第十六周-day65-shell编程day02
友情链接:ZeroOne01
https://blog.51cto.com/zero01/2046242?tdsourcetag=s_pctim_aiomsg
1.运算符与运算命令
[root@shell scripts]# a=8
[root@shell scripts]# echo $((a%6))
2
[root@shell scripts]# echo $a
8
[root@shell scripts]# echo $((a%=6))
2
[root@shell scripts]# echo $a
2
练习取值
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 1+1 | bc
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 3.3*8.7 | bc
28.7
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo "scale=4;3.3*8.7" | bc
28.71
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo "scale=4;3.33*8.7" | bc
28.971
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo "scale=4;3.333*8.7" | bc
28.9971
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo "scale=4;3.3333*8.7" | bc
28.9997
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo "scale=10;3.3333*8.7" | bc
28.99971
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 1 2 | awk '{print $1}'
1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 1 2 | awk '{print $1+$2}'
3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 3.4 2 | awk '{print $1+$2}'
5.4
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 3.4 2.444444 | awk '{print $1+$2}'
5.84444
[root@oldboyedu ~]# let a=1+1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# let a=1.1+1
-bash: let: a=1.1+1: syntax error: invalid arithmetic operator (error token is ".1+1")
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $?
1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 1 + 1
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $?
0
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 1.1 + 1
expr: non-integer argument
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $?
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 3/2 | bc
1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((2**3))
8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# let a=2**3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $a
8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# let b=2**3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $b
8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 ** 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 * * 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 \** 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 \*\* 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr "2 ** 3"
2 ** 3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 "**" 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 ^ 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 2 \^ 3
expr: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $[2**3]
8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# declare -i c=2**3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $c
8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 2**3 | bc
(standard_in) 1: syntax error
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo 2^3 | bc
8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# a=1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo a++
a++
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((a++))
1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((a++))
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((a++))
3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((a++))
4
[root@oldboyedu ~]# a=1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((++a))
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((++a))
3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((++a))
4
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((++a))
5
[root@oldboyedu ~]#
[root@oldboyedu ~]# a=1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# b=1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# x=a++
[root@oldboyedu ~]# y=++b
[root@oldboyedu ~]#
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo a
a
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $a
1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $x
a++
[root@oldboyedu ~]# x=$((a++))
[root@oldboyedu ~]# y=$((++b))
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $a
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# a=1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# b=1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# x=$((a++))
