刘铁猛《C#语言入门详解》快速学习
================2023-08-12 => 2023-08-13第一次overload =>2023-08-14第二次overload ===========
文章目录
- C#的基本元素
- 类型、变量、对象
-
- 类型
- 变量
- 对象
- 方法
- 操作符(数值提升)
- 表达式、语句
- 字段、属性、索引器、常量(存储数据)
-
- 字段/成员变量:
- 属性 **propfull**:
- 索引器 indexer
- 常量 const
- 参数:传值、输出、引用、数组、具名、可选、扩展方法/this参数
-
- 传值参数:
- 引用参数 ref:
- 输出参数 out :
- 数组形参 params:
- 扩展方法 this:
- 委托 delegate
- 事件 Event:
- 类
-
- 继承
- 多态
- 接口、抽象类、SOLID设计原则、单元测试、反射
-
- 抽象类与开闭原则 abstract
- 接口
- 依赖反转 DIP
- 单元测试 Fact
- 接口隔离原则
- 反射与依赖注入 DI
- SOLID设计原则
- 泛型、部分类、枚举、结构体
-
- 泛型
- 枚举
- 结构体
C#的基本元素
关键词keyword、操作符operator、标识符identifier(可读性)、标点符号、文本(字面值)、注释与空白(非标记)
程序=数据(变量)+算法(方法)
// 三种方法,有输入有输出,无输入有输出,有输入无输出
class Super
{
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
public string GetToday()
{
int day = DateTime.UtcNow.Day;
return day.ToString();
}
public void PrintSum(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine(a + b);
}
}
类型、变量、对象
类型
Data Type:数据在内存中存储的型号(C#强类型)
**类型在C#的作用:**内存大小、值表示范围、包含成员、何基类(动态-反射、静态-编译)、内存位置、允许操作
内存位置:外存(硬盘、编译-静态)-内存(内存条、执行-动态):Stack 小(函数调用- stack overflow)+ heap 大(存储对象-内存泄漏/忘记回收) performance monitor perfmon
变量
变量:以变量名所对应的内存地址为起点,以其数据类型所要求的存储空间为长度的一块内存区域
(高位存储、取反-全部取反+1、正数第一位0)
int a = 100;
声明变量 初始化器
short s;
s = -1000;
string str = Convert.ToString(s, 2);
值类型:起点+长度+放入
引用类型:声明:起点+4个字节(存放实例的内存编号)
实例后:长度(存放实例的具体内容)
class Program{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1;
stu1 = new Student();
Student stu2;
stu2 = stu1;
}
}
class Student {
uint ID;
string Name;
}
对象
装箱、拆箱 损失性能
装箱:引用类型引用的地址在栈—将栈放堆(复制栈上内容),将堆地址作为引用的地址
拆箱:把堆内容复制到栈上
int x = 100;
object obj;
obj = x; // 装箱
int y = (int)obj // 拆箱
方法
方法是什么:类/结构体的成员(还有一个字段)
方法和函数的作用:隐藏复杂逻辑、分解算法、重用
构造器/构造函数 construct ctor
析构器 ~
方法重载:方法签名(方法名称,形参个数/类型/种类),不包括返回值
step into 仔细寻找,step over 定位,step out
操作符(数值提升)
操作符的本质:操作符是函数的简计,离不开关联的数据类型
类型转换-隐式(子类-父类,装箱)、显式(丢失精度,拆箱、Convert、ToString、Parse、TryParse)
-
带有赋值的操作符:从右往左
-
default : 引用类型null,值类型0,enum为0/对应的类型
-
var: person = new {}; 匿名创建,显式使用
-
check: 检查是否溢出
-
delegate: 匿名函数 {} =》{} lambda
-
is: 对实例检测,从基类判断 ;as
-
?:可空类型,Nullable x = null 或 int? x = null;
-
??:空值默认
-
?: :条件 if语句的简写
-
int? x = null; int y = x ?? 1; string z = (y == 1) ? "equal 1" : "unequal 1"; Console.WriteLine(y); Console.WriteLine(z); -
成员访问dot:访问的是类成员,而不是类实例的成员
-
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Animal animal = new Human(); animal.Eat(); Human human = new Human(); human.Walk(); } } public class Animal { public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("I can Eat"); } } public class Human : Animal { public void Walk() { Console.WriteLine("I can Walk"); } } public class Teacher : Human { public void Teach() { Console.WriteLine("I can Teach"); } }
表达式、语句
表达式是什么:一连串的操作数、操作符得到的value\object\method\namespace,是算法逻辑最小单元
语句:陈述算法思想,控制逻辑走向,完成有意义的动作,出现在方法体中
-
try catch finally 捕捉错误信息在finally
-
do while 至少一次,while 0次
-
foreach = 继承IEnumerable可以遍历,继承IEnumerator的类有 GetEnumerator,包含MOveNext\Reset\Current 指月
int[] intArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
IEnumerator enumerable = intArray.GetEnumerator(); // 指月
while (enumerable.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerable.Current);
}
Console.WriteLine(enumerable.MoveNext());
enumerable.Reset();
Console.WriteLine(enumerable.MoveNext());
字段、属性、索引器、常量(存储数据)
类体内为字段、属性、索引器、常量
字段/成员变量:
实例字段(对象状态,对象创建时初始化)、静态字段(类型状态,加载数据类型的时候初始化 :静态只读字段 =》静态构造器 static xxx/声明)
属性 propfull:
访问对象类型特征的成员 -属性暴露数据/防止非法值的污染
try
{
student2.Height = 3000;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
