File与Io流
IO(Input/Output)是指计算机与外部世界进行数据交换的过程。在程序中,IO通常用于读取输入数据或将输出数据写入到外部设备或文件中。
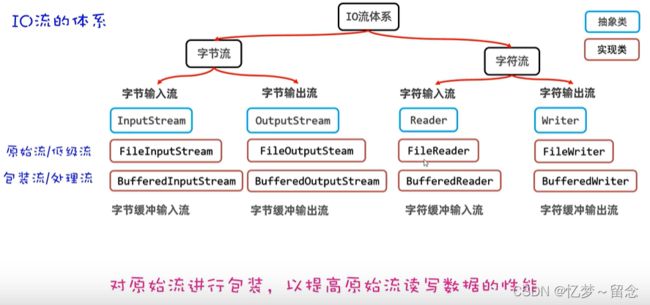
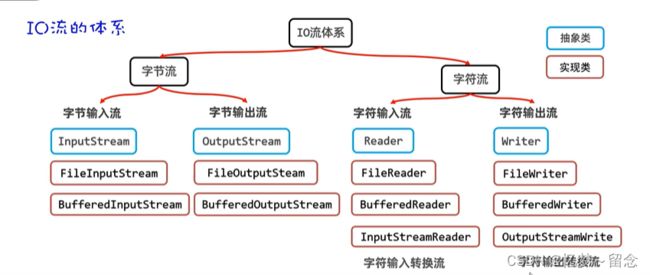
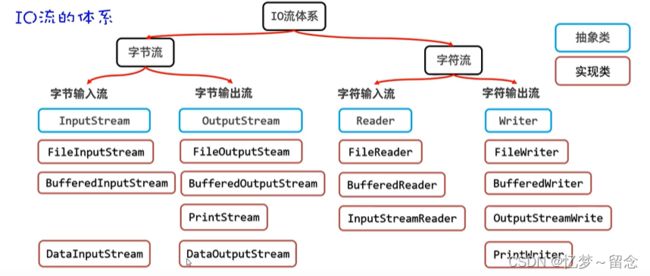
Java的IO库主要分为两种类型:字节流和字符流。
-
字节流(Byte Stream):
- InputStream和OutputStream:用于处理字节数据的输入和输出。InputStream用于从字节源(如文件、网络连接等)读取数据,而OutputStream用于将字节数据写入到目标位置。
- FileInputStream和FileOutputStream:用于读取和写入字节文件的输入和输出流。
- BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream:用于提供缓冲功能,提高IO性能。
-
字符流(Character Stream):
- Reader和Writer:用于处理字符数据的输入和输出。Reader用于从字符源(如文件、网络连接等)读取数据,而Writer用于将字符数据写入到目标位置。
- FileReader和FileWriter:用于读取和写入字符文件的输入和输出流。
- BufferedReader和BufferedWriter:用于提供缓冲功能,提高IO性能。
除了字节流和字符流之外,Java还提供了一些其他类型的流,用于处理特定的IO需求:
- ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream:用于读取和写入Java对象。
- ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream:用于读取和写入字节数组。
- InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter:用于处理字节流和字符流之间的转换。
- DataInputStream和DataOutputStream:用于读取和写入基本数据类型。
File
File是java.io.包下的类,File类的对象,用于代表当前操作系统的文件(可以是文件、或文件夹)。
File类只能对文件本身进行操作,不能读写文件里面存储的数据。
是文件和目录路径名的抽象表示
常用方法
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
//1.检查D盘下是否存在文件a.txt,如果不存在则创建该文件
public class Panduan {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1、创建一个File对象,指代某个具体的文件。(或者文件夹)
// File对象可以指代一个不存在的文件路径
// 绝对路径
File file = new File("D:\\a.txt");
// File file = new File("D:/a.txt"); // 另一种写法
// File file = new File("D:"+File.separator+"a.txt"); // 另一种写法
//相对路径〈重点》﹔不带盘符,默认是直接去工程下寻找文件的。
// 获取绝对路径
File abs = file.getAbsoluteFile();
System.out.println("寻找文件:"+abs);
// 判断是否存在
boolean exists = file.exists();
boolean newFile = file.createNewFile();// 判断该文件是否存在不存在就会创建存在就不管
if (newFile==true){
System.out.println("该文件原本不存在现在已创建!");
long length = file.length();// 文件的大小 字节数
boolean file1 = file.isFile();// 判断当前文件对象指代的是否是文件。是文件返回true,反之false。
boolean directory = file.isDirectory();// 判断当前文件对象指代的是否是文件夹,是文件夹返true,反之false。
String name = file.getName(); // 获取文件后缀
long l = file.lastModified(); // 获取文件最后修改时间
String path = file.getPath();// 获取文件创建路径
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
String time = simpleDateFormat.format(path);
}else{
System.out.println("该文件已存在!");
}
}
}
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class MyFileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1、public boolean mkdir():用于创建文件夹,注意。只能创建一级文件必
File file1 = new File("D:/resource");
boolean mkdir = file1.mkdir();
// 2、public boolean createNewFile()。创建一个新文件(文件内容为空》,创建成功返回true,反之false.
