代码随想录算法训练营第18天 | 513.找树左下角的值 112. 路径总和 113.路径总和ii 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
目录
513.找树左下角的值
解题思路
迭代法
实现代码
112. 路径总和
解题思路
这道题我们要遍历从根节点到叶子节点的路径看看总和是不是目标和。
实现代码
113.路径总和ii
解题思路
实现代码
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
解题思路
实现代码
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
解题思路
实现代码
513.找树左下角的值
题目链接:513.找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
示例 1:
示例 2:
解题思路
在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
首先要是最后一行,然后是最左边的值。
如果使用递归法,如何判断是最后一行呢,其实就是深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。
所以要找深度最大的叶子节点。
那么如何找最左边的呢?可以使用前序遍历(当然中序,后序都可以,因为本题没有 中间节点的处理逻辑,只要左优先就行),保证优先左边搜索,然后记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值。
递归三部曲:
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为void。
本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxLen用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
代码如下:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN; // 全局变量 记录最大深度
int result; // 全局变量 最大深度最左节点的数值
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth)
- 确定终止条件
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
代码如下:
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth; // 更新最大深度
result = root->val; // 最大深度最左面的数值
}
return;
}
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
在找最大深度的时候,递归的过程中依然要使用回溯,代码如下:
// 中
if (root->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度加一
traversal(root->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度减一
}
if (root->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度加一
traversal(root->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度减一
}
return;
迭代法
本题使用层序遍历再合适不过了,比递归要好理解得多!
只需要记录最后一行第一个节点的数值就可以了。
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int result = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i == 0) result = node->val; // 记录最后一行第一个元素
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
实现代码
// 递归法
class Solution {
private int Deep = -1;
private int value = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
value = root.val;
findLeftValue(root,0);
return value;
}
private void findLeftValue (TreeNode root,int deep) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (deep > Deep) {
value = root.val;
Deep = deep;
}
}
if (root.left != null) findLeftValue(root.left,deep + 1);
if (root.right != null) findLeftValue(root.right,deep + 1);
}
}
//迭代法
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int res = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = queue.poll();
if (i == 0) {
res = poll.val;
}
if (poll.left != null) {
queue.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
queue.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
112. 路径总和
题目链接:112. 路径总和
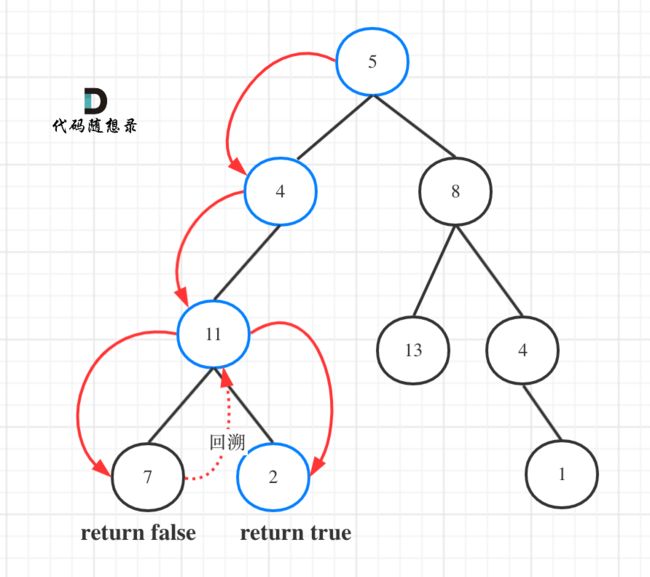
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
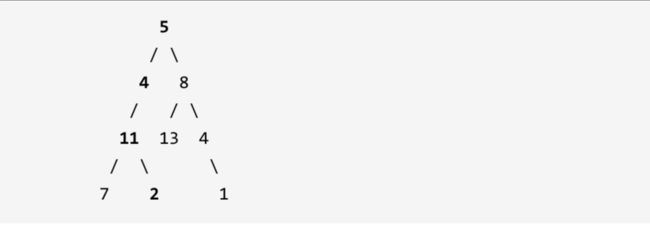
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
解题思路
递归函数什么时候需要返回值?什么时候不需要返回值?这里总结如下三点:
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。
- 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)
这道题我们要遍历从根节点到叶子节点的路径看看总和是不是目标和。
首先计数器如何统计这一条路径的和呢?
