spark-sql字段血缘实现
spark-sql字段血缘实现
背景
Apache Spark是一个开源的大数据处理框架,它提供了一种高效、易于使用的方式来处理大规模数据集。在Spark中,数据是通过DataFrame和Dataset的形式进行操作的,这些数据结构包含了一系列的字段(也称为列)。字段血缘是Spark中的一个关键概念,它帮助我们理解数据的来源和流向,从而更好地理解和控制数据处理过程。
字段血缘是指在数据处理过程中,一个字段的值是如何从源数据产生并传递给目标数据的。在Spark中,字段血缘是通过依赖关系进行管理的。每个字段都有一个或多个依赖关系,这些依赖关系定义了字段的值如何从其他字段或数据源产生。
前提
spark版本:2.4.3
使用语言:java+scala
技术实现
1. spark-sql的执行计划,了解如何实现字段血缘解析
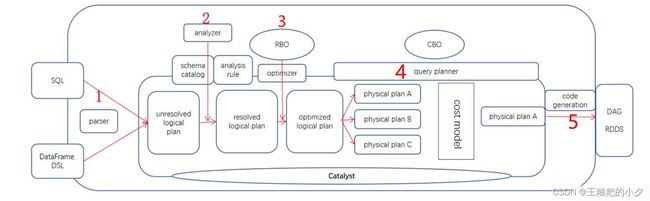
一个sql会经历一些列的处理,最终生成spark-core的代码,提交到集群运行。
首先看一下一个简单的sql生成的逻辑执行计划长什么样子
insert into default.jy_test
select * from default.jy_test
未解析的逻辑执行计划:
'InsertIntoTable 'UnresolvedRelation `default`.`jy_test`, false, false
+- 'Project [*]
+- 'UnresolvedRelation `default`.`jy_test`
解析后(analyzer)的逻辑执行计划:
InsertIntoHiveTable `default`.`jy_test`, org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe, false, false, [id, name]
+- Project [id#0, name#1]
+- SubqueryAlias `default`.`jy_test`
+- HiveTableRelation `default`.`jy_test`, org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe, [id#0, name#1]
优化后(optimizer)的逻辑执行计划:
InsertIntoHiveTable `default`.`jy_test`, org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe, false, false, [id, name]
+- HiveTableRelation `default`.`jy_test`, org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe, [id#0, name#1]
重点来了
- 所谓的逻辑执行计划就是一个树形结构
- 树形结构中的叶子结点,就是hive的表信息:库名、表名、字段信息,并且spark给每一个字段生成了一个唯一的id
- 树形结构中的非叶子只包含了字段信息,不包含库表信息
所以想要实现字段血缘,我们需要做的就是通过那个生成的唯一id去一层层的关联,当关联到叶子结点的时候,就找到了库名表名
2. 构建一颗与解析后的逻辑执行计划一模一样的树形结构
- 首先定义node对象,用来存放节点信息
public abstract class Node {
private String name;
private List<Column> columnList = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
private Node parentNode;
private String graphId;
}
- 其次定义column对象,用来存放字段信息
public class Column {
private String name;
private Long exprId;
private String ColumnType;
private ArrayList<Column> child = new ArrayList<Column>();
private String tableName;
private String process;
}
-
根据spark-sql生成的逻辑执行计划,我们为每一个逻辑节点创建对应的结点,由于结点很多,我这里直接给个截图,源码会在文章最后提供出来
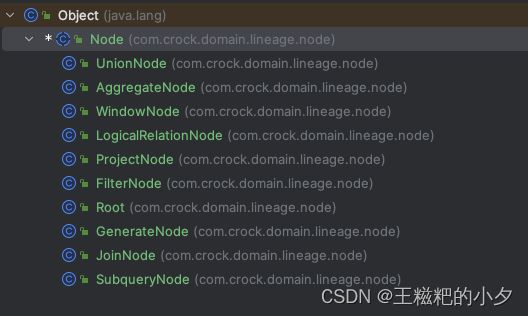
-
解析spark-sql生成的解析后的逻辑执行计划
首先获取逻辑执行计划,这里提供两种方式:
1.通过spark-session获取,该方法可以用来做测试,非常的方便LogicalPlan logicalPlan = spark.sessionState().sqlParser().parsePlan(sql); LogicalPlan analyzer = spark.sessionState().analyzer().execute(logicalPlan); -
解析spark生成的analyzer,构建我们自己的树形结构
这里贴一下主要的逻辑,使用scala去递归解析抽象语法树会方便很多
def resolveLogicPlan(plan: LogicalPlan, root: Node): Unit = {
plan match {
case plan: InsertIntoHadoopFsRelationCommand =>
val node = root.asInstanceOf[Root]
node.setName(NodeType.INSERTINTOHIVETABLE.getName)
val database: String = plan.catalogTable.get.identifier.database.getOrElse("default")
val table: String = plan.catalogTable.get.identifier.table
val fullTableName = database + "." + table
plan.catalogTable.get.schema.foreach { field => {
val column = new Column()
column.setName(field.name)
column.setTableName(fullTableName)
node.getColumnList.add(column)
}
}
resolveLogicPlan(plan.query, node)
case plan: SaveIntoDataSourceCommand =>
val table: String = plan.options.get("dbtable").getOrElse("")
val url: String = plan.options.get("url").getOrElse("")
