序
本文主要研究下FluxFlatMap的concurrency及prefetch参数
实例
@Test
public void testConcurrencyAndPrefetch(){
int concurrency = 3;
int prefetch = 6;
Flux.range(1,100)
.log()
.flatMap(i -> Flux.just(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10).log(),
concurrency,prefetch)
.subscribe();
}
部分输出
23:29:38.515 [main] DEBUG reactor.util.Loggers$LoggerFactory - Using Slf4j logging framework
23:29:38.534 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Range.1 - | onSubscribe([Synchronous Fuseable] FluxRange.RangeSubscription)
23:29:38.537 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Range.1 - | request(3)
23:29:38.537 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Range.1 - | onNext(1)
23:29:38.538 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onSubscribe([Synchronous Fuseable] FluxArray.ArraySubscription)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | request(6)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(1)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(2)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(3)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(4)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(5)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | request(5)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(6)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(7)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(8)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(9)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onNext(10)
23:29:38.539 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | request(5)
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.2 - | onComplete()
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Range.1 - | request(1)
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Range.1 - | onNext(2)
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.3 - | onSubscribe([Synchronous Fuseable] FluxArray.ArraySubscription)
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.3 - | request(6)
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.3 - | onNext(1)
23:29:38.540 [main] INFO reactor.Flux.Array.3 - | onNext(2)
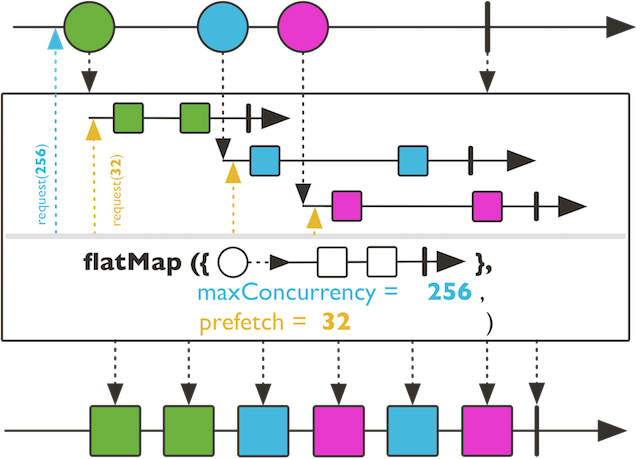
但看外内两个flux的第一次request,可以初步看到分别是concurrency及prefetch
源码解析
Flux
reactor-core-3.1.5.RELEASE-sources.jar!/reactor/core/publisher/Flux.java
/**
* Transform the elements emitted by this {@link Flux} asynchronously into Publishers,
* then flatten these inner publishers into a single {@link Flux} through merging,
* which allow them to interleave.
*
* There are three dimensions to this operator that can be compared with
* {@link #flatMapSequential(Function) flatMapSequential} and {@link #concatMap(Function) concatMap}:
*
* - Generation of inners and subscription: this operator is eagerly
* subscribing to its inners.
* - Ordering of the flattened values: this operator does not necessarily preserve
* original ordering, as inner element are flattened as they arrive.
* - Interleaving: this operator lets values from different inners interleave
* (similar to merging the inner sequences).
*
* The concurrency argument allows to control how many {@link Publisher} can be
* subscribed to and merged in parallel. The prefetch argument allows to give an
* arbitrary prefetch size to the merged {@link Publisher}.
