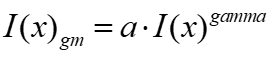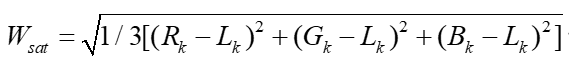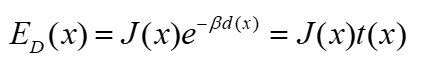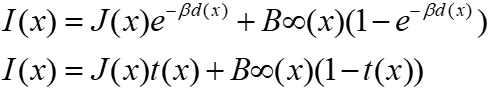论文笔记:Color Balance and Fusion for Underwater Image Enhancement(论文及源代码下载链接+公式分析+论文实验MATLAP代码分析)
计算机的小白,跨考计算机类的研究生,所以对于代码就是一点一点的学习分析,本文适合和我一样不懂MATLAP代码的伙伴们!
因个人能力有限,可能会有不太准确的地方,若有错误,欢迎大家指出。 ♥
♥论文下载链接:
♥代码下载链接:
目录
2 公式以及对应编码:
2.1 Red channel compensated
2.2 White-balance
2.3 Gamma correction
2.4 sharpen
2.5 Multiscale fusion(三种权重图都是分别对伽马校正过的图和锐化图进行处理)
2.6 其余公式
3.有关问题进行实验.
2 公式以及对应编码:
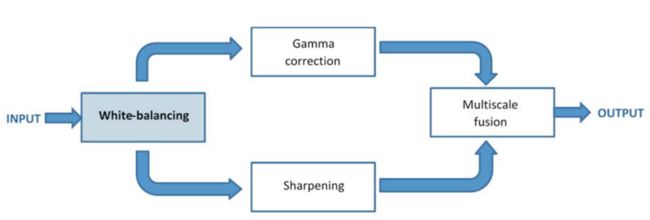
Red channel compensated / White-balanced / Gamma correction / sharpen / Multiscale fusion
2.1 Red channel compensated
| 颜色校正/ Color correcting |
function ret = redCompensate( im, w ) a = 1; |
| r = im2double(im(:,:,1)); g = im2double(im(:,:,2)); b = im2double(im(:,:,3)); %将unite8类型转换为im2double类型。 |
|
| ret = im; for i = 1:height for j = 1:width slider = padr(i:i+w-1,j:j+w-1);? slideg = padg(i:i+w-1,j:j+w-1); r_mean = mean(mean(slider));%求数组的平均数或者均值 g_mean = mean(mean(slideg)); |
|
| 公式(4) |
Irc = r(i,j) + a * (g_mean - r_mean) * (1-r(i,j)) * g(i,j); |
| Irc = uint8(Irc * 255); ret(i, j, 1) = Irc; end end end |
|
| 公式(5)蓝色通道补偿同理,当原始退化图像红色通道/蓝色衰减强烈时,进行红色/蓝色通道的色彩补偿,属于对图像进行颜色校正的一种方法。 |
|
2.2 White-balance
| 论文中未提到此模块的公式。 |
|
| % 对图像进行灰度世界白平衡处理 [43] G. Buchsbaum, “A spatial processor model for object colour perception,” J. Franklin Inst., vol. 310, no. 1, pp. 1–26, Jul. 1980. Gray Word. |
function output = simple_color_balance(image) num = 255; r = image(:, :, 1); g = image(:, :, 2); b = image(:, :, 3); Ravg = mean(mean(r)); Gavg = mean(mean(g)); Bavg = mean(mean(b)); Max = max([Ravg, Gavg, Bavg]); ratio = [Max / Ravg, Max / Gavg, Max / Bavg]; satLevel = 0.005 * ratio; [m,n,p] = size(image); imgRGB_orig = zeros(p, m*n); for i = 1 : p imgRGB_orig(i, : ) = reshape(double(image(:, :, i)), [1, m * n]); end imRGB = zeros(size(imgRGB_orig)); %在灰度世界的基础上? |
| %直方图对比度调整 %结果图 |
for ch = 1 : p q = [satLevel(ch), 1 - satLevel(ch)]; tiles = quantile(imgRGB_orig(ch, :), q); temp = imgRGB_orig(ch, :); temp(find(temp < tiles(1))) = tiles(1); temp(find(temp > tiles(2))) = tiles(2); imRGB(ch, :) = temp; pmin = min(imRGB(ch, :)); pmax = max(imRGB(ch, :));
