VD6283TX环境光传感器(2)----移植闪烁频率代码
VD6283TX环境光传感器----2.移植闪烁频率代码
- 闪烁定义
- 视频教学
- 样品申请
- 源码下载
- 参考代码
- 硬件准备
- 开发板设置
- 生成STM32CUBEMX
- 串口配置
- IIC配置
- X-CUBE-ALS
- ADC使用定时器触发采样
- KEIL配置
- FFT代码配置
- app_x-cube-als.c
- 需要添加函数
- 演示结果
闪烁定义
光学闪烁是指人造光源产生的光的脉冲或波动现象。在低频下,闪烁是肉眼可见的,即人眼能够感知到光的闪动。然而,当频率超过100 Hz时,虽然闪烁对人眼不再可见,它仍然存在并可能对人体产生一定影响。大部分人造光源,如家庭和商业办公室使用的,会在接入电网时产生闪烁,其频率通常由所在国家的电力频率决定,一般为50 Hz或60 Hz。由于电流在光源中的交替流动,这些光源会在50 Hz或60 Hz的电网下产生100 Hz或120 Hz的闪烁频率。为了消除这种可见闪烁并减少其对人体的潜在影响,许多LED灯采用了脉冲宽度调制(PWM)的调光方法,从而实现更高的闪烁频率。VD6283传感器能够检测高达2 kHz的光闪烁频率,从而为光质量的监测提供精准数据。
最近在弄ST的课程,需要样片的可以加群申请:615061293 。
![]()
视频教学
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1pt4y1f7eh/
VD6283TX环境光传感器(2)----移植闪烁频率代码
样品申请
https://www.wjx.top/vm/OhcKxJk.aspx#
源码下载
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_24312945/88671493
参考代码
https://www.st.com/zh/ecosystems/x-cube-als.html
在下面目录下有对应的程序。
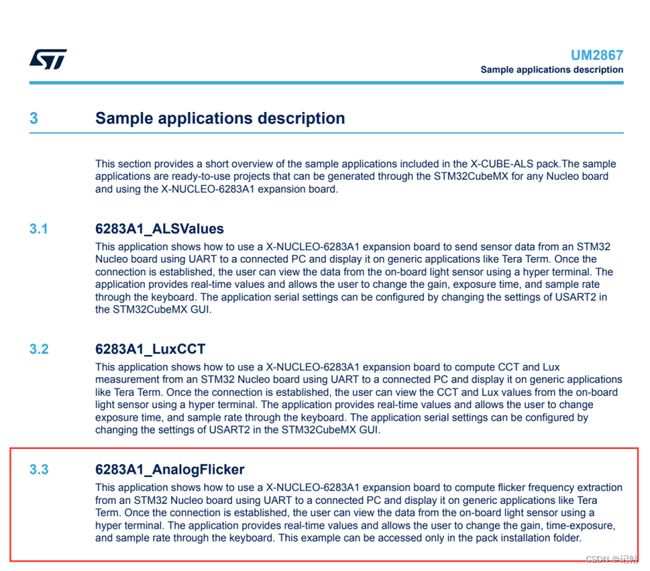
这个应用程序演示了如何使用X-NUCLEO-6283A1扩展板,通过UART从连接的STM32 Nucleo板向PC传输数据,并在通用应用程序(如Tera Term)上显示闪烁频率提取结果。一旦建立连接,用户可以使用超级终端查看来自板载光传感器的数据。该应用程序提供实时数值,并允许用户通过键盘更改增益、曝光时间和采样率。这个示例只能在软件包安装文件夹中访问。
硬件准备
首先需要准备一个开发板,这里我准备的是自己绘制的开发板:
最近在弄ST和瑞萨RA的课程,需要样片的可以加群申请:615061293 。

开发板设置
在手册种给出了,闪烁手册可以查看AN5639,资料链接如下。
https://www.st.com/content/ccc/resource/technical/document/application_note/group1/9f/7e/8c/ce/36/85/4c/08/DM00776948/files/DM00776948.pdf/jcr:content/translations/en.DM00776948.pdf
![]()
在AN5639手册中,需要对SB3进行连接。
![]()
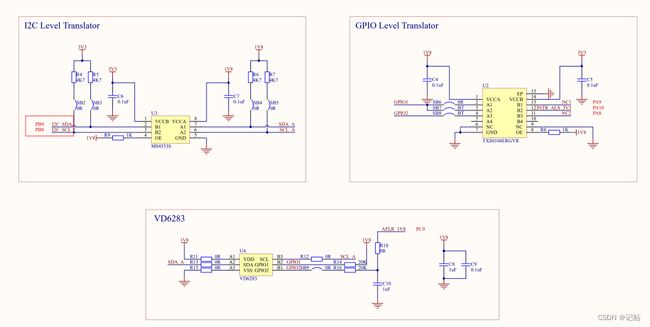
同时GPIO2需要接到MCU的ADC通道中。
![]()
查看X-NUCLEO-6283A1手册,可以看到VD6283TX的GPIO2连接到MCU的ADC端口0-2。
![]()
在本章使用的测试板中,AFLR_1V8接入到MCU的PC0接口。

需要将AFLR_1V8接到开发板的A0端口中。
![]()
生成STM32CUBEMX
用STM32CUBEMX生成例程,这里使用MCU为STM32WB55RG。
配置时钟树,配置时钟为32M。

串口配置
查看原理图,PB6和PB7设置为开发板的串口。
IIC配置
X-CUBE-ALS
ADC使用定时器触发采样
在app_als_adc_utils.c中,定义了ADC使用的频率,为8000Hz。