private int height;
public int Height
{
set
{
if (value>200)
{
throw new Exception("too height");
}
else
{
this.Height = value;
}
}
}
索引器 indexer
try
{
Students students = new Students();
students["Math"] = 0;
var results = students["Math"];
Console.WriteLine(results);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
class Students
{
private Dictionary scoreDictionary = new Dictionary();
public int? this[string subject]
{
get
{
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
return scoreDictionary[subject];
}
else {
throw new Exception("No score for this name!");
}
}
set
{
if (value.HasValue == false) throw new Exception("Score should not be null");
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value;
}
else
{
scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value.Value);
}
}
}
}
常量 const
隶属于类型,可读性和效率
参数:传值、输出、引用、数组、具名、可选、扩展方法/this参数
GetHashCode
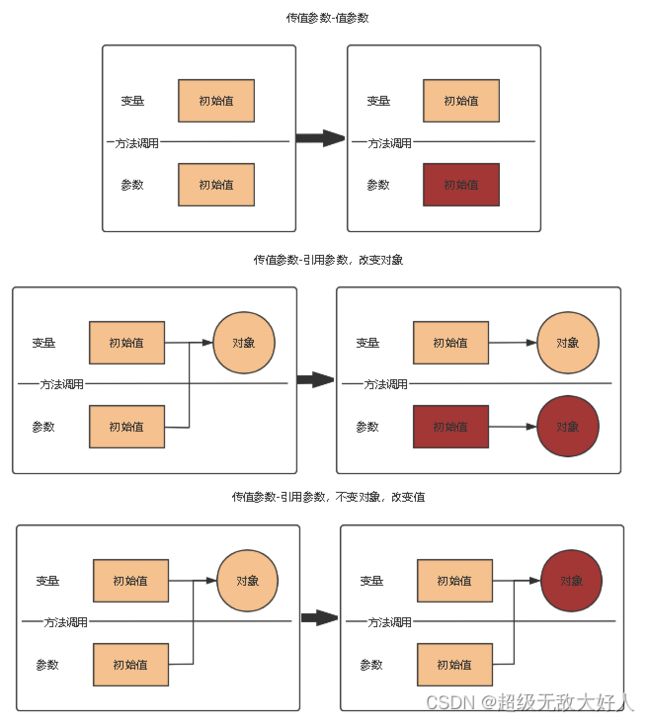
传值参数:
只有传值参数是引用类型,且修改参数实例的值才会影响变量的值;
引用参数 ref:
有意的改变实际参数的值
输出参数 out :
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool CanEnroll = StudentSchool.EnrollNewStudent(24, "nn",out Student student);
if (CanEnroll)
{
Console.WriteLine($"new student's Age:{student.Age},Name:{student.Name}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("cannot enroll!");
}
}
}
class Student {
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class StudentSchool
{
public static bool EnrollNewStudent(int Age, string Name, out Student student)
{
student = null;
if (Age<20||Age>80)
{
return false;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(Name))
{
return false;
}
student = new Student() { Age = Age, Name = Name };
return true;
}
}
数组形参 params:
params在参数列表的最后一个
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int result = CalSum(1,2,3,4,5,6);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static int CalSum(params int[] intArray)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < intArray.Length; i++)
{
sum += intArray[i];
}
return sum;
}
具名参数:可读性,顺序不受限制
扩展方法 this:
共有静态、第一个参数用this修饰{调用类}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 3.14159;
double y = Math.Round(x, 4);
Console.WriteLine(y);
double z = x.Round(2);
Console.WriteLine(z);
}
}
public static class DoubleExtension{
public static double Round(this double x, int y)
{
return Math.Round(x, y);
}
}
委托 delegate
间接调用:通过函数指针来获取地址(class平行)
委托类型参数封装一个外部方法,传入方法内部进行间接调用
一般使用:方法当作参数传给另外一个方法,复用
public delegate int SuperCal(int x, int y);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 自带委托
Cal cal = new Cal();
Action action = new Action(cal.ReportMassage);
action(); //action.invoke();
Func func = new Func(cal.Add);
int result = func(20, 20);
Console.WriteLine(result);
//构造委托
SuperCal superCal = new SuperCal(cal.Add);
int results = superCal(20, 30);
Console.WriteLine(results);
}
}
class Cal {
public void ReportMassage()
{
Console.WriteLine("REPROT");
}
public int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
public int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
}
// 模板方法-ProductFactor
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WrapProduct wrapProduct = new WrapProduct();
ProductFactor productFactor = new ProductFactor();
Box milkBox = wrapProduct.wrapProduct(productFactor.MilkProduct);
Box fruitBox = wrapProduct.wrapProduct(productFactor.FruitProduct);
Console.WriteLine(milkBox.product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(fruitBox.product.Name);
}
}
