《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》- 平衡搜索树 -全网唯一完整详细实现插入和删除操作的模板类
平衡搜索树
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_34Balanced search tree
概述
本章会讲AVL、红-黑树、分裂树、B-树。
平衡搜索树的应用?
AVL 和红-黑树和分裂树适合内部存储的应用。
B-树适合外部存储的应用,例如,存储在磁盘上的大型词典。
STL类map 和 multimap使用的是红-黑树结构,以保证查找、插入和删除操作具有对数级的时间性能。
什么时候适合用平衡搜索树?
- 按关键字实施字典操作,而且操作时间不能超过指定的范围。
- 按名次实施的查找和删除操作。
- 不按精确的关键字匹配所进行的字典操作(例如寻找关键字大于k的最小元素)。
AVL和红-黑树的旋转?
AVL树对每个插人操作最多需要一次旋转,对每个删除操作最多需要O(logn)次旋转。
红-黑树对每个插入和删除操作,都只需要一次旋转。
当一次旋转只需用时 Θ ( 1 ) \Theta(1) Θ(1)时,他们之间的区别不明显。但是当一次旋转的时间复杂度比较高时,比如平衡优先搜索树。平衡优先搜索树用于描述具有二维关键字的元素,此时,每个关键字是一数对(x,y)。它是关于y的优先队列,同时又是关于x的搜索树。在这样的树中,每一次旋转都需耗时 O(logn)。如果用红-黑树来描述平衡优先搜索树,则因为每一次插入或删除仅需要执行一次旋转,所以插入或删除操作的总时间仍保持为O(logn)。当使用AVL树时,则删除操作的时间将变为 O ( l o g 2 n ) O(log^2n) O(log2n)。
AVL树
定义
如果搜索树的高度总是O(logn),我们就能保证查找、插人和删除的时间为O(logn)。最坏情况下的高度为O(logn)的树称为平衡树(balanced tree)。比较流行的一种平衡树是AVL树(AVL tree),它是Adelson-Velskii 和 Landis在 1962年提出的。
定义15-1一棵空的二叉树是AVL树;如果T是一棵非空的二叉树, T L T_L TL和 T R T_R TR分别是其左子树和右子树,那么当T满足以下条件时,T是一棵AVL树:
1) T L T_L TL和 T R T_R TR是AVL树;2) ∣ h L − h R ∣ < 1 |h_L-h_R|<1 ∣hL−hR∣<1,其中 h L h_L hL和 h R h_R hR分别是 T L T_L TL和 T R T_R TR的高。
一棵AVL搜索树既是二叉搜索树,也是AVL树。
一棵索引AVL搜索树既是索引二叉搜索树,也是AVL树。
用AVL搜索树来描述字典的要求
如果用AVL搜索树来描述字典,并在对数级时间内完成每一种字典操作,那么,我们必须确定AVL树的下述特征:
1)一棵n个元素的AVL树,其高度是O(logn)。
2)对于每一个n, n ≥ 0 n\geq 0 n≥0,都存在一棵AVL树。
3)对一棵n元素的AVL搜索树,在O(高度)=O(logn)的时间内可以实现查找。
4)将一个新元素插入一棵n元素的AVL搜索树中,可以得到一棵n+1个元素的AVL树,而且插人用时为O(logn)。
5)一个元素从一棵n元素的AVL搜索树中删除,可以得到一棵n-1个元素的AVL树,而且删除用时为O(logn)。
AVL树的高度
对一棵高度为h的AVL树,令 N h N_h Nh是其最少的节点数。在最坏情况下,根的一棵子树的高度是h-1,另一棵子树的高度是h-2,而且两棵子树都是AVL树。因此有:
N h = N h − 1 + N h − 2 + 1 , N 0 = 0 且 N 1 = 1 N_h=N_{h-1}+N_{h-2}+1,N_0=0且N_1=1 Nh=Nh−1+Nh−2+1,N0=0且N1=1
N h N_h Nh的定义与斐波拉契数列的定义是相似的:
F n = F n − 1 + F n − 2 , F 0 = 0 且 F 1 = 1 F_n = F_{n - 1} + F_{n-2}, F_0=0且F_1 = 1 Fn=Fn−1+Fn−2,F0=0且F1=1
经分析可得 N h N_h Nh的列表为:1,2,4,7,12,20,33…
F n F_n Fn的列表为:1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34…
因此 N h N_h Nh可以表示为:
N h = F h + 2 − 1 , h ≥ 0 N_h=F_{h+2}-1,h\geq 0 Nh=Fh+2−1,h≥0
由斐波拉契定理可知:
F h = ϕ h 5 F_h=\frac{\phi^h}{\sqrt{5}} Fh=5ϕh,其中 ϕ = 1 + 5 2 \phi=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2} ϕ=21+5,因此 N h ≈ ϕ h + 2 5 − 1 N_h\approx\frac{\phi^{h+2}}{\sqrt{5}}-1 Nh≈5ϕh+2−1。如果树中有n个节点,那么树的最大高度为: l o g ϕ ( 5 ( n + 1 ) ) − 2 ≈ 1.44 l o g 2 ( n + 2 ) = O ( l o g n ) log_{\phi}(\sqrt{5}(n+1))-2\approx1.44log_2(n+2)=O(logn) logϕ(5(n+1))−2≈1.44log2(n+2)=O(logn)。
证明了AVL树的最大高度满足O(logn)。
AVL树的描述
链表描述-平衡因子
AVL树一般用链表描述。但是,为简化插入和删除操作,我们为每个节点增加一个平衡因子bf。节点x的平衡因子bf(x)定义为:x的左子树高度-x的右子树高度