File file = new File("D:/resource/1.txt");
boolean newFile = file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("newFile = " + newFile);
//3、public boolean mkdirs()。用于创建文件夹,注意。可以创建多级文件夹
File file2 = new File("D:/resource/aa/bb");
boolean mkdirs = file2.mkdirs();
//4、public boolean delete():剧除文件,或者空文件,注意。不能删除非空文件夹。
boolean delete = file2.delete();
}
}
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class MyFileCreate2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、public String[] list():获取当前目录下所有的"一级文件名称""到一个字符串数组中去返回。
File file = new File("D:/resource");
String[] list = file.list();
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println("s = " + s);
}
// 2、public File[] listFiles():获取当前目录下所有的"一级文件对象到一个文件对象数组中去返回
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File file1 : files) {
System.out.println("file1 = " + file1);
}
}
}
方法递归
递归思想
什么是方法递归?
递归是一种算法,在程序设计语言中广泛应用。
从形式上说:方法调用自身的形式称为方法递归( recursion)。
递归的形式
直接递归:方法自己调用自己。
间接递归:方法调用其他方法,其他方法又回调方法自己。
package com.text01;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class RecursionTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test01();
}
public static void test01(){
test01();//直接方法递归
}
//间接方法递归
public static void test02(){
test03();
}
public static void test03(){
test02();
}
}
案例
计算n的阶乘
package com.text01;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class RecursionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("5的阶乘为:"+f(5));
}
public static int f(int n){
//终结点
if(n==1){
return 1;
}else {
return f(n-1)*n;
}
}
}
文件搜索
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class RecursionTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
searchFile(new File("D:/"),"QQ.exe");
}
public static void searchFile(File dir,String fileName) throws IOException {
// 1.把非法情况进行拦截
if (dir == null || !dir.exists() || dir.isFile()){
return;//无法搜索
}
// 2.获取当前目录下的一级文件夹
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
// 3.判断当前目录是否存在一级文件夹对象,以及是否可以拿到一级文件对象
if (files != null && files.length > 0){
// 遍历全部一级目录
for (File file : files) {
// 判断是文件还是文件夹
if (file.isFile()){
//是文件 判断是不是要找的
if (file.getName().contains(fileName)){
System.out.println("找到了:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
//启动
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}else {
//是文件夹 递归查询
searchFile(file,fileName);
}
}
}
}
}
字符集
Unicode是一种字符集,用于表示世界上所有的文字和符号。它定义了每个字符的唯一编号,称为码点(code point),通常用“U+”加上十六进制数表示。(万国码)
utf-8 是Unicode字符集的一种编码方案,采取可变长编码方案,共分四个长度区:1个字节,2个字节,3个字节,4个字节
英文字符、数字等只占1个字节(兼容标准ASCII编码),汉字字符占用3个字节。
ASCII字符集:只有英文、数字、符号等,占1个字节。
GBK字符集:汉字占2个字节,英文、数字占1个字节。
UTF-8字符集:汉字占3个字节,英文、数字占1个字节。
字符编码时使用的字符集,和解码时使用的字符集必须一致,否则会出现乱码
英文,数字一般不会乱码,因为很多字符集都兼容了ASCII编码。
编码解码

package com.text01;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class RecursionTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.编码
String data = "a我b";
byte[] bytes = data.getBytes();// bytes = [97, -26, -120, -111, 98]
byte[] bytes1 = data.getBytes("GBK");// bytes1 = [97, -50, -46, 98]
System.out.println("bytes = " + Arrays.toString(bytes1) );
//解码
String string = new String(bytes);// string = a我b
String string1 = new String(bytes1,"GBK");// string1 = a我b
System.out.println("string1 = " + string1);
}
}
IO
分类
字节输入流:以内存为基准,来自磁盘文件/网络中的数据以字节的形式读入到内存中去的流
字节输出流:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字节写出到磁盘文件或者网络中去的流。
字符输入流:以内存为基准,来自磁盘文件/网络中的数据以字符的形式读入到内存中去的流。