class Product { public string Name { get; set; } }
class Box {
public Product product { get; set; }
}
class WrapProduct
{
public Box wrapProduct(Func getProduct)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.product = getProduct();
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactor
{
public Product MilkProduct()
{
Product product = new Product() { Name = "Milk" };
return product;
}
public Product FruitProduct()
{
Product product = new Product() { Name = "Fruit" };
return product;
}
}
// 回调方法-logger
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
WrapProduct wrapProduct = new WrapProduct();
ProductFactor productFactor = new ProductFactor();
Logger log = new Logger();
Box milkBox = wrapProduct.wrapProduct(productFactor.MilkProduct,log.Log);
Box fruitBox = wrapProduct.wrapProduct(productFactor.FruitProduct, log.Log);
Console.WriteLine(milkBox.product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(fruitBox.product.Name);
}
}
class Logger
{
public void Log(Product product)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{product.Name} is wraped at {DateTime.UtcNow},price:{product.price}");
}
}
class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public int price { get; set; } }
class Box {
public Product product { get; set; }
}
class WrapProduct
{
public Box wrapProduct(Func getProduct, Action logger)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.product = getProduct();
int price = getProduct().price;
if (price>30)
{
logger(box.product);
}
return box;
}
}
class ProductFactor
{
public Product MilkProduct()
{
Product product = new Product() { Name = "Milk" , price = 55 };
return product;
}
public Product FruitProduct()
{
Product product = new Product() { Name = "Fruit", price = 30 };
return product;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID = 1, penColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
Student student2 = new Student() { ID = 2, penColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow };
Student student3 = new Student() { ID = 3, penColor = ConsoleColor.White };
// 隐式异步委托
Task task1 = new Task(new Action(student1.DoHomeWork));
Task task2 = new Task(new Action(student2.DoHomeWork));
Task task3 = new Task(new Action(student3.DoHomeWork));
task1.Start();
task2.Start();
task3.Start();
//Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomeWork);
//Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomeWork);
//Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomeWork);
// 多播委托
//action1 += action2;
//action1 += action3;
//action1.Invoke();
// 显式异步委托,主线程结束,其他线程直接结束
//action1.BeginInvoke(null,null);
//action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);
//action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Blue;
Console.WriteLine($"Main thread {i}");
Thread.Sleep(400);
}
}
}
class Student {
public int ID;
public ConsoleColor penColor { get; set; }
public void DoHomeWork()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = this.penColor;
Console.WriteLine($"student{ID} is doing homework {i} hours");
Thread.Sleep(300);
}
}
}
事件 Event:
定义:能够发生的什么事情,使对象或类具备通知能力的成员
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// timer 事件拥有者
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.Interval = 500;
// boy 事件订阅者
Boy boy = new Boy();
// 事件成员 订阅 事件处理器
timer.Elapsed += boy.JumpAction;
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
internal void JumpAction(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Jump!");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 事件的订阅者