*
*
*  *
* @param mapper the {@link Function} to transform input sequence into N sequences {@link Publisher}
* @param concurrency the maximum number of in-flight inner sequences
* @param prefetch the maximum in-flight elements from each inner {@link Publisher} sequence
* @param
*
* @param mapper the {@link Function} to transform input sequence into N sequences {@link Publisher}
* @param concurrency the maximum number of in-flight inner sequences
* @param prefetch the maximum in-flight elements from each inner {@link Publisher} sequence
* @param the merged output sequence type
*
* @return a merged {@link Flux}
*/
public final Flux flatMap(Function> mapper, int
concurrency, int prefetch) {
return flatMap(mapper, false, concurrency, prefetch);
}
final Flux flatMap(Function> mapper, boolean delayError, int concurrency, int prefetch) {
return onAssembly(new FluxFlatMap<>(
this,
mapper,
delayError,
concurrency,
Queues.get(concurrency),
prefetch,
Queues.get(prefetch)
));
}
这里使用的是FluxFlatMap
FluxFlatMap
reactor-core-3.1.5.RELEASE-sources.jar!/reactor/core/publisher/FluxFlatMap.java
FluxFlatMap(Flux source,
Function> mapper,
boolean delayError,
int maxConcurrency,
Supplier> mainQueueSupplier,
int prefetch,
Supplier> innerQueueSupplier) {
super(source);
if (prefetch <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("prefetch > 0 required but it was " + prefetch);
}
if (maxConcurrency <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxConcurrency > 0 required but it was " + maxConcurrency);
}
this.mapper = Objects.requireNonNull(mapper, "mapper");
this.delayError = delayError;
this.prefetch = prefetch;
this.maxConcurrency = maxConcurrency;
this.mainQueueSupplier =
Objects.requireNonNull(mainQueueSupplier, "mainQueueSupplier");
this.innerQueueSupplier =
Objects.requireNonNull(innerQueueSupplier, "innerQueueSupplier");
}
@Override
public void subscribe(CoreSubscriber actual) {
if (trySubscribeScalarMap(source, actual, mapper, false)) {
return;
}
source.subscribe(new FlatMapMain<>(actual,
mapper,
delayError,
maxConcurrency,
mainQueueSupplier,
prefetch, innerQueueSupplier));
}
这里可以看到subscribe的时候使用了FlatMapMain
FlatMapMain
static final class FlatMapMain extends FlatMapTracker>
implements InnerOperator {
FlatMapMain(CoreSubscriber actual,
Function> mapper,
boolean delayError,
int maxConcurrency,
Supplier> mainQueueSupplier,
int prefetch,
Supplier> innerQueueSupplier) {
this.actual = actual;
this.mapper = mapper;
this.delayError = delayError;
this.maxConcurrency = maxConcurrency;
this.mainQueueSupplier = mainQueueSupplier;
this.prefetch = prefetch;
this.innerQueueSupplier = innerQueueSupplier;
this.limit = Operators.unboundedOrLimit(maxConcurrency);
}
@Override
public void request(long n) {
if (Operators.validate(n)) {
Operators.addCap(REQUESTED, this, n);
drain();
}
}
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Subscription s) {
if (Operators.validate(this.s, s)) {
this.s = s;
actual.onSubscribe(this);
s.request(Operators.unboundedOrPrefetch(maxConcurrency));
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public void onNext(T t) {
if (done) {
Operators.onNextDropped(t, actual.currentContext());
return;
}
Publisher p;
try {
p = Objects.requireNonNull(mapper.apply(t),
"The mapper returned a null Publisher");
}
catch (Throwable e) {
onError(Operators.onOperatorError(s, e, t, actual.currentContext()));
return;
}
if (p instanceof Callable) {
R v;
try {
v = ((Callable) p).call();
}
catch (Throwable e) {
if (!delayError || !Exceptions.addThrowable(ERROR, this, e)) {
onError(Operators.onOperatorError(s, e, t, actual.currentContext()));
}
return;
}
tryEmitScalar(v);
}
else {
FlatMapInner inner = new FlatMapInner<>(this, prefetch);
if (add(inner)) {
p.subscribe(inner);
}
}
}
//...
}
这个可以理解为对外层flux的操作,可以看到onSubscribe的时候,其内部request的大小为Operators.unboundedOrPrefetch(maxConcurrency),也就是第一个参数concurrency
在onNext操作里头,对里头的flux使用了FlatMapInner
FlatMapInner
static final class FlatMapInner
implements InnerConsumer, Subscription {
FlatMapInner(FlatMapMain parent, int prefetch) {
this.parent = parent;
this.prefetch = prefetch;
// this.limit = prefetch >> 2;
this.limit = Operators.unboundedOrLimit(prefetch);
}
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Subscription s) {
if (Operators.setOnce(S, this, s)) {
if (s instanceof Fuseable.QueueSubscription) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Fuseable.QueueSubscription f =
(Fuseable.QueueSubscription) s;
int m = f.requestFusion(Fuseable.ANY | Fuseable.THREAD_BARRIER);
if (m == Fuseable.SYNC) {
sourceMode = Fuseable.SYNC;
queue = f;
done = true;
parent.drain();
return;
}
if (m == Fuseable.ASYNC) {
sourceMode = Fuseable.ASYNC;
queue = f;
}
// NONE is just fall-through as the queue will be created on demand
}
s.request(Operators.unboundedOrPrefetch(prefetch));
}
}
@Override
public void request(long n) {
long p = produced + n;
if (p >= limit) {
produced = 0L;
s.request(p);
}
else {
produced = p;
}
}
}
subscribe的时候,request的数量为Operators.unboundedOrPrefetch(prefetch)
这里可以看到这里对prefetch进行右移2操作,相当于除以4,作为limit,limit是个判断,用来对inner的flux的request数量进行限制
小结
flatMap的两个参数concurrency及prefetch,分别是作用于外头及里头的两个flux,第一次request都是使用该值,后续的话,其内部会对request的数量进行判断和调整。
doc
- webflux-concurrency-model