val user: String = plan.options.get("user").getOrElse("")
val password: String = plan.options.get("password").getOrElse("")
// 定义匹配数据库名称的正则表达式模式
val pattern: Regex = ".*://[^/]+/(\\w+)".r
// 使用正则表达式进行匹配
val dbNameOption: Option[String] = pattern.findFirstMatchIn(url).map(_.group(1))
val fullTableName = dbNameOption.getOrElse("") + "." + table
val node = root.asInstanceOf[Root]
node.setName(NodeType.SAVEINTODATASOURCECOMMAND.getName)
// 连接mysql,根据库名表明获取字段列表
val fieldsList = getFieldsListFromMysql(url, user, password, table)
fieldsList.foreach { field => {
val column = new Column()
column.setName(field)
column.setTableName(fullTableName)
node.getColumnList.add(column)
}
}
resolveLogicPlan(plan.query, node)
case plan: InsertIntoHiveTable =>
val node = root.asInstanceOf[Root]
node.setName(NodeType.INSERTINTOHIVETABLE.getName)
val database: String = plan.table.identifier.database.getOrElse("default")
val table: String = plan.table.identifier.table
val fullTableName = database + "." + table
node.setTableName(fullTableName)
plan.table.schema.foreach { field => {
val column = new Column()
column.setName(field.name)
column.setTableName(fullTableName)
node.getColumnList.add(column)
}
}
resolveLogicPlan(plan.query, node)
case plan: Aggregate =>
val node = new AggregateNode()
insertNodeColumnsFromNamedExpression(node, plan.aggregateExpressions)
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.child, node)
case plan: Project =>
val node = new ProjectNode()
insertNodeColumnsFromNamedExpression(node, plan.projectList)
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.child, node)
case plan: LogicalRelation =>
val node = new LogicalRelationNode()
dfsLogicalRelation(plan, node)
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
case plan: HiveTableRelation =>
val node = new LogicalRelationNode()
dfsLogicalRelation(plan, node)
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
case plan: Filter =>
val node = new FilterNode()
node.setParentNode(root)
node.setCondition(plan.condition.toString)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.child, node)
case plan: Join =>
val node = new JoinNode()
node.setName(plan.joinType.toString + " " + node.getName)
node.setParentNode(root)
node.setCondition(plan.condition.toString)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.left, node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.right, node)
case plan: Window =>
val node = new WindowNode()
insertNodeColumnsFromNamedExpression(node, plan.windowExpressions)
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.child, node)
case plan: Union =>
val node = new UnionNode()
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
plan.children.foreach(resolveLogicPlan(_, node))
case plan: SubqueryAlias =>
val node = new SubqueryNode()
node.setName(node.getName + " " + plan.name.toString())
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.child, node)
case plan: Generate =>
val node = new GenerateNode()
processGenerate(plan, node)
node.setParentNode(root)
root.getChildren.add(node)
resolveLogicPlan(plan.child, node)
case _ =>
