MVCC 并发控制原理-源码解析(非常详细)
基础概念
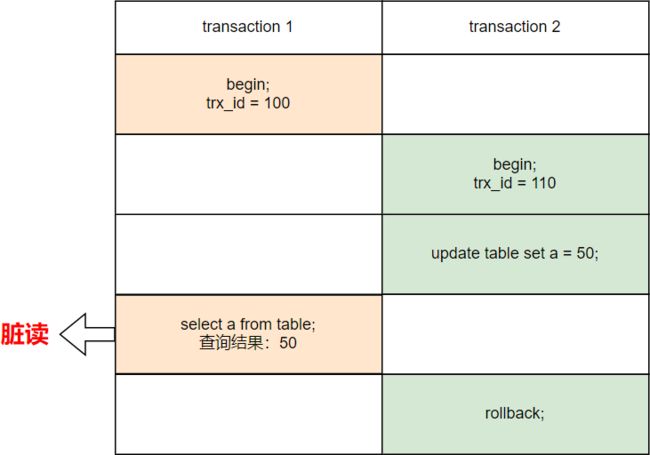
并发事务带来的问题
1)脏读:一个事务读取到另一个事务更新但还未提交的数据,如果另一个事务出现回滚或者进一步更新,则会出现问题。
2)不可重复读:在一个事务中两次次读取同一个数据时,由于在两次读取之间,另一个事务修改了该数据,所以出现两次读取的结果不一致。
3)幻读:在一个事务中使用相同的 SQL 两次读取,第二次读取到了其他事务新插入的行。
要解决这些并发事务带来的问题,一个比较简单粗暴的方法是加锁,但是加锁必然会带来性能的降低,因此 MySQL 使用了 MVCC 来提升并发事务下的性能。
MVCC 带来的好处
如果没有 MVCC,为了保证并发事务的安全,一个比较容易想到的办法就是加读写锁,实现:读读不冲突、读写冲突、写读冲突,写写冲突,在这种情况下,并发读写的性能必然会收到严重影响。
而通过 MVCC,我们可以做到读写之间不冲突,我们读的时候只需要将当前记录拷贝一份到内存中(ReadView),之后该事务的查询就只跟 ReadView 打交道,不影响其他事务对该记录的写操作。
事务隔离级别
1)读未提交(Read Uncommitted):最低的隔离级别,会读取到其他事务还未提交的内容,存在脏读。
2)读已提交(Read Committed):读取到的内容都是已经提交的,可以解决脏读,但是存在不可重复读。
3)可重复读(Repeatable Read):在一个事务中多次读取时看到相同的内容,可以解决不可重复读,但是存在幻读。在 InnoDB 中不存在幻读问题,对于快照读,InnoDB 使用 MVCC 解决幻读,对于当前读,InnoDB 通过 gap locks 或 next-key locks 解决幻读。
4)串行化(Serializable):最高的隔离级别,串行的执行事务,没有并发事务问题。
InnoDB MVCC 实现
核心数据结构
trx_sys_t:事务系统中央存储器数据结构
struct trx_sys_t {
TrxSysMutex mutex; /*! 互斥锁 */
MVCC *mvcc; /*! mvcc */
volatile trx_id_t max_trx_id; /*! 要分配给下一个事务的事务id*/
std::atomic min_active_id; /*! 最小的活跃事务Id */
// 省略...
trx_id_t rw_max_trx_id; /*!< 最大读写事务Id */
// 省略...
trx_ids_t rw_trx_ids; /*! 当前活跃的读写事务Id列表 */
Rsegs rsegs; /*!< 回滚段 */
// 省略...
}; MVCC:MVCC 读取视图管理器
class MVCC {
public:
// 省略...
/** 创建一个视图 */
void view_open(ReadView *&view, trx_t *trx);
/** 关闭一个视图 */
void view_close(ReadView *&view, bool own_mutex);
/** 释放一个视图 */
void view_release(ReadView *&view);
// 省略...
/** 判断视图是否处于活动和有效状态 */
static bool is_view_active(ReadView *view) {
ut_a(view != reinterpret_cast(0x1));
return (view != NULL && !(intptr_t(view) & 0x1));
}
// 省略...
private:
typedef UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(ReadView) view_list_t;
/** 空闲可以被重用的视图*/
view_list_t m_free;
/** 活跃或者已经关闭的 Read View 的链表 */
view_list_t m_views;
}; ReadView:视图,某一时刻的一个事务快照
class ReadView {
// 省略...
private:
/** 高水位,大于等于这个ID的事务均不可见 */
trx_id_t m_low_limit_id;
/** 低水位,小于这个ID的事务均可见 */
trx_id_t m_up_limit_id;
/** 创建该 Read View 的事务ID */
trx_id_t m_creator_trx_id;
/** 创建视图时的活跃事务id列表*/
ids_t m_ids;
/** 配合purge,标识该视图不需要小于 m_low_limit_no 的 UNDO LOG,
如果其他视图也不需要,则可以删除小于 m_low_limit_no 的 UNDO LOG */
trx_id_t m_low_limit_no;
/** 标记视图是否被关闭*/
bool m_closed;
// 省略...