![]()
定时器的arr设置为4000-1,那么定时器频率为8000Hz。
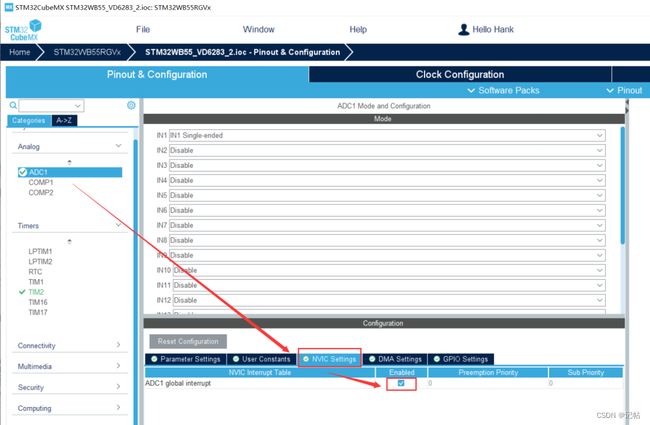
Trigger Event Selection :update event 定时器自动更新。
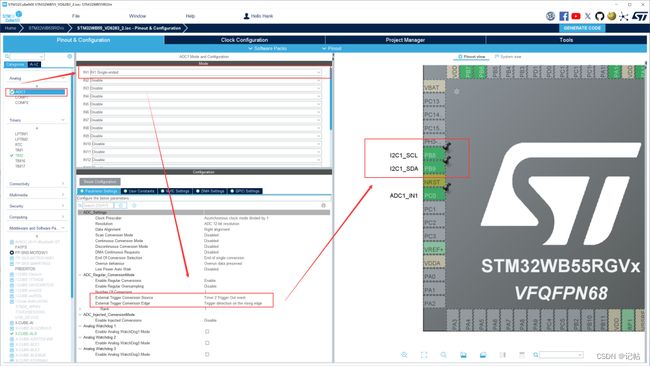
配置ADC检测VD6283TX的GPIO2管脚的AD值。
设置触发方式为外部触发,选择刚刚配置的TIM2,触发方式为上升沿触发。
KEIL配置
![]()
FFT代码配置
arm_cortexM4lf_math.lib 库包含了一系列数学函数,特别是适用于基于Cortex-M4和Cortex-M7处理器的浮点运算单元的优化数学例程。这些例程涵盖了常见的数学运算,如信号处理、滤波、变换等。
arm_math.h 这个头文件包含了CMSIS-DSP库的函数声明、宏定义和结构体定义等,可以通过包含这个头文件,使用库中提供的各种数学函数,包括信号处理、滤波、变换等。
添加arm_cortexM4lf_math.lib文件。
![]()
![]()
同时导入arm_math.h文件。
![]()
app_x-cube-als.c
由于需要进行FFT算法,所以需要添加对应数学头文件。
#define ARM_MATH_CM4
#include "arm_math.h"
#include "app_als_adc_utils.h"
添加对应的函数申明。
#define FLK_CHANNEL (5U)
/*
* Increasing the value of the FLK_DATA_SIZE symbol will increase
* processing time, flicker accuracy and memory footprint
*/
#define FLK_DATA_SIZE (1024U)
#define FFT_SIZE (FLK_DATA_SIZE)
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
static uint8_t is_quit_requested;
static uint8_t is_autogain_requested;
static int16_t flk_data[FLK_DATA_SIZE];
volatile uint8_t ALS_EventDetected;
/*
* The FFT of a real N-point sequence has even symmetry in the frequency domain.
* The second half of the data equals the conjugate of the first half flipped in frequency.
* Looking at the data, we see that we can uniquely represent the FFT using only N/2 complex numbers.
* These are packed into the output array in alternating real and imaginary components:
* X = { real[0], imag[0], real[1], imag[1], real[2], imag[2] ... real[(N/2)-1], imag[(N/2)-1 }
*/
static arm_rfft_fast_instance_f32 instance_fft;
static float32_t fft_in[FLK_DATA_SIZE];
static float32_t fft_out_tmp[FFT_SIZE];
static float32_t fft_out[FFT_SIZE/2];
/*
* The FFT of a real N-point sequence has even symmetry in the frequency domain.
