mysql基础教学
mysql基础教学
-
- 1.安装MySQL
-
- 1.1 下载
- 1.2 安装
- 1.3 创建配置文件
- 1.4 初始化
- 2.启动MySQL
- 3.连接测试
-
- 3.1 设置密码
- 3.2 查看已有的文件夹(数据库)
- 3.3 退出(关闭连接)
- 3.4. 再连接MySQL
- 4.忘记密码
- 小结
- 5.MySQL指令
-
- 5.1 数据库管理(文件夹)
- 5.2 数据表的管理(文件)
- 5.3 数据行操作
-
- 1. 新增数据
- 2.删除数据
- 3.修改数据
- 4.查询数据
- 小结
- 6.案例:员工管理
-
- 6.1 创建表结构
- 6.2 Python操作MySQL
-
- 1.创建数据
- 2.查询数据
- 3.删除数据
- 4.修改数据
- 7.案例:Flask+MySQL
-
- 7.1 新增用户
- 7.2 查询所有用户
概要:
- MySQL安装 & 配置
- MySQL的启动和关闭
- 指令(*)
- Python第三方模块,发送指令并获取MySQL返回的结果。
各位小伙伴想要博客相关资料的话,关注公众号:chuanyeTry即可领取相关资料!
1.安装MySQL
MySQL,本质上就是一个软件。
1.1 下载
https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/
![]()
- MySQL压缩包
1.2 安装
mysql-8.1.0-winx64.zip 是免安装的版本。
- 解压zip文件
- 将解压后的文件夹放入路径(不要有中文路径)
![]()
1.3 创建配置文件
![]()
1.4 初始化
-
打开终端 & 以管理员的权限去运行
-
输入初始化的命令
"C:\Program Files\mysql-8.1.0-winx64\bin\mysqld.exe" --initialize-insecure
[mysqld]
port=3306
basedir=D:\\mysql//替换成自己地址
datadir=D:\\mysql\\data//替换成自己地址
![]()
至此,MySQL的安装已完成。
2.启动MySQL
启动MySQL一般有两种方式:
-
临时启动(不建议)
>>> "C:\Program Files\mysql-8.1.0-winx64\bin\mysqld.exe"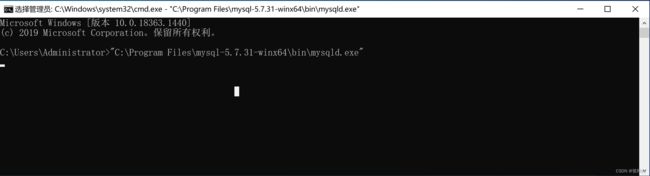
-
制作成Windows服务,服务来进行关闭和开启。
-
制作服务
"C:\Program Files\mysql-8.1.0-winx64\bin\mysqld.exe" --install mysql57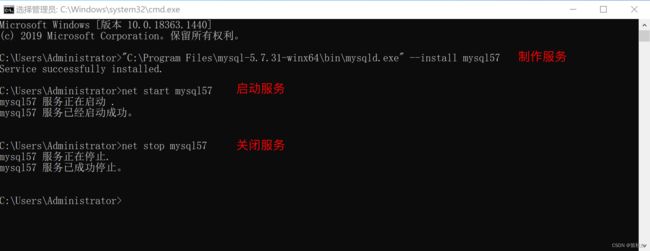
>>> net start mysql57 >>> net stop mysql57 -
启动和关闭服务
-
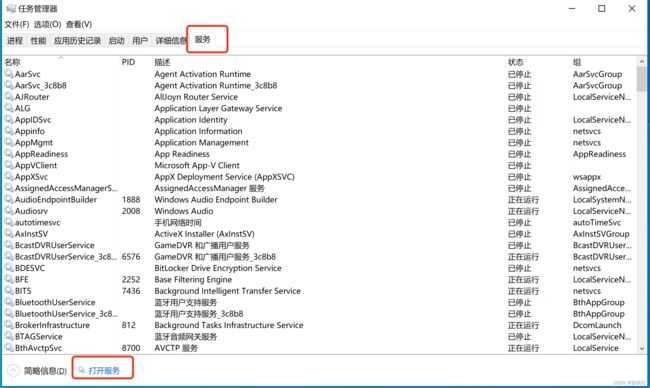
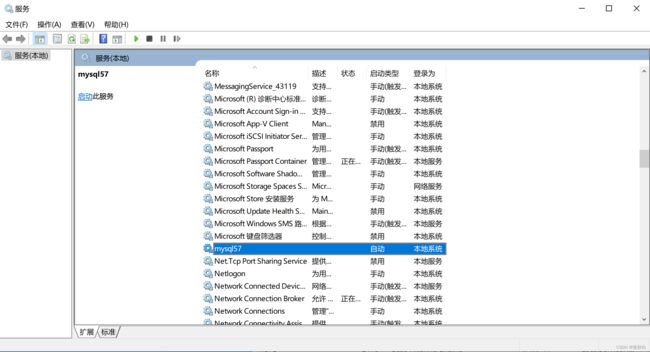
也可以在window的服务管理中点击按钮启动和关闭服务。例如:
-
3.连接测试
![]()
>>>"C:\Program Files\mysql-8.1.0-winx64\bin\mysql.exe" -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 -u root -p //127.0.0.1为连接的电脑ip, -P 3306为端口,-u为账号,
>>>"C:\Program Files\mysql-8.1.0-winx64\bin\mysql.exe" -u root -p
如果你将 C:\Program Files\mysql-8.1.0-winx64\bin\添加到了系统环境变量。
>>> mysql -u root -p
![]()
![]()
3.1 设置密码
set password = password('root123');
![]()
3.2 查看已有的文件夹(数据库)
show databases;
![]()
3.3 退出(关闭连接)
exit;
![]()
3.4. 再连接MySQL
![]()
汇总命令:
C:\Users\Administrator>mysql -u root -p
mysql> set password = password('root123');
mysql> show databases;
mysql> exit;
C:\Users\Administrator>mysql -u root -p
输入密码
mysql>exit;
4.忘记密码
默认情况下,启动MySQL时,需要用户输入账户名、密码。
修改MySQL配置,重新启动MySQL(无账号模式)
mysql -u root -p
重新设置密码
退出
再重新修MySQL配置文件,重新启动MySQL(需要账号的模式)
mysql -u root -p
新密码
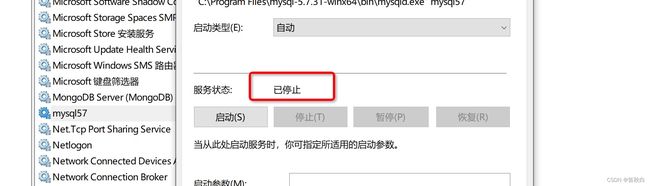
-
停止现在MySQL服务
-
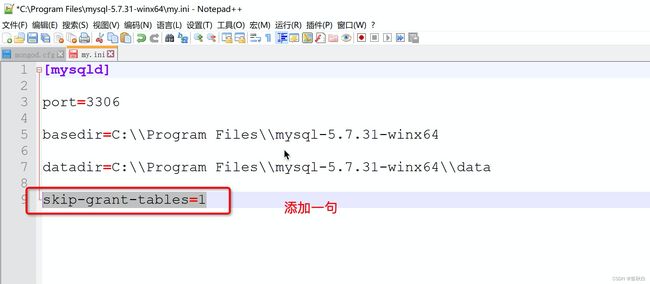
修改MySQL配置文件(以无账号模式)
-
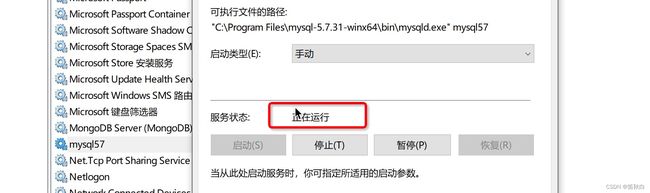