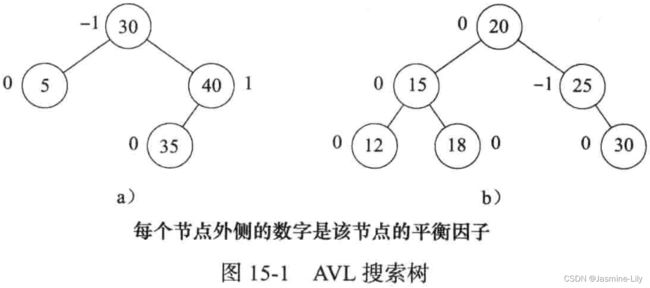
从AVL树的定义可以知道,平衡因子的可能取值为-1、0和1。图15-1是两棵带有平衡因子的AVL搜索树。
AVL树的搜索
与二叉搜索树的搜索方法一致。
假设要查找关键字为theKey的元素。先从根开始查找。如果根为空,那么搜索树不包含任何元素,即查找失败。如果不空,则将 theKey与根的关键字相比较。如果 theKey小,那么就不必在右子树中查找,只要查找左子树。如果theKey大,则正好相反,只需查找右子树。如果 theKey等于根的关键字,则查找成功。时间复杂度为O(n)。
AVL树的插入
插入新的元素可能会导致不平衡。在插入之前,从根节点往下移动寻找插入新元素的位置时,设X是最后一个具有-1或1平衡因子的节点。
如果节点X不存在,那么从根节点至新插入节点的途径中,所有节点在插入前的平衡因子都是0。由于插人操作只会使平衡因子增减0或1,并且只有从根节点至新插入节点的途径中的节点的平衡因子会被改变,所以插入后,树的平衡不会被破坏。因此,只有插人后的树是不平衡的,X才存在。
一棵树从平衡变为不平衡的唯一过程是:在插人操作之后,平衡因子bf(X)的值由-1变为-2,或者由1变为2。当插入元素后,X是离新插入节点最近的祖先,且平衡因子是-2或2。
节点X的不平衡情况有两类:L型不平衡(新插人节点在X的左子树中)和R型不平衡。
L型不平衡可以分为两类:
- LL:新插入节点在X节点的左子树的左子树中
- LR:新插入节点在X节点的左子树的右子树中
R型不平衡可以分为两类:
- RL:新插入节点在X节点的右子树的左子树中
- RR:新插入节点在X节点的右子树的右子树中
因此,AVL树中插入节点可能会导致不平衡的情况总共分为四类。
解决不平衡的方法:
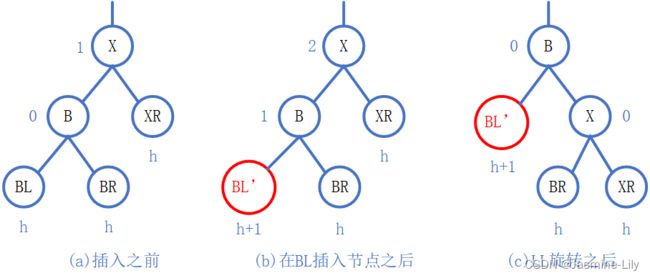
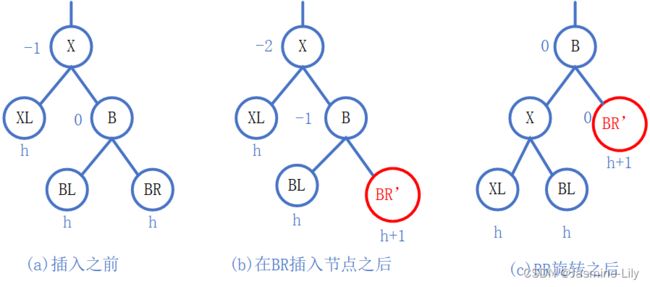
LL旋转
下图是一种普通的LL型不平衡。图a是插入前的条件,图b是在节点B的左子树BL中插人一个元素后的情形。恢复平衡所进行的子树移动如图c所示。原来以X为根节点的子树,现在以B为根节点,BL’仍然是B的左子树,X变成B的右子树的根,BR变成X的左子树,X的右子树不变。随着X的平衡因子的改变,在从B到新插入节点的路径上,BL’的所有节点的平衡因子都要改变。其他节点的平衡因子与旋转前的一致。因为图a和图c的子树的高度是一样的,所以它们的祖父节点如果存在的话,其平衡因子与插入前是一样的。因此所有节点的平衡因子都是-1、0或1。
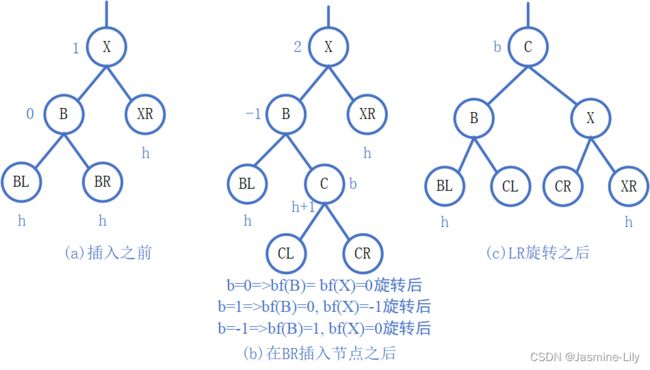
LR旋转
下图给出了一种普通的LR型不平衡。因为插人操作发生在B的右子树,所以这棵子树在插入后不可能为空,因此节点C是存在的。但是,C的子树CL和CR有可能为空。为了恢复平衡,需要对子树进行重新整理,如图c所示,将C作为根,B作为C的左子树,B的左子树不变,B的右子树指向C的左子树;X作为C的右子树,X的左子树指向C的右子树,X的右子树不变。重新整理后,bf(B)和 bf(X)的值取决于bf(C)在插入之后、重新整理之前的值b。重新整理后的子树仍是二叉搜索树。另外,因为图a 和图c的子树的高度是相同的,所以它们的祖先如果存在,其平衡因子在插入前与在插入后也是相同的。因此,在节点A的一个LR旋转即可完成整个树的重新平衡。
可以理解为X的左孩子的RR旋转和X的LL旋转。
注意事项:需要检查X的左孩子的右孩子是否存在,如果存在,则执行此算法;如果不存在,则需要执行LL算法。
RR旋转
下图是一种普通的RR型不平衡。图a是插入前的条件,图b是在节点B的右子树BR中插人一个元素后的情形。恢复平衡所进行的子树移动如图c所示。原来以X为根节点的子树,现在以B为根节点,BR’仍然是B的右子树,X变成B的左子树的根,BL变成X的右子树,X的左子树不变。随着X的平衡因子的改变,在从B到新插入节点的路径上,BR’的所有节点的平衡因子都要改变。其他节点的平衡因子与旋转前的一致。因为图a和图c的子树的高度是一样的,所以它们的祖父节点如果存在的话,其平衡因子与插入前是一样的。因此所有节点的平衡因子都是-1、0或1。
RL旋转
下图给出了一种普通的RL型不平衡。因为插人操作发生在B的左子树,所以这棵子树在插入后不可能为空,因此节点C是存在的。但是,C的子树CL和CR有可能为空。为了恢复平衡,需要对子树进行重新整理,如图c所示,将C作为根,B作为C的右子树,B的右子树不变,B的左子树指向C的右子树;X作为C的左子树,X的右子树指向C的左子树,X的左子树不变。重新整理后,bf(B)和 bf(X)的值取决于bf(C)在插入之后、重新整理之前的值b。重新整理后的子树仍是二叉搜索树。另外,因为图a 和图c的子树的高度是相同的,所以它们的祖先如果存在,其平衡因子在插入前与在插入后也是相同的。因此,在节点A的一个RL旋转即可完成整个树的重新平衡。
可以理解为X的右孩子的LL旋转和X的RR旋转。
注意事项:需要检查X的右孩子的左孩子是否存在,如果存在,则执行此算法;如果不存在,则需要执行LL算法。
插入节点的步骤
使用递归的方法:沿着从根节点开始的路径,根据新元素的关键字,去寻找新元素的插入位置。
- 终止条件:所传递的参数cur节点为nullptr。new一个新的AVLTreeNode节点。
- 如果插入元素的键值大于当前节点的键值,则递归到当前节点的左孩子。根据当前cur的bf值决定是否执行LL旋转或LR旋转。
- 如果插入元素的键值小于当前节点的键值,则递归到当前节点的右孩子。根据当前cur的bf值决定是否执行RR旋转或RL旋转。
- 如果插入元素的键值等于当前节点的键值,则更新当前节点的值为新的值。
- 每轮递归都要更新当前节点的高度。
AVL树的删除