字符输出流:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字符写出到磁盘文件或者网络介质中去的流。
体系
字节流
FileInPutStream(文件字节输入流)
以内存为基准,可以把磁盘文件中的数据以字节的形式读入到内存中去。
使用FileInputStream每次读取一个字节,读取性能较差,并且读取汉字输出会乱码。
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class FileInPutStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.创建文件输入流管道,与文件联通 相对路径
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt"));
// FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt");
// 2.开始读取文件数据
// public int read() 每次读取一个字节返回 没有返回-1
// int read = inputStream.read();
// 3.循环读取数据
int b;
while ((b = inputStream.read()) !=-1){
System.out.print((char) b);
}// 读取性能差
// 读取汉字不可避免会乱码
//流使用后要关闭
inputStream.close();
}
}
使用FileInputStream每次读取多个字节,读取性能得到了提升,但读取汉字输出还是会乱码。
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class FileInPutStreamTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.创建文件输入流管道,与文件联通 相对路径
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt"));
// 2.设置读取数据单次的字节数
byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
// int len = inputStream.read(buffer);
//
// String res =new String(buffer,0,len);
// System.out.println("res = " + res);
// 3.循环读取数据
int len;// 记住每次读取多少字节
while ((len = inputStream.read(buffer)) !=-1){
// 读多少倒多少
System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
// 性能提升
// 不能避免读取汉字乱码
//流使用后要关闭
inputStream.close();
}
}
文件字节输入流:一次读取全部字节
package com.text01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.logging.Filter;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class FileInPutStreamTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.创建文件输入流管道,与文件联通 相对路径
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt");
// 一次读取全部方案1
File file = new File("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt");
long length = file.length();
byte[] buffer = new byte[(int)length];
int len = inputStream.read(buffer);
String res =new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println("res = " + res);
//流使用后要关闭
inputStream.close();
}
}
在Java 9中,InputStream和Reader都添加了一个新的readAllBytes()方法,可以一次性读取所有字节或字符数据。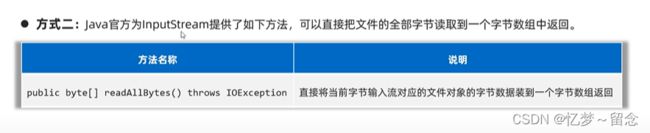
FileOutPutStream(文件字节输出流)
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class FileOutPutStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通。 会覆盖之前的数据 没有文件会自己创建
// FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\2.txt");
//接着写不会覆盖之前的数据
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\2.txt",true);
// 换行 \r\n 通用换行符
outputStream.write("\r\n".getBytes());
// 2.写数据
// 写一个字节
outputStream.write(97); // a
// 写一个字符
outputStream.write('b'); // b
//写一个字符串
byte[] bytes="新年快乐!".getBytes();
outputStream.write(bytes);
//写入字符串的一部分 由于我用的是utf-8 一个汉字3个字节所有下面输入的为新年
outputStream.write(bytes,0,6);
//关闭流
outputStream.close();
}
}
文件复制
原理
操作
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 创建一个字节输入流管道与目标文件接通
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/resource/tupian.png");
// 创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通 文件名称必须写可以不一样
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/resource/aa/tupian.png");
// 创建一个字节数组 负责转移字节数据
byte[] bytes= new byte[1024];// 1kB
//从字节输入流中读取字节数据。写出去到字节输出流中。读多少写出去多少。
int len ;
while ((len= inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
outputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}
字节流非常适合做一切文件的复制操作
任何文件的底层都是字节,字节流做复制,是一字不漏的转移完全部字节,只要复制后的文件格式一致就没问题!
