postgresql 15源码浅析(3)—— 信号“1“的使命
摘要
这篇实际上是要说说配置文件的加载问题,有些标题党了。准确说是如何在线加载配置,用户通过向postgres进程发送信号SIGHUP触发服务端完成配置的刷新。这部分看下来代码还是有点多,挑选几段我认为比较重要的片段和大家一起学习一下。
信号
信号也是进程间通信的一种手段,之前在《postgresql 15源码浅析(1)—— postgres中的1号数据库》介绍了通过管道完成向psql客户端进程传递BKI命令的进程间通信方式,同样,信号是另一种进程间传递信息的方式,相对传统的共享内存和消息队列方式,信号要简单的多。
信号简介
信号机制是一种使用信号来进行进程之间的传递消息的方法,其中信号的全称为软中断信号,简称软中断。
我们最常用的一个就是 9) SIGKILL ,kill -9 ,我想这个大家应该都用过。实际上,Linux内核支持64种不同的信号,这些信号种的大部分都有了预先定义好的意义,但是都支持自定义动作,并且还提供了类似SIGUSR1这样由应用程序来定义的信号。
同样在C./C++中也可以使用类似方法,使用kill函数,传入进程号pid和信号值sig,即可以向指定进程发送特定的信号。
信号的处理
我们处理信号的方式大体有3种:
- 捕获信号,并忽略它,常用于在某些处理过程中不希望被终端打断的场景,如某些初始化过程。
- 不做任何捕获操作,使用信号的默认行为,信号的默认行为大部分是要终止进程。
- 捕获信号,并重新赋予被捕获信号新的使命。这里点题了。“信号1的使命”。
信号实际上在核心场景下并不是一个好的选择,它涉及中断,同时需要内核态和用户态的切换,效率不高,开销太大,且与其它进程通信方式相比,能够传递的信息有限。
再推荐一本书吧,有兴趣转行的同学可以看看《Linux C程序设计大全》,是一本贼厚的蓝皮书,也是我入行时的第一本工具书。
修改PostgreSQL的配置
配置文件在哪?
在初始化之后,数据库集簇目录下回创建4个配置文件。
也可以通过命令查看配置文件所在位置
配置文件生效的方法
修改配置文件后,配置项生效的方法共有四种:
- 重新启动数据库服务,这是网吧管理员的做法,除非是一些参数要求重启服务,否则不需要这么干;
- 使用超级用户执行
select pg_reload_conf();留个坑,后续补充这个函数的执行流程; - bash下执行 kill -HUP 或 kill -1 ,这个就是今天要撸的代码;
- 使用pg_ctl工具执行 pg_ctl reload 这个命令实际上就是触发了SIGHUP信号;
GucContext
上文提到,不是所有的配置都可以动态的加载生效的,有些配置需要重新启动数据库服务。
通过select distinct(context) from pg_settings;命令列出所有配置的类型(共7种)。
postgres@/tmp:postgres> select distinct(context) from pg_settings;
+-------------------+
| context |
|-------------------|
| postmaster |
| superuser-backend |
| user |
| internal |
| backend |
| sighup |
| superuser |
+-------------------+
SELECT 7
Time: 0.005s
对应的正是代码中GucContext的枚举类型(共7种)。
/*
* Certain options can only be set at certain times. The rules are
* like this:
*
* INTERNAL options cannot be set by the user at all, but only through
* internal processes ("server_version" is an example). These are GUC
* variables only so they can be shown by SHOW, etc.
*
* POSTMASTER options can only be set when the postmaster starts,
* either from the configuration file or the command line.
*
* SIGHUP options can only be set at postmaster startup or by changing
* the configuration file and sending the HUP signal to the postmaster
* or a backend process. (Notice that the signal receipt will not be
* evaluated immediately. The postmaster and the backend check it at a
* certain point in their main loop. It's safer to wait than to read a
* file asynchronously.)
*
* BACKEND and SU_BACKEND options can only be set at postmaster startup,
* from the configuration file, or by client request in the connection
* startup packet (e.g., from libpq's PGOPTIONS variable). SU_BACKEND
* options can be set from the startup packet only when the user is a
* superuser. Furthermore, an already-started backend will ignore changes
* to such an option in the configuration file. The idea is that these
* options are fixed for a given backend once it's started, but they can
* vary across backends.
*
* SUSET options can be set at postmaster startup, with the SIGHUP
* mechanism, or from the startup packet or SQL if you're a superuser.
