求最长公共子序列
"In biological applications , we often want to compare the DNA of two (or more) different organisms.....
For example, the DNA of one organism may be
S1= { ACCGGTCGAGTGCGCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA}
S2= {GTCGTTCGGAATGCCGTTGCTCTGTAAA}
one goal of comparing two strands of DNA is to determine how "similar" the two strands are, as some measure of how closely related the two organisms are."
------------------------------------------摘自Introduction to algorithms[算法导论]
现在,我们遇到求公共子序列的时候,公共子序列意味着什么?匹配?相似度?怎么求最长公共子序列(longest common subsequence)?本文将告诉你其算法并给出c/c++ 与Java实现源代码.
[1] 定义:何为最长公共子序列?
eg: X = {A,B,C,B,D,A,B} Y = {B,D,C,A,B,A}此两序列的最长公共子序列是LCS={B,C,B,A}
定义我就不多说了,自己感受咯.
[2] 一个相关的定理:
若X = {x1,x2,...,xm} , Y = {y1,y2,...,yn}的LCS是Z={z1,z2,...,zk}那么有:
1) 如果xm = yn , 则zk = xm = yn 并且 Zk-1 是Xm-1和Yn-1的LCS.
2)如果xm ≠ yn, 那么zk ≠ xm意味着Z 是Xm-1和Y的LCS.
3)如果xm ≠ yn, 那么zk ≠ yn 意味着Z是X和Yn-1的LCS.
这个定理其实不难理解,用反证法可以证明之.但是却暗含递归思想.
let us define c[i,j] to be the length of an LCS of the sequence Xi and Yj.
整理一下.有如下的递归关系:
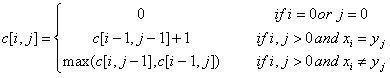
[3]算法源程序
那么Java怎么样?JAVA支持多维数组啦,因此java写起来"好看"多了.^_^
class TestLCS
{
final static int NorthWest = 2 ;
final static int UP = 1 ;
final static int LEFT = 0 ;
private static int [][] LCS_length(String X, String Y)
{
int m = X.length() + 1 ;
int n = Y.length() + 1 ;
int [][] c = new int [m][n];
int [][] flag = new int [m][n];
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 0 ;j < n; ++ j)
flag[i][j] = LEFT;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i) // 递归表达式2
c[i][ 0 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < n; ++ i)
c[ 0 ][i] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 1 ;j < n; ++ j)
{
if ( X.charAt(i - 1 ) == Y.charAt(j - 1 ))
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; // 递归表达式3
flag[i][j] = NorthWest; //
}
else
{
if (c[i - 1 ][j] > c[i][j - 1 ])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j];
flag[i][j] = UP; //
}
else
{
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1 ];
}
}
}
return flag;
}
private static void LCS(String X, int m, int n, int [][] flag)
{
if (m == 0 || n == 0 ) return ;
if (flag[m][n] == NorthWest)
{
LCS(X,m - 1 ,n - 1 ,flag);
System.out.print(X.charAt(m - 1 ));
}
else if (flag[m][n] == UP)
{
LCS(X,m - 1 ,n,flag);
}
else
{
LCS(X,m,n - 1 ,flag);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// String X = "ABCBDAB";
// String Y = "BDCABA";
String X = " ACCGGTCGAGTGCGCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA " ;
String Y = " GTCGTTCGGAATGCCGTTGCTCTGTAAA " ;
int m = X.length();
int n = Y.length();
int [][] flag = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ];
flag = LCS_length(X,Y);
LCS(X,m,n,flag);
// 程序输出:GTCGTCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA
}
}
本文完.如有问题欢迎留言讨论.
参考资料:<Introduction to algorithms>
For example, the DNA of one organism may be
S1= { ACCGGTCGAGTGCGCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA}
S2= {GTCGTTCGGAATGCCGTTGCTCTGTAAA}
one goal of comparing two strands of DNA is to determine how "similar" the two strands are, as some measure of how closely related the two organisms are."
------------------------------------------摘自Introduction to algorithms[算法导论]
现在,我们遇到求公共子序列的时候,公共子序列意味着什么?匹配?相似度?怎么求最长公共子序列(longest common subsequence)?本文将告诉你其算法并给出c/c++ 与Java实现源代码.
[1] 定义:何为最长公共子序列?
eg: X = {A,B,C,B,D,A,B} Y = {B,D,C,A,B,A}此两序列的最长公共子序列是LCS={B,C,B,A}
定义我就不多说了,自己感受咯.
[2] 一个相关的定理:
若X = {x1,x2,...,xm} , Y = {y1,y2,...,yn}的LCS是Z={z1,z2,...,zk}那么有:
1) 如果xm = yn , 则zk = xm = yn 并且 Zk-1 是Xm-1和Yn-1的LCS.
2)如果xm ≠ yn, 那么zk ≠ xm意味着Z 是Xm-1和Y的LCS.
3)如果xm ≠ yn, 那么zk ≠ yn 意味着Z是X和Yn-1的LCS.
这个定理其实不难理解,用反证法可以证明之.但是却暗含递归思想.
let us define c[i,j] to be the length of an LCS of the sequence Xi and Yj.