* The second half of the data equals the conjugate of the first half flipped in frequency.
* Looking at the data, we see that we can uniquely represent the FFT using only N/2 complex numbers.
* These are packed into the output array in alternating real and imaginary components:
* X = { real[0], imag[0], real[1], imag[1], real[2], imag[2] ... real[(N/2)-1], imag[(N/2)-1 }
*/
static arm_rfft_fast_instance_f32 instance_fft;
static void MX_VD6283A1_AnalogFlicker_Process(void);
static float32_t complex_abs(float32_t real, float32_t complex);
static void init_fft(arm_rfft_fast_instance_f32 *instance, uint32_t size);
static void perform_fft(arm_rfft_fast_instance_f32 *instance, int16_t *data, float32_t *ffti, float32_t *ffto, uint32_t size);
static void find_flk_freq(uint32_t fs, float32_t *ffto, uint32_t *freq, uint8_t skip_dc, uint32_t size);
static int32_t flicker_autogain(uint8_t Instance, uint32_t *pAppliedGain, uint32_t timeoutMs);
static void display_gain(uint32_t gain);
在MX_VD6283A1_LuxCCT_Init()函数中添加init_fft快速傅里叶变换初始化。
![]()
static void MX_VD6283A1_LuxCCT_Init(void)
{
/* Initialize Virtual COM Port */
BSP_COM_Init(COM1);
printf("VD6283TX Lux / CCT Example\n\n");
display_commands_banner();
/* initialize ARM FFT library */
init_fft(&instance_fft, FFT_SIZE);
status = VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_Init(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0);
if (status)
{
printf("VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_Init failed\n");
while(1);
}
}
初始化完毕之后,添加频率获取函数。
static void MX_VD6283A1_AnalogFlicker_Process(void)
{
uint32_t fs; /* sampling frequency */
uint32_t pos = 0;
uint32_t flk_freq = 0;
uint32_t index;
uint32_t current_gain;
uint32_t current_exposure;
/* initialize exposure time */
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_SetExposureTime(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0, 100000);
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_GetExposureTime(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0, ¤t_exposure);
printf("Exposure set to %lu us\n", (unsigned long)current_exposure);
/* initialize gain */
flicker_autogain(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0, ¤t_gain, 1);
printf("Channel %u gain set to", FLK_CHANNEL);
display_gain(current_gain);
status = als_adc_start(&fs);
if (status)
{
printf("ADC Start failed\n");
while (1);
}
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_StartFlicker(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0, FLK_CHANNEL, LIGHT_SENSOR_FLICKER_ANALOG);
while (!is_quit_requested)
{
status = als_adc_get_frame(&flk_data[pos], &index);
/* fill the ADC frame buffer */
if (status == 0)
{
pos += ADC_FRAME_SIZE;
}
/* if the ADC frame buffer is full, then process it */
if (pos == FLK_DATA_SIZE)
{
perform_fft(&instance_fft, flk_data, fft_in, fft_out, FFT_SIZE);
find_flk_freq(fs, fft_out, &flk_freq, 1, FFT_SIZE);
pos = 0; /* reset position index */
printf("Flicker freq: %4lu Hz\r", (unsigned long)flk_freq);
fflush(stdout);
if (is_autogain_requested == 1)
{
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_StopFlicker(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0);
flicker_autogain(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0, ¤t_gain, 1);
printf("Channel %u gain set to", FLK_CHANNEL);
display_gain(current_gain);
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_StartFlicker(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0, FLK_CHANNEL, LIGHT_SENSOR_FLICKER_ANALOG);
is_autogain_requested = 0;
}
}
handle_cmd(get_key());
}
als_adc_stop();
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_StopFlicker(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0);
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_DeInit(LIGHT_SENSOR_INSTANCE_0);
printf("Quitting the demo...\n");
while (1);
}
在MX_X_CUBE_ALS_Process函数中开启频率获取函数,关闭光强获取函数MX_VD6283A1_LuxCCT_Process。
![]()
添加增益设置函数。
/*
* @brief find and apply appropriate gain value depending on saturation value
* @warning this function mustn't be called when a capture is ongoing
*/
static int32_t flicker_autogain(uint8_t Instance, uint32_t *pAppliedGain, uint32_t timeoutMs)
