【C++】STL 容器 - list 双向链表容器 ① ( 容器特点 | 容器操作时间复杂度 | 构造函数 )
文章目录
- 一、 list 双向链表容器简介
-
- 1、容器特点
- 2、容器操作时间复杂度
- 3、遍历访问
- 5、头文件
- 二、 list 双向链表容器 构造函数
-
- 1、默认无参构造函数
- 2、创建包含 n 个相同元素的 list 双向链表
- 3、使用初始化列表构造 list 双向链表
- 4、使用另外一个 list 容器 构造 list 双向链表容器
一、 list 双向链表容器简介
1、容器特点
list 双向链表容器 可以在 任意位置 高效的 进行 插入 / 删除 元素 ;
list 双向链表容器 的 元素的指针 : 容器 中的元素 , 包含 2 个指针 , 一个指向该元素的前驱 , 一个指向该元素的后继 ;
2、容器操作时间复杂度
list 双向链表容器 操作时间复杂度 :
- 头部和尾部插入或删除元素的时间复杂度是 O(1) ;
- 表中间插入或删除元素 , 最坏情况可能需要移动 n 个元素 , 时间复杂度是 O(n) ;
3、遍历访问
迭代器 : list 双向链表容器 提供了 迭代器 功能 , 可以使用 迭代器 遍历 容器中的元素 ;
list 双向链表容器 不能 随机存储访问 , 也就是 不能 根据下标 获取元素 , 不能使用 at() 函数 和 [] 操作符访问容器中的元素 ;
5、头文件
使用 list 双向链表容器 , 需要导入 头文件 ;
#include
二、 list 双向链表容器 构造函数
list 双向链表容器 常用操作 , 基本与 vector 相同 , 这里进行简单介绍 ;
1、默认无参构造函数
list 双向链表容器 默认的无参构造函数 , 构造格式如下 :
list<T> lstT
在尖括号中的 T 泛型类型是 list 双向链表 容器中存储的元素类型 ;
lstT 是双向链表容器的 变量名 ;
该默认无参构造函数 会创建空的 list 双向链表 ;
代码示例 :
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
int main() {
// 默认无参构造函数 会创建空的 list 双向链表
// list 双向链表容器, 存储 int 类型元素
list<int> lstInt;
// list 双向链表容器, 存储 float 类型元素
list<float> lstFloat;
// list 双向链表容器, 存储 string 类型元素
list<string> lstString;
// 控制台暂停 , 按任意键继续向后执行
system("pause");
return 0;
};
2、创建包含 n 个相同元素的 list 双向链表
创建包含 n 个相同元素的 list 双向链表 , 构造函数会将 n 个相同的元素 拷贝到 容器中 ;
函数原型如下 :
list(size_type n, const value_type& value = value_type(), const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
该 构造函数会创建一个包含 n 个元素的新列表 , 每个元素的值都初始化为 value ;
如果没有提供 value , 则元素初始化为默认值 , 使用提供的 alloc 来分配内存 ;
如 : 如果是 int 类型的元素 , 则初始化为 0 ;
代码示例 :
// list 双向链表容器, 存储 3 个 int 类型元素 666
list<int> lstInt(3, 666);
完整代码示例 :
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
// 打印 list 容器内容
void printL(list<int>& lst) {
// 获取迭代器起始位置
list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
cout << "list 容器内容 : ";
// 循环判定, 如果没有迭代到最后一个元素的后一个位置, 那么一直循环
while (it != lst.end())
{
// 获取元素值
cout << *it << " ";
// 迭代器指向下一个元素
it++;
}
// 回车换行
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// list 双向链表容器, 存储 3 个 int 类型元素 666
list<int> lstInt(3, 666);
// 打印 list 容器内容
printL(lstInt);
// 控制台暂停 , 按任意键继续向后执行
system("pause");
return 0;
};
执行结果 :
list 容器内容 : 666 666 666
请按任意键继续. . .