};基本理论基础
当前读和快照读
当前读:官方叫做 Locking Reads(锁定读取),读取数据的最新版本。常见的 update/insert/delete、还有 select ... for update、select ... lock in share mode 都是当前读。
官方文档:MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 15.7.2.4 Locking Reads
快照读:官方叫做 Consistent Nonlocking Reads(一致性非锁定读取,也叫一致性读取),读取快照版本,也就是 MVCC 生成的 ReadView。用于普通的 select 的语句。MySQL 默认快照读。
官方文档:MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 15.7.2.3 Consistent Nonlocking Reads
低水位线与高水位线
- m_up_limit_id:低水位线,活跃事务的最小 ID
- m_low_limit_id:高水位线,活跃事务的最大 ID + 1
当一个事务修改一条记录时,会将该事务 ID 插入到当前记录,并存储与 DB_TRX_ID 字段中。
活跃事务是指在创建 ReadView 时,启动但未提交的事务,MySQL 源码中使用 m_ids(m_ids 中的元素递增存储的)结构保存活跃事务 ID。
事务可见性与高低水位线的关系:
1)已提交事务对当前事务一定可见;
2)未开始事务对当前事务一定不可见;
3)当事务 ID 介于 m_up_limit_id 和 m_low_limit_id 之间时,需判断事务 ID 是否位于 m_ids 中:
- 如果事务 ID 位于 m_ids 中,则对当前事务不可见,因为事务还未提交
- 否则,对当前事务可见
增加隐藏字段
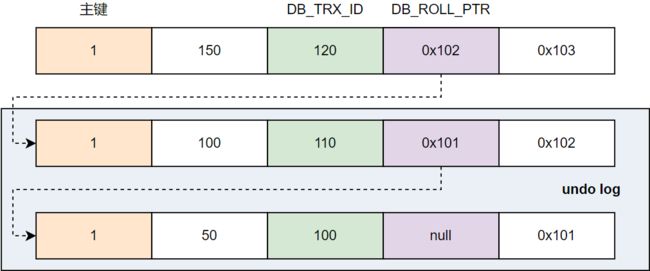
为了实现 MVCC,InnoDB 会向表中添加三个隐藏字段:DB_ROW_ID、DB_TRX_ID、DB_ROLL_PTR。
- DB_ROW_ID:该字段占 6 个字节,在建表时如果没有显示指定主键,InnoDB 会首先判断该表中是否有非空唯一索引,如果有,则该索引即为主键并将主键值存放到该字段中(如果存在多个非空唯一索引,则选择第一个创建的非空唯一索引为主键);如果没有非空唯一索引,InnoDB 会隐式生成主键并存储于当前字段中;
- DB_TRX_ID:该字段占 6 个字节,用于存储最近修改或插入当前记录的事务ID;
- DB_ROLL_PTR:该字段占 7 个字节,指向写入回滚段的 undo log 记录。每次对某条记录进行更新时,会通过 undo log 记录更新前的行记录内容,更新后的行记录会通过 DB_ROLL_PTR 指向该 undo log 。当某条记录被多次修改时,该行记录会存在多个版本,通过 DB_ROLL_PTR 链接形成一个类似版本链的概念,大致如下图所示。
说明:隐藏列 DB_ROW_ID 是早期 MySQL 版本的叫法,在后续版本中,为了与应用程序更好地兼容,这个列的名称被更改为 _rowid。
隐藏字段源码解析
上述三个隐藏字段在 MySQL 源码 .\mysql\storage\innobase\dict\dict0dict.cc 文件的 dict_table_add_system_columns 函数中,具体函数内容如下:
/** Adds system columns to a table object. // 添加系统列到表对象
@param[in,out] table Table
@param[in] heap Temporary heap */
void dict_table_add_system_columns(dict_table_t *table, mem_heap_t *heap) {
ut_ad(table);
ut_ad(table->n_def == (table->n_cols - table->get_n_sys_cols()));
ut_ad(table->magic_n == DICT_TABLE_MAGIC_N);
ut_ad(!table->cached);
/* NOTE: the system columns MUST be added in the following order
(so that they can be indexed by the numerical value of DATA_ROW_ID,
etc.) and as the last columns of the table memory object.
The clustered index will not always physically contain all system
columns.