*
* USERSET options can be set by anyone any time.
*/
typedef enum
{
PGC_INTERNAL,
PGC_POSTMASTER,
PGC_SIGHUP,
PGC_SU_BACKEND,
PGC_BACKEND,
PGC_SUSET,
PGC_USERSET
} GucContext;
注释中对每个选项的表述都比较良心,等级是从严到松的顺序。
如果配置项的context小于PGC_SIGHUP,那么需要重新启动生效,当然PGC_INTERNAL是只读的,当然PGC_INTERNAL的配置也不会出现在postgresql.conf文件中,所以只要context属性是PGC_POSTMASTER的配置项需要重启后会生效。
看一下这些配置在PostgreSQL 15中的分布情况:
postgres@/tmp:postgres> select context,count(*) from pg_settings group by context;
+-------------------+-------+
| context | count |
|-------------------+-------|
| postmaster | 55 |
| superuser-backend | 4 |
| user | 136 |
| internal | 20 |
| backend | 2 |
| sighup | 92 |
| superuser | 44 |
+-------------------+-------+
SELECT 7
Time: 0.006s
postgres@/tmp:postgres>
可以通过查询pg_settings表的context字段来确定,修改的配置是否允许动态加载。
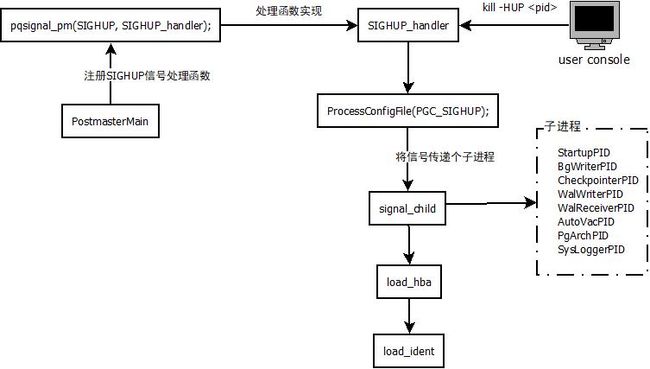
信号处理流程
整理流程如上图,1.进程启动时,注册信号捕获处理函数;2.用户发送信号,并被进程捕获,交由SIGHUP_handler处理;3.主进程先处理配置文件重加载流程,并把信号传递个各个子进程;4.分别对hba和ident两个配置文件进程加载处理;
注册信号处理函数
/*
* Postmaster main entry point
*/
void
PostmasterMain(int argc, char *argv[])
在父进程(主进程)postmaster的入口函数PostmasterMain中注册信号处理函数。
pqsignal_pm(SIGHUP, SIGHUP_handler); /* reread config file and have
* children do same */
pqsignal_pm(SIGINT, pmdie); /* send SIGTERM and shut down */
pqsignal_pm(SIGQUIT, pmdie); /* send SIGQUIT and die */
pqsignal_pm(SIGTERM, pmdie); /* wait for children and shut down */
pqsignal_pm(SIGALRM, SIG_IGN); /* ignored */
pqsignal_pm(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); /* ignored */
pqsignal_pm(SIGUSR1, sigusr1_handler); /* message from child process */
pqsignal_pm(SIGUSR2, dummy_handler); /* unused, reserve for children */
pqsignal_pm(SIGCHLD, reaper); /* handle child termination */
其中pqsignal_pm(SIGHUP, SIGHUP_handler);注册了对新SIGHUP的处理函数SIGHUP_handler,
SIGHUP_handler
核心代码:
ereport(LOG,(errmsg("received SIGHUP, reloading configuration files")));
ProcessConfigFile(PGC_SIGHUP);
SignalChildren(SIGHUP);
if (StartupPID != 0)
signal_child(StartupPID, SIGHUP);
if (BgWriterPID != 0)
signal_child(BgWriterPID, SIGHUP);
if (CheckpointerPID != 0)
signal_child(CheckpointerPID, SIGHUP);
if (WalWriterPID != 0)
signal_child(WalWriterPID, SIGHUP);
if (WalReceiverPID != 0)
signal_child(WalReceiverPID, SIGHUP);
if (AutoVacPID != 0)
signal_child(AutoVacPID, SIGHUP);
if (PgArchPID != 0)
signal_child(PgArchPID, SIGHUP);
if (SysLoggerPID != 0)
signal_child(SysLoggerPID, SIGHUP);
/* Reload authentication config files too */
if (!load_hba())
ereport(LOG,
/* translator: %s is a configuration file */