正确的释放资源
try-catch-finally
作用:一般用于在程序执行完成后进行资源的释放操作(专业级做法)。
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
// 创建一个字节输入流管道与目标文件接通
inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/resource/tupian.png");
// 创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通 文件名称必须写可以不一样
outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/resource/aa/tupian.png");
// 创建一个字节数组 负责转移字节数据
byte[] bytes= new byte[1024];// 1kB
//从字节输入流中读取字节数据。写出去到字节输出流中。读多少写出去多少。
int len ;
while ((len= inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
outputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
try {
if (outputStream != null)
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (inputStream != null)
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
try-with-resource
try()括号中只能放资源
什么是资源呢?
资源都是会实现AutoCloseable接口 资源都会有一个close方法,并且资源放到这里后 用完后会自动调用close方法进行关闭
字符流
字节流:适合复制文件等,不适合读写文本文件
字符流:适合读写文本文件内容
FileReader
作用:以内存为基准,可以把文件中的数据以字符的形式读入到内存中去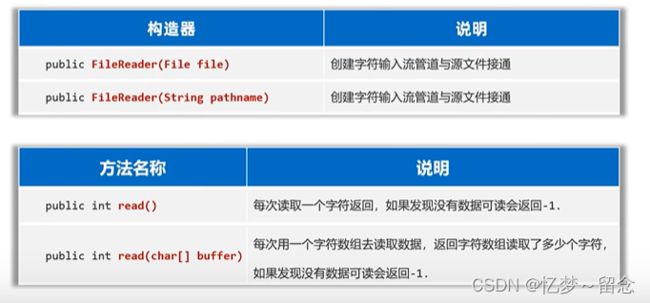
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileReader;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.创建一个文件输入流管道与目标文件接通
try (
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt");
){
// // 2.读取文本文件类容
// int c;// 记住每次读取字符编号
// while ((c=fileReader.read())!=-1){
//
// System.out.print((char) c);
// }
// 每次读取多个字符
char[] buffer=new char[3];
int len;// 记住每次读取字符个数
while ((len=fileReader.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
FileWriter
作用:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字符的形式写出到文件中去。
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class FileWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// // 0、创建一个文件字符输出流管道与目标文件接通。
// FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("day_22_i0\\src\\2.txt");
// 0、创建一个文件字符输出流管道与目标文件接通。 数据追加
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("day_22_i0\\src\\2.txt",true);
){
// 1、public void write(int c):写一个字符出去
fileWriter.write('q');
fileWriter.write(97);
fileWriter.write('好');
// 2.public void write(String c)写一个字符串出去
fileWriter.write("新年好");
// 3、public void write(String c ,int pos ,int len):写字符串的一部分出去
fileWriter.write("小女孩",0,1);
//4、public void write(char[ ] buffer):写一个字符数组出去
char[] buffer={'小','男','孩'};
fileWriter.write(buffer);
// 换行
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
//5、public void write(char[ ] buffer ,int pos ,int len):写字符数组的一部分出去
fileWriter.write(buffer,0,1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符输出流写出数据后,必须刷新流,或者关闭流,写出去的数据才能生效
flush()
关闭流包含刷新操作关闭后流不能继续用,刷新可以
缓冲流
体系
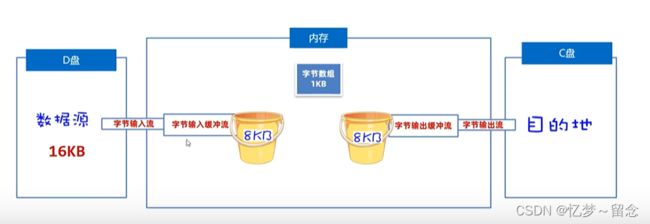