Intrinsic table don't need DB_ROLL_PTR as UNDO logging is turned off
for these tables. */
// 添加主键 ID
dict_mem_table_add_col(table, heap, "DB_ROW_ID", DATA_SYS,
DATA_ROW_ID | DATA_NOT_NULL, DATA_ROW_ID_LEN, false);
// 添加事务 ID
dict_mem_table_add_col(table, heap, "DB_TRX_ID", DATA_SYS,
DATA_TRX_ID | DATA_NOT_NULL, DATA_TRX_ID_LEN, false);
if (!table->is_intrinsic()) { // 判断是否是内部表
// 添加回滚指针
dict_mem_table_add_col(table, heap, "DB_ROLL_PTR", DATA_SYS,
DATA_ROLL_PTR | DATA_NOT_NULL, DATA_ROLL_PTR_LEN,
false);
/* This check reminds that if a new system column is added to
the program, it should be dealt with here */
}
}增删改的底层操作
更新操作
当我们更新一条数据时,InnoDB 会进行如下操作:
- 加锁:对要更新的行记录加排他锁;
- 写 undo log:将更新前的记录写入 undo log,并构建指向该 undo log 的回滚指针 roll_ptr;
- 更新行记录:更新行记录的 DB_TRX_ID 属性为当前的事务 ID,更新 DB_ROLL_PTR 属性为步骤 2 生成的回滚指针,将此次要更新的属性列更新为目标值;
- 写 redo log:DB_ROLL_PTR 使用步骤 2 生成的回滚指针,DB_TRX_ID 使用当前的事务 ID,并填充更新后的属性值;
- 处理结束,释放排他锁;
删除操作
删除操作在底层实现中使用更新来实现,逻辑基本和更新操作一样,如下是几个需要注意的点:
1)写 undo log 期间,会通过 type_cmpl 来标识是删除操作还是更新操作,且不记录列的旧值;
2)这边不会直接删除,只会给行记录的 info_bits 打上删除标识(REC_INFO_DELETED_FLAG),之后会由专门的 purge 线程来执行真正的删除操作;
插入操作
插入操作相比于更新操作更为简单,就是新增一条记录,DB_TRX_ID 使用当前的事务Id,同样会有 undo log 和 redo log。
更新记录源码解析
更新行记录在 MySQL 源码 .\mysql\storage\innobase\btr\btr0cur.cc 文件的 btr_cur_update_in_place 函数中,具体函数内容如下:
/** Updates a record when the update causes no size changes in its fields. */
dberr_t btr_cur_update_in_place(ulint flags, btr_cur_t *cursor, ulint *offsets,
const upd_t *update, ulint cmpl_info,
que_thr_t *thr, trx_id_t trx_id, mtr_t *mtr) {
// 省略...
// 通过 B+ 树游标获取当前记录
rec = btr_cur_get_rec(cursor);
index = cursor->index; // 或者当前游标所指的索引
// 省略...
// 写 undo log
err = btr_cur_upd_lock_and_undo(flags, cursor, offsets, update, cmpl_info,
thr, mtr, &roll_ptr);
// 省略...
if (!(flags & BTR_KEEP_SYS_FLAG) && !index->table->is_intrinsic()) {
// 更新 rec 的 trx_id、roll_ptr 属性值
row_upd_rec_sys_fields(rec, nullptr, index, offsets, thr_get_trx(thr),
roll_ptr);
}
// 获取记录的删除标记,如果记录被标记为删除,则返回 true
was_delete_marked =
rec_get_deleted_flag(rec, page_is_comp(buf_block_get_frame(block)));
// 省略...
// 将 rec 要更新的属性列更新为目标值
row_upd_rec_in_place(rec, index, offsets, update, page_zip);
// 写 redo log
btr_cur_update_in_place_log(flags, rec, index, update, trx_id, roll_ptr, mtr);
// 如果当前记录被标记为删除且还没有被删除,则取消删除标记,因为字段的所有权已经转移到了新记录上
if (was_delete_marked &&
!rec_get_deleted_flag(rec, page_is_comp(buf_block_get_frame(block)))) {
/* The new updated record owns its possible externally
stored fields */
lob::BtrContext btr_ctx(mtr, nullptr, index, rec, offsets, block);
btr_ctx.unmark_extern_fields();
}
// 省略...
