【Pytorch】搭建一个简单的泰坦尼克号预测模型
介绍
本文使用PyTorch构建一个简单而有效的泰坦尼克号生存预测模型。通过这个项目,你会学到如何使用PyTorch框架创建神经网络、进行数据预处理和训练模型。我们将探讨如何处理泰坦尼克号数据集,设计并训练一个神经网络,以预测乘客是否在灾难中幸存。
主要内容包括:
- 数据准备:介绍如何加载和预处理泰坦尼克号数据集,包括处理缺失值、对类别特征进行编码等。
- 构建神经网络模型:定义一个简单的神经网络模型,包括输入层、隐藏层和输出层,并选择适当的激活函数。
- 模型训练与评估:通过将数据集划分为训练集和测试集,展示如何训练模型并评估其性能。
- 结果预测:对测试集数据进行处理和预测,并将最终结果导出。
通过这个简单的项目,展示如何构建一个简单但实用的预测模型。
目录
-
- 介绍
- 1. 数据准备
-
- 数据导入
- 特征转换
- 缺失值处理
- 删除多余数据
- 2. 模型搭建
- 3. 模型训练
- 4. 结果预测
-
- 测试集数据处理
- 预测计算
- 结果导出
1. 数据准备
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import os
from scipy import stats
import pandas as pd
数据导入
titanic_data =pd.read_csv('train.csv')
titanic_data.columns
特征转换
df=pd.concat([titanic_data,
pd.get_dummies(titanic_data['Sex']).astype(int),
pd.get_dummies(titanic_data['Embarked'],prefix='Embarked').astype(int),
pd.get_dummies(titanic_data['Pclass'],prefix='class').astype(int)],axis=1)
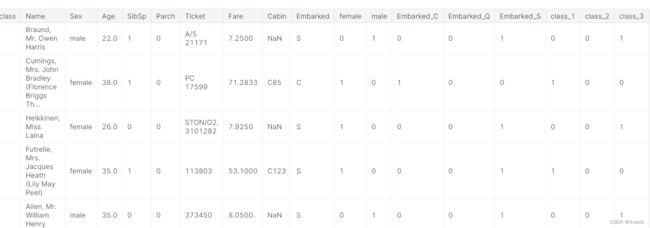
df.head()
缺失值处理
df['Age']=df['Age'].fillna(df.Age.mean())
df['Fare']=df['Fare'].fillna(df.Fare.mean())
删除多余数据
df_clean=df.drop(['PassengerId','Name','Ticket','Cabin','Sex','Embarked','Pclass'],axis=1)
df_clean.head()
labels=df_clean['Survived'].to_numpy()
df_clean=df_clean.drop(['Survived'],axis=1)
data=df_clean.to_numpy()
feature_names=list(df_clean.columns)
np.random.seed(10)
train_indices=np.random.choice(len(labels),int(0.7*len(labels)),replace=False)
test_indices=list(set(range(len(labels)))-set(train_indices))
train_features=data[train_indices]
train_labels=labels[train_indices]
test_features=data[test_indices]
test_labels=labels[test_indices]
len(test_labels)
2. 模型搭建
# 定义Mish激活函数
class Mish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
# Mish激活函数的前向传播过程
x = x * (torch.tanh(F.softplus(x)))
# 返回经过Mish激活函数的结果
return x
# 设置随机种子
torch.manual_seed(0)
# 定义ThreelinearModel模型
class ThreelinearModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 定义三个线性层,用于处理输入特征
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(12, 12)
self.mish1 = Mish() # 使用自定义激活函数Mish
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(12, 8)
self.mish2 = Mish() # 使用Mish作为第二个激活函数
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(8, 2) # 输出层,用于生成分类结果
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) # 对输出进行Softmax,将结果转为概率分布
self.criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 交叉熵损失函数,用于计算模型误差
def forward(self, x):
# 模型的前向传播过程
lin1_out = self.linear1(x)
out1 = self.mish1(lin1_out)
out2 = self.mish2(self.linear2(out1))
# 经过线性层和激活函数后,通过Softmax得到最终的概率分布
return self.softmax(self.linear3(out2))
def getloss(self, x, y):
# 计算模型预测值与实际标签之间的交叉熵损失
y_pred = self.forward(x)
loss = self.criterion(y_pred, y)
# 返回计算得到的损失值
return loss
3. 模型训练
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建 ThreelinearModel 的神经网络模型
net = ThreelinearModel()
# 设置训练轮数为200次,选择Adam优化器,学习率为0.04
num_epochs = 200
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.04)
# 将训练数据转换为PyTorch张量格式
input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(train_features).type(torch.FloatTensor)
label_tensor = torch.from_numpy(train_labels)
# 用于存储每轮训练的损失值
losses = []
# 开始训练循环
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 计算当前模型在训练数据上的损失值
loss = net.getloss(input_tensor, label_tensor)
# 记录损失值
losses.append(loss.item())
# 清零梯度,防止梯度累积
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 反向传播,计算梯度
loss.backward()
# 更新模型参数
optimizer.step()
# 每20轮打印一次训练损失
if epoch % 20 == 0:
print('Epoch {}/{} => Loss: {:.2f}'.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, loss.item()))
# 创建'models'文件夹(如果不存在),保存训练好的模型参数
os.makedirs('models', exist_ok=True)
torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'models/titanic_model.pt')
# 使用训练好的模型进行训练集的预测
out_probs = net(input_tensor).detach().numpy()
out_classes = np.argmax(out_probs, axis=1)
# 输出训练集准确率
print("Training Accuracy: ", sum(out_classes == train_labels) / len(train_labels))
# 使用训练好的模型进行测试集的预测
test_input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(test_features).type(torch.FloatTensor)
out_probs = net(test_input_tensor).detach().numpy()
out_classes = np.argmax(out_probs, axis=1)
# 输出测试集准确率
print("Testing Accuracy: ", sum(out_classes == test_labels) / len(test_labels))
4. 结果预测
测试集数据处理
test=pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/titanic/test.csv')
test_df=pd.concat([test,
pd.get_dummies(test['Sex']).astype(int),
pd.get_dummies(test['Embarked'],prefix='Embarked').astype(int),
pd.get_dummies(test['Pclass'],prefix='class').astype(int)],axis=1)
test_df['Age']=test_df['Age'].fillna(df.Age.mean())
test_df['Fare']=test_df['Fare'].fillna(df.Fare.mean())
Id=test_df['PassengerId']
test_df_clean=test_df.drop(['PassengerId','Name','Ticket','Cabin','Sex','Embarked','Pclass'],axis=1)
pred_features=test_df_clean.to_numpy()
预测计算
pred_input_tensor=torch.from_numpy(pred_features).type(torch.FloatTensor)
pred_out_probs=net(pred_input_tensor).detach().numpy()
pred_classes=np.argmax(pred_out_probs,axis=1)
结果导出
submission= pd.DataFrame({
'PassengerId': Id,
'Survived': pred_classes[:],
})
# Save the submission file
submission.to_csv('submission.csv', index=False)