删除一个节点后,记录其父亲节点q。如果要删除图15-1b中关键字为25的元素,那么该元素的节点被删除,并且根节点的右孩子指针指向被删除节点的唯一孩子。因为根节点是被删除节点的父节点,所以q就是根节点。如果要删除的是关键字为15的元素,那么该元素的节点将被关键字为12的元素所占用,而
12的原节点被删除。这时的q是原15的节点(根的左孩子)。
**从根到q的路径上的一些节点或全部节点的平衡因子都可能会改变,所以要从q沿原路折回,可以使用栈存储被删除节点的所有祖先,以便后续调整平衡树。**如果删除发生在q的左子树,那么bf(q)减1。如果删除发生在q的右子树,那么bf(q)加1。下面是删除的几种情形:
- D1:如果q的新平衡因子是0,那么它的高度减少了1,这时需要改变它的父节点(如果有的话)的平衡因子,而且可能需要改变其他祖先节点的平衡因子。
- D2:如果q的新平衡因子是-1或1,那么它的高度与删除前相同,而且无需改变其祖先的平衡因子值。
- D3:如果q的新平衡因子是-2或2,那么树在q处是不平衡的。
从q到根节点的路径上,节点的平衡因子可能发生很大变化,有的节点的平衡因子有可能变为-2或2。令A是第一个这样的节点。要恢复A节点的平衡,需要根据不平衡的类型而定。如果删除发生在A的左子树,那么不平衡类型是L型;否则,不平衡类型就是R型。如果在删除后,bf(A)=2,那么在删除前,bf(A)的值一定为1。因此,A有一棵以B为根的左子树。根据bf(B)的值,可以把一个R型不平衡细分为R0,R1和R-1,把一个L型不平衡细分为L0,L1和L-1。
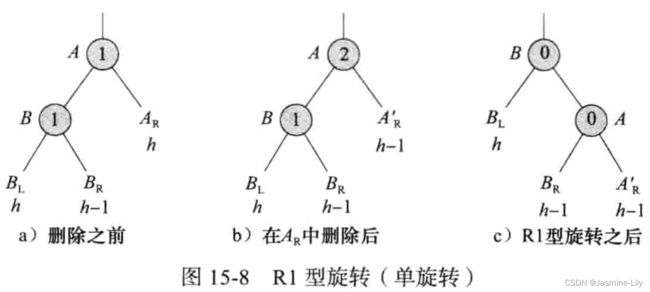
- R0型:就是B节点的bf为0。子树的高度在删除前和删除后都是h+2,因此,到根节点途径上的剩余节点没有改变平衡因子,整棵树在一次旋转后获得平衡。其实和LL旋转一样的操作。
- R1型:B节点的bf为1。旋转后子树的高度是h+1,比删除前减少了1。因此,如果A不是根节点,它的某些祖先的平衡因子将产生变化,可能需要进行旋转以保持平衡。R1旋转后,必须继续检查至根节点路径上的节点。其实和LL旋转一样的操作。
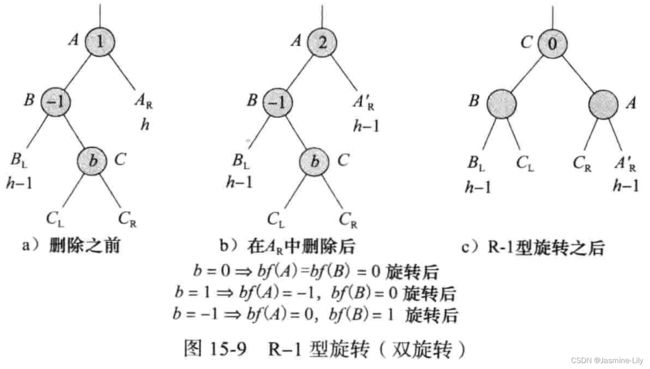
- R-1型:B节点的bf为-1。节点A和B在旋转后的平衡因子取决于B的右孩子的平衡因子b。这次旋转得到了一棵高度为h1的子树,而删除前的子树高度是h+2,因此,在至根节点的路径上需要继续旋转。先来一次B节点的L0旋转,再来一次A节点的R0旋转。
L0,L1,L-1与R0,R1和R-1差不多,只是方向不同。
代码
AVLTree.h
/*
Project name : _34Balanced_search_tree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月27日10点57分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: AVL树模板类
*/
#ifndef _34BALANCED_SEARCH_TREE_AVLTREE_H
#define _34BALANCED_SEARCH_TREE_AVLTREE_H
#include "AVLTreeNode.h"
#include "dictionary.h"
#include >*
static void output(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* t) { cout << *t << endl; }
static void inOrder(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* t);
static void preOrder(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* t);
void rotateLL(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x);
void rotateLR(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x);
void rotateRR(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x);
void rotateRL(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x);
void insert(pair<K, E>& thePair, AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& cur);
};
/*私有静态成员初始化*/
/*这里是静态函数指针成员的初始化,不初始化会引发LINK错误*/
template<class K, class E>
void (*AVLTree<K,E>::visit)(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*) = 0; // visit function
/*中序遍历 递归*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::inOrder(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* t)
{
if (t != nullptr)
{
inOrder(t->leftChild);/*中序遍历左子树*/
visit(t);/*访问树根*/
inOrder(t->rightChild);/*中序遍历右子树*/
}
}
/*前序遍历 递归*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::preOrder(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* t)