return (err);
}构建一致性读取视图(ReadView)
当我们的隔离级别为 RR 时:每开启一个事务,系统会给该事务会分配一个事务 Id,在该事务执行第一个 select 语句的时候,会生成一个当前时间点的事务快照 ReadView,核心属性如下:
- m_ids:创建 ReadView 时当前系统中活跃的事务 Id 列表,可以理解为生成 ReadView 那一刻还未执行提交的事务,并且该列表是个升序列表。
- m_up_limit_id:低水位(小于低水位的事务都可见),取 m_ids 列表的第一个节点,因为 m_ids 是升序列表,因此也就是 m_ids 中事务 Id 最小的那个。
- m_low_limit_id:高水位(大于等于高水位的事务都不可见),生成 ReadView 时系统将要分配给下一个事务的 Id 值(即 m_ids 列表的最后一个节点加 1)。
- m_creator_trx_id:创建 ReadView 的事务 Id。
一致性读取视图源码解析
一致性读取视图在 MySQL 源码 .\mysql\storage\innobase\read\read0read.cc 文件的 ReadView::prepare 函数中,具体函数内容如下:
调用堆栈:row_search_mvcc => trx_assign_read_view => MVCC::view_open => ReadView::prepare
/**
Opens a read view where exactly the transactions serialized before this
point in time are seen in the view.
@param id Creator transaction id */
void ReadView::prepare(trx_id_t id) {
ut_ad(trx_sys_mutex_own());
m_creator_trx_id = id; // 创建 ReadView 的事务 ID
m_low_limit_no = trx_get_serialisation_min_trx_no(); // 视图不需要查看小于该值的事务 ID
// 高水位
m_low_limit_id = trx_sys_get_next_trx_id_or_no();
ut_a(m_low_limit_no <= m_low_limit_id);
// 如果事务系统的活跃事务列表不为空,则将其拷贝至 m_ids
if (!trx_sys->rw_trx_ids.empty()) {
/*
1) copy_trx_ids 函数通过调用 m_up_limit_id = m_ids.front() 将 m_ids 中的最小事务 id 赋值给 m_up_limit_id;
2) 使用二分查找算法,查找 trx_id 是否在 m_ids 中;
*/
copy_trx_ids(trx_sys->rw_trx_ids);
} else { // 否则清空 ReadView 的活跃事务列表
m_ids.clear();
}
/* The first active transaction has the smallest id. */
m_up_limit_id = !m_ids.empty() ? m_ids.front() : m_low_limit_id;
ut_a(m_up_limit_id <= m_low_limit_id);
ut_d(m_view_low_limit_no = m_low_limit_no);
m_closed = false;
}最后,会将这个创建的 ReadView 添加到 MVCC 的 m_views 中。
一致性视图可见性判断
SQL 查询走聚簇索引
有了这个 ReadView,在访问某条记录时,只需要按照如下步骤即可判断当前记录的某个版本是否可见:
1)如果被访问记录的 trx_id 与 ReadView 中 的 m_creator_trx_id 值相同,则意味着当前事务在访问它自己修改过的记录,所以该记录可以被当前事务访问。
2)如果被访问记录的 trx_id 小于 ReadView 中的 m_up_limit_id(低水位),表明该版本记录的事务在当前事务生成 ReadView 前已经提交,所以该版本记录可以被当前事务访问。
3)如果被访问记录的 trx_id 大于等于 ReadView 中的 m_low_limit_id(高水位),表明该版本记录的事务在当前事务生成 ReadView 后才开启,所以该版本不可以被当前事务访问。
4)如果被访问记录的 trx_id 属性值在 ReadView 的 m_up_limit_id 和 m_low_limit_id 之间,那就需要判断 trx_id 属性值是不是在 m_ids 列表中,源码中会通过二分法查找。如果在,说明创建 ReadView 时生成该版本记录的事务还是活跃的,该版本记录不可以被访问;如果不在,说明创建 ReadView 时生成该版本记录的事务已经被提交,该版本可以被访问。
在进行判断时,首先会拿记录的最新版本来比较,如果该版本记录无法被当前事务看到,则通过记录的 DB_ROLL_PTR 找到上一个版本,重新进行比较,直到找到一个能被当前事务看到的版本。
而对于删除,其实就是一种特殊的更新,InnoDB 在 info_bits 中用一个标记位 delete_flag 标识是否删除。当我们在进行判断时,会检查下 delete_flag 是否被标记,如果是,则会根据情况进行处理:
- 如果索引是聚簇索引,并且具有唯一特性(主键、唯一索引等),则返回 DB_RECORD_NOT_FOUND;
- 否则,会寻找下一条记录继续流程;
其实很容易理解,如果是唯一索引查询,必然只有一条记录,如果被删除了则直接返回空,而如果是普通索引,可能存在多个相同值的行记录,该行不存在,则继续查找下一条。
注意:以上内容是对于 RR(可重复读)级别来说,而对于 RC(读提交)级别,其实整个过程几乎一样,唯一不同的是生成 ReadView 的时机,RR 级别只在事务第一次 select 时生成一次,之后一直使用该 ReadView。而 RC 级别则在每次 select 时,都会生成一个 ReadView。
聚簇索引可见性源码解析
走聚簇索引的核心流程在 row_search_mvcc 函数中,具体调用堆栈:row_search_mvcc => lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees => changes_visible。
1)row_search_mvcc 函数
// 功能:使用游标在数据库中搜索行
dberr_t row_search_mvcc(byte *buf, page_cur_mode_t mode,
row_prebuilt_t *prebuilt, ulint match_mode,
const ulint direction) {
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
// 阶段1:尝试从记录缓冲区或预取缓存中弹出行
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
// 阶段2:如果可能的话,尝试快速自适应散列索引搜索
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
// 阶段3:打开或恢复索引游标位置
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* 阶段4:在一个循环中查找匹配的记录 */
// 省略...