[root@oldboyedu ~]# y=$((++b))
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $a
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $x
1
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $b
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $y
2
[root@oldboyedu ~]# 8%5
-bash: 8%5: command not found
[root@oldboyedu ~]# expr 8 % 5
3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# a=8
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((a%=5))
3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $a
3
[root@oldboyedu ~]# echo $((a=a%5))
3
2. 使用脚本传参的方式实现整数的加、减、乘、除、取余、幂运算
x=$1
y=$2
echo 1.利用'$(())'计算
echo 加:$1\+$2="$(($x+$y))"
echo 减:$1\-$2="$(($x-$y))"
echo 乘:$1\*$2="$(($x*$y))"
echo 除:$1\/$2="$(($x/$y))"
echo 幂:$1\**$2="$(($x**$y))"
echo 余:$1\%$2="$(($x%$y))"
echo 2.利用awk计算
echo 加:$1+$2=`awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x+y}"`
echo 减:$1+$2=`awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x-y}"`
echo 乘:$1+$2=`awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x*y}"`
echo 除:$1+$2=`awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x/y}"`
echo 幂:$1+$2=`awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x**y}"`
echo 余:$1+$2=`awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x%y}"`
[root@shell scripts]# sh bc03.sh 2 6
1.利用$(())计算
加:2+6=8
减:2-6=-4
乘:2*6=12
除:2/6=0
幂:2**6=64
余:2%6=2
2.利用awk计算
加:2+6=8
减:2+6=-4
乘:2+6=12
除:2+6=0.333333
幂:2+6=64
[root@shell scripts]# cat bc02.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: bc03.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
x=$1
y=$2
echo="echo $1 $2"
echo 1.利用'$(())'计算
echo 加:$1\+$2="$(($x+$y))"
echo 减:$1\-$2="$(($x-$y))"
echo 乘:$1\*$2="$(($x*$y))"
echo 除:$1\/$2="$(($x/$y))"
echo 幂:$1\**$2="$(($x**$y))"
echo 余:$1\%$2="$(($x%$y))"
echo '###################'
echo 2.利用awk计算
echo 加:$1+$2=`$echo|awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x+y}"`
echo 减:$1+$2=`$echo|awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x-y}"`
echo 乘:$1+$2=`$echo|awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x*y}"`
echo 除:$1+$2=`$echo|awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x/y}"`
echo 幂:$1+$2=`$echo|awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x**y}"`
echo 余:$1+$2=`$echo|awk -vx=$x -vy=$y "BEGIN{print x%y}"`
[root@shell scripts]# sh bc02.sh 6 3
1.利用$(())计算
加:6+3=9
减:6-3=3
乘:6*3=18
除:6/3=2
幂:6**3=216
余:6%3=0
###################
2.利用awk计算
加:6+3=9
减:6+3=3
乘:6+3=18
除:6+3=2
幂:6+3=216
余:6+3=0
3.条件测试表达式
3.2 文件测试表达式
[root@shell scripts]# test -L "/bin/sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -s "/bin/sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -d "/root" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -x "ip.sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture #文件可执行
[root@shell scripts]# test -x "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false #文件不可执行
[root@shell scripts]# test ! -x "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture #取反
[root@shell scripts]# test -s "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture #文件存在非空
[root@shell scripts]# test ! -s "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false #取反
##############
#测试表达式
##############
[root@shell scripts]# test -f "/etc/hosts" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -f "/etc/host" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell scripts]# test -e "/etc/" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -e "/etcetc/" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell scripts]# test -d "/etc/hosts" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell scripts]# test -d "/etc/" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -L "/bin/sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -L "/bin/ls" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell scripts]# test -s "1.sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# touch 2.sh
[root@shell scripts]# test -s "2.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false
############
#取反
############
[root@shell scripts]# test ! -x "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture #取反
