Lecture01:市场出清问题的优化建模
目录
1 一个简单案例
1.1 问题描述
1.2 模型构建
1.3 更一般的模型
2 电力网络中的出清问题
2.1 问题描述
2.2 模型构建
2.3 GAMS求解模型代码
3 原始模型和对偶模型
1 一个简单案例
1.1 问题描述
现有两个发电厂和两个用户,发电厂的产量、售价及用户的需求量和购买价格见下表:
发电厂:
| 发电能力 | 发电成本 | |
| 发电厂1 | 100 MW | 12 CNY / MWh |
| 发电厂2 | 80 MW | 20 CNY / MWh |
用户:
| 用电量 | 投标成本 | |
| 用户1 | 80 MW | 40 CNY / MWh |
| 用户2 | 50 MW | 35 CNY / MWh |
问:该电力系统的各电厂产量、用户需求量和出清价格是多少?
1.2 模型构建
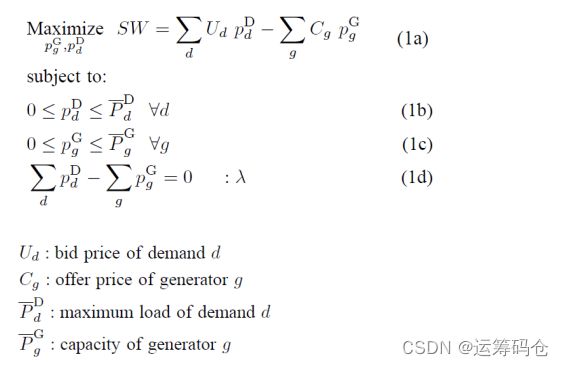
优化目标:最大化市场的社会总福利,即基于投标成本的总需求效用 - 基于总销售价格的总生产成本
约束条件:
- 发电厂发电能力和用户需求约束
- 电力系统平衡条件
模型公式表述如下:
在这个模型中,平衡条件的约束的对偶变量定义了市场的出清价格。对偶变量也成拉格朗日乘子,或单纯形橙子,或影子价格,他用来表示目标函数对该约束的敏感性。
但是上述模型存在一个明显的缺点,就是在求解时,得到的最优解不是唯一的,具有多重性。
1.3 更一般的模型
从上面的例子中,我们可以提炼出一个更紧凑的模型:
2 电力网络中的出清问题
2.1 问题描述
给定如下电力网络,电厂到用户之间使用电线连接、交流电的容量和电纳
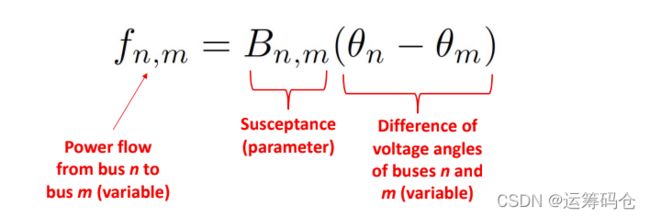
任意bus m 到 bus n 的功率流表达式为:
 2.2 模型构建
2.2 模型构建
由此可以建立如下数学模型:
注意:
- 电量平衡约束是在节点上而不是电线上。
- 每条交流电的容量是双向的,所以取 -100 到 100
- 强加最后一个约束,是为了能够保证模型得到唯一的解
使用GAMS对上述问题进行求解,结果如下:
- sw.L = 3550.000 social welfare of the market [$]
- p_G.L Production level of generator g [MW] G1 100.000, G2 50.000
- p_D.L Consumption level of demand d [MW] D1 100.000, D2 50.000
- Power flow from bus n to m [Mw]
N1 N2 N3
N1 50.000 50.000
N2 -50.000
N3 -50.000
- cons6.M
N1 20.000, N2 20.000, N3 20.000
上述模型更紧凑的形式为:
2.3 GAMS求解模型代码
上述问题的GAMS求解代码:
sets
g generators /G1*G2/
n buses /N1*N3/
d demands /D1*D2/
alias(n,m)
Sets
MapN(n,n) Network topology /
N1.N2
N1.N3
N2.N3
N2.N1
N3.N1
N3.N2/
MapG(g,n) Location of generators /
G1.N1
G2.N2/
MapD (d,n) Location of demands /
D1.N2
D2.N3/;
Parameter PGmax(g) Capacity of generators [MW]/
G1 100
G2 80/ ;
Parameter C(g) offer price of generators [$ per MWh]/
G1 12
G2 20/;
Parameter L(d) Maximum load of demands [Mw]/
D1 100
D2 50/;
Parameter U(d) utility of demands [$ per MWh]/
D1 40
D2 35/;
Table Fmax (n,n) capacity of transmission lines [MW]
N1 N2 N3
N1 0 100 100
N2 100 0 100
N3 100 100 0;
Table B(n,n) susceptance of transmission lines [Ohm^{-1}]
N1 N2 N3
N1 0 500 500
N2 500 0 500
N3 500 500 0;
Free variable
sw social welfare of the market [$]
f(n,m) Power flow from bus n to m [Mw]
theta(n) voltage angle of bus n [rad.];
Positive variable
p_D(d) Consumption level of demand d [MW]
p_G(g) Production level of generator g [MW];
Equations
objective, cons1, cons2, cons3, cons4, cons5,cons6;
objective.. sw =e= sum(d,U(d)*p_D(d)) - sum(g,c(g)*p_G(g));
cons1(g).. p_G(g) =l= PGmax(g);
cons2(d).. p_D(d) =l= L(d);
cons3(n,m).. f(n,m) =e= B(n, m)*(theta(n)-theta(m));
cons4(n,m).. f(n,m) =l= Fmax (n,m);
cons5.. theta('N1') =e=0;
cons6(n).. -sum(g$MapG(g,n),p_G(g))+sum(d$MapD(d,n),p_D(d)) +sum(m$MapN(n,m),f(n,m)) =e=0;
Model Market_clearing /all/ ;
solve Market_clearing using lp maximizing sw;
Display sw.l, p_G.l, p_D.l, f.l, cons6.m;3 原始模型和对偶模型
原始模型及各约束对应的对偶变量:
原模型的对偶模型:
如何有原始模型生成最优条件和对偶问题呢?且听下回分解。