单向循环链表练习
链表课后练习
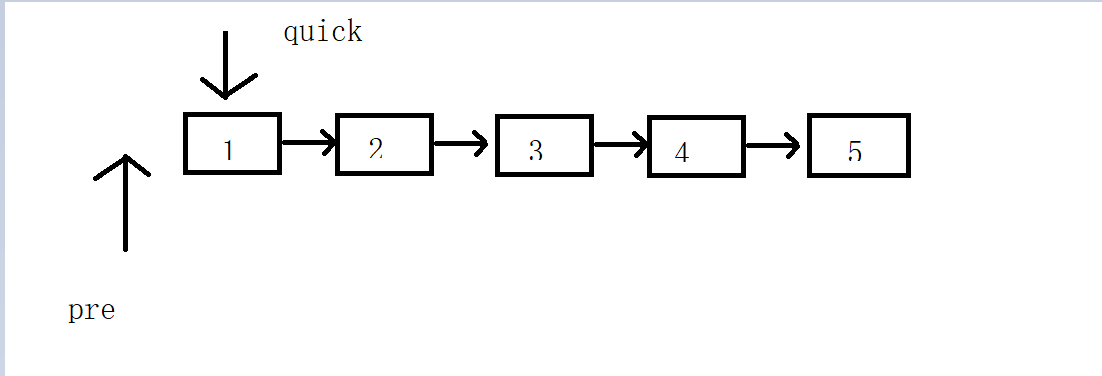
203. 移除链表元素
使用一个指针代表前一个,一个指针向后移动,循环当quick没走到尾时,如果quick指向的值和val相等,判断pre是否指向的时NULL,如果pre为NULL,那就说明目前没有符合条件的节点,这个节点也是没用的,将quick指向quick的下一个节点,将head也指向quick的下一个节点,如果pre不为NULL,说明目前已经有符合条件的节点了,那么pre->next=quick,所以将pre->next设置为quick->next,quick=pre->next,因为这个节点是不符合要求的。如果quick指向的值和val不相等,直接将pre指向quick,将quick指向quick->next。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = head;
while(tail){
if(tail->val==val)
{
if(pre)
{ //3
pre->next=tail->next;
free(tail);
tail=pre->next;
}
else
{
struct ListNode* tmp = tail->next;
free(tail);
tail = tmp;
head = tmp; //1
}
}
else{
pre = tail;//2
tail = tail->next;
}
}
return head;
}
没给pre赋值前,一直将head向后移动,直到pre有值。
牛客 链表中倒数第k个结点
使用快慢指针,让quick指针先走k-1步(因为k>=1),slow指针不动,那么quick与slow的距离就是k-1,最后quick会移动到倒数第一个。slow就是倒数第1+k-1个,要注意判断,如果quick指针在第一次单独走时候变成了NULL,那么k一定是不合法的。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
#include 142. 环形链表 II
使用两个指针fast和slow,slow每回合走一步,fast每次走两步。假设从链表的头到环形列表的入口(不包括入口)有a个节点,链表的环有b个节点,两个指针一定会在环内相遇,走过的路程一定相差环的整数倍。如果fast走过的路程为f,slow为s,可以得出
f = 2 s f=2s f=2s
f − s = N ∗ b f-s=N*b f−s=N∗b
联立计算出
s = N ∗ b s=N*b s=N∗b
如果要让指针指向环的头节点,必须要让指针slow走a+nb步。两指针相遇时,slow已经走了nb步,所以只需要让fast移动到链表的头,当fast==slow时,slow就是环形链表的第一个头节点。
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode* f=head,*s=head;
struct ListNode* p = head;
while(f!=NULL)
{
f=f->next;
if(f==NULL)return NULL;
f=f->next;
s=s->next;
if(s==f)
{
s=head;
while(s!=f)
{
s=s->next;
f=f->next;
}
return s;
}
}
return NULL;
}
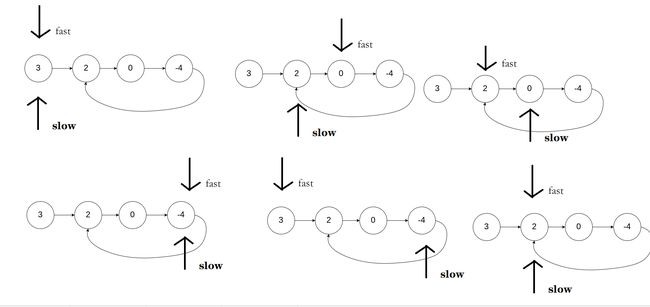
141. 环形链表
和环形链表2一样。使用fast和slow一快一慢,循环判断,如果快指针为NULL那就说明没有环,如果两个指针指向同一位置,返回true。注意判断f->next的空指针。
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode *f = head,*s=head;
while(f)
{
f=f->next;
if(!f)return false;
f=f->next;
s=s->next;
if(f==s)return true;
}
return false;
}
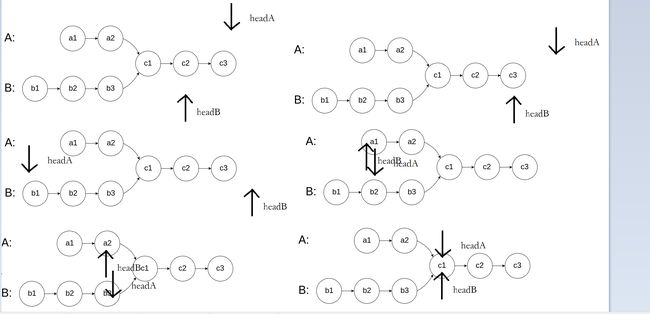
160. 相交链表
设第一个链表的长度为a,第二个链表的长度b,链表共同的长度为c,定义两个指针分别为headA与headB,headA从链表A开始向后移动,headB从链表B开始向后移动。假设链表有公共节点,headA遍历完A在走到第一个公共节点的距离为a+b-c,headB在遍历完B在走到第一个公共节点的距离为b+a-c,所以两个节点从两个头开始走,走到头在交换着走,最后停止时就会停在第一个节点。如果没有交点,headA走a+b,headB走b+a,结果也是正确的。
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode *A=headA,*B=headB;
while(A!=B)
{
if(A==NULL)
{
A=headB;
}
else if(B==NULL)
{
B=headA;
}
else{
A=A->next;
B=B->next;
}
}
return B;
}
138. 随机链表的复制
这道题的意思就是复制一个和他一模一样的链表,链表的结构体有两个指针,一个是next,一个是随机的,这道题的关键就是怎么复制random指针。
第一步,在每个节点的next指针后创建要拷贝的节点