3、使用初始化列表构造 list 双向链表
使用初始化列表构造 list 双向链表 函数原型如下 :
list(std::initializer_list<value_type> init, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
该 构造函数会创建一个列表 , 其元素是从 init 初始化器列表复制的 ;
代码示例 :
// list 双向链表容器 使用初始化列表构造
list<int> lstInt{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
完整代码示例 :
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
// 打印 list 容器内容
void printL(list<int>& lst) {
// 获取迭代器起始位置
list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
cout << "list 容器内容 : ";
// 循环判定, 如果没有迭代到最后一个元素的后一个位置, 那么一直循环
while (it != lst.end())
{
// 获取元素值
cout << *it << " ";
// 迭代器指向下一个元素
it++;
}
// 回车换行
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// list 双向链表容器 使用初始化列表构造
list<int> lstInt{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 打印 list 容器内容
printL(lstInt);
// 控制台暂停 , 按任意键继续向后执行
system("pause");
return 0;
};
执行结果 :
list 容器内容 : 1 2 3 4 5
请按任意键继续. . .
4、使用另外一个 list 容器 构造 list 双向链表容器
使用另外一个 list 容器 构造 list 双向链表容器 , 有 3 种方式 :
- 参数为另一个 list 容器引用 : 构造函数会创建一个新的列表 , 它是另一个列表 other 的副本 ;
list(const list& other);
// list 双向链表容器 使用初始化列表构造
list<int> lstInt{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 是 lstInt 的副本
list<int> lstInt2 (lstInt);
- 参数为另一个 list 容器 指定区间范围的 迭代器 : 该 构造函数会创建一个新的列表 , 其元素是从范围 [first, last) 复制的 , 注意是 前闭后开区间 ; 这个范围可以是任何类型的输入迭代器 , 包括但不限于指针和 std::vector、std::deque 等容器的迭代器 ;
list(InputIt first, InputIt last);
// list 双向链表容器 使用初始化列表构造
list<int> lstInt{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 注意是前闭后开区间
list<int> lstInt3( ++lstInt.begin(), lstInt.end());
代码示例 :
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "list"
// 打印 list 容器内容
void printL(list<int>& lst) {
// 获取迭代器起始位置
list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
cout << "list 容器内容 : ";
// 循环判定, 如果没有迭代到最后一个元素的后一个位置, 那么一直循环
while (it != lst.end())
{
// 获取元素值
cout << *it << " ";
// 迭代器指向下一个元素
it++;
}
// 回车换行
cout << endl;
}
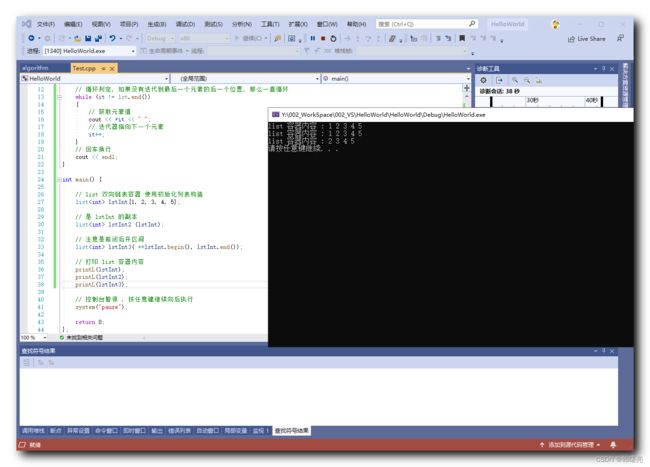
int main() {
// list 双向链表容器 使用初始化列表构造
list<int> lstInt{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 是 lstInt 的副本
list<int> lstInt2 (lstInt);
// 注意是前闭后开区间
list<int> lstInt3( ++lstInt.begin(), lstInt.end());
// 打印 list 容器内容
printL(lstInt);
printL(lstInt2);
printL(lstInt3);
// 控制台暂停 , 按任意键继续向后执行
system("pause");
return 0;
};
执行结果 :
list 容器内容 : 1 2 3 4 5
list 容器内容 : 1 2 3 4 5
list 容器内容 : 2 3 4 5
请按任意键继续. . .