// 检查隔离级别是否是读未提交,如果是,什么也不做
if (trx->isolation_level == TRX_ISO_READ_UNCOMMITTED) {
/* Do nothing: we let a non-locking SELECT read the
latest version of the record */
} else if (index == clust_index) { /*------ 聚簇索引 ------*/
/* --------------------------------------------------- */
// 判断 rec 在 ReadView 中是否可见
if (srv_force_recovery < 5 &&
!lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees(rec, index, offsets,
trx_get_read_view(trx))) {
rec_t *old_vers;
// 获取 rec 的上一个版本,并将其赋值给 old_vers
err = row_sel_build_prev_vers_for_mysql(
trx->read_view, clust_index, prebuilt, rec, &offsets, &heap,
&old_vers, need_vrow ? &vrow : nullptr, &mtr,
prebuilt->get_lob_undo());
if (err != DB_SUCCESS) {
goto lock_wait_or_error;
}
// 如果旧版本中的行记录也为空或不可见,则继续处理下一条记录
if (old_vers == nullptr) {
goto next_rec;
}
rec = old_vers; // 记录指针更新为先前版本的记录
prev_rec = rec;
}
} else { /*------ 非聚簇索引 ------*/
/* --------------------------------------------------- */
// 判断 rec 在 ReadView 中的可见性
if (!srv_read_only_mode &&
!lock_sec_rec_cons_read_sees(rec, index, trx->read_view)) {
/*
注:lock_sec_rec_cons_read_sees 函数判断可见性逻辑:page页最大事务ID小于低水位,即可见;
page页最大事务ID大于等于低水位时认为是不可见,但在goto requires_clust_rec时会进一步判断当前记录的可见性
*/
switch (row_search_idx_cond_check(buf, prebuilt, rec, offsets)) {
case ICP_NO_MATCH: // 不满足二级索引条件,当有多条记录时排除其它记录,icp下推二级索引过滤
goto next_rec;
case ICP_OUT_OF_RANGE: // 超出二级索引范围
err = DB_RECORD_NOT_FOUND;
goto idx_cond_failed;
case ICP_MATCH: // 满足二级索引条件,通过回表查找当前记录的事务id,以获取当前事务的上一版本数据
goto requires_clust_rec;
}
ut_error; // 出现了意外情况,抛出错误
}
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* 阶段5:将光标移动到下一个索引记录 */
// 省略...
}2)lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees 函数
/** Checks that a record is seen in a consistent read.
@return true if sees, or false if an earlier version of the record
should be retrieved */
bool lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees(
const rec_t *rec, /*!< in: user record which should be read or
passed over by a read cursor */
dict_index_t *index, /*!< in: clustered index */
const ulint *offsets, /*!< in: rec_get_offsets(rec, index) */
ReadView *view) /*!< in: consistent read view */
{
ut_ad(index->is_clustered());
ut_ad(page_rec_is_user_rec(rec));
ut_ad(rec_offs_validate(rec, index, offsets));
/* Temp-tables are not shared across connections and multiple
transactions from different connections cannot simultaneously
operate on same temp-table and so read of temp-table is
always consistent read. */
/*
如果数据库处于只读模式或者表是临时的,则返回true,表示始终可以看到该记录。
这是因为临时表在多个连接和事务中不是共享的,所以读取总是具有一致性。
*/
if (srv_read_only_mode || index->table->is_temporary()) {
ut_ad(view == nullptr || index->table->is_temporary());
return (true);
}
/* NOTE that we call this function while holding the search
system latch. */
// 获取当前记录的事务ID
// 主键索引扫描时,rec是一条完整记录,可以直接获取当前记录的事务id
trx_id_t trx_id = row_get_rec_trx_id(rec, index, offsets);
// 判断 ReadView 对当前记录的可见性
return (view->changes_visible(trx_id, index->table->name));
}3)changes_visible 函数
/** Check whether the changes by id are visible.