Form form = new Form();
// 事件的拥有者
FormController formController = new FormController(form);
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class FormController {
private Form _form;
public FormController(Form form)
{
if(form != null)
{
this._form = form;
// 事件成员 订阅 事件处理器
this._form.Click += _form_Click;
}
}
private void _form_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this._form.Text = "SHOW~!";
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 事件的订阅者与接收者
MyForm form = new MyForm();
// form.Click += form.Action; form在mc中对click事件已有默认的订阅,无法添加,通过继承实现
form.Click += form.ClickAction;
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form
{
internal void ClickAction(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = "MYFORM";
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 事件的订阅者与接收者
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
// 事件的订阅者
class MyForm : Form
{
// 事件的拥有者:事件订阅者的字段成员
private Button _button = new Button();
private TextBox _textBox = new TextBox();
public MyForm()
{
// _button.Click += (object sender, EventArgs e)=> { _textBox.Text = "haha!!!!!!!!!!!!!"; };
// _button.Click += new EventHandler(_button_Click);
_button.Click += _button_Click;
this.Controls.Add(_textBox);
this.Controls.Add(_button);
_button.Top = 100;
}
private void _button_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
_textBox.Text = "haha!!!!!!!!!!!!!";
}
}
从事件拥有者-事件订阅者-事件成员(委托方法创建+参数传递)-事件处理器-订阅-事件拥有者拥有事件
事件的触发者只能是自己,因此OnOrder(this,…); 触发之前先判断是否为空
// 自定义 EventHandler
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.ReadLine();
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
// 5.subscribe 4.eventhandler
customer.orderEventHandler += waiter.Action;
customer.Action();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public string size;
public string dishName;
}
// 委托类型 event's scoures
public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
// 1.event's scoures
public class Customer
{
public float bill;
public string size;
public string dishName;
// 3.event member
public event OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler;
public void WalkIn()
{
Console.WriteLine("WalkIn...");
}
public void SetDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("SetDown...");
}
public void Thick()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let's me thick...");
Thread.Sleep(300);
}
OnOrder("KFC", "Big");
}
protected void OnOrder(string dishName, string size)
{
// 防止事件列表为空
if (this.orderEventHandler != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.dishName = dishName;
e.size = size;
// event's link
this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action(){
WalkIn();
SetDown();
Thick();
Console.WriteLine($"I will pay {bill}");
}
}
// 2.event's subscribe
class Waiter
{
private float money = 10;
internal void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e)
{
string order_size = e.size;
switch (order_size)
{
case "Small":
money *= 0.5f;
break;
case "Big":
money *= 1.5f;
break;
default:
break;
}
Console.WriteLine($"I will serve {e.dishName}, price is {money}");
customer.bill = money;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.ReadLine();
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
// 5.subscribe 4.eventhandler
customer.orderEventHandler += waiter.Action;
customer.Action();
}
}
public class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public string size;