{
if (t != nullptr)
{
visit(t);/*访问树根*/
preOrder(t->leftChild);/*中序遍历左子树*/
preOrder(t->rightChild);/*中序遍历右子树*/
}
}
/* 查找元素
* 输入:theKey表示需要查找元素的键值
* 输出:键值为theKey的节点的pair地址
* 时间复杂度:O(logn),n表示节点个数
*/
template<class K, class E>
pair<K, E>* AVLTree<K,E>::find(K theKey) const
{
// 返回值是匹配数对的指针
// 如果没有匹配的数对,返回值为nullptr
// p从根节点开始搜索,寻找关键字等于theKey的一个元素
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> > *p = root;
while (p != nullptr)
// 检查元素 p->element
if (theKey < p->element.first)
p = p->leftChild;
else
if (theKey > p->element.first)
p = p->rightChild;
else // 找到匹配的元素
return &p->element;
// 没找到匹配的元素
return nullptr;
}
/*
* LL旋转:在x的左孩子的左孩子插入元素的时候使用
* 输入:AVLTreeNode>* x,x表示从根节点往下移动寻找插入新元素的位置时,最后一个具有-1或1平衡因子的节点。
* 输出:void
* 时间复杂度:O(1)
*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::rotateLL(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x){
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* b = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = b->rightChild;
b->rightChild = x;
// 更新x的高度
if(x->leftChild != nullptr && x->rightChild != nullptr)
x->height = max(x->leftChild->height, x->rightChild->height) + 1;
else if(x->leftChild != nullptr)
x->height = x->leftChild->height + 1;
else if(x->rightChild != nullptr)
x->height = x->rightChild->height + 1;
else
x->height = 1;
// 更新b的高度
if(b->leftChild != nullptr && b->rightChild != nullptr)
b->height = max(b->leftChild->height, b->rightChild->height) + 1;
else if(b->leftChild != nullptr)
b->height = b->leftChild->height + 1;
else if(x->rightChild != nullptr)
b->height = b->rightChild->height + 1;
else
b->height = 1;
x = b;
}
/*
* RR旋转:在x的右孩子的右孩子插入元素的时候使用
* 输入:AVLTreeNode>* x,x表示从根节点往下移动寻找插入新元素的位置时,最后一个具有-1或1平衡因子的节点。
* 输出:void
* 时间复杂度:O(1)
*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::rotateRR(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x){
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>* b = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = b->leftChild;
b->leftChild = x;
// 更新x的高度
if(x->leftChild != nullptr && x->rightChild != nullptr)
x->height = max(x->leftChild->height, x->rightChild->height) + 1;
else if(x->leftChild != nullptr)
x->height = x->leftChild->height + 1;
else if(x->rightChild != nullptr)
x->height = x->rightChild->height + 1;
else
x->height = 1;
// 更新b的高度
if(b->leftChild != nullptr && b->rightChild != nullptr)
b->height = max(b->leftChild->height, b->rightChild->height) + 1;
else if(b->leftChild != nullptr)
b->height = b->leftChild->height + 1;