(errmsg("%s was not reloaded", "pg_hba.conf")));
if (!load_ident())
ereport(LOG,
(errmsg("%s was not reloaded", "pg_ident.conf")));
- 处理配置文件加载ProcessConfigFile。
- 将捕获信号传递给子进程signal_child,子进程kill(-pid, signal);
- 加载hba配置文件load_hba();
- 加载ident配置文件load_ident();
子进程处理
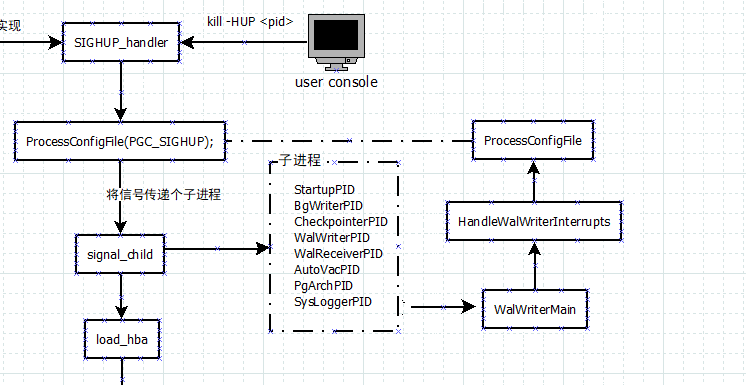
子进程收到父进程传递过来的信号好,进入处理流程。
以WalWriter进程为例,入口函数WalWriterMain在backend/postmaster/walwriter.c中。主要处理过程为与postmaster主进程类似,最终也将调用guc_file.c中的ProcessConfigFile函数;
子进程的处理需要注意的是,收到HUP信号后,并不是立即进入处理流程,而是设置重载标志,在下一次loop forever中检查标志,如果为true则调用配置文件重新加载的流程。
- 设置标记ConfigReloadPending
/*
* Simple signal handler for triggering a configuration reload.
*
* Normally, this handler would be used for SIGHUP. The idea is that code
* which uses it would arrange to check the ConfigReloadPending flag at
* convenient places inside main loops, or else call HandleMainLoopInterrupts.
*/
void
SignalHandlerForConfigReload(SIGNAL_ARGS)
{
int save_errno = errno;
ConfigReloadPending = true;
SetLatch(MyLatch);
errno = save_errno;
}
- 读取标记ConfigReloadPending,是否需要重新加载配置文件
/*
* Interrupt handler for main loops of WAL writer process.
*/
static void
HandleWalWriterInterrupts(void)
{
if (ProcSignalBarrierPending)
ProcessProcSignalBarrier();
if (ConfigReloadPending)
{
ConfigReloadPending = false;
ProcessConfigFile(PGC_SIGHUP);
}
if (ShutdownRequestPending)
{
/*
* Force reporting remaining WAL statistics at process exit.
*
* Since pgstat_report_wal is invoked with 'force' is false in main
* loop to avoid overloading the cumulative stats system, there may
* exist unreported stats counters for the WAL writer.
*/
pgstat_report_wal(true);
proc_exit(0);
}
/* Perform logging of memory contexts of this process */
if (LogMemoryContextPending)
ProcessLogMemoryContextInterrupt();
}
ProcessConfigFile
改函数时处理配置文件重新加载的核心部分,整体流程如下:
这部分代码量比较大,宏观的看一下重点,这部分处理使用了递归处理,主要是处理postgressql.conf中include子配置文件是需要递归。
if (guc_name_compare(opt_name, "include_dir") == 0)
{
/*
* An include_dir directive isn't a variable and should be
* processed immediately.
*/
if (!ParseConfigDirectory(opt_value,
config_file, ConfigFileLineno - 1,
depth + 1, elevel,
head_p, tail_p))
……
}
else if (guc_name_compare(opt_name, "include_if_exists") == 0)
{
/*
* An include_if_exists directive isn't a variable and should be
* processed immediately.
*/
if (!ParseConfigFile(opt_value, false,
config_file, ConfigFileLineno - 1,
depth + 1, elevel,
head_p, tail_p))
……
}
else if (guc_name_compare(opt_name, "include") == 0)
{
/*
* An include directive isn't a variable and should be processed
* immediately.