% fac(A) = Amin + (A - Alow) * (Amax -Amin)/(Ahigh - Alow) % 对于8bit图像,Amin = 0,Amax = 255 imRGB(ch, :) = (imRGB(ch, :) - pmin) * num /(pmax - pmin); end output = zeros(size(image)); for i = 1 : p output(:, :, i) = reshape(imRGB(i, :), [m, n]); end |
2.3 Gamma correction
| 论文中未写此公式。
|
function [ result ] = gammaCorrection(image, a, gamma) image = im2double(image); result = a * (image .^ gamma); end |
| 论文中设置伽马值为1.2,下拱使图像整体变暗,扩展更多暗部细节。非线性拉伸。 |
|
|
|
|
2.4 sharpen
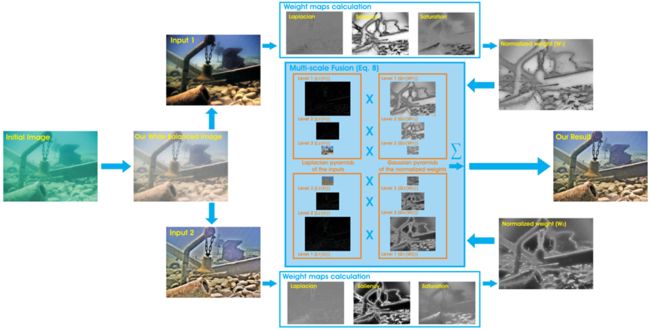
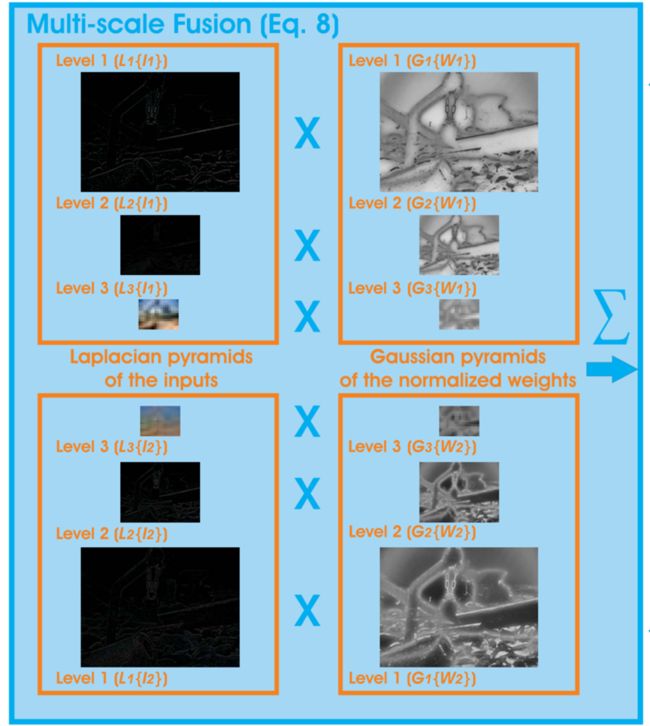
2.5 Multiscale fusion(三种权重图都是分别对伽马校正过的图和锐化图进行处理)
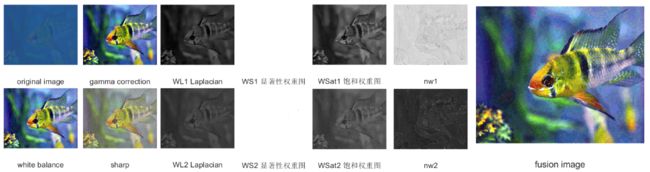
| 1.calculate weight double(lab1(:, :, 1)/255)将亮度通道中的像素值归一化到0到1之间,并将其转换为double类型。这里的目的是为了后续的计算方便,因为double类型可以存储更高的精度和更大的数值范围。 这行代码实现了将RGB图像转换为LAB颜色空间,并将亮度通道的像素值赋值给变量R1,R2以便进行后续的图像处理。 |
lab1 = rgb_to_lab(input1);%图像格式由RGB转化为LAB,Lab有更宽的色域,调整L/明度/亮度/通道时, lab2 = rgb_to_lab(input2);%色相不会改变。a,b通道控制色彩。 R1 = double(lab1(:, :, 1)/255); R2 = double(lab2(:, :, 1)/255); |
|
|
|
| Laplacian contrast weight imfilter(R1, fspecial('Laplacian'), 'replicate', 'conv') 使用该模板对输入图像R1进行滤波,其中'replicate'表示使用边缘像素进行边缘扩展,'conv'表示使用卷积操作进行滤波。 abs() 函数用于获取滤波结果的绝对值,这是因为Laplacian滤波器产生了正负两种极性的响应,我们只需要对边缘的强度进行测量,因此取绝对值。 最后,将滤波结果赋值给变量WL1。 因此,这行代码实现了对输入图像R1进行Laplacian滤波,得到边缘图像WL1。 |
WL1 = abs(imfilter(R1, fspecial('Laplacian'), 'replicate', 'conv')); WL2 = abs(imfilter(R2, fspecial('Laplacian'), 'replicate', 'conv')); % abs函数求绝对值
|
| 2.Saliency weight(显著性权重)%采用了Achantay等人的显著性估计器 %旨在强调在水下场景中失去其突出性的突出物体。 |
WS1 = saliency_detection(input1); WS2 = saliency_detection(input2); |
| 在MATLAB中,imfilter函数用于对图像进行滤波操作。它接受三个主要参数:输入图像 img、滤波器核 fspecial('gaussian', 3, 3) 和滤波方式 'symmetric'。 fspecial('gaussian', 3, 3) 创建了一个3x3的高斯滤波器核。这个核是一个二维的高斯函数,用于模糊图像以减少噪声和细节。 'symmetric' 是指在滤波时处理图像边界的方式。对于边界像素,使用对称扩展的方式来处理,即用图像中对称位置的像素值来填充边界像素,以保持图像大小不变。 最后,imfilter函数将输入图像 img 和滤波器核进行卷积操作,得到滤波后的输出图像 gfrgb。该图像是对原始图像进行了高斯滤波处理后的结果。 高斯滤波是一种常用的图像滤波方法,它可以平滑图像、去除噪声和细节,使图像变得更加模糊。 |