else if(x->rightChild != nullptr)
b->height = b->rightChild->height + 1;
else
b->height = 1;
x = b;
}
/*
* LR旋转:在x的左孩子的右孩子插入元素的时候使用
* 输入:AVLTreeNode>* x,x表示从根节点往下移动寻找插入新元素的位置时,最后一个具有-1或1平衡因子的节点。
* 输出:void
* 时间复杂度:O(1)
*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::rotateLR(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x){
rotateRR(x->leftChild);
rotateLL(x);
}
/*
* RL旋转:在x的右孩子的左孩子插入元素的时候使用
* 输入:AVLTreeNode>* x,x表示从根节点往下移动寻找插入新元素的位置时,最后一个具有-1或1平衡因子的节点。
* 输出:void
* 时间复杂度:O(1)
*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::rotateRL(AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& x){
rotateLL(x->rightChild);
rotateRR(x);
}
/*
* 插入元素
* 输入:const pair thePair表示需要插入的键值对
* 输出:void
* 时间复杂度:O(logn),表示节点个数
*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::insert(pair<K, E>& thePair, AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>*& cur)
{
if(cur == nullptr)
{
cur = new AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> > (thePair, nullptr, nullptr);
treeSize++;
}
else if(thePair.first < cur->element.first){
insert(thePair, cur->leftChild);
// 计算bf,检查bf是否 == 2,如果是需要调整平衡
int bf = 0;
if(cur->leftChild != nullptr && cur->rightChild != nullptr)
bf = cur->leftChild->height - cur->rightChild->height;
else if(cur->leftChild != nullptr)
bf = cur->leftChild->height;
else if(cur->rightChild != nullptr)
bf = 0 - cur->rightChild->height;
else
bf = 0;
if(bf == 2){
if(thePair.first < cur->leftChild->element.first)// 左左插入
rotateLL(cur);// 单旋转
else // 左右插入
{
if(cur->leftChild->rightChild == nullptr)
rotateLL(cur);// 当当前节点的左孩子的右孩子为空时,找不到示意图中替换的C节点
else
rotateLR(cur);
}
}
}
else if(thePair.first > cur->element.first){
insert(thePair, cur->rightChild);
// 计算bf,检查bf是否等于-2,如果是需要调整平衡
int bf = 0;
if(cur->leftChild != nullptr && cur->rightChild != nullptr)
bf = cur->leftChild->height - cur->rightChild->height;
else if(cur->leftChild != nullptr)
bf = cur->leftChild->height;
else if(cur->rightChild != nullptr)
bf = 0 - cur->rightChild->height;
else
bf = 0;
if(bf == -2){
if(thePair.first > cur->rightChild->element.first) // 右右插入
rotateRR(cur);// 单旋转
else // 右左插入
{
if(cur->rightChild->leftChild == nullptr)
rotateRR(cur);// 当当前节点的左孩子的右孩子为空时,找不到示意图中替换的C节点
else
rotateRL(cur);
}
}
}
else// 如果键值已经存在的话,就更新元素
cur->element.second = thePair.second;
// 更新cur节点的高度
if(cur->leftChild != nullptr && cur->rightChild != nullptr)
cur->height = max(cur->leftChild->height, cur->rightChild->height) + 1;
else if(cur->leftChild != nullptr)
cur->height = cur->leftChild->height + 1;
else if(cur->rightChild !=nullptr)