[root@shell scripts]# test -s "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
ture #文件存在非空
[root@shell scripts]# test ! -s "bc.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false #取反
######################
#测试文件可读可写可执行
######################
[root@shell scripts]# su - oldboy #切换到普通用户下
Last login: Thu May 16 17:01:19 CST 2019 on pts/0
[oldboy@shell ~]$
[oldboy@shell ~]$ test -r "test_01.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false
[oldboy@shell ~]$ test -w "test_01.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false
[oldboy@shell ~]$ test -x "test_01.sh" && echo ture||echo false
false
练习
采坑:
read读入方式定义的变量写为$1 $2了,与取参的$1 $2冲突了
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-1.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: testday2-1.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
read -p "请输入两个文件的路径: " a b
[ -f $a ]&& echo $a||{
echo "第一个文件${a}不存在"
}
[ -f $b ]&& echo $b||{
echo "第二个文件${b}不存在"
exit
}
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-2.sh
请输入两个文件的路径: xxx yyy
第一个文件xxx不存在
第二个文件yyy不存在
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-2.sh
请输入两个文件的路径: bc.sh xxx
bc.sh
第二个文件xxx不存在
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-2.sh
请输入两个文件的路径: xxx bc.sh
第一个文件xxx不存在
bc.sh
#2.0版 自动化
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-1-1.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入指定文件路径: " file
for f in `echo $file`
do
[ -f $f ]&&echo ${file}存在||{
echo "${f}不存在"
}
done
[root@shell scripts]# sh 1.sh
请输入指定文件路径: /server/scripts/1.sh /etc/hosts /etc/hostname
/server/scripts/1.sh /etc/hosts /etc/hostname存在
/server/scripts/1.sh /etc/hosts /etc/hostname存在
/server/scripts/1.sh /etc/hosts /etc/hostname存在
3.3 字符串测试表达式
#################
#判断变量是否存在
#################
[root@shell ~]# a=111
[root@shell ~]# b=1111
[root@shell ~]# test "$a" = "$b" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell ~]# test "$a"="$b" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell ~]# echo $a
111
[root@shell ~]# echo $b
1111
[root@shell scripts]# test -n "$a" && echo ture||echo false
ture
[root@shell scripts]# test -z "$a" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell scripts]# echo $a
123
[root@shell scripts]# unset a
[root@shell scripts]# test -n "$a" && echo ture||echo false
false
[root@shell scripts]# test -z "$a" && echo ture||echo false
ture
※3.4 练习
1. 方法第一种
#第二种
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-3-2.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 判断传入参数的个数
[ "$#" != "2" ] && {
echo "参数必须为2 Usage <$0 arg1 arg2>"
exit 1
}
# 判断传参是否为整数
expr $1 + $2 + 1 &> /dev/null
[ "$?" != "0" ] && {
echo "参数必须为整数"
exit 2
}
echo -n '相加: '; echo $(($1+$2))
echo -n '相减: '; echo $(($1-$2))
echo -n '相乘: '; echo $(($1*$2))
echo -n '幂运算: '; echo $(($1**$2))
# 判断除数是否为0
[ "$2" = "0" ] && {
echo "除数必须不能为0!!!"
exit 3
}
echo -n '相除: '; echo $(($1/$2))
echo -n '取余: '; echo $(($1%$2))
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-3-2.sh 5 6.1
参数必须为整数
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-3-2.sh 5 6 7
参数必须为2 Usage
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-3-2.sh 5 0
相加: 5
相减: 5
相乘: 0
幂运算: 1
除数必须不能为0!!!
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-3-2.sh 6 3
相加: 9
相减: 3
相乘: 18
幂运算: 216
相除: 2
取余: 0
2.方法第二种
#第三种 read读入默认2个参数
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-5.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: testday2-5.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
read -p "请输入需要计算的内容:" m n
# 判断传参是否为整数
expr $m + $n + 1 &> /dev/null
[ "$?" != "0" ] && {
echo "参数必须为整数"
exit 2
}
echo -n '相加: '; echo $(($m+$n))
echo -n '相减: '; echo $(($m-$n))
echo -n '相乘: '; echo $(($m*$n))
echo -n '幂运算: '; echo $(($m**$n))
# 判断除数是否为0
[ "$n" = "0" ] && {
echo "除数必须不能为0!!!"
exit 3
}
echo -n '相除: '; echo $(($m/$n))
echo -n '取余: '; echo $(($m%$n))
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-5.sh
请输入需要计算的内容:5 6 7
参数必须为整数
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-5.sh
请输入需要计算的内容:5 6.1
参数必须为整数
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-5.sh
请输入需要计算的内容:5 0
相加: 5
相减: 5
相乘: 0
幂运算: 1
除数必须不能为0!!!