@param[in] id transaction id to check against the view
@param[in] name table name
@return whether the view sees the modifications of id. */
[[nodiscard]] bool changes_visible(trx_id_t id,
const table_name_t &name) const {
ut_ad(id > 0); // 事务id一般是正整数,0 可能表示“没有事务”或“无效事务”
/*
m_up_limit_id 为低水位线,小于低水位线的事务ID都可见
m_creator_trx_id 为当前事务id,记录被当前事务修改时也一定可见
*/
if (id < m_up_limit_id || id == m_creator_trx_id) {
return (true);
}
// 检查事务ID是否有效
check_trx_id_sanity(id, name);
// m_low_limit_id 为高水位线,所有大于高水位线的事务ID都不可见
if (id >= m_low_limit_id) {
return (false);
// 判断创建 ReadView 时的活跃事务列表是否为空,若为空,则当前记录可见
} else if (m_ids.empty()) {
return (true);
}
const ids_t::value_type *p = m_ids.data();
// 使用二分查找在 m_ids 中查找当前记录的事务ID,若找到,则当前记录不可见;若未找到,则可见
return (!std::binary_search(p, p + m_ids.size(), id));
}获取当前记录的上一个版本源码解析
获取当前记录的上一个版本,主要是通过 DB_ROLL_PTR 来实现,核心流程如下:
1)获取当前记录的回滚指针 DB_ROLL_PTR、获取当前记录的事务 ID;
2)通过回滚指针拿到对应的 undo log;
3)解析 undo log,并使用 undo log 构建用于更新向量 UPDATE;
4)构建记录的上一个版本:先用记录的当前版本填充,然后使用 UPDATE(undo log)进行覆盖。
获取当前记录的上一个版本的核心流程在 row_search_mvcc 函数中,具体调用堆栈:row_search_mvcc => row_sel_build_prev_vers_for_mysql => row_vers_build_for_consistent_read => trx_undo_prev_version_build。
bool trx_undo_prev_version_build(
const rec_t *index_rec ATTRIB_USED_ONLY_IN_DEBUG,
mtr_t *index_mtr ATTRIB_USED_ONLY_IN_DEBUG, const rec_t *rec,
const dict_index_t *const index, ulint *offsets, mem_heap_t *heap,
rec_t **old_vers, mem_heap_t *v_heap, const dtuple_t **vrow, ulint v_status,
lob::undo_vers_t *lob_undo) {
// 省略...
// 1) 获取 rec 的回滚指针 roll_ptr
roll_ptr = row_get_rec_roll_ptr(rec, index, offsets);
*old_vers = nullptr;
if (trx_undo_roll_ptr_is_insert(roll_ptr)) {
/* The record rec is the first inserted version */
return true;
}
// 2) 获取 rec 的事务 ID
rec_trx_id = row_get_rec_trx_id(rec, index, offsets);
/* REDO rollback segments are used only for non-temporary objects.
For temporary objects NON-REDO rollback segments are used. */
bool is_temp = index->table->is_temporary();
ut_ad(!index->table->skip_alter_undo);
// 3) 通过回滚指针获取 undo log 记录,拷贝到 heap 中,并且填充给 undo_rec
if (trx_undo_get_undo_rec(roll_ptr, rec_trx_id, heap, is_temp,
index->table->name, &undo_rec)) {
// 省略...
}
// 4) 开始解析 undo log,填充给对应的参数(参考 undo log 的构造图,这边会按构造顺序依次读取填充)
type_cmpl_t type_cmpl;
// 4.1) 通过 undo_rec 读取 type、undo_no、cmpl_info、table_id 的值,并填充到形参变量中
// 读取这些值后,将 undo log 的剩余部分返回,并赋值给 ptr
ptr = trx_undo_rec_get_pars(undo_rec, &type, &cmpl_info, &dummy_extern,
&undo_no, &table_id, type_cmpl);
// 省略...
// 4.2) 从 ptr 读取 trx_id、roll_ptr、info_bits 的值,并填充到形参参的变量中
// 读取这些值后,将 undo log 的剩余部分返回,并赋值给 ptr
ptr = trx_undo_update_rec_get_sys_cols(ptr, &trx_id, &roll_ptr, &info_bits);
// 4.3) undo log 跳过行引用
ptr = trx_undo_rec_skip_row_ref(ptr, index);
// 4.4) 通过 undo log 的剩余部分(roll_ptr、info_bts等)构建 update(就是填充到update变量中)
ptr = trx_undo_update_rec_get_update(ptr, index, type, trx_id, roll_ptr,
info_bits, nullptr, heap, &update,
lob_undo, type_cmpl);
ut_a(ptr);
if (row_upd_changes_field_size_or_external(index, offsets, update)) {
// 省略...