cur->height = cur->rightChild->height + 1;
else
cur->height = 1;
}
/*
* 删除元素
* 输入:const K theKey表示需要删除元素的键值
* 输出:void
* 时间复杂度:O(logn),n表示节点个数
*/
template<class K, class E>
void AVLTree<K,E>::erase(K theKey)
{
// 删除关键字等于theKey的数对
// 查找关键字为theKey的节点
// 前面的删除节点的步骤与二叉搜索树的一致;但是要记录一下路径st
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> > *p = root,
*pp = nullptr;
stack<AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> > *> st;// 记录轨迹
while (p != nullptr && p->element.first != theKey)
{
pp = p;
st.push(pp);// 记录轨迹
if (theKey < p->element.first)
p = p->leftChild;
else
p = p->rightChild;
}
if (p == nullptr)
return; // 不存在与关键字theKey匹配的数对
// 重新组织树结构
// 当p有两个孩子时的处理
if (p->leftChild != nullptr && p->rightChild != nullptr)
{
// 两个孩子
// 在P的左子树中寻找最大元素
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> > *s = p->leftChild,
*ps = p; // s的父节点
while (s->rightChild != nullptr)
{// 移动到更大的pair
ps = s;
st.push(ps);// 记录轨迹
s = s->rightChild;// 右孩子比较大
}
// 将最大元素s移到p
// p->element = s->element 的键值是 const
// 当最大值就是p的左孩子时,new的元素不能直接指向p的左孩子,而要指向p的左孩子的左孩子(此时p的左孩子没有右孩子),因为到时候s会被delete掉,这个问题在后面的p至多有一个孩子那里解决的
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> >* q = nullptr;
q = new AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> >(s->element, p->leftChild, p->rightChild, p->height);
// pp是p的父节点
// 如果p没有父节点
if (pp == nullptr)
root = q;
else if (p == pp->leftChild)// 如果p是pp的左孩子
pp->leftChild = q;
else// 如果p是pp的右孩子
pp->rightChild = q;
// 如果s的父节点就是p,说明p节点的左子树只有左子树没有右子树
// 那么删除p后pp就是其父节点
if (ps == p) pp = q;
else pp = ps;// 反之ps是其父节点
delete p;
p = s;
}
// p至多只有一个孩子
// 把孩子的指针存放到c
AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E> > *c;
if (p->leftChild != nullptr)
c = p->leftChild;
else
c = p->rightChild;
// 删除p
if (p == root)
root = c;
else
{// p是pp的左孩子还是右孩子
if (p == pp->leftChild)
pp->leftChild = c;
else pp->rightChild = c;
}
treeSize--;
delete p;
// 调整平衡
int bf = 0;
bool isRoot = false;// 如果当前节点是根节点,当调整树之后,需要更新root指向的节点
while(!st.empty()){
p = st.top();
st.pop();
// 更新p节点的高度和其bf值
if(p->leftChild != nullptr && p->rightChild != nullptr)
{
p->height = max(p->leftChild->height, p->rightChild->height) + 1;
bf = p->leftChild->height - p->rightChild->height;
}
else if(p->leftChild != nullptr){
p->height = p->leftChild->height + 1;
bf = p->leftChild->height;
}
else if(p->rightChild != nullptr){
p->height = p->rightChild->height + 1;
bf = 0 - p->rightChild->height;
}
else{
p->height = 1;// 只有它自己
bf = 0;
}
if(bf == 2) // 说明被删除节点在当前节点的右子树,是R型不平衡
{
// 计算当前节点左孩子的bf值
int bfL = 0;
// p的左孩子一定存在
