Windows 下用 C++ 调用 Python
文章目录
- Part.I Introduction
-
- Chap.I Information
- Chap.II 预备知识
- Part.II 语法
-
- Chap.I PyRun_SimpleString
- Chap.II C++ / Python 变量之间的相互转换
- Part.III 实例
-
- Chap.I 文件内容
- Chap.II 基于 Visual Studio IDE
- Chap.III 基于 cmake
- Chap.IV 运行结果
- Part.IV 可能出现的问题
-
- Chap.I 无法打开 python311_d.lib
- Chap.II 导入模块报错
- Chap.I PyEval_CallObject 调用报错
- Reference
Part.I Introduction
本文主要介绍一下如何使用 C++ 调用 Python。包括运行 python 脚本;C++ 和 Python 之间参数的相互转换和传递。
Chap.I Information
下面是笔者python 相关的目录,可参考
python.exe所在目录:A:\Programs\Python\Python11_4python311.lib所在目录:A:\Programs\Python\Python11_4\libsinclude所在目录:A:\Programs\Python\Python11_4\include
Chap.II 预备知识
Part.II 语法
Chap.I PyRun_SimpleString
Python 库函数 PyRun_SimpleString 可以执行字符串形式的Python代码。不过在使用 PyRun_SimpleString 之前需要先初始化(Py_Initialize()),执行完之后需要释放资源Py_Finalize(),示例:
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello!')");
Py_Finalize();
Chap.II C++ / Python 变量之间的相互转换
有待总结和补充,可看下面的实例。
Part.III 实例
Chap.I 文件内容
所用到的几个文件组织结构如下
test
│ CMakeLists.txt
│ hello.py
│ main.cpp
└─build
hello.py中有两个小函数,内容如下:
def add(a,b):
return a+b
def get_name(first):
return "your name is {} alice".format(first)
main.cpp文件内容如下:
#include CMakeLists.txt 文件内容等会儿说;build 是一个空文件,生成的二进制文件等放这里面。
Chap.II 基于 Visual Studio IDE
1、首先新建一个工程,将main.cpp添加进去,然后将hello.py放在和main.cpp一样的路径下。
2、将 IDE 上方『解决方案平台』设置为x64,最好将『解决方案配置』设置为Release(debug 需要*_d.lib)
3、将include添加到 C/C++ 附加包含目录中:项目右键→属性→C/C++→附加包含目录→添加 python 的 include

右键属性→链接器→常规→附加库目录→将 python 的 libs 加进去

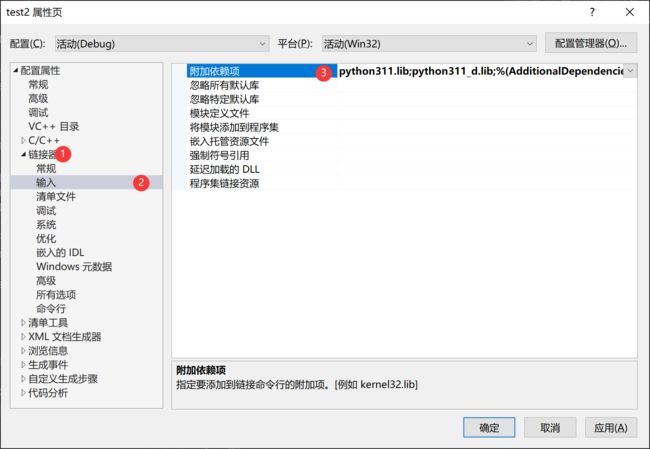
3、将*.lib添加到附加依赖项中:项目右键→属性→链接器→输入→将python311.lib和python311_d.lib加进去。
Chap.III 基于 cmake
cmake 自动搜寻 python
CMakeLists.txt文件内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 3.20 )
project( test )
set( PRJ_INCLUDE_DIRS )
set( PRJ_COMPILE_FEATURES )
set( PRJ_LIBRARIES )
list( APPEND PRJ_COMPILE_FEATURES cxx_std_20 )
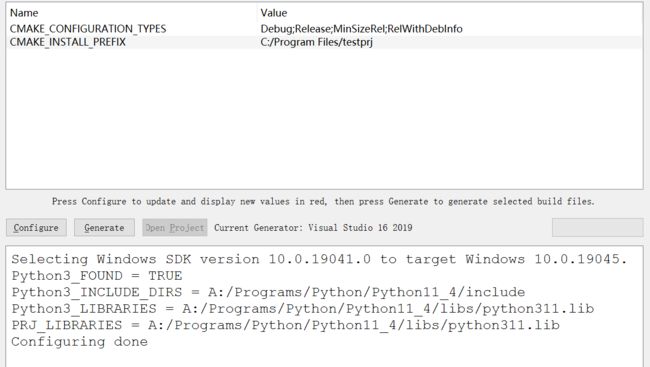
find_package(Python3 COMPONENTS Interpreter Development)
message( STATUS "Python3_FOUND = ${Python3_FOUND} " )
message( STATUS "Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS = ${Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS} " )
message( STATUS "Python3_LIBRARIES = ${Python3_LIBRARIES} " )
if( ${Python3_FOUND} )
#include_directories(${Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS})
else()
message( FATAL_ERROR "Python3 not found, please install it." )
endif()
list( APPEND PRJ_INCLUDE_DIRS ${Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
list( APPEND PRJ_LIBRARIES ${Python3_LIBRARIES} )
message( STATUS "PRJ_LIBRARIES = ${PRJ_LIBRARIES} " )
add_executable( ${PROJECT_NAME}
main.cpp
)