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-5.sh
请输入需要计算的内容:4 6
相加: 10
相减: -2
相乘: 24
幂运算: 4096
相除: 0
取余: 4
4. 整数二元比较操作符
查看当前磁盘/当前状态,如果使用率超过10%,则触发报警发邮件
[root@shell scripts]# df -h|awk 'NR==2{print $(NF-1)}'
11%
[root@shell scripts]# df -h|awk 'NR==2{print $(NF-1)}'
11%
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-6.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: testday2-6.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
#查看当前磁盘/当前状态,如果使用率超过10%,则触发报警发邮件
use=`df -h|awk 'NR==2{print $(NF-1)}'`
userNum=${use/\%/}
[ $userNum -gt 10 ] && {
echo "shell服务器磁盘使用率超过$use"
echo "shell服务器磁盘使用率超过$use"|mail -s "磁盘不足" [email protected]
}
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-6.sh
shell服务器磁盘使用率超过11%
image.png
查看内存使用状况,如果占用超过10%,则触发报警
[root@shell day02]# cat testday2-7.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: testday2-7.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
#查看内存使用状况,如果占用超过10%,则触发报警
free=`free -h|awk 'NR==2{print $3/$2*100}'`
freeNum=${free/.*/}
[ $freeNum -gt 5 ] && {
echo "shell服务器内存使用率超过${freeNum}%"
echo "shell服务器内存使用率超过${freeNum}%"|mail -s "内存不足" [email protected]
}
[root@shell day02]# sh testday2-7.sh
shell服务器内存使用率超过9%
5.逻辑操作符
#练习查看结果
# [ -f ip.sh -a 2 -lt 3 ]&& echo 0||echo 1
0
# [ -f ip.sh -a 2 -lt 3 -a 5 -gt 6 ]&& echo 0||echo 1
1
# [ -f ip.sh -o 2 -gt 3 ]&& echo 0||echo 1
0
# [ -f ip1.sh -o 2 -gt 3 ]&& echo 0||echo 1
1
# [ ! -f ip1.sh -o 2 -gt 3 ]&& echo 0||echo 1
0
# [ -f ip.sh ] && [ 2 -lt 3 ] && [ 2 -lt 3 ]&&echo 0||echo 1
0
# [ -f ip.sh ] && [ 2 -lt 3 ] && [ 2 -eq 3 ]&&echo 0||echo 1
1
# [ -f ip.sh ] && [ 2 -lt 3 ] && [ 2 -lt 3 ]&&echo 0||echo 1
0
# [[ -f ip.sh ]] && [[ 2 -lt 3 ]] && [[ 3 -gt 2 ]]&&echo 0||echo 1
0
6. 练习
1、 输入或者通过命令传入一个字符或者数字,如果传入的数字等于1就打印1,如果等于2就打印2;如果不等于1也不等于2,就提示输入不对,然后退出程序。(两种比较方式任选其一:数字比较或字符串比较)
[root@shell day02]# cat testday2-10.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: testday2-10.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
read -p "请输入一个字符或者数字:" a
[ $a -eq 1 ]&& {
echo $a
exit 0
}||
[ $a -eq 2 ]&& {
echo $a
exit 0
}||
echo 输入错误!
exit 1
}
#[ $a -ne 1 -a $a -ne 2 ]&& echo 输入错误!
[root@shell day02]# sh testday2-10.sh
请输入一个字符或者数字:1
1
[root@shell day02]# sh testday2-10.sh
请输入一个字符或者数字:2
2
[root@shell day02]# sh testday2-10.sh
请输入一个字符或者数字:3
输入错误!
2、 开发shell脚本,分别以脚本传参方式和read读入方式比较两个整数大小,用条件表达式(禁止if)进行判断并以屏幕输出的方式提醒用户比较结果。(一共需要开发2个脚本,在传参和read读入方式实现时,需要对变量是否为数字及传参个数是否正确给予提示)
1)判断是否是两个参数
2)判断是否为整数
3)[ 2 -gt 3 ] && echo “2大于3”|| echo “2等于3”|| echo “2小于3“
第一种read读入方式
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-8.sh
#!/bin/bash
#read读入方式
read -p "请输入两个整数: " a b
#判断是否为整数
expr $a + $b &> /dev/null
[ $? -eq 0 ]&& echo 参数正确!||{
echo "参数必须为整数"
exit 2
}
[ $a -gt $b ]&& {
echo "数值对比: [$a] > [$b]"
}||{
[ $a -lt $b ]&& {
echo "数值对比: [$a] < [$b] "
}||{
[ $a -eq $b ]&& {
echo "数值对比: [$a] = [$b]"
}
}
}
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-8.sh
请输入两个整数: 5 6
参数正确!
数值对比: [5] < [6]
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-8.sh
请输入两个整数: 8 1
参数正确!
数值对比: [8] > [1]
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-8.sh
请输入两个整数: 8 8
参数正确!