function sm = saliency_detection(img) gfrgb = imfilter(img, fspecial('gaussian', 3, 3), 'symmetric', 'conv'); cform=makecform('srgb2lab','AdaptedWhitePoint',whitepoint('d65')); lab = applycform(gfrgb,cform); l = double(lab(:,:,1)); lm = mean(mean(l)); a = double(lab(:,:,2)); am = mean(mean(a)); b = double(lab(:,:,3)); bm = mean(mean(b)); sm = (l-lm).^2 + (a-am).^2 + (b-bm).^2; end
|
| cform = makecform('srgb2lab', 'AdaptedWhitePoint', whitepoint('d65')); |
这段代码创建了一个颜色转换结构体 `cform`,用于将图像从sRGB颜色空间转换到Lab颜色空间,并使用适应性白点 `whitepoint('d65')` 进行转换。 在MATLAB中,颜色转换函数 `makecform` 用于创建颜色转换结构体。它接受两个主要参数:源颜色空间和目标颜色空间。在这里,源颜色空间是sRGB,目标颜色空间是Lab。 `srgb2lab` 是指将sRGB颜色空间转换为Lab颜色空间的转换公式。sRGB是一种广泛使用的红绿蓝(RGB)颜色空间,而Lab是一种基于人类感知的颜色空间,用于表示颜色的亮度、色度和色调。 `'AdaptedWhitePoint', whitepoint('d65')` 部分是可选的参数,它指定了适应性白点为D65。白点是颜色空间中的一个参考点,用于表示不同光源的颜色特性。在这里,使用D65作为适应性白点,以匹配标准观察条件下的光源。 因此,该代码行的含义是创建一个颜色转换结构体 `cform`,用于将sRGB图像转换为Lab颜色空间,并使用适应性白点设置为D65进行转换。这种转换可以用于在Lab颜色空间中进行颜色分析和处理。 |
| lab = applycform(gfrgb,cform); |
将先前经过高斯滤波处理后的图像 gfrgb应用到颜色转换结构体 cform 上,进行从sRGB到Lab颜色空间的转换。 applycform 函数用于将颜色转换结构体应用到图像上。它接受两个参数:输入图像和颜色转换结构体。在这里,输入图像是经过高斯滤波处理后的图像 `gfrgb`,颜色转换结构体是先前创建的 `cform`。 |
|
|
|
| 3. Saturation weight(饱和权重) 使得融合算法能够通过高度饱和的区域优势来适应彩色信息. WSat1 = Saturation_weight(input1); WSat2 = Saturation_weight(input2); |
|
融合:
| 1.normalized weight map: [W1, W2] = norm_weight(WL1, WS1, WSat1, WL2 , WS2, WSat2); |
先经过一个normalized weight map,归一化权重图,将三种权重图(拉普拉斯/显著/饱和)计算到一起。 |
|
| function [nw1, nw2] = norm_weight(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6) K = 2; delta = 0.1; nw1 = w1 + w2 + w3; nw2 = w4 + w5 + w6; w = nw1 + nw2; nw1 = (nw1 + delta) ./ (w + K * delta); nw2 = (nw2 + delta) ./ (w + K * delta); end |
|
|
|
W1,W2 |
这两张输出,进行拉普拉斯和高斯金字塔处理,多尺度融合 |
|
| %% image fusion ♥ % R(x,y) = sum G{W} * L{I} %.................................................% level = 3;%设置金字塔为三层, % weight gaussian pyramid(权重高斯金字塔) Weight1 = gaussian_pyramid(W1, level);%输入的是归一化权重图.W1,W2 Weight2 = gaussian_pyramid(W2, level); %是一个1*3的cell, % image laplacian pyramid(图像拉普拉斯金字塔) % input1 r1 = laplacian_pyramid(double(double(input1(:, :, 1))), level); g1 = laplacian_pyramid(double(double(input1(:, :, 2))), level); b1 = laplacian_pyramid(double(double(input1(:, :, 3))), level); % input2 r2 = laplacian_pyramid(double(double(input2(:, :, 1))), level); g2 = laplacian_pyramid(double(double(input2(:, :, 2))), level); b2 = laplacian_pyramid(double(double(input2(:, :, 3))), level); % fusion for i = 1 : level R_r{i} = Weight1{i} .