重新启动MySQL
-
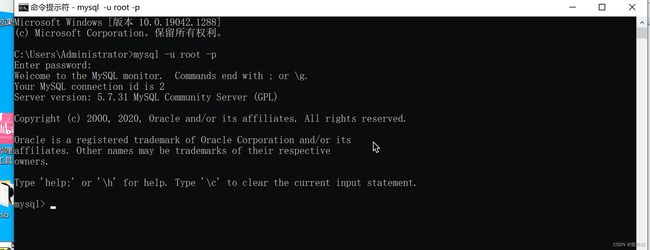
再次登录MySQL(无需密码)
-
执行命令设置密码
use mysql;update user set authentication_string = password('新密码'),password_last_changed=now() where user='root'; update user set authentication_string = password('root123'),password_last_changed=now() where user='root'; -
重新修改配置文件(需要账号的模式登录)【服务停掉】
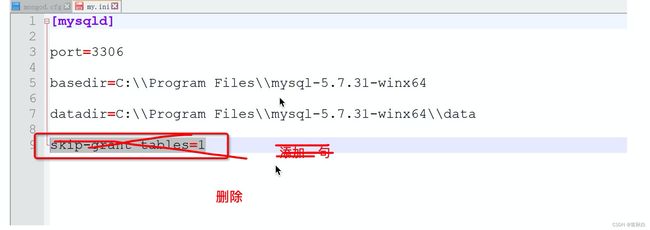
-
重新启动MySQL
-
登录时候输入新的密码即可。
小结
支持,MySQL的环境搭建相关的事全部搞定了。
- 安装
- 配置
- 启动
- 连接(密码、忘记密码)
以后我们再操作MySQL时:
-
关闭和开启MySQL服务
-
用MySQL自动工具连接MySQL并发送指令
myql -u root -p
接下来,我们的重点:
![]()
5.MySQL指令
![]()
在MySQL和我们平时认知不同的概念。
| MySQL | 认知 |
|---|---|
| 数据库 | 文件夹 |
| 数据表 | 文件(Excel文件) |
5.1 数据库管理(文件夹)
-
查看已有的数据库(文件夹)
show databases; -
创建数据库(文件夹)
create database 数据库名字 DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;monitor -
删除数据库(文件夹)
drop database gx_day14; -
进入数据库(进入文件夹)
use gx_day14; -
查看文件夹下所有的数据表(文件)
show tables;
5.2 数据表的管理(文件)
-
进入数据库(进入文件夹)
use 数据库; use gx_day14; -
查看当前数据库下的所有 表(文件)
show tables; -
创建表(文件文件)
create table 表名称( 列名称 类型, 列名称 类型, 列名称 类型 )default charset=utf8;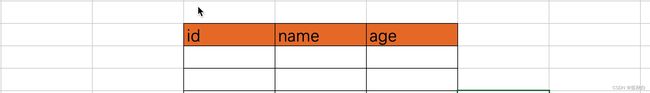
create table tb1(id int, name varchar(16),age int) default charset=utf8;//varchar(16)为字符串,最多存16个字符
mysql没有;号表示指令没有结束
create table tb1(
id int,
name varchar(16),
age int
) default charset=utf8;
create table tb1(
id int,
name varchar(16) not null, -- 不允许为空
age int null, -- 允许为空(默认)
) default charset=utf8;
create table tb1(
id int,
name varchar(16),
age int default 3 -- 插入数据时,age列的值默认3
) default charset=utf8;
create table tb1(
id int primary key, -- 主键(不允许为空,不允许重复)
name varchar(16),
age int
) default charset=utf8;
主键一般用于表示当前行的数据的编号(类似于人的身份证)。
create table tb1(
id int auto_increment primary key, -- 内部维护,自增
name varchar(16),
age int
) default charset=utf8;
一般情况下,我们再创建表时都会这样来写:【标准】
create table tb1(
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(16),
age int
) default charset=utf8;
mysql> desc tb1;
有几列 类型 是否为空 是否主键 是否自增 是否有默认值
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(16) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
删除表
drop table 表名称;
常用数据类型:
-
tinyint
有符号,取值范围:-128 ~ 127 (有正有负)【默认】 无符号,取值范围:0 ~ 255(只有正)create table tb2( id int not null auto_increment primary key, age tinyint -- 有符号:取值范围:-128 ~ 127 ) default charset=utf8;create table tb3( id int not null auto_increment primary key, age tinyint unsigned -- 无符号:取值范围:0 ~ 255 ) default charset=utf8; -