数值对比: [8] = [8]
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-8.sh
请输入两个整数: 2.1 1
参数必须为整数
第二种传参方式
[root@shell scripts]# cat testday2-9.sh
#!/bin/bash
#传参方式
#判断是否是两个参数
[ $# -ne 2 ]&&{
echo "请输入两个参数进行对比!"
exit
}
#判断是否为整数
expr $1 + $2 &> /dev/null
[ $? -eq 0 ]&& echo 参数正确!||{
echo "参数必须为整数"
exit
}
#数值对比
[ $1 -gt $2 ]&& {
echo "数值对比: [$1] > [$2]"
}
[ $1 -lt $2 ]&& {
echo "数值对比: [$1] < [$2] "
}
[ $1 -eq $2 ]&& {
echo "数值对比: [$1] = [$2]"
}
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-9.sh 8 8
参数正确!
数值对比: [8] = [8]
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-9.sh 8 6
参数正确!
数值对比: [8] > [6]
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-9.sh 6 8
参数正确!
数值对比: [6] < [8]
[root@shell scripts]# sh testday2-9.sh 6 8.1
参数必须为整数
3、 打印菜单,按照选择项选择你喜欢的美女
示例菜单:
[root@oldboy scripts]# sh meinv.sh 1.heijiajia 2.高圆圆 3.蔡徐坤 please input the num you like:要求:
1)当用户输入1时,输出“I guess you like heijiajia”,然后退出脚本
2)当用户输入非1-3的字符时,输出“I guess you are not man”,然后退出脚本
[root@shell scripts]# cat caidan.sh
#!/bin/bash
prefix="I guess you like "
#菜单
cat <7.Shell练习作业
1.检查OSPF route-ID配置,配置如下,请用shell编写代码,条件如下:
检查OSPF route-ID配置,配置如下,请用shell编写代码,条件如下:
1、检查ospf的route-id值
2、route-id值必须与interface LoopBack0的IP地址值相同
grep -A 1 "interface LoopBack0" 3.txt | sed -n '$p' | awk '{print $3}
3、如果两个值不相等,或ospf的route-id值不以139开头,则打印出route-id的值
ofpf 100
route-id 139.11.0.1
area 0.0.0.0
network 139.11.0.1 0.0.0.0
network 140.11.0.0 0.0.0.3
network 140.11.0.8 0.0.0.3
network 140.11.0.16 0.0.0.3
network 140.11.0.24 0.0.0.3
network 140.11.0.32 0.0.0.3
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 139.11.0.1 255.255.255.255
#
[root@shell day02]# vim zuoye01.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 ##############################################################
3 # File Name: zuoye01.sh
4 # Version: V1.0
5 # Author: lcx
6 # Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
7 ##############################################################
8 #ospf route-ID配置文件路径/server/scripts/day02/3.txt
9 dir=/server/scripts/day02/3.txt
10 routeID=`cat $dir |awk 'NR==2{print $2}'`
11 interfaceIP=`grep -A 1 "interface LoopBack0" $dir|awk 'NR==2{print $3}'`
12 routeIPhead=`cat $dir |awk -F"[ .]+" 'NR==2{print $2}'`
13 head="139"
14 #检查ospf的route-id值
15 echo "osps的route-id为: $routeID"