* r1{i} + Weight2{i} .* r2{i}; G_g{i} = Weight1{i} .* g1{i} + Weight2{i} .* g2{i}; B_b{i} = Weight1{i} .* b1{i} + Weight2{i} .* b2{i}; end % pyramin reconstruct(重建) R = pyramid_reconstruct(R_r); G = pyramid_reconstruct(G_g); B = pyramid_reconstruct(B_b); fusion = cat(3, R,G,B); %连接三维矩阵 uciqe = UCIQE(fusion)%两个专为水下图像设计的评价指标。 uiqm = UIQM(fusion) figure,imshow(fusion),xlabel('fusion image'); |
level:这是一个变量或参数,表示拉普拉斯金字塔的级别数量。它指定了金字塔的层数,也就是图像降采样的次数。 gaussian_pyramid,和laplacian_pyramid可以拿来直接用。 |
|
| 融合金字塔重建: 这段代码实现了金字塔的重建操作,将金字塔的每一层进行上采样并叠加,最终得到原始尺寸的图像。 下面是对代码的详细解释: 1. 函数定义:`function output = pyramid_reconstruct(pyramid)`,接受一个金字塔 `pyramid` 作为输入,输出重建后的图像 `output`。 2. 获取金字塔层数:`level = length(pyramid);`,通过获取 `pyramid` 的长度,即金字塔的层数。 3. 重建过程:从金字塔的最高层开始逐层向下重建。 4. 循环遍历:`for i = level : -1 : 2`,从最高层开始,逐层向下,直到第二层。 5. 获取上一层的尺寸:`[m, n] = size(pyramid{i - 1});`,获取上一层金字塔的尺寸,用于上采样操作。 6. 上采样并叠加:`pyramid{i - 1} = pyramid{i - 1} + imresize(pyramid{i}, [m, n]);`,将当前层金字塔进行上采样,并与上一层金字塔叠加。 7. 重建完成:重建后的金字塔存储在 `pyramid{1}` 中。 8. 输出结果:`output = pyramid{1};`,将重建后的金字塔的第一层作为输出结果。 这段代码实现了对金字塔进行反向操作,将金字塔的每一层进行上采样并叠加,最终得到原始尺寸的图像作为输出结果。 |
function output = pyramid_reconstruct(pyramid) level = length(pyramid); for i = level : -1 :2 [m, n] = size(pyramid{i - 1}); pyramid{i - 1} = pyramid{i -1} + imresize(pyramid{i}, [m, n]); end output = pyramid{1}; end |
|
|
|
||
2.6 其余公式
| Underwater optical model |
|
| (1) |
where J(x) is the radiance of the object, d(x) is the distance between the observer and the object, and η is the attenuation coefficient. The exponential term e−ηd(x) is also known as the transmission t(x) through the underwater medium. |
| Back scattering (2) |
where B∞(x) is a color vector known as the back-scattered light. |
| Underwater optical model (3) |
类比大气散射模型:/the light propagation model.
均匀介质下,以此模型为基础的方法图像处理效果较好. |
3.有关问题进行实验.
- 关于实验图片Salience权重图处理效果不像作者的图一样,选择和作者一样的图进行实验。
问老师,老师说是进行一定的处理,可能类似放大纹理,或者进行了参数的调整。目前还不知道怎么实现的。