} else {
buf = static_cast(mem_heap_alloc(heap, rec_offs_size(offsets)));
// 5) 构建 old_vers:先用 rec 填充,再用 update 覆盖(也就是 rec 的 roll_ptr 指向的 undo 1og 的内容)
// 5.1) 将 rec 拷贝到 buf 中,同时返回指向 buf 数据部分的指针,赋值给 old_vers
*old_vers = rec_copy(buf, rec, offsets);
rec_offs_make_valid(*old_vers, index, offsets);
// 5.2) 使用 update 覆盖 old_vers,相当于先将 old_vers 赋值为 rec(当前版本),然后用 undo log 来覆盖
row_upd_rec_in_place(*old_vers, index, offsets, update, nullptr);
}
// 省略...
} SQL 查询走非聚簇索引
当走普通索引时,判断逻辑如下:
1)判断被访问索引记录所在页的最大事务 Id 是否小于 ReadView 中的 m_up_limit_id(低水位),如果是,则代表该页的最后一次修改事务 ID 在 ReadView 创建前之前已经提交,所以一定可以访问;如果不是,并不代表一定不可以访问,道理跟走聚簇索引一样,事务 ID 大的也可能提交比较早,所以需要做进一步判断,见步骤 2。
2)根据索引信息,使用 ICP(Index Condition Pushdown)来判断搜索条件是否满足,主要目的是,在使用聚簇索引判断记录可见性之前先进行过滤(可以减少不必要的回表操作),这边有三种情况:
- ICP 判断不满足条件但没有超出扫描范围,则获取下一条记录继续查找;
- 如果不满足条件并且超出扫描返回,则返回 DB_RECORD_NOT_FOUND;
- 如果 ICP 判断符合条件,则会获取对应的聚簇索引来进行可见性判断。
说明:在进行非聚簇索引可见性判断时,若不可见,但满足 ICP 条件,则会继续调用 lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees 函数再次判断当前记录的可见性。
非聚簇索引可见性判断源码解析
走非聚簇索引的核心流程在 row_search_mvcc 函数中,具体调用堆栈:row_search_mvcc => lock_sec_rec_cons_read_seese。
1)row_search_mvcc 函数
// 功能:使用游标在数据库中搜索行
dberr_t row_search_mvcc(byte *buf, page_cur_mode_t mode,
row_prebuilt_t *prebuilt, ulint match_mode,
const ulint direction) {
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
// 阶段1:尝试从记录缓冲区或预取缓存中弹出行
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
// 阶段2:如果可能的话,尝试快速自适应散列索引搜索
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
// 阶段3:打开或恢复索引游标位置
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* 阶段4:在一个循环中查找匹配的记录 */
// 省略...
// 检查隔离级别是否是读未提交,如果是,什么也不做
if (trx->isolation_level == TRX_ISO_READ_UNCOMMITTED) {
/* Do nothing: we let a non-locking SELECT read the
latest version of the record */
} else if (index == clust_index) { /*------ 聚簇索引 ------*/
/* --------------------------------------------------- */
// 判断 rec 在 ReadView 中是否可见
if (srv_force_recovery < 5 &&
!lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees(rec, index, offsets,
trx_get_read_view(trx))) {
rec_t *old_vers;
// 获取 rec 的上一个版本,并将其赋值给 old_vers
err = row_sel_build_prev_vers_for_mysql(
trx->read_view, clust_index, prebuilt, rec, &offsets, &heap,
&old_vers, need_vrow ? &vrow : nullptr, &mtr,
prebuilt->get_lob_undo());
if (err != DB_SUCCESS) {
goto lock_wait_or_error;
}
// 如果旧版本中的行记录也为空或不可见,则继续处理下一条记录
if (old_vers == nullptr) {
goto next_rec;
}
rec = old_vers; // 记录指针更新为先前版本的记录
prev_rec = rec;
}
} else { /*------ 非聚簇索引 ------*/
/* --------------------------------------------------- */
// 判断 rec 在 ReadView 中的可见性
if (!srv_read_only_mode &&
!lock_sec_rec_cons_read_sees(rec, index, trx->read_view)) {
/*
注:lock_sec_rec_cons_read_sees 函数判断可见性逻辑:page页最大事务ID小于低水位,即可见;
page页最大事务ID大于等于低水位时认为是不可见,但在goto requires_clust_rec时会进一步判断当前记录的可见性
*/
switch (row_search_idx_cond_check(buf, prebuilt, rec, offsets)) {
case ICP_NO_MATCH: // 不满足二级索引条件,当有多条记录时排除其它记录,icp下推二级索引过滤
goto next_rec;
case ICP_OUT_OF_RANGE: // 超出二级索引范围
err = DB_RECORD_NOT_FOUND;
goto idx_cond_failed;
case ICP_MATCH: // 满足二级索引条件,通过回表查找当前记录的事务id,以获取当前事务的上一版本数据
goto requires_clust_rec;
}
ut_error;
}
}
}
// 省略...
