数学知识:约数
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、约数,质因子
- 二、例题,代码
-
- AcWing 869. 试除法求约数
-
- 本题解析
- AC代码
- AcWing 870. 约数个数
-
- 本题解析
- AC代码
- AcWing 871. 约数之和
-
- 本题解析
- AC代码
- AcWing 872. 最大公约数
-
- 本题解析
- AC代码
- 三、时间复杂度
前言
复习acwing算法基础课的内容,本篇为讲解数学知识:约数,关于时间复杂度:目前博主不太会计算,先鸽了,日后一定补上。
一、约数,质因子
约数(又称因数)是指若整数a除以整数b(b≠0)除得的商正好是整数而没有余数,就说a能被b整除,或b能整除a,其中a称为b的倍数,b称为a的约数。
质因子就是质数的因子,也称质因数或质约数。 255的因子有1 、3、5、15、17、51、85、255。其中是质数的是1、3、5、17 所以255的质因子就是1、3、5、17
二、例题,代码
AcWing 869. 试除法求约数
本题链接:AcWing 869. 试除法求约数
本博客提供本题截图:

本题解析
用到了vector,用法见:STL—vector
AC代码
#include AcWing 870. 约数个数
本题链接:AcWing 870. 约数个数
本博客提供本题截图:

本题解析
约数个数计算公式:首先把这个数写成质因数的乘积的形式:
![]()
这个数的约数的个数就是:
![]()
用到了unordered_map,用法同map,见:STL—map
AC代码
#include AcWing 871. 约数之和
本题链接:AcWing 871. 约数之和
本博客提供本题截图:

本题解析
计算约数之和的公式:首先把这个数写成质因数的乘积的形式:
![]()
这个数的约数之和就是:

如何凑出:
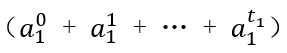
利用:
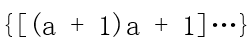
AC代码
#include AcWing 872. 最大公约数
本题链接:AcWing 872. 最大公约数
本博客提供本题截图:

本题解析
求最大公约数模板:(需要背过)
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
AC代码
#include 三、时间复杂度
关于约数各步操作的时间复杂度以及证明,后续会给出详细的说明以及证明过程,目前先鸽了。