代码随想录算法训练营Day18 | 二叉搜索树中的插入操作、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先、删除二叉搜索树的节点、修剪二叉搜索树、二叉搜索树转换成累加树、将有序数组转换成二叉搜索树
LeetCode 701 二叉搜索树的插入操作
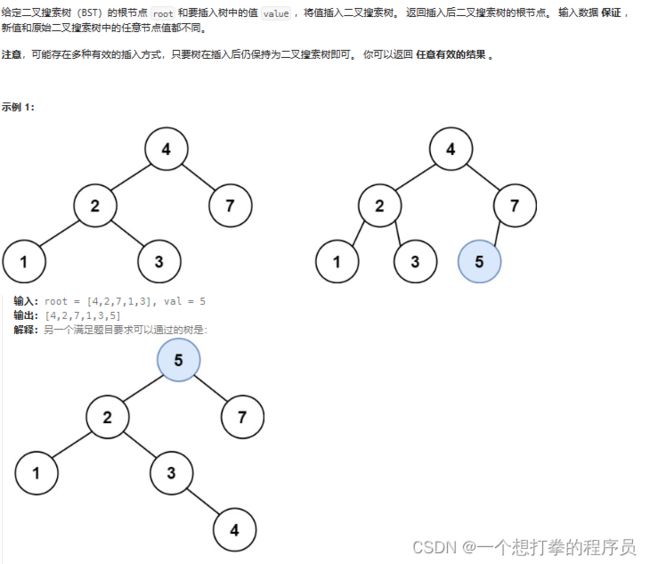
本题思路:既然是二叉搜索树,那么插入就变得比较简单了。因为二叉搜索树的左树节点值都小于根节点值,右树节点值都大于根节点值。
直接将要插入的节点值和根节点进行对比,如果比它小,就往左孩子走,比他大,就往右孩子走。最右直到为空的时候,此时这个位置就是要插入的位置。 再移动的过程中,可以用一个指针来记录父节点的位置。再定义一个标识来判断是走的左孩子还是右孩子。
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
boolean flag = true;
if(cur == null){
return node;
}
while(cur != null){
if(node.val > cur.val){
pre = cur;
cur = cur.right;
flag = true;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.left;
flag = false;
}
}
if(flag){
pre.right = node;
}else{
pre.left = node;
}
return root;
}
}
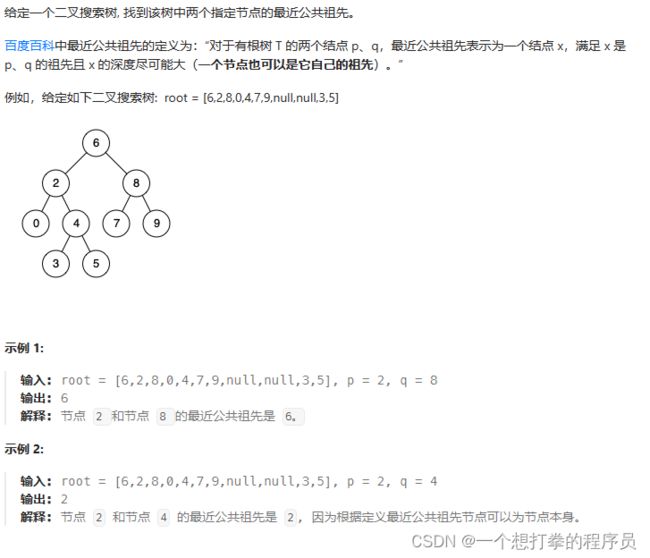
LeetCode 235 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 如果根节点为空,或者 等于 q ,等于 p,直接返回即可
- 再判断左树中,是否有 p、q 节点
- 再判断右树中,是否有 p、q 节点
- 最后,在进行最终判断
- 如果左树右树都不为空,则 root 节点就是 最近公共祖先
- 如果左树为空,右树不为空,则最近公共祖先就是 右树的不为空的节点
- 如果右树为空,左树不为空,则最近公共祖先就是 左树的不为空的节点
- 如果两个都为空,直接返回 null
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == q || root == p){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left != null && right != null){
return root;
}else if(left != null && right == null){
return left;
}else if(left == null && right != null){