整理一下.有如下的递归关系:
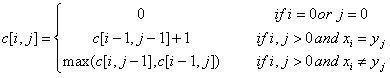
[3]算法源程序
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include < string .h >
int * LCS_length( char * X, char * Y)
{
int m = strlen(X) + 1 ;
int n = strlen(Y) + 1 ;
int ( * c)[n] = new int [m][n];
int ( * b)[n] = new int [m][n];
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 0 ;j < n; ++ j)
b[i][j] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i)
c[i][ 0 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < n; ++ i)
c[ 0 ][i] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 1 ;j < n; ++ j)
{
if (X[i - 1 ] == Y[j - 1 ])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ;
b[i][j] = 2 ; // 比较相等之标记
}
else
{
if ( c[i - 1 ][j] >= c[i][j - 1 ])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j];
b[i][j] = 1 ; //
}
else
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1 ];
}
}
delete[] c;
return ( int * )b;
}
void LCS( char * X, char * Y, int m, int n, int * b)
{
if (m == 0 || n == 0 )
return ;
if (b[m * (strlen(Y) + 1 ) + n] == 2 )
{
LCS(X,Y,m - 1 ,n - 1 ,b);
printf( " %c " ,X[m - 1 ]);
}
else if (b[m * (strlen(Y) + 1 ) + n] == 1 )
{
LCS(X,Y,m - 1 ,n,b);
}
else
{
LCS(X,Y,m,n - 1 ,b);
}
}
int main()
{
// char* X = "ABCBDAB";
// char* Y = "BDCABA";
char * X = " ACCGGTCGAGTGCGCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA " ;
char * Y = " GTCGTTCGGAATGCCGTTGCTCTGTAAA " ;
int m = strlen(X) + 1 ;
int n = strlen(Y) + 1 ;
int * c = NULL;
c = LCS_length(X,Y);
LCS(X,Y,strlen(X),strlen(Y),c);
delete[] c;
getchar();
return 0 ;
}
以上程序在VC6.0下是不能正常编译的.推荐用Dev-C++来调试.我用的版本是4.9.9.0.以上程序或许有点费解,主要是C++对动态的多维数组不支持! 您看,我到求LCS时变二维为一维来求了,但愿你能根据前面的定理看懂我这糟糕的程序咯.
#include < string .h >
int * LCS_length( char * X, char * Y)
{
int m = strlen(X) + 1 ;
int n = strlen(Y) + 1 ;
int ( * c)[n] = new int [m][n];
int ( * b)[n] = new int [m][n];
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 0 ;j < n; ++ j)
b[i][j] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i)
c[i][ 0 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < n; ++ i)
c[ 0 ][i] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 1 ;j < n; ++ j)
{
if (X[i - 1 ] == Y[j - 1 ])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ;
b[i][j] = 2 ; // 比较相等之标记
}
else
{
if ( c[i - 1 ][j] >= c[i][j - 1 ])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j];
b[i][j] = 1 ; //
}
else
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1 ];
}
}
delete[] c;
return ( int * )b;
}
void LCS( char * X, char * Y, int m, int n, int * b)
{
if (m == 0 || n == 0 )
return ;
if (b[m * (strlen(Y) + 1 ) + n] == 2 )
{
LCS(X,Y,m - 1 ,n - 1 ,b);
printf( " %c " ,X[m - 1 ]);
}
else if (b[m * (strlen(Y) + 1 ) + n] == 1 )
{
LCS(X,Y,m - 1 ,n,b);
}
else
{
LCS(X,Y,m,n - 1 ,b);
}
}
int main()
{
// char* X = "ABCBDAB";
// char* Y = "BDCABA";
char * X = " ACCGGTCGAGTGCGCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA " ;
char * Y = " GTCGTTCGGAATGCCGTTGCTCTGTAAA " ;
int m = strlen(X) + 1 ;
int n = strlen(Y) + 1 ;
int * c = NULL;
c = LCS_length(X,Y);
LCS(X,Y,strlen(X),strlen(Y),c);
delete[] c;
getchar();
return 0 ;
}
那么Java怎么样?JAVA支持多维数组啦,因此java写起来"好看"多了.^_^
class TestLCS
{
final static int NorthWest = 2 ;
final static int UP = 1 ;
final static int LEFT = 0 ;
private static int [][] LCS_length(String X, String Y)
{
int m = X.length() + 1 ;
int n = Y.length() + 1 ;
int [][] c = new int [m][n];
int [][] flag = new int [m][n];
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 0 ;j < n; ++ j)
flag[i][j] = LEFT;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < m; ++ i) // 递归表达式2
c[i][ 0 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ;i < n; ++ i)
c[ 0 ][i] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 ;i < m; ++ i)
for ( int j = 1 ;j < n; ++ j)
{
if ( X.charAt(i - 1 ) == Y.charAt(j - 1 ))
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; // 递归表达式3
flag[i][j] = NorthWest; //
}
else
{
if (c[i - 1 ][j] > c[i][j - 1 ])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1 ][j];
flag[i][j] = UP; //
}
else
{
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1 ];
}
}
}
return flag;
}
private static void LCS(String X, int m, int n, int [][] flag)
{
if (m == 0 || n == 0 ) return ;
if (flag[m][n] == NorthWest)
{
LCS(X,m - 1 ,n - 1 ,flag);
System.out.print(X.charAt(m - 1 ));
}
else if (flag[m][n] == UP)
{
LCS(X,m - 1 ,n,flag);
}
else
{
LCS(X,m,n - 1 ,flag);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// String X = "ABCBDAB";
// String Y = "BDCABA";
String X = " ACCGGTCGAGTGCGCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA " ;
String Y = " GTCGTTCGGAATGCCGTTGCTCTGTAAA " ;
int m = X.length();
int n = Y.length();
int [][] flag = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ];
flag = LCS_length(X,Y);
LCS(X,m,n,flag);
// 程序输出:GTCGTCGGAAGCCGGCCGAA
}
}
本文完.如有问题欢迎留言讨论.
参考资料:<Introduction to algorithms>