int
int 表示有符号,取值范围:-2147483648 ~ 2147483647 int unsigned 表示无符号,取值范围:0 ~ 4294967295 -
bigint
有符号,取值范围:-9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 无符号,取值范围:0 ~ 18446744073709551615练习题:
# 创建表 create table tb2( id bigint not null auto_increment primary key, salary int, age tinyint ) default charset=utf8; # 插入数据 insert into tb2(salary,age) values(10000,18);//salary为10000,age为18 insert into tb2(salary,age) values(20000,28); insert into tb2(salary,age) values(30000,38),(40000,40); # 查看表中的数据 select * from tb2;mysql> show tables; +--------------------+ | Tables_in_gx_day14 | +--------------------+ | tb1 | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> create table tb2( -> id bigint not null auto_increment primary key, -> salary int, -> age tinyint -> ) default charset=utf8; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) mysql> show tables; +--------------------+ | Tables_in_gx_day14 | +--------------------+ | tb1 | | tb2 | +--------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into tb2(salary,age) values(10000,18); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into tb2(salary,age) values(20000,28); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into tb2(salary,age) values(30000,38),(40000,40); Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from tb2; +----+--------+------+ | id | salary | age | +----+--------+------+ | 1 | 10000 | 18 | | 2 | 20000 | 28 | | 3 | 30000 | 38 | | 4 | 40000 | 40 | +----+--------+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
float
-
double
-
decimal
system clear
//清屏准确的小数值,m是数字总个数(负号不算),d是小数点后个数。 m最大值为65,d最大值为30。 decimal(m,d); 例如: create table tb3( id int not null primary key auto_increment, salary decimal(8,2) )default charset=utf8; insert into tb3(salary) values(1.28);//默认四舍五入 insert into tb3(salary) values(5.289); insert into tb3(salary) values(5.282); insert into tb3(salary) values(122115.11); select * from tb3; -
char(m),速度快。
定长字符串,m代表字符串的长度,最多可容纳255个字符。 char(11),固定用11个字符串进行存储,哪怕真是没有11个字符,也会按照11存储。 create table tb4( id int not null primary key auto_increment, mobile char(11) )default charset=utf8; insert into tb4(mobile) values("151"); insert into tb4(mobile) values("15131255555"); -
varchar(m),节省空间。