if(p->leftChild->leftChild != nullptr && p->leftChild->rightChild != nullptr)
bfL = p->leftChild->leftChild->height - p->leftChild->rightChild->height;
else if(p->leftChild->leftChild != nullptr)
bfL = p->leftChild->leftChild->height;
else if(p->leftChild->rightChild != nullptr)
bfL = 0 - p->leftChild->rightChild->height;
else
bfL = 0;
// R0型
if(bfL == 0){
if(p == root)
isRoot = true;
rotateLL(p);
if(isRoot)
root = p;
break;// 不用检查其父节点了
}
else if(bfL == 1)// R1型
{
if(p == root)
isRoot = true;
rotateLL(p);// 需要继续检查其父节点
if(isRoot)
root = p;
}
else if(bfL == -1)// R-1型
{
if(p == root)
isRoot = true;
if(p->leftChild->rightChild == nullptr)
rotateLL(p);// 当当前节点的左孩子的右孩子为空时,找不到示意图中替换的C节点
else
rotateLR(p);//需要继续检查其父节点
if(isRoot)
root = p;
}
else{}// 其他,基本上不存在别的什么情况了
}
else if(bf == -2) // 说明被删除节点在当前节点的左子树,是L型不平衡
{
// 计算当前节点左孩子的bf值
int bfR = 0;
// p的右孩子一定存在
if(p->rightChild->leftChild != nullptr && p->rightChild->rightChild != nullptr)
bfR = p->rightChild->leftChild->height - p->rightChild->rightChild->height;
else if(p->rightChild->leftChild != nullptr)
bfR = p->rightChild->leftChild->height;
else if(p->rightChild->rightChild != nullptr)
bfR = 0 - p->rightChild->rightChild->height;
else
bfR = 0;
// L0型
if(bfR == 0){
if(p == root)
isRoot = true;
rotateRR(p);//需要继续检查其父节点
if(isRoot)
root = p;
break;// 不用检查其父节点了
}
else if(bfR == 1)// L1型
{
if(p == root)
isRoot = true;
rotateRR(p);//需要继续检查其父节点
if(isRoot)
root = p;
}
else if(bfR == -1)// L-1型
{
if(p == root)
isRoot = true;
if(p->rightChild->leftChild == nullptr)
rotateRR(p); // 当当前节点的右孩子的左孩子为空时,找不到示意图中替换的C节点
else
rotateRL(p);//需要继续检查其父节点
if(isRoot)
root = p;
}
else{}// 其他,基本上不存在别的什么情况了
}
else{}// 其他不操作
}
}
// overload << for pair
template <class K, class E>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const pair<K, E>& x)
{out << x.first << ":" << x.second; return out;}
template <class K, class E>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const AVLTreeNode<pair<K, E>>& x)
{out << x.element.first << ":" << x.element.second << " h = " << x.height; return out;}
#endif //_34BALANCED_SEARCH_TREE_AVLTREE_H
AVLTree.cpp
/*
Project name : _34Balanced_search_tree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月27日10点57分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: AVL树测试函数
*/
#include "AVLTree.h"
#includeAVLTreeNode.h
/*
Project name : _34Balanced_search_tree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月27日10点57分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: AVL树节点模板类
*/
#ifndef _34BALANCED_SEARCH_TREE_AVLTREENODE_H
#define _34BALANCED_SEARCH_TREE_AVLTREENODE_H