public string dishName;
}
// event's scoures
//public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);
// 1.event's scoures
public class Customer
{
public float bill;
public string size;
public string dishName;
// 3.event member
public event EventHandler orderEventHandler;
public void WalkIn()
{
Console.WriteLine("WalkIn...");
}
public void SetDown()
{
Console.WriteLine("SetDown...");
}
public void Thick()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Let's me thick...");
Thread.Sleep(300);
}
OnOrder("KFC", "Big");
}
protected void OnOrder(string dishName, string size)
{
// 防止事件列表为空
if (this.orderEventHandler != null)
{
OrderEventArgs e = new OrderEventArgs();
e.dishName = dishName;
e.size = size;
// event's link
this.orderEventHandler.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
public void Action(){
WalkIn();
SetDown();
Thick();
Console.WriteLine($"I will pay {bill}");
}
}
// 2.event's subscribe
class Waiter
{
private float money = 10;
internal void Action(Object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Customer customer = sender as Customer;
OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = e as OrderEventArgs;
string order_size = orderEventArgs.size;
switch (order_size)
{
case "Small":
money *= 0.5f;
break;
case "Big":
money *= 1.5f;
break;
default:
break;
}
Console.WriteLine($"I will serve {orderEventArgs.dishName}, price is {money}");
customer.bill = money;
}
}
}
类
**定义:**数据结构、数据类型、代表现实世界中的种类(类和对象:现实,类和实例:程序)
- 类库引用:使用namespace的物理基础(DLL黑盒-强依赖、项目白盒)
- namespace 以树形结构组织类
- 依赖关系:类或对象的耦合关系:高内聚,低耦合。
- UML通用建模语言
引用变量与实例:孩子和气球,气球不一定要孩子牵着,多个孩子用同一个绳子/不同绳子牵同一个气球
Form form = new Form () {text = "hello"};
创建引用变量 赋值 实例对象 构造器 初始化器
Form myForm1;
Form myForm2;
myForm1 = new Form();
myForm2 = myForm1;
myForm2.Text = "haha";
myForm1.ShowDialog();
类的三大成员:属性(存储数据,表示状态)、方法(构成逻辑)、事件(通知)
模型类 Entity Framework 工具类 math console 通知类 timer
静态成员与实例成员:类的成员,对象的成员
继承
定义:全盘继承(父类成员)+横向扩展(类成员数量增加)+纵向扩展(类成员的功能/版本扩展)
- 构造器、sealed类不被继承
- 类成员访问级别最高为类的访问级别,子类级别不能超过基类级别
- 实现借口,继承基类
- 纵向扩展:virtual - override,重写后方法遵循最新版本
- private 类内/可继承但不可访问 ---- internal 同个程序集 ---- protected 继承类间
是一个is a :派生类的实例在语义上也是基类的实例
- A:B ==》 A is B / B b = new A();
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Animal animal = new Human();
animal.Eat(); // I can Walk
}
}
public class Animal
{
public virtual void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("I can Eat");
}
}
public class Human : Animal
{
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("I can Walk");
}
}
多态
父类类型调用子类实例的方法时,具体行为由对象决定:重写后方法遵循继承链最新版本
- virtual - override
接口、抽象类、SOLID设计原则、单元测试、反射
抽象类与开闭原则 abstract
定义:函数成员没有被完全实现的类
什么时候用:函数作为基类方法,但是自身永远不执行,下推给子类去实现/override
- 专门作为基类,
- 多态:以基类作为引用类型以完成功能的子类创建实例
- 发展顺序:继承—重写override—抽象abstract
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 以基类作为引用类型以完成功能的子类创建实例
Vehicle v = new Car();
v.Run();
v.Stop();
}
}
abstract class Vehicle
{
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("Stop!");
}
public abstract void Run();
}
class Car : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running...");
}
}
class Tank : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tank is running...");
}
}
接口
特点:所有的方法都是抽象
作用:约束供需双方,降低耦合(因为遵守接口)
- 将接口作为引用参数,实现了遵守接口(实现)的类的功能
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int[] ints = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5,6 };
Console.WriteLine(Sum(arrayList));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(ints));
}