target_include_directories( ${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
${PRJ_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
target_link_libraries( ${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
${PRJ_LIBRARIES}
)
target_compile_features( ${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
${PRJ_COMPILE_FEATURES}
)
cmake 手动设置 Python 路径
CMakeLists.txt文件内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 3.20 )
project( test )
set( PRJ_INCLUDE_DIRS )
set( PRJ_COMPILE_FEATURES )
set( PRJ_LIBRARIES )
list( APPEND PRJ_COMPILE_FEATURES cxx_std_20 )
set( Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS "A:/Programs/Python/Python11_4/include")
set( Python3_LIBRARIES "A:/Programs/Python/Python11_4/libs/python311.lib"
"A:/Programs/Python/Python11_4/libs/python311_d.lib" )
message( STATUS "Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS = ${Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS} " )
message( STATUS "Python3_LIBRARIES = ${Python3_LIBRARIES} " )
list( APPEND PRJ_INCLUDE_DIRS ${Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
list( APPEND PRJ_LIBRARIES ${Python3_LIBRARIES} )
message( STATUS "PRJ_LIBRARIES = ${PRJ_LIBRARIES} " )
add_executable( ${PROJECT_NAME}
main.cpp
)
target_include_directories( ${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
${PRJ_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
target_link_libraries( ${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
${PRJ_LIBRARIES}
)
target_compile_features( ${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
${PRJ_COMPILE_FEATURES}
)
Chap.IV 运行结果
---------- Hello Python form C/C++ ----------
curr sys.path ['A:\\Programs\\Python\\Python11_4\\python311.zip', 'A:\\Programs\\Python\\Python11_4\\DLLs', 'A:\\Programs\\Python\\Python11_4\\Lib', 'A:\\aWork\\scripts\\test1\\test\\build\\Debug', 'A:\\Programs\\Python\\Python11_4', 'A:\\Programs\\Python\\Python11_4\\Lib\\site-packages', '../']
1 + 3 = 4
your name is summer alice
Part.IV 可能出现的问题
Chap.I 无法打开 python311_d.lib
无法打开 python311_d.lib 的问题:笔者使用的 python 版本是 Python 11.4,它的libs中没有python311_d.lib,只有python311.lib(因为安装的时候没有勾选安装 debug 的 lib),解决方法有三个:
- 不使用
debug模式运行程序,使用release或其他模式运行 C++ 程序 - 找到
pyconfig.h文件(一般在py_dir/include文件夹下),注释下面的内容(有点危险)
#ifdef _DEBUG
# define Py_DEBUG
#endif
- 安装 python 的 debug 版本库:安装程序→更改→勾选
Download debug binaries (requires VS 2017 or later)
Chap.II 导入模块报错
这种情况下是没有把 python 脚本所在的路径加到sys.path里面,使用sys.path.append(your_path_xx)添加一下就可以了。
Chap.I PyEval_CallObject 调用报错
报错内容:
'PyEval_CallObjectWithKeywords': deprecated in 3.9
将PyEval_CallObject替换为PyObject_CallObject就行了。
Reference
- Linux 系统下通过 cmake 使 C++ 调用 Python