*/
if (!ParseConfigFile(opt_value, true,
config_file, ConfigFileLineno - 1,
depth + 1, elevel,
head_p, tail_p))
……
}
else
{
……
}
且递归深度不能超过10级。
/*
* Reject too-deep include nesting depth. This is just a safety check to
* avoid dumping core due to stack overflow if an include file loops back
* to itself. The maximum nesting depth is pretty arbitrary.
*/
if (depth > 10)
{
ereport(elevel,
(errcode(ERRCODE_PROGRAM_LIMIT_EXCEEDED),
errmsg("could not open configuration file \"%s\": maximum nesting depth exceeded",
config_file)));
record_config_file_error("nesting depth exceeded",
calling_file, calling_lineno,
head_p, tail_p);
return false;
}
所有的配置保存在静态变量guc_variables中:
/*
* Actual lookup of variables is done through this single, sorted array.
*/
static struct config_generic **guc_variables;
config_generic结构如下:
/*
* Generic fields applicable to all types of variables
*
* The short description should be less than 80 chars in length. Some
* applications may use the long description as well, and will append
* it to the short description. (separated by a newline or '. ')
*
* Note that sourcefile/sourceline are kept here, and not pushed into stacked
* values, although in principle they belong with some stacked value if the
* active value is session- or transaction-local. This is to avoid bloating
* stack entries. We know they are only relevant when source == PGC_S_FILE.
*/
struct config_generic
{
/* constant fields, must be set correctly in initial value: */
const char *name; /* name of variable - MUST BE FIRST */
GucContext context; /* context required to set the variable */
enum config_group group; /* to help organize variables by function */
const char *short_desc; /* short desc. of this variable's purpose */
const char *long_desc; /* long desc. of this variable's purpose */
int flags; /* flag bits, see guc.h */
/* variable fields, initialized at runtime: */
enum config_type vartype; /* type of variable (set only at startup) */
int status; /* status bits, see below */
GucSource source; /* source of the current actual value */
GucSource reset_source; /* source of the reset_value */
GucContext scontext; /* context that set the current value */
GucContext reset_scontext; /* context that set the reset value */
GucStack *stack; /* stacked prior values */
void *extra; /* "extra" pointer for current actual value */
char *last_reported; /* if variable is GUC_REPORT, value last sent
* to client (NULL if not yet sent) */
char *sourcefile; /* file current setting is from (NULL if not
* set in config file) */
int sourceline; /* line in source file */
};
注意
几种不能设置参数的情况,未一一列举:
ereport(elevel,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_TRANSACTION_STATE),
errmsg("cannot set parameters during a parallel operation")));
case PGC_INTERNAL:
if (context != PGC_INTERNAL)
{
ereport(elevel,
(errcode(ERRCODE_CANT_CHANGE_RUNTIME_PARAM),
errmsg("parameter \"%s\" cannot be changed",
name)));
return 0;
}
break;
else if (context != PGC_POSTMASTER)
{
ereport(elevel,
(errcode(ERRCODE_CANT_CHANGE_RUNTIME_PARAM),
errmsg("parameter \"%s\" cannot be changed without restarting the server",
name)));
return 0;
}
case PGC_SIGHUP:
if (context != PGC_SIGHUP && context != PGC_POSTMASTER)
{
ereport(elevel,
(errcode(ERRCODE_CANT_CHANGE_RUNTIME_PARAM),
errmsg("parameter \"%s\" cannot be changed now",
name)));
return 0;
}
/*
* Hmm, the idea of the SIGHUP context is "ought to be global, but
* can be changed after postmaster start". But there's nothing
* that prevents a crafty administrator from sending SIGHUP
* signals to individual backends only.
*/
break;
case PGC_SU_BACKEND:
if (context == PGC_BACKEND)
{
/*
* Check whether the current user has been granted privilege
* to set this GUC.
*/
AclResult aclresult;
aclresult = pg_parameter_aclcheck(name, GetUserId(), ACL_SET);
if (aclresult != ACLCHECK_OK)
{
/* No granted privilege */
ereport(elevel,
(errcode(ERRCODE_INSUFFICIENT_PRIVILEGE),
errmsg("permission denied to set parameter \"%s\"",
name)));
return 0;
}
}
结构
其中涉及一些内存结构:
整体调用逻辑:
总结
这篇的内容比较多,有其是解析流程和参数设置的过程,这部分代码经过10几年的打磨,应该是很成熟了,但是面向过程的涉及显得代码有点冗长,后续看看openGauss对这部分的处理是否有改进。