16 #检查route-id与interface LoopBack0IP是否相同
17 [ "$routeID" != "$interfaceIP" ]&&{
18 echo "1.IP与ID不相等 IP为:$interfaceIP ID为$routeID"
19 }
20 [ "$routeIPhead" != "139" ]&&{
21 echo "2.route-id的值不是139开头 routeID为:$routeID"
22 }
[root@shell day02]# sh zuoye01.sh
osps的route-id为: 239.11.0.1
1.IP与ID不相等 IP为:139.11.0.1 ID为239.11.0.1
2.route-id的值不是139开头 routeID为:239.11.0.1
[root@shell day02]# sh zuoye01.sh
osps的route-id为: 139.11.0.1
2.处理以下文件内容,将域名提取并进行计数排序,如处理:
处理以下文件内容,将域名提取并进行计数排序,如处理:
http://www.baidu.com/index.html
http://www.baidu.com/1.html
http://post.baidu.com/index.html
http://mp3.baidu.com/index.html
http://www.baidu.com/3.html
http://post.baidu.com/2.html
得到如下结果:
域名的出现次数 域名
3 www.baidu.com
2 post.baidu.com
1 mp3.baidu.com
思路:
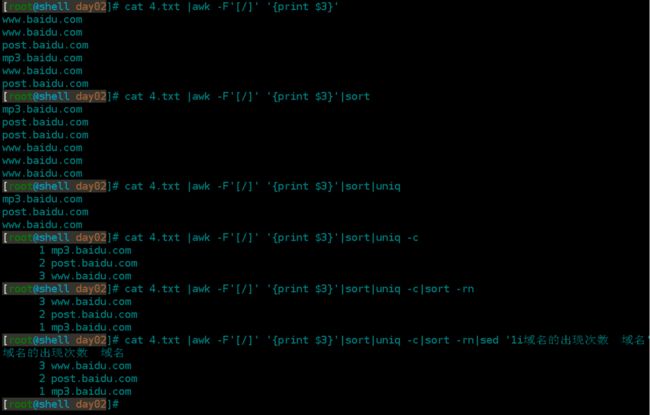
[root@shell day02]# cat 4.txt |awk -F'[/]' '{print $3}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -rn|sed '1i域名的出现次数 域名'
域名的出现次数 域名
3 www.baidu.com
2 post.baidu.com
1 mp3.baidu.com
3.打印菜单,按照选择项一键安装不同的web服务
打印菜单,按照选择项一键安装不同的web服务
示例菜单:
[root@oldboy scripts]# sh menu.sh
1.[install lnmp]
2.[install lamp]
3.[exit]
please input the num you want:
要求:
1)当用户输入1时,输出“start installing lamp提示”,然后执行/server/scripts/lamp.sh,(执行方式使用全路径方式执行)。
脚本内容输出“lamp is installed”并退出脚本,此为工作中的一键安装lamp脚本
2)当用户输入2时,输出“start installing lnmp提示”,然后执行/server/scripts/lnmp.sh, (执行方式使用 全路径方式执行)。
脚本内容输出“lnmp is installed”并退出脚本,此为工作中的一键安装lnmp脚本
3)当输出3时,退出当前菜单及脚本
4)当用户输入非1-3的字符时,输出“Input Error”,然后退出脚本
5)对执行的脚本进行相关的条件判断,例如:脚本是否存在,是否可执行等操作,尽量使用今天讲的知识点
#技术水平有限,不求精简只求实现
[root@shell day02]# cat zuoye02.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: zuoye02.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
#检测脚本是否存在且非空,是否可执行
file1=`[ -s /server/scripts/lamp.sh ]&& echo ture||echo fluse`
file2=`[ -s /server/scripts/lnmp.sh ]&& echo ture||echo fluse`
exec1=`[ -x /server/scripts/lamp.sh ]&& echo ture||echo fluse`
exec2=`[ -x /server/scripts/lnmp.sh ]&& echo ture||echo fluse`
[ $file1 = "ture" ]&& echo lamp.sh脚本文件存在且非空||{
echo "lamp.sh脚本文件不存在或是一个空文件!!!"
}&&{
[ $exec1 = "ture" ]&& echo lamp.sh脚本文件可以执行||{
echo "lamp.sh脚本文件不可执行!!!"
}&&{
[ $file2 = "ture" ]&& echo lnmp.sh脚本文件存在且非空||
echo -eq "lnmp.sh脚本文件不存在或是一个空文件!!!"
}&&{
[ $exec2 = "ture" ]&& echo lnmp.sh脚本文件可以执行||{
echo "lnmp.sh脚本文件不可执行!!!"
exit
}
}
}
#打印菜单,按照选择项一键安装不同的web服务
cat <测试结果