变长字符串,m代表字符的长度。 最大65535字节/3 = 最大的m//中文3个字节 varchar(11),真实数据有多少长久按照多长存储。 create table tb5( id int not null primary key auto_increment, mobile varchar(11) )default charset=utf8; insert into tb5(mobile) values("151"); insert into tb5(mobile) values("15131255555"); -
text
text数据类型用于保存变长的大字符串,可以组多到65535 (2**16 − 1)个字符。 一般情况下,长文本会用text类型。例如:文章、新闻等。 create table tb6( id int not null primary key auto_increment, title varchar(128), content text )default charset=utf8; -
mediumtext
A TEXT column with a maximum length of 16,777,215 (2**24 − 1) characters. -
longtext
A TEXT column with a maximum length of 4,294,967,295 or 4GB (2**32 − 1) -
datetime
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS(1000-01-01 00:00:00/9999-12-31 23:59:59) -
date
YYYY-MM-DD(1000-01-01/9999-12-31)
练习题:用户表
create table tb7(
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(64) not null,
password char(64) not null,
email varchar(64) not null,
age tinyint,
salary decimal(10,2),
ctime datetime
)default charset=utf8;
insert into tb7(name,password,email,age,salary,ctime) values("武沛齐","123","[email protected]",19,1000.20,"2011-11-11 11:11:10");
insert into tb7(name,password,email,age,salary,ctime) values("张电摩","123","[email protected]",19,1000.20,"2011-11-11 11:11:10");
insert into tb7(name,password,email,age,salary,ctime) values("庞小青","123","[email protected]",19,1000.20,"2011-11-11 11:11:10");
insert into tb7(name,password,email,age,salary,ctime) values("谢涛","123","[email protected]",19,1000.20,"2011-11-11 11:11:10");
insert into tb7(name,password,email,age,salary,ctime) values("谢鹏","123","[email protected]",19,1000.20,"2011-11-11 11:11:10");
select * from tb7;
+----+-----------+----------+-------------+------+---------+---------------------+
| id | name | password | email | age | salary | ctime |
+----+-----------+----------+-------------+------+---------+---------------------+
| 1 | 武沛齐 | 123 | xx@live.com | 19 | 1000.20 | 2011-11-11 11:11:10 |
+----+-----------+----------+-------------+------+---------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL还有很多其他的数据类型,例如:set、enum、TinyBlob、Blob、MediumBlob、LongBlob 等,详细见官方文档:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/data-types.html
我们平时开发系统时,一般情况下:
- 创建数据库
- 创建表结构
都是需要提前通过上述命令创建。
5.3 数据行操作
1. 新增数据
insert into 表名(列名,列名) values(值,值);
insert into 表名(列名,列名) values(值,值),(值,值),(值,值),(值,值);//新增多行数据。
2.删除数据
delete from 表名;
delete from 表名 where 条件;//符合条件删除
delete from tb7;