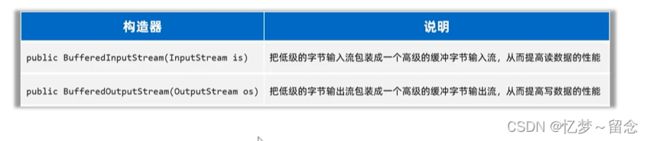
BufferedInputStream(字节缓冲输入流)BufferedOutputStream(字节缓冲输出流)
原理
字节缓冲输入流自带了8KB缓冲池;字节缓冲输出流也自带了8KB缓冲池。
package com.text01;
import jdk.nashorn.internal.ir.CallNode;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class BufferInPutStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try ( // 创建一个字节输入流管道与目标文件接通
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/resource/1.txt");
// 1、定义一个字节缓冲输入流包装原始的字节输入流
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream= new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
// 创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通 文件名称必须写可以不一样
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/resource/aa/2.txt");
// 2、定文一个字节锾冲输出流包装原始的字节输出流
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream=new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
){
// 创建一个字节数组 负责转移字节数据
byte[] bytes= new byte[1024];// 1kB
//从字节输入流中读取字节数据。写出去到字节输出流中。读多少写出去多少。
int len ;
while ((len= bufferedInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
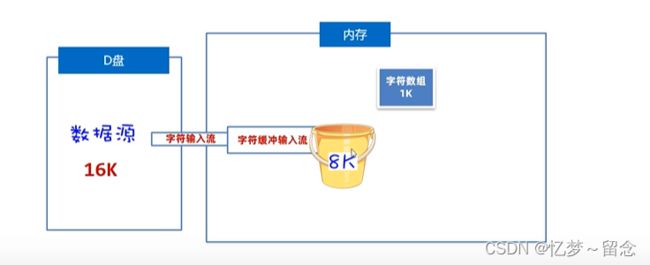
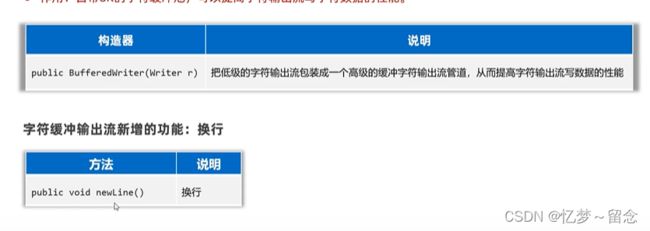
BufferedReader(字符缓冲输入流)
作用:自带8K(8192)的字符缓冲池,可以提高字符输入流读取字符数据的性能。
package com.text01;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class BufferReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.创建一个文件输入流管道与目标文件接通
try (
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("day_22_i0\\src\\1.txt");
//创建一个字符缓冲输入流包装原始的字符输入流
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(fileReader);
){
// 2.读取文本文件类容
// char[] buffer=new char[3];
// int len;// 记住每次读取字符个数
//
// while ((len=bufferedReader.read(buffer))!=-1){
// System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
// }
String line;// 每次读取类容
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.print(line);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BufferedWriter(字符缓冲输出流)
package com.text01;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class BufferedWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 0、创建一个文件字符输出流管道与目标文件接通。 数据追加
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("day_22_i0\\src\\2.txt",true);
//创建一个字符缓冲输出流管道包装原始的字符输出流
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter=new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
){
bufferedWriter.write("新年好");
//换行
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.write("小女孩");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
转换流
不同编码读出现乱码的问题
解决方法
如果代码编码和被读取的文本文件的编码是一致的,使用字符流读取文本文件时不会出现乱码!
如果代码编码和被读取的文本文件的编码是不一致的,使用字符流读取文本文件时就会出现乱码!
