SPFA算法
目录
spfa求最短路
spfa判断负环
spfa求最短路
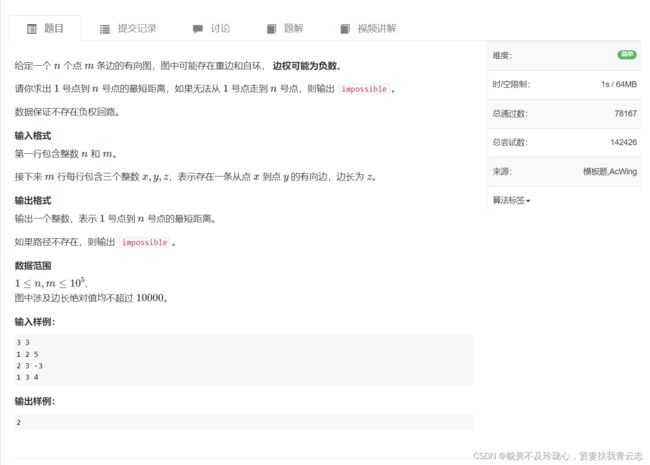
题目如下:
st数组的作用:判断当前的点是否已经加入到队列当中了;已经加入队列的结点就不需要反复的把该点加入到队列中了,就算此次还是会更新到源点的距离,那只用更新一下数值而不用加入到队列当中。即便不使用st数组最终也没有什么关系,但是使用的好处在于可以提升效率。
由于SPFA算法是由Bellman_ford算法优化而来,在最坏的情况下时间复杂度和它一样即时间复杂度为 O(nm)假如题目时间允许可以直接用SPFA算法去解Dijkstra算法的题目。
求负环一般使用SPFA算法,方法是用一个cnt数组记录每个点到源点的边数,一个点被更新一次就+1,一旦有点的边数达到了n那就证明存在了负环。
解题代码
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10;
#define fi first
#define se second
typedef pair PII;//到源点的距离,下标号
int h[N],e[N],w[N],ne[N],idx=0;
int dist[N];//各点到源点的距离
bool st[N];
int n,m;
void add(int a,int b,int c){
e[idx]=b;w[idx]=c;ne[idx]=h[a];h[a]=idx++;
}
int spfa(){
queue q;
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[1]=0;
q.push({0,1});
st[1]=true;
while(q.size()){
PII p=q.front();
q.pop();
int t=p.se;
st[t]=false;//从队列中取出来之后该节点st被标记为false,代表之后该节点如果发生更新可再次入队
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[t]+w[i]){
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
if(!st[j]){//当前已经加入队列的结点,无需再次加入队列,即便发生了更新也只用更新数值即可,重复添加降低效率
st[j]=true;
q.push({dist[j],j});
}
}
}
}
if(dist[n]==0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
else return dist[n];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
while(m--){
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
add(a,b,c);
}
int res=spfa();
if(res==-1) puts("impossible");
else printf("%d",res);
return 0;
} 算法板子:
int n; // 总点数
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx; // 邻接表存储所有边
int dist[N]; // 存储每个点到1号点的最短距离
bool st[N]; // 存储每个点是否在队列中
// 求1号点到n号点的最短路距离,如果从1号点无法走到n号点则返回-1
int spfa()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
queue q;
q.push(1);
st[1] = true;
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if (!st[j]) // 如果队列中已存在j,则不需要将j重复插入
{
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
} spfa判断负环
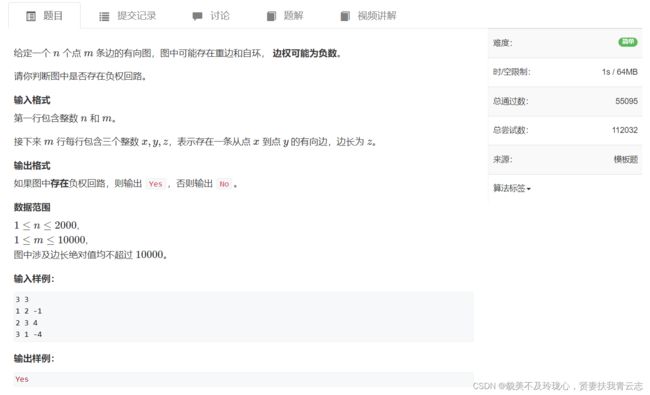
题目如下:
每次做一遍spfa()一定是正确的,但时间复杂度较高,可能会超时。初始时将所有点插入队列中可以按如下方式理解:
在原图的基础上新建一个虚拟源点,从该点向其他所有点连一条权值为0的有向边。那么原图有负环等价于新图有负环。此时在新图上做spfa,将虚拟源点加入队列中。然后进行spfa的第一次迭代,这时会将所有点的距离更新并将所有点插入队列中。执行到这一步,就等价于视频中的做法了。那么视频中的做法可以找到负环,等价于这次spfa可以找到负环,等价于新图有负环,等价于原图有负环。得证。
- dist[x] 记录虚拟源点到x的最短距离
- cnt[x] 记录当前x点到虚拟源点最短路的边数,初始每个点到虚拟源点的距离为0,只要他能再走n步,即cnt[x] >= n,则表示该图中一定存在负环,由于从虚拟源点到x至少经过n条边时,则说明图中至少有n + 1个点,表示一定有点是重复使用
- 若dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i],则表示从t点走到j点能够让权值变少,因此进行对该点j进行更新,并且对应cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1,往前走一步
注意:该题是判断是否存在负环,并非判断是否存在从1开始的负环,因此需要将所有的点都加入队列中,更新周围的点
解题代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010, M = 10010;
int n, m;
int h[N], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], cnt[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
bool spfa()
{
queue q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
st[i] = true;
q.push(i);
}
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if (cnt[j] >= n) return true;
if (!st[j])
{
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
if (spfa()) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
return 0;
} 算法板子
int n; // 总点数
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx; // 邻接表存储所有边
int dist[N], cnt[N]; // dist[x]存储1号点到x的最短距离,cnt[x]存储1到x的最短路中经过的点数
bool st[N]; // 存储每个点是否在队列中
// 如果存在负环,则返回true,否则返回false。
bool spfa()
{
// 不需要初始化dist数组
// 原理:如果某条最短路径上有n个点(除了自己),那么加上自己之后一共有n+1个点,由抽屉原理一定有两个点相同,所以存在环。
queue q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
q.push(i);
st[i] = true;
}
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if (cnt[j] >= n) return true; // 如果从1号点到x的最短路中包含至少n个点(不包括自己),则说明存在环
if (!st[j])
{
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}