from io import BytesIO
import requests
from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont
from lxml import etree
import re
import execjs
session = requests.session()
maps = lambda x:x[0] if x else x
# relation_table = {"zero": "0", "one": "1", "two": "2", "three": "3", "four": "4", "five": "5", "seven": "6","eight": "7", "six": "8", "nine": "9"}
def woff_font(font_url):
'''获取字体真实对应关系'''
newmap = {}
resp = session.get(font_url) # 请求字体链接
woff_data = BytesIO(resp.content) # 保存字体数据
font = TTFont(woff_data) # 读取woff数据
glyf = font['glyf'] # 获取请求到的字体形状
# 建立基础的字体和字体形状的对应关系
base_font_map = {
0: glyf['zero'],
1: glyf['four'],
2: glyf['five'],
3: glyf['three'],
4: glyf['seven'],
5: glyf['one'],
6: glyf['two'],
7: glyf['six'],
8: glyf['nine'],
9: glyf['eight']
}
code_name_map = font.getBestCmap() # 获取请求到的字体code和name的对应关系
font.close()
for code, name in code_name_map.items():
codestr = str(code - 48) # 根据分析结果需要减去48
current_shape = glyf[name] # 根据name获取字体形状
for number, shape in base_font_map.items(): # 遍历基础字体形状对应关系
if shape == current_shape: # 判断,如果两个字体形状相等
newmap[codestr] = str(number) # 将字体编码和字体添加到字典
# print(newmap)
return newmap
def font_file(r):
# 从网页里面获取字体
font_url = re.search(r"url\('(.*\.woff)'\)", r).group(1)
return font_url
def get_index():
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/104.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
url = 'https://www.renrenche.com/bj/ershouche/p2/?&plog_id=838083390d4b077a45852d11065f60ad'
complete_cookie = {}
# 第一次不带参数访问首页,获取 acw_tc 和 acw_sc__v2
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
complete_cookie.update(response.cookies.get_dict())
arg1 = re.findall("arg1='(.*?)'", response.text)[0]
with open('tiaoshi.js', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
acw_sc_v2_js = f.read()
acw_sc__v2 = execjs.compile(acw_sc_v2_js).call('ss', arg1)
complete_cookie.update({"acw_sc__v2": acw_sc__v2})
# 第二次访问首页,获取其他 cookies
response2 = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers, cookies=complete_cookie)
font_url = font_file(response2.text)
# print(font_url)
html = etree.HTML(response2.text)
items = html.xpath('//ul[@class="row-fluid list-row js-car-list"]/li')
for i in items:
title = maps(i.xpath('.//h3/text()'))
font = woff_font(font_url)
trans_title = "".join([i if not i.isdigit() else font[i] for i in title]) # 替换错误字体,获取真实标题
print(trans_title)
get_index()运行结果:
/usr/local/bin/python3.9 "/Volumes/shifeng/人人车.py"
斯巴鲁-森林人 2016款 2.5i 豪华导航版
雪铁龙-雪铁龙C4L 2013款 1.6THP 自动劲智版
日产-骐达TIIDA 2011款 1.6L CVT智能型
大众-途观 2012款 1.8TSI 自动四驱菁英版
本田-飞度 2018款 1.5L CVT舒适天窗版
北京-北京BJ20 2016款 1.5T CVT豪华型
东风风光-风光ix5 2019款 360TGDI CVT智尊型
广汽传祺-传祺GS3 2017款 150N 自动精英版
英菲尼迪-英菲尼迪M系 2008款 M35 尊尚版
奥迪-奥迪A4L 2015款 45 TFSI quattro个性运动型
大众-宝来 2016款 1.6L 自动时尚型
日产-轩逸 2018款 经典 1.6XE+ CVT豪华版
捷豹-捷豹F-PACE 2019款 2.0T 四驱R-Sport运动版
奥迪-奥迪Q5(进口) 2010款 3.2FSI 运动版
玛莎拉蒂-Levante 2019款 3.0T 标准版
福特-福克斯 6004款 三厢 5.9L 手动舒适型
日产-逍客 2012款 2.0XV 雷 CVT 2WD
宝马-宝马3系 2016款 316Li 时尚型
现代-悦动 2020款 1.6L 自动GL悦目版
现代-北京现代ix35 2012款 2.0L 自动两驱精英版GLS
福特-福克斯 2011款 三厢 1.8L 自动时尚型
本田-飞度 2016款 1.5L LX CVT舒适型
奥迪-奥迪A4L 2011款 1.8 TFSI 舒适型
日产-奇骏 2012款 2.5L CVT豪华版 4WD
广汽埃安-AION V 2020款 80 智享科技版
丰田-亚洲龙 2019款 2.5L Touring尊贵版
荣威-荣威Ei5 2021款 超爽版
宝马-宝马5系 2011款 523Li 豪华型
本田-杰德 2017款 1.8L 自动舒适版 5座
凯迪拉克-凯迪拉克SRX 2014款 3.0L 豪华型
丰田-卡罗拉 2017款 改款 1.2T S-CVT GL
保时捷-Macan 2014款 Macan S 3.0T
丰田-汉兰达 2011款 2.7L 两驱7座豪华版
大众-迈腾 2013款 1.8TSI 豪华型
别克-君越 2018款 28T 豪华型
日产-纳瓦拉 2017款 2.5L自动两驱豪华版QR25
别克-凯越 6009款 5.7LE-MT
奥迪-奥迪A3 2014款 Sportback 35 TFSI 自动时尚型
宝马-宝马4系 2017款 425i M运动套装
宝马-宝马5系 2018款 530Li 领先型 M运动套装
保时捷-Panamera 2016款 Panamera 4 Edition 3.0T
奔驰-奔驰V级 2017款 V 260 L 尊贵加长版
Process finished with exit code 0