lnputStreamReader(字符输入转换流)
解决不同编码时,字符流读取文本内容乱码的问题。
解决思路︰先获取文件的原始字节流,再将其按真实的字符集编码转成字符输入流,这样字符输入流中的字符就不乱码了。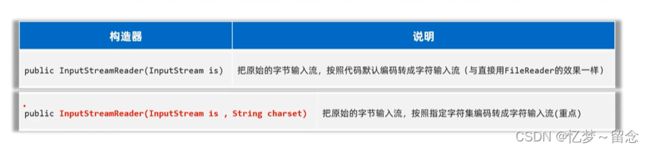
package com.text01;
import sun.nio.cs.ext.GBK;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class InPutStreamReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//1、得到文件的原始字节流(GBK的字节流形式)
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\3.txt");
//2。把原始的字节输入流按照指定的字符集编码转换成字符输入流
Reader reader=new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "GBK");
//3.把字符输入流包装成字符缓冲输入流
BufferedReader bufferedReader= new BufferedReader(reader);
){
String line;
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
如果需要控制写出去的'字符使用什么字符胰编码
OutputStreamWriter(字符输出转换流)
作用:可以控制写出去的字符使用什么字符集编码。
解决思路︰获取字节输出流,再按照指定的字符集编码将其转换成字符输出流,以后写出去的字符就会用该字符集编码了。
package com.text01;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class OutputStreamWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//1.创建一个字符输出流
FileOutputStream fileWriter = new FileOutputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\4.txt");
// 2、把原始的字节输出流。按照指定的字符集编码转换成字符输出转换流。
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileWriter,"GBK");
// 3把字符输出流包装成缓冲字符输出流
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter)
){
bufferedWriter.write("新年好");
bufferedWriter.write("大家好");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
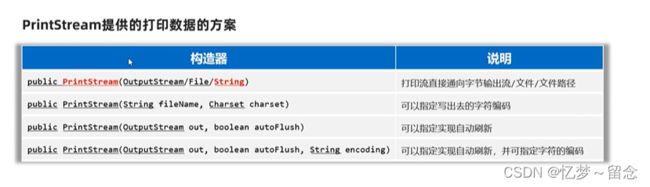
PrintStream/Printwriter打印流
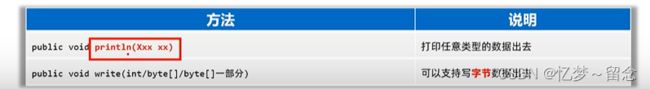
打印流可以实现更方便、更高效的打印数据出去,能实现打印啥出去就是啥出去。
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class PrintStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1.创建一个打印流管道
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream("day_22_i0\\src\\5.txt", String.valueOf(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
){
printStream.println(97);
printStream.println('a');
printStream.println("你好呀");
printStream.println(true);
printStream.println(12.89);
printStream.write(97);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.text01;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class PrintWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1.创建一个打印流管道
PrintWriter pipedWriter = new PrintWriter("day_22_i0\\src\\6.txt", String.valueOf(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
){
pipedWriter.println(97);
pipedWriter.println('a');
pipedWriter.println("你好呀");
pipedWriter.println(true);
pipedWriter.println(12.89);
pipedWriter.write('a');
pipedWriter.write(97);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PrintStream和PrintWriter的区别
打印数据的功能上是一模一样的:都是使用方便,性能高效(核心优势)
PrintStream继承自字节输出流OutputStream,因此支持写字节数据的方法。
PrintWriter继承自字符输出流Writer,因此支持写字符数据出去。
输出语句的重定向
可以把输出语句的打印位置改到某个文件中去。
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
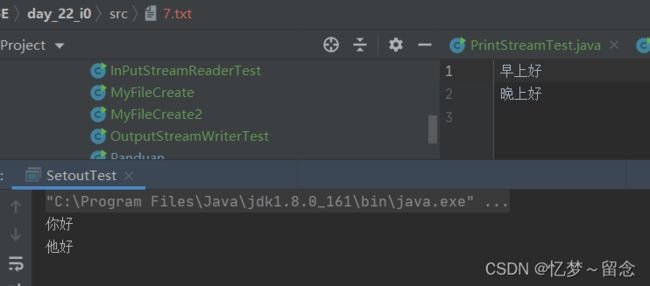
public class SetoutTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("你好");
System.out.println("他好");
try (
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream("day_22_i0\\src\\7.txt");
){
System.setOut(printStream);
System.out.println("早上好");
System.out.println("晚上好");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
数据流
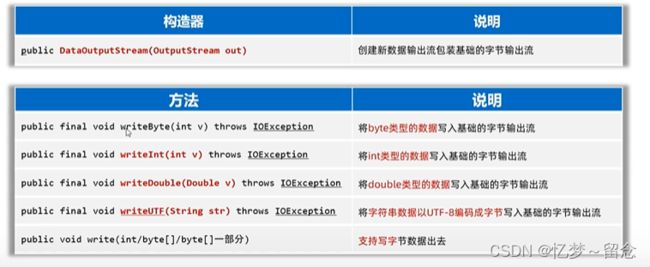
DataOutputStream(数据输出流)
允许把数据和其类型一并写出去。
package com.text01;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class DataOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//1、创建一个数据输出流包装低级的字节输出流