这样旧节点就与新节点有联系了。继续完成第二步
第二步 ,完成新节点random指针的拷贝
使用两个指针,pre指向头节点head,tail指向头节点head的next,通过pre更改tail的random,然后将pre设为tail->next,将tail设为pre->next。循环的结束条件是pre!=NULL。然后开始第三步(pre找到的random不是要连接到新节点的,random->next才是,注意判断random是否问NULL)
最后要把原链表归位,也就是将一个链表拆分成两个链表。pre指向头,tail指向pre->next,head指向pre->next。循环条件是True就行。因为在循环内部pre会变成null,循环的出口设置值循环内部
- 将pre->next改变为tail->next
- 将pre改变为pre->next
- 判断pre是否为NULL
- 将tail->next改变为pre->next
- 将tail改变为tail->next
最后返回ans
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
if(head==NULL)return head;
struct Node* next = head;
struct Node* tmp = NULL;
struct Node* ans = NULL;
while(next)
{
// printf("1");
tmp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
tmp->val=next->val;
tmp->next=next->next;
next->next=tmp;
next=tmp->next;
}
// while(head)
// { printf("2");
// head=head->next;
// }
// printf("%d\n%d\n",head->val,head->next->val);
// printf("%d\n%d\n",head->next->next->random->val,1);
// printf("%d\n%d\n",head->random->val,1);
next=head;
// return head;
while(next)
{
// printf("4");
tmp=next->random;
if(tmp)(next->next)->random=tmp->next;
else (next->next)->random=NULL;
// printf("3");
next=next->next->next;
}
// printf("SSS");
ans = head->next;
next=head;
tmp = ans;
while(1){
next->next=tmp->next;
next=next->next;
if(!next)return ans;
tmp->next=next->next;
tmp=tmp->next;
}
return ans;
}
206. 反转链表
使用两个指针pre初始化成空,tail初始化成head。循环遍历链表,条件为tail是否为空,tail为空时,pre正好指向新链表的头。
中间需要使用临时变量存储一下tail->next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = head;
struct ListNode* tmp = NULL;
while(tail)
{
tmp = tail->next;
tail->next=pre;
pre=tail;
tail=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
21. 合并两个有序链表
判断l1与l2谁指向的小,指向小的那个向后移动。循环条件是两个指针指向的都不为空,如果其中一个变为空,那么直接指向剩余的那个链表即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next=NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(list1&&list2){
if(list1->valval)
{
cur->next = list1;
cur = cur->next;
list1=list1->next;
}else
{
cur->next = list2;
cur = cur->next;
list2=list2->next;
}
}
if(list1){
cur->next=list1;
}
if(list2)
{
cur->next=list2;
}
return head->next;
}
链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
使用哨兵节点先把符合条件的节点拿出来,使用两个指针方便删除节点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
#include 链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
- 找到链表的中间节点(链表节点为奇数时找到中间节点的下一个)
- 从中间节点开始进行链表翻转
- 对链表进行对比
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
//1 2 3 4 5
#include