不要去累加然后判断是否等于目标和,那么代码比较麻烦,可以用递减,让计数器count初始为目标和,然后每次减去遍历路径节点上的数值。
如果最后count == 0,同时到了叶子节点的话,说明找到了目标和。
如果遍历到了叶子节点,count不为0,就是没找到。
实现代码
class solution {
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
targetsum -= root.val;
// 叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return targetsum == 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
boolean left = haspathsum(root.left, targetsum);
if (left) { // 已经找到
return true;
}
}
if (root.right != null) {
boolean right = haspathsum(root.right, targetsum);
if (right) { // 已经找到
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
113.路径总和ii
题目链接:113. 路径总和 II
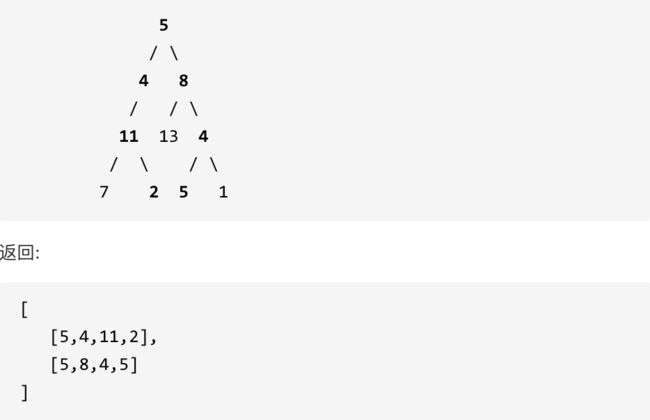
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
解题思路
113.路径总和ii要遍历整个树,找到所有路径,所以递归函数不要返回值!
实现代码
class Solution {
public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List> res=new ArrayList<>();
List path=new LinkedList<>();
if(root==null) return res;
sumDfs(root,targetSum,path,res);
return res;
}
public void sumDfs(TreeNode root,int targetSum,List path,List> res){
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
if(targetSum-root.val==0){
res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
}
return;
}
if(root.left!=null){
sumDfs(root.left,targetSum-root.val,path,res);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}if(root.right!=null){
sumDfs(root.right,targetSum-root.val,path,res);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
} 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目链接:106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
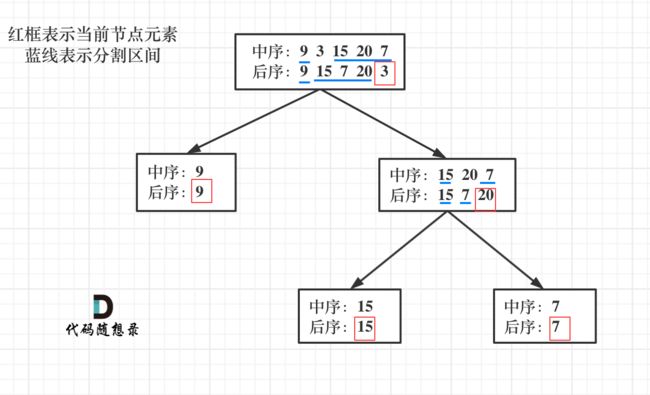
- 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
- 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 返回如下的二叉树:
解题思路
以 后序数组的最后一个元素为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来再切后序数组。一层一层切下去,每次后序数组最后一个元素就是节点元素。
如果让我们肉眼看两个序列,画一棵二叉树的话,应该分分钟都可以画出来。
流程如图:
那么代码应该怎么写呢?
说到一层一层切割,就应该想到了递归。
来看一下一共分几步:
-
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
-
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
-
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
-
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
-
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
-
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
实现代码
class Solution {
Map map; // 方便根据数值查找位置
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder,0, postorder.length); // 前闭后开
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
return null;
}
int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1]); // 找到后序遍历的最后一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定后序数列的个数
root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex,
postorder, postBegin, postBegin + lenOfLeft);
root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd,
postorder, postBegin + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(postorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0)
return null;
return buildHelper(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
}
private TreeNode buildHelper(int[] inorder, int inorderStart, int inorderEnd, int[] postorder, int postorderStart, int postorderEnd){
if(postorderStart == postorderEnd)
return null;
int rootVal = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
int middleIndex;
for (middleIndex = inorderStart; middleIndex < inorderEnd; middleIndex++){
if(inorder[middleIndex] == rootVal)
break;
}
int leftInorderStart = inorderStart;
int leftInorderEnd = middleIndex;
int rightInorderStart = middleIndex + 1;
int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;
int leftPostorderStart = postorderStart;
int leftPostorderEnd = postorderStart + (middleIndex - inorderStart);
int rightPostorderStart = leftPostorderEnd;
int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1;
root.left = buildHelper(inorder, leftInorderStart, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderStart, leftPostorderEnd);
root.right = buildHelper(inorder, rightInorderStart, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderStart, rightPostorderEnd);
return root;
}
}
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目链接:105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7] 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 返回如下的二叉树:
解题思路
和上题思路相同
实现代码
class Solution {
Map map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length); // 前闭后开
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
if (preBegin >= preEnd || inBegin >= inEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
return null;
}
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]); // 找到前序遍历的第一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定前序数列的个数
root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
inorder, inBegin, rootIndex);
root.right = findNode(preorder, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1, preEnd,
inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}