template<class T>
struct AVLTreeNode {
T element;
AVLTreeNode<T> *leftChild, // 左子树
*rightChild; // 右子树
// 记录height即可,需要bf的值可以根据height来计算,但是bf值本身没有特别的意义,只是为了方便分析各种不平衡的情况
int height;
AVLTreeNode() {
leftChild = rightChild = nullptr;
height = 0;
}
explicit AVLTreeNode(T &theElement) : element(theElement) {
leftChild = rightChild = nullptr;
height = 0;
}
explicit AVLTreeNode(T &theElement,
AVLTreeNode *theLeftChild,
AVLTreeNode *theRightChild)
: element(theElement), leftChild(theLeftChild), rightChild(theRightChild) {
height = 0;
}
explicit AVLTreeNode(T &theElement,
AVLTreeNode *theLeftChild,
AVLTreeNode *theRightChild, int theHeight)
: element(theElement), leftChild(theLeftChild), rightChild(theRightChild) {
height = theHeight;
}
};
#endif //_34BALANCED_SEARCH_TREE_AVLTREENODE_H
dictionary.h
/*
Project name : _33Search_tree
Last modified Date: 2023年12月21日11点13分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 字典虚基类
*/
#ifndef _33SEARCH_TREE_DICTIONARY_H
#define _33SEARCH_TREE_DICTIONARY_H
#include main.cpp
#include 运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_34Balanced search tree\cmake-build-debug\_34Balanced_search_tree.exe"
*************************AVLTreeTest() begin*******************************
Tree size is 10
Elements in ascending order are
2:d h = 1
5:b h = 2
30:a h = 1
31:i h = 3
32:g h = 2
33:j h = 1
35:e h = 4
60:c h = 1
80:f h = 2
85:h h = 1
Search for 60 succeeds
60 c
60 deleted
Tree size is 9
Elements in ascending order are
2:d h = 1
5:b h = 2
30:a h = 1
31:i h = 3
32:g h = 2
33:j h = 1
35:e h = 4
80:f h = 2
85:h h = 1
Search for 80 succeeds
80 f
80 deleted
Tree size is 8
Elements in ascending order are
2:d h = 1
5:b h = 2
30:a h = 1
31:i h = 4
32:g h = 2
33:j h = 1
35:e h = 3
85:h h = 1
Search for 30 succeeds
30 a
30 deleted
Tree size is 7
Elements in ascending order are
2:d h = 1
5:b h = 2
31:i h = 4
32:g h = 2
33:j h = 1
35:e h = 3
85:h h = 1
Search for 35 succeeds
35 e
35 deleted
Tree size is 6
Elements in ascending order are
2:d h = 1
5:b h = 2
31:i h = 4
32:g h = 1
33:j h = 3
85:h h = 1
Search for 2 succeeds
2 d
2 deleted
Tree size is 5
Elements in ascending order are
5:b h = 1
31:i h = 2
32:g h = 1
33:j h = 3
85:h h = 1
Search for 32 succeeds
32 g
32 deleted
Tree size is 4
Elements in ascending order are
5:b h = 1
31:i h = 2
33:j h = 3
85:h h = 1
Search for 5 succeeds
5 b
5 deleted
Tree size is 3
Elements in ascending order are
31:i h = 1
33:j h = 2
85:h h = 1
***************************AVLTreeTest() end*******************************
Process finished with exit code 0