delete from tb7 where id = 3;//id为3删除
delete from tb7 where id = 4 and name="谢涛";//id为4并且name为谢涛的数据删除
delete from tb7 where id = 4 or name="谢涛";
delete from tb7 where id > 4;
delete from tb7 where id >= 4;
delete from tb7 where id != 4;
delete from tb7 where id in (1,5);//删除1和5的删除
3.修改数据
update 表名 set 列=值;
update 表名 set 列=值,列=值;
update 表名 set 列=值 where 条件;
update tb7 set password="哈哈哈";//表中password这一列全部改为哈哈哈
update tb7 set email="哈哈哈" where id > 5;//表中idda大于5的Email这列数据全部改为哈哈哈
update tb7 set age=age+10 where id > 5;
4.查询数据
select * from 表名称;
select 列名称,列名称 from 表名称;
select 列名称,列名称 from 表名称 where 条件;
select * from tb7;
select id,name from tb7;//展示id,name两列。
select id,name from tb7 where id > 10;//满足条件展示
select id,name from tb7 where name="xx" and password="xx";
小结
我们平时开发系统时,一般情况下:
- 创建数据库
- 创建表结构
都是需要提前通过工具+命令创建。
但是,表中的数据一般情况下都是通过程序来实现增删改查。
6.案例:员工管理
-
使用MySQL内置工具(命令)
-
创建数据库:unicom
-
数据一张表:admin
表名:admin 列: id,整型,自增,主键。 username 字符串 不为空, password 字符串 不为空, mobile 字符串 不为空
-
-
Python代码实现:
- 添加用户
- 删除用户
- 查看用户
- 更新用户信息
![]()
6.1 创建表结构
create database unicom DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
use unicom;
create table admins(
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
username varchar(16) not null,
password varchar(64) not null,
mobile char(11) not null
) default charset=utf8;
6.2 Python操作MySQL
用Python代码连接MySQL并发送指令。
pip install pymysql
1.创建数据
import pymysql
# 1.连接MySQL host=localhost
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="root123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')//连接当前主机,端口,用户名,密码,编码方式,数据表
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)//收发数据的工具
# 2.发送指令
cursor.execute("insert into admins(username,password,mobile) values('wupeiqi','qwe123','15155555555')")//cursor.execute为发送一行指令,创建一行数据//生成命令
conn.commit()//提交命令
# 3.关闭
cursor.close()
conn.close()
import pymysql
# 1.连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="root123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 2.发送指令(千万不要用字符串格式化去做SQL的拼接,安全隐患SQL注入)不能做format或%格式化
# sql = "insert into admin(username,password,mobile) values(%s,%s,%s)"
# cursor.execute(sql, ["韩超", "qwe123", "1999999999"])
# sql = "insert into admin(username,password,mobile) values( %(n1)s, %(n2)s, %(n3)s)"//这样也可以,不过只能传字典
# cursor.execute(sql, {"n1": "集宁", "n2": "qwe123", "n3": "1999999999"})
conn.commit()
# 3.关闭
cursor.close()