// 如果不是在主键上扫描,则判断是否需要回表
if (index != clust_index && prebuilt->need_to_access_clustered) { // MRR 的情况下 need_to_access_clustered = false
requires_clust_rec: // 主要用于非聚簇索引情况下的回表
// 省略...
// 使用二级索引对应的主键进行回表,拿到完整记录后,会在该函数中调用lock_clust_rec_cons_read_sees函数再次判断当前记录的可见性
err = row_sel_get_clust_rec_for_mysql(
prebuilt, index, rec, thr, &clust_rec, &offsets, &heap,
need_vrow ? &vrow : nullptr, &mtr, prebuilt->get_lob_undo());
// 省略...
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* 阶段5:将光标移动到下一个索引记录 */
// 省略...
}2)lock_sec_rec_cons_read_sees 函数
/** Checks that a non-clustered index record is seen in a consistent read. */
bool lock_sec_rec_cons_read_sees(
const rec_t *rec, /*!< in: user record which
should be read or passed over
by a read cursor */
const dict_index_t *index, /*!< in: index */
const ReadView *view) /*!< in: consistent read view */
{
ut_ad(page_rec_is_user_rec(rec));
/* NOTE that we might call this function while holding the search
system latch. */
// 当crash时,使用redo log恢复记录期间为false
if (recv_recovery_is_on()) {
return (false);
// 临时表的读取始终是一致的,因为临时表在多个连接和事务中不是共享的,所以读取总是具有一致性
} else if (index->table->is_temporary()) {
return (true);
}
// 从记录所在页获取最大事务ID(是一种优化,以减少回表)
// 二级索引扫描 rec 中存储的只是主键 id,如果不使用 page 的最大事务 ID,可能需要进行大量回表,以获取当前记录的事务 ID
trx_id_t max_trx_id = page_get_max_trx_id(page_align(rec));
ut_ad(max_trx_id > 0); // 确保最大的事务ID大于0
// sees 函数通过判断 max_trx_id 是否小于低水位线(m_up_limit_id),若小于,则可见
return (view->sees(max_trx_id));
}MVCC 是否解决了幻读
MVCC 解决了部分幻读,但并没有完全解决幻读。
对于快照读,MVCC 因为从 ReadView 读取,所以必然不会看到新插入的行,解决了幻读问题。
对于当前读,MVCC 无法解决幻读。需要使用 Gap Lock 或 Next-Key Lock(Gap Lock + Record Lock)来解决。
其实原理也很简单,用上面的例子稍微修改下以触发当前读:select * from user where id < 10 for update,当使用了 Gap Lock 时,Gap 锁会锁住 id < 10 的整个范围,因此其他事务无法插入 id < 10 的数据,从而防止了幻读。
Repeatable Read 如何解决幻读
SQL 标准中规定的 RR 并不能消除幻读,但是 MySQL InnoDB 的 RR 可以,靠的就是 Gap 锁。在 RR 级别下,Gap 锁是默认开启的,而在 RC 级别下,Gap 锁是关闭的。
RR 与 RC 生成 ReadView 的时机与区别
假设有一张表,其结构和数据如下:
mysql> show create table t;
+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| t | CREATE TABLE `t` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`a` int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `a` (`a`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci |
+-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t;
+----+------+
| id | a |
+----+------+
| 1 | 50 |
+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
RR 或 RC 生成 ReadView 的时机
解析:RR 生成 ReadView 的时机是事务第一个 select 的时候,而不是事务开始的时候。右边的例子中,事务1在事务2提交了修改后才执行第一个 select,因此生成的 ReadView 中,a 的是 100 而不是事务1刚开始时的 50。
RR 与 RC 生成 ReadView 的区别
解析:RR 只在事务第一次执行 select 时生成 ReadView ,之后一直使用该 ReadView。而 RC 级别则在每次执行 select 时,都会生成一个 ReadView,所以在第二次执行 select 时,读取到了事务 2 对于 a 的修改值。
如果需要本文 WORD、PDF 相关文档请在评论区留言!!!
如果需要本文 WORD、PDF 相关文档请在评论区留言!!!
如果需要本文 WORD、PDF 相关文档请在评论区留言!!!
参考
MVCC的底层原理_mysql mvcc 高水位低水位-CSDN博客
MVCC原理分析 + 源码解读 -- 必须说透_mvcc mysql源码解析-CSDN博客
MySQL 8.0 MVCC 核心原理解析(核心源码) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
InnoDB MVCC 详解-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)