// arraylist 和 [] 共同遵守IEnumerable的接口
static int Sum(IEnumerable enumerable)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var enu in enumerable)
{
sum += (int)enu;
}
return sum;
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NokiaPhone nokiaPhone = new NokiaPhone();
MotoPhone motoPhone = new MotoPhone();
PhoneUser phoneUser = new PhoneUser(motoPhone);
phoneUser.UsePhone();
}
}
class PhoneUser
{
private IPhone _phone { get; set; }
public PhoneUser(IPhone phone)
{
this._phone = phone;
}
public void UsePhone()
{
_phone.Call();
_phone.Diag();
}
}
interface IPhone
{
void Diag();
void Call();
}
class NokiaPhone : IPhone
{
public void Call()
{
Console.WriteLine($"NokiaPhone is calling...");
}
public void Diag()
{
Console.WriteLine($"NokiaPhone is diaging...");
}
}
class MotoPhone : IPhone
{
public void Call()
{
Console.WriteLine($"MotoPhone is calling...");
}
public void Diag()
{
Console.WriteLine($"MotoPhone is diaging...");
}
}
什么时候用:所有的方法都不自己实现,交给子类实现.子类未实现的方法标记abstract public,实现用override
发展顺序:抽象类—接口
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle v = new Car();
v.Run();
v.Stop();
IVehicle ivehicle = new Tank();
ivehicle.Run();
ivehicle.Stop();
}
}
interface IVehicle
{
void Stop();
void Run();
}
abstract class Vehicle:IVehicle
{
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("Stop!");
}
public abstract void Run();
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running...");
}
}
class Tank : Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tank is running...");
}
}
依赖反转 DIP
单元测试 Fact
。。。
接口隔离原则
接口隔离:将多个功能的接口拆分成多个小接口
- 保障接口调用者不会多调
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Driver driver = new Driver(new LightTank());
driver.Run();
}
}
class Driver
{
private IVehicle vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle)
{
this.vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Run()
{
this.vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle
{
void Run();
}
class Car : IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Car is running...");
}
}
class Truck : IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Truck is running...");
}
}
interface IWeapon
{
void Fire();
}
interface ITank:IVehicle
{
}
class LightTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine($"LightTank is fire...");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine($"ka ka ka ...");
}
}
class MediumTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine($"MediumTank is fire...");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine($"ka! ka! ka! ...");
}
}
- 将接口多余的功能隐藏
。。。。
-
接口的显示实现
-
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var wk = new WarmKiller(); wk.Love(); IKiller killer = (IKiller)wk; killer.Kill(); } } interface IGentlemen { void Love(); } interface IKiller { void Kill(); } class WarmKiller : IKiller, IGentlemen { public void Love() { Console.WriteLine("I will love"); } // Implicty void IKiller.Kill() { Console.WriteLine("i will kill enemy..."); } }
反射与依赖注入 DI
反射:以不变应万变(不用new创建对象,访问成员)
- 主题程序与插件。。。。SDK,API
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 静态
ITank mediumTank = new MediumTank();
// 动态
var t = mediumTank.GetType();
object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);
MethodInfo fireMi = t.GetMethod("Fire");
MethodInfo runMi = t.GetMethod("Run");
fireMi.Invoke(o, null);
runMi.Invoke(o, null);
// 依赖注入
}
}
interface ITank : IVehicle
{
}
class MediumTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine($"MediumTank is fire...");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine($"ka! ka! ka! ...");
}
}
SOLID设计原则
Single Responsibility Principle(SRP):单一职责原则
一个类或者一个模块只做一件事。让一个类或者一个模块专注于单一的功能,减少功能之间的耦合程度。这样做在需要修改某个功能时,就不会影响到其他的功能。
Open Closed Principle(OCP):开闭原则
对扩展开放,对修改关闭。一个类独立之后就不应该去修改它,而是以扩展的方式适应新需求。{除非修bug或添功能}
Liskov Substitution Principle(LSP):里氏替换原则
所有基类出现的地方都可以用派生类替换而不会让程序产生错误,派生类可以扩展基类的功能,但不能改变基类原有的功能。
Interface Segregation Principle(ISP):接口隔离原则
一个接口应该拥有尽可能少的行为,使其精简单一。对于不同的功能的模块分别使用不同接口,而不是使用同一个通用的接口。
Dependence Inversion Principle(DIP):依赖倒置原则
高级模块不应该依赖低级模块,而是依赖抽象接口,通过抽象接口使用对应的低级模块。
泛型、部分类、枚举、结构体
泛型
泛型类:
一个商品一个盒子,店的扩展:
- 商品和盒子倍增(类型膨胀)/ 一个盒子有不同的属性(成员膨胀)/用object属性进行代替(as 访问困难)
- 利用泛型刻画盒子(类型参数,强类型)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 构造器ctor 初始化器:赋值prop
//AppleBox box = new AppleBox(apple) { };
Apple apple = new Apple() { Size = "Big" };
Book book = new Book() { Name = "book" };
Box box = new Box() {Cargon = apple };
Box box1 = new Box() {Cargon = book };
Console.WriteLine(box.Cargon.Size);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Cargon.Name);
}
}
class Apple
{
public string Size;
}
class Book
{
public string Name;
}
class Box
{
public TCargon Cargon;
}
泛型接口
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student() { id = 1 , Name = "N1"};
Student1 student1 = new Student1() { id = 2, Name = "N2" };
}
}
interface IUnique
{
// 属性进行抽象
TId id { get; set; }
}
// 第一种泛型接口
class Student : IUnique
{
public TId id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
// 第二种泛型接口
class Student1 : IUnique
{
public ulong id { get ; set ; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
泛型方法
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] a1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int[] a2 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6 };
double[] a3 = { 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 };
double[] a4 = { 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,1.5 };
var result = Zip(a1, a2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",",result));
var result1 = Zip(a3, a4);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", result1));
}
static T[] Zip(T[] a, T[] b)
{
T[] zipped = new T[a.Length + b.Length];
int ai = 0;
int bi = 0;
int zi = 0;
do
{
if (ai 泛型委托
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// action 没有返回值, func 有返回值
Action action = Say;
action("Xue");
Action action1 = Mul;
action1(25);
}
static void Say(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hello, {str}");
}
static void Mul(int x)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Result:{x*100}");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Func func = Mul;
//Func func = (float x) => { return (int)x * 100; };
var Result = func(23.4f);
Console.WriteLine(Result);
}
static int Mul(int x)
{
return x * 100;
}
static int Mul(float x)
{
return (int)x * 100;
}
枚举
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
person.level = Level.BogBoss | Level.Boss | Level.Employee | Level.Manager;
Console.WriteLine((person.level & Level.Manager) == Level.Manager) ;
}
}
enum Level
{
Employee = 1,
Manager = 2,
Boss = 4,
BogBoss = 8,
}
class Person
{
public Level level { get; set; }
}
结构体
关联的内存地址是不同的
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student1 = new Student() { ID = 1, Name = "xue" };
Student student2 = student1;
student1.ID = 2;
Console.WriteLine(student2.ID);
}
}
struct Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}