conn.close()
import pymysql
while True:
user = input("用户名:")
if user.upper() == 'Q':
break
pwd = input("密码:")
mobile = input("手机号:")
# 1.连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="root123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 2.发送指令(千万不要用字符串格式化去做SQL的拼接,安全隐患SQL注入)
sql = "insert into admin(username,password,mobile) values(%s,%s,%s)"
cursor.execute(sql, [user, pwd, mobile])
conn.commit()
# 3.关闭
cursor.close()
conn.close()
2.查询数据
import pymysql
# 1.连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 2.发送指令( *** 千万不要用字符串格式化去做SQL的拼接,安全隐患SQL注入***)
cursor.execute("select * from admins where id > %s", [2, ])
# 获取符合条件的所有数据,得到的是 [ 字典,字典, ] 空列表
data_list = cursor.fetchall()
# //获取数据库返回回来的值,data_list是一个列表
for row_dict in data_list:
print(row_dict)
# 3.关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
import pymysql
# 1.连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="root123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 2.发送指令( *** 千万不要用字符串格式化去做SQL的拼接,安全隐患SQL注入***)
cursor.execute("select * from admin where id > %s", [2, ])
# 获取符合条件的第一条数据,字典 没有数据则None
res = cursor.fetchone()
print(res) # {'id': 3, 'username': '集宁', 'password': 'qwe123', 'mobile': '1999999999'}
# 3.关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
3.删除数据
import pymysql
# 1.连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="root123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 2.发送指令( *** 千万不要用字符串格式化去做SQL的拼接,安全隐患SQL注入***)
cursor.execute("delete from admin where id=%s", [3, ])
# 删除id为3的数据
conn.commit()
# 3.关闭
cursor.close()
conn.close()
4.修改数据
import pymysql
# 1.连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user='root', passwd="root123", charset='utf8', db='unicom')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 2.发送指令( *** 千万不要用字符串格式化去做SQL的拼接,安全隐患SQL注入***)
cursor.execute("update admin set mobile=%s where id=%s", ["1888888888", 4, ])
# 修改数据id为4的mobile数据
conn.commit()
# 3.关闭
cursor.close()
conn.close()
强调:
-
在进行 新增、删除、修改时,一定要记得commit,不然数据库么有数据。
cursor.execute("..") conn.commit() -
在查询时,不需要commit,执行fetchall / fetchone
cursor.execute("...") # 第一条数据,字典,无数据时是空列表 v1 = cursor.fetchone() # 所有数据,列表套字典,无数据时是None v1 = cursor.fetchall() -
对于SQL语句不要用Python的字符串格式化进行拼接(会被SQL注入),一定要用execute+参数
cursor.execute(".%s..... %s", ["xx","xx"])
7.案例:Flask+MySQL
7.1 新增用户
补充代码实现
7.2 查询所有用户
![]()