plan.children.foreach(resolveLogicPlan(_, root))
}
}
-
到这里,我们已经得到了自己的树形结构。接下来要通过唯一id进行关联,补充库表信息。
不知道大家注意没有,我们在node对象中有一个方法,
这里主要说一下Visitor的定义及方法:processColumn方法主要是拿自己的ExprId和所有孩子结点的ExprId比较,如果相等的话,说明是同一个字段,那就表名复制过来。
public interface Visitor {
void visit(Node node);
default void processColumn(Node node) {
for (Column column1 : node.getColumnList()) {
for (Node nd : node.getChildren()) {
for (Column column2 : nd.getColumnList()) {
processColumn(column1, column2);
}
}
}
}
default void processColumn(Column column1, Column column2) {
List<Column> child = column1.getChild();
child.forEach(ch -> processColumn(ch, column2));
if (column1.getExprId().equals(column2.getExprId())) {
if(column2.getTableName() != null) {
column1.setTableName(column2.getTableName());
} else {
column1.getChild().addAll(column2.getChild());
}
}
}
}
LineageVisitor是Visitor的实现类, 主要用来做模式匹配,不同的结点处理方式会有不同,感兴趣的同学看一下这块的代码。
public class LineageVisitor implements Visitor{
@Override
public void visit(Node node) {
switch (node.getClass().getSimpleName()) {
case "FilterNode" :
case "SubqueryNode" :
case "JoinNode" : copyChildColumnToThis(node); break;
case "WindowNode" :
case "GenerateNode" : copyChildColumnToThisWithProcess(node); break;
case "Root" : processColumn((Root)node); break;
case "UnionNode" : processColumn((UnionNode)node); break;
default : processColumn(node);
}
}
@Override
public void processColumn(Node node) {
node.getChildren().forEach( child -> child.accept(this));
Visitor.super.processColumn(node);
}
public void copyChildColumnToThis(Node node) {
node.getChildren().forEach( child -> child.accept(this));
for (Node child : node.getChildren()) {
node.getColumnList().addAll(child.getColumnList());
}
}
public void copyChildColumnToThisWithProcess(Node node) {
node.getChildren().forEach( child -> child.accept(this));
Visitor.super.processColumn(node);
for (Node child : node.getChildren()) {
node.getColumnList().addAll(child.getColumnList());
}
}
public void processColumn(Root node) {
node.getChildren().forEach( child -> child.accept(this));
if(node.getColumnList().size() > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < node.getChildren().get(0).getColumnList().size(); i++) {
for (Node child : node.getChildren()) {
node.getColumnList().get(i).getChild().add(child.getColumnList().get(i));
}
}
}
}
public void processColumn(UnionNode node) {
node.getChildren().forEach( child -> child.accept(this));
int size = node.getChildren().get(0).getColumnList().size();
for (Column column : node.getChildren().get(0).getColumnList()) {
Column column1 = new Column();
column1.setName(column.getName());
column1.setExprId(column.getExprId());
node.getColumnList().add(column1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (Node child : node.getChildren()) {
node.getColumnList().get(i).getChild().add(child.getColumnList().get(i));
}
}
}
}
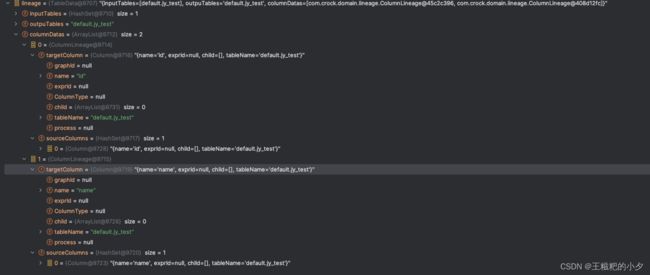
成果展示
还是拿最开始的sql ,看一下最终生成的字段血缘
insert into default.jy_test select * from default.jy_test
最后
字段血缘实现起来还是比较困难的,需要了解spak-sql的底层原理和一些技巧。
这里方便大家使用、学习、交流,所以贡献自己的源码,仓库地址:https://gitee.com/chenxiaoliang0901/crock/tree/main