{
int32_t res;
uint8_t i, j;
uint8_t idx = 7; /* start with mid-table value */
const uint8_t sat_limit = 2;
uint32_t saturation;
/* duplicate 0x42AB to avoid 100x and keep multiples of 2 for array size */
const uint16_t Gains[] = {
0x42AB, 0x42AB, 0x3200, 0x2154, 0x1900, 0x10AB, 0x0A00, 0x0723,
0x0500, 0x0354, 0x0280, 0x01AB, 0x0140, 0x0100, 0x00D4, 0x00B5
};
/* clip timeout value */
timeoutMs = timeoutMs == 0 ? 1 : timeoutMs;
timeoutMs = timeoutMs >= 100 ? 100 : timeoutMs;
for (i = 0; i <= 3; i++)
{
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_SetGain(Instance, FLK_CHANNEL, Gains[idx]);
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_GetGain(Instance, FLK_CHANNEL, pAppliedGain);
res = VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_StartFlicker(Instance, FLK_CHANNEL, LIGHT_SENSOR_FLICKER_ANALOG);
if (res)
return res;
/* read saturation value each ms so we can exit early if saturation detected */
for (j = 0; j < timeoutMs; j++)
{
HAL_Delay(1);
res = VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_GetSaturation(Instance, &saturation);
if (res)
return res;
if (saturation > sat_limit)
break;
}
res = VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_StopFlicker(Instance);
if (res)
return res;
/* update index to next value */
if (i)
idx += saturation > sat_limit ? 1 << (i - 1) : -(1 << (i - 1));
else if (saturation > sat_limit)
idx++;
}
/* clip index if it reaches max value */
if (idx > 15)
idx = 15;
VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_SetGain(Instance, FLK_CHANNEL, Gains[idx]);
res = VD6283A1_LIGHT_SENSOR_GetGain(Instance, FLK_CHANNEL, pAppliedGain);
return res;
}
在下方添加函数的定义。
/*
* @brief initilize arm rfft library
*/
static void init_fft(arm_rfft_fast_instance_f32 *instance, uint32_t size)
{
arm_rfft_fast_init_f32(instance, size);
}
打印增益函数。
/*
* @brief normalize, convert and dislay gain
*/
static void display_gain(uint32_t gain)
{
uint32_t g = (gain * 100) / 256;
printf(" %3lu.%02lu\n", (unsigned long)g / 100, (unsigned long)(g % 100));
}
执行FFT。
/*
* @brief perform fft on the input buffer using arm rfft library
*/
static void perform_fft(arm_rfft_fast_instance_f32 *instance, int16_t *flk, float32_t *ffti, float32_t *ffto, uint32_t size)
{
uint32_t i;
uint32_t index = 0;
/* copy the ADC sampled signal into the fft input buffer
* this allows to convert the data from int16_t to float32_t */
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
ffti[i] = flk[i];
}
/* Perform the FFT on the input buffer:
* results are packed in a way so that even indexes contain real values
* and odd indexes contain the complex value of each bin.
* Therefore the fft_output array contains FFT_SIZE / 2 bins */
arm_rfft_fast_f32(instance, ffti, fft_out_tmp, 0);
/* Calculate the magnitude for each bin from the temp fft output buffer */
for (i = 0; i < size; i += 2)
{
ffto[index] = complex_abs(fft_out_tmp[i], fft_out_tmp[i+1]);
if (ffto[index] < 0) ffto[index] = 0;
index++;
}
}
查找峰值频率值。
/*
* @brief find peak frequency value
*/
static void find_flk_freq(uint32_t fs, float32_t *ffto, uint32_t *freq, uint8_t skip_dc, uint32_t size)
{
uint32_t i;
uint32_t res;
uint32_t index_max = 0;
uint32_t limit = size / 2;
float32_t max_value = -1;
/* do not take account of the DC value if the flag skip_dc is set */
skip_dc ? (i = 1) : (i = 0);
/* run through the output array to detect the peak */
for (; i < limit; i++)
{
if (ffto[i] > max_value)
{
index_max = i;
max_value = ffto[i];
}
}
/* convert index of the bin into frequency */
res = (index_max * fs) / size;
/* return the result if the pointer is valid */
if (freq)
{
*freq = res;
}
}
计算一个复数的绝对值。
/*
* @brief compute absolute value of a complex number
*/
static float32_t complex_abs(float32_t real, float32_t complex)
{
float32_t res;
arm_sqrt_f32(real * real + complex * complex, &res);
return res;
}
需要添加函数
arm_cortexM4lf_math.lib 库包含了一系列数学函数,特别是适用于基于Cortex-M4和Cortex-M7处理器的浮点运算单元的优化数学例程。这些例程涵盖了常见的数学运算,如信号处理、滤波、变换等。
arm_math.h 这个头文件包含了CMSIS-DSP库的函数声明、宏定义和结构体定义等,可以通过包含这个头文件,使用库中提供的各种数学函数,包括信号处理、滤波、变换等。
app_als_adc_utils.c功能主要包括启动和停止ADC采样,获取采样数据,ADC采样速度设置,以及处理相关的硬件中断。
app_als_adc_utils.h是app_als_adc_utils.c对应头文件。