return right;
}else{
return null;
}
}
}
LeetCode 450 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
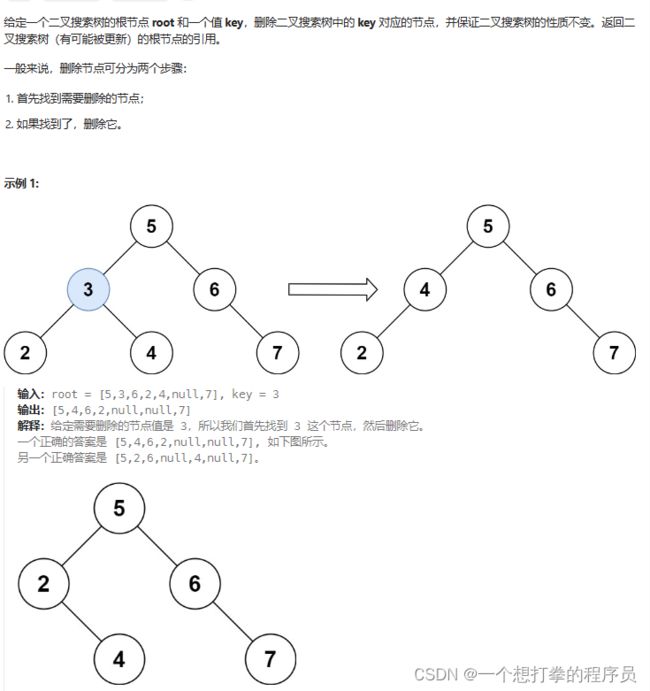
本题思路:删除二叉搜索树中的节点,和在 二叉搜索中插入节点差不多。
判断要删的节点的值和当前节点是否一样,如果一样就删除,不一样,就根据节点值大小,往左或者往右移动。只不过在删除的时候,比较麻烦。
- 首先是递归的出口,如果根节点为空,直接返回 null
- 先处理根节点,如果 根节点的值等于要删除的节点,此时又分为以下几种情况
- 如果根节点的左树为空,则直接返回根节点的右孩子
- 如果根节点的右树为空,则直接返回根节点的左孩子
- 如果都不为空,则往根节点的右孩子的左孩子找,一直找到最小的左孩子
- 然年让该左孩子的 左孩子为,根节点的左树
- 根节点更换为根节点的右孩子节点
- 如果节点的值大于根节点,就处理右树,在右树中寻找
- 如果节点的值小于根节点,就处理左树,在左树中寻找
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null){
return root;
}
if(key == root.val){
if(root.left == null){
return root.right;
}else if(root.right == null){
return root.left;
}else{
TreeNode cur = root.right;
// 找到该节点右树中,最左边最小的节点
while(cur.left != null){
cur = cur.left;
}
// 让最小节点的 left 等于这个节点
cur.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
}
}
if(key > root.val){
// 当前根节点的右树,为在右树上找到删除的节点后,新构造的树
root.right = deleteNode(root.right,key);
}
if(key < root.val){
// 当前根节点的左树,为在左树上找到删除的节点后,新构造的树
root.left = deleteNode(root.left,key);
}
return root;
}
}
LeetCode 108 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
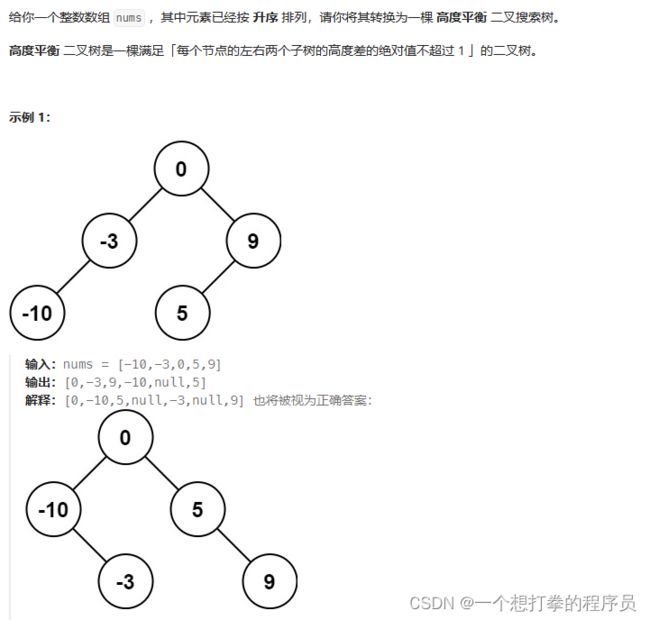
本题思路:利用中序遍历来构造。由于构造的必须是二叉平衡树。所以我们构造的时候,将树均匀分成两份,取中间节点作为根节点,然后更新左中序树,更新右中序树。再递归构造即可!