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\8.txt"));
){
dataOutputStream.writeInt(1);
dataOutputStream.writeChar('a');
dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutputStream.writeDouble(1.23);
dataOutputStream.writeUTF("小明");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DatalnputStream(数据输入流)
用于读取数据输出流写出去的数据。
package com.text01;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FilterInputStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class DataInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\8.txt"));
){
//对应写的顺序进行读取
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readInt());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readChar());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readDouble());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
序列化流
对象序列化:把Java对象写入到文件中去
对象反序列化:把文件里的Java对象读出来
objectOutputStream(对象字节输出流)
![]()
package com.text01;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
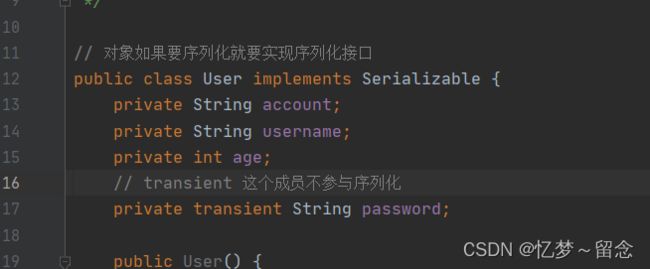
// 对象如果要序列化就要实现序列化接口
public class User implements Serializable {
private String account;
private String username;
private int age;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String account, String username, int age, String password) {
this.account = account;
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
this.password = password;
}
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"account='" + account + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class ObjectOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
// 2.创建一个对象输出流包装一个原始字节输出流
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\9.txt"));
) {
// 1.创建一个对象
User user = new User("admin","李四",28,"admin123");
// 3.序列化对象到文件中
objectOutputStream.writeObject(user);
System.out.println("序列化成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
objectInputStream(对象字节输入流)
可以把Java对象进行反序列化:把存储在文件中的Java对象读入到内存中来。

package com.text01;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class ObjectInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\9.txt"));
){
User user = (User) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println("user = " + user);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
如果要一次序列化多个对象
可以用一个ArrayList集合存储多个对象,然后直接对集合进行序列化即可
注意:ArrayList集合已经实现了序列化接口!
package com.text01;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author cqh
* @date 2024/1/7
* @Description
*/
public class ObjectOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
// 2.创建一个对象输出流包装一个原始字节输出流
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day_22_i0\\src\\9.txt"));
) {
// 1.创建一个对象
User user = new User("admin","李四",28,"admin123");
User user2 = new User("zhangshan","张三",20,"zhangShan123");
final ArrayList users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(user);
users.add(user2);
// 3.序列化对象到文件中
objectOutputStream.writeObject(users);
//objectOutputStream.writeObject(user);
System.out.println("序列化成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO框架
什么是框架
解决某类问题,编写的一套类、接口等,可以理解成一个半成品,大多框架都是第三方研发的。
好处:在框架的基础上开发,可以得到优秀的软件架构,并能提高开发效率
框架的形式:一般是把类、接口等编译成class形式,再压缩成一个.jar结尾的文件发行出去。
什么是io框架
封装了java提供的对文件、数据进行操作的代码,对外提供了更简单的方式来对文件进行操作,对数据进行读写等。
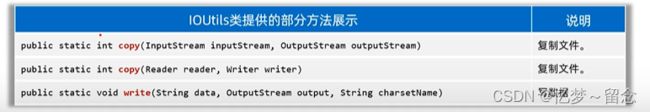
Commons-io
Commons-io是apache开源基金组织提供的一组有关IO操作的小框架,目的是提高IO流的开发效率。