【c++逆向 - 2】初识类
初识类
一个 demo 完事:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Student {
enum { SEX_LEN = 5 };
string name;
string id;
char sex[SEX_LEN];
unsigned int age;
public:
Student();
Student(const string &name, const string &id, const char* sex, unsigned int age);
void show() const;
const Student& who_age(const Student& stu) const;
};
int main()
{
Student Bob("Bob", "20213333", "m", 18);
Student Tom{"Tom", "22223333", "m", 20};
Bob.who_age(Tom).show();
return 0;
}
Student::Student()
{
name = "No";
id = "No";
strcpy(sex, "No");
age = 0;
}
Student::Student(const string &name, const string &id, const char* sex, unsigned int age)
{
this->name = name;
this->id = id;
strncpy(this->sex, sex, SEX_LEN-1);
this->age = age;
}
void Student::show() const
{
cout << "Name: " << name << ", "
<< "id: " << id << ", "
<< "sex: " << sex << ", "
<< "age: " << age << endl;
}
const Student& Student::who_age(const Student& stu) const
{
return stu.age>age?stu:*this;
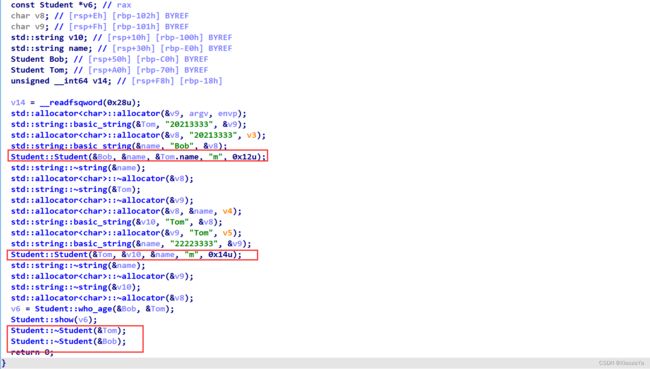
} 主要来看下 IDA,感觉识别的不是很好啊:
当然这里涉及到了 string 类了,这里后面 STL 的时候再说吧。
运算符重载与友元
运算符函数格式:operatorop(arg-list) ==> operator=() 表示重载 = 运算符
一个 demo 完事:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Point {
private:
int x;
int y;
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Point &p);
friend Point operator*(const Point& p, int n);
friend Point operator*(int n, const Point& p);
public:
Point() { x = 0; y = 0; }
Point(int x, int y);
Point operator+(const Point& p) const;
Point operator*(const Point& p) const;
Point operator++(); // 前置++
Point operator++(int); // 后置++
void show() const;
};
int main()
{
Point p1(2, 3);
Point p2(1, 2);
Point p3(4, 2);
Point p = p1 + p2 * p3;
p.show();
Point p4 = ++p1;
Point p5 = p4++;
cout << "p4 = " << p4 << endl;
cout << "p5 = " << p5 << endl;
cout << "p5*2 = " << p5*2 << endl;
cout << "2*p4 = " << 2*p4 << endl;
return 0;
}
Point::Point(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
Point Point::operator+(const Point& p) const
{
cout << "oprator +\n";
return Point(x+p.x, y+p.y);
}
Point Point::operator*(const Point& p) const
{
cout << "oprator *\n";
return Point(x*p.x, y*p.y);
}
Point Point::operator++()
{
cout << "oprator ++p\n";
return Point(++x, ++y);
}
Point Point::operator++(int)
{
cout << "oprator p++\n";
return Point(x++, y++);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Point& p)
{
out << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y << ")";
return out;
}
Point operator*(const Point& p, int n)
{
return Point(p.x*n, p.y*n);
}
Point operator*(int n, const Point& p)
{
return Point(p.x*n, p.y*n);
}
void Point::show() const
{
cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")\n";
} 这里关键的地方就是对二元运算符的重载,比如在重载 * 运算符时,我们希望 2*p,但是我们知道成员函数的第一个参数才是 this 指针,所以这里通过成员函数就无法完成重载,这里就得使用友元函数。
友元有友元函数,友元类,友元成员函数,这里仅仅用到友元函数,简单来说就是友元函数与成员函数具有相同的访问私有数据的权限。
使用也很简单:
1)加上 friend 关键字
2)将函数声明放在类中
最后输出如下:
oprator *
oprator +
(6, 7)
oprator ++p
oprator p++
p4 = (4, 5)
p5 = (3, 4)
p5*2 = (6, 8)
2*p4 = (8, 10)可以看到是先运算的乘法在运算的加法,所以可以知道重载运算符不改变运算符的优先级和结合性。
还有就是注意下前置++和后置++重载的区别。
类 类型转换
todo(感觉不是很重要,所以并不打算写,但是如果后面遇到的话,再回来补)