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return travl(nums,0,nums.length);
}
public TreeNode travl(int[] nums, int start, int end){
if(start == end){
return null;
}
int index = (start + end) >> 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[index]);
if(nums.length == 1){
return root;
}
int startleft = start;
int endleft = index;
int startright = index + 1;
int endright = end;
root.left = travl(nums,startleft,endleft);
root.right = travl(nums,startright,endright);
return root;
}
}
LeetCode 669 修剪二叉搜索树
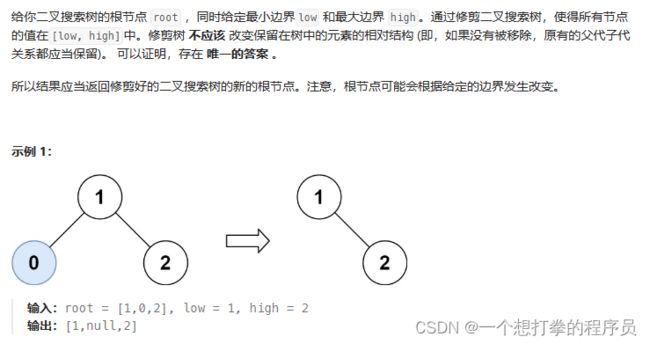
本题思路:判断当前节点的值,是否在区间内,如果不在,不能直接删除,因为它的左树或者右数中可能存在符合的节点!
- 首先找到递归的出口 root == null,直接返回 null
- 如果当前节点小于区间,但是它的右树中,可能存在符合区间内的节点,所以不能直接删除当前节点,需要递归进行 传入该节点的右子树
- 如果当前节点大于区间,但是它的左树种,可能存在符合区间内的节点,所以不能直接删除当前节点,需要递归进行 传入该节点的左子树
- 然后在左树中,删除节点
- 然后在右树中,删除节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
// 如果当前节点值 小于区间
if(root.val < low){
// 此时虽然当前节点值小于 low, 但是它的右树中,可能存在符合区间内的节点,所以不能直接删除当前节点
return trimBST(root.right,low,high);
}
// 如果当前节点值 大于区间
if(root.val > high){
// 此时虽然当前节点值大于 high, 但是它的左树中,可能存在符合区间内的节点,所以也不能直接删除
return trimBST(root.left,low,high);
}
root.left = trimBST(root.left,low,high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root;
}
}
LeetCode 538 把二叉搜索树转换累加树
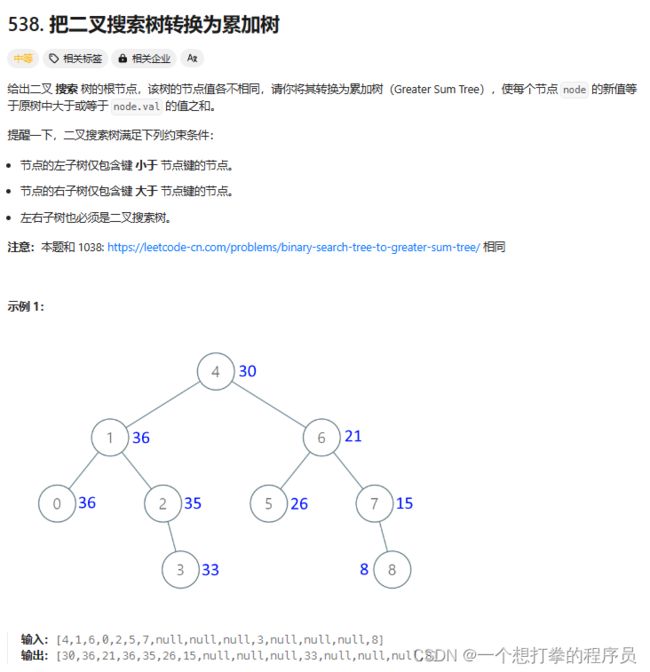
本题思路:可以看出,遍历的顺序是 右 根 左, 我们可以用双指针的操作,来完成累加。 定义一个 pre = 0 , cur 指向 8 , 当前的节点值 就等于 cur.val + pre
class Solution {
int pre = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
travel(root);
return root;
}
public void travel(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
travel(root.right);
root.val += pre;
